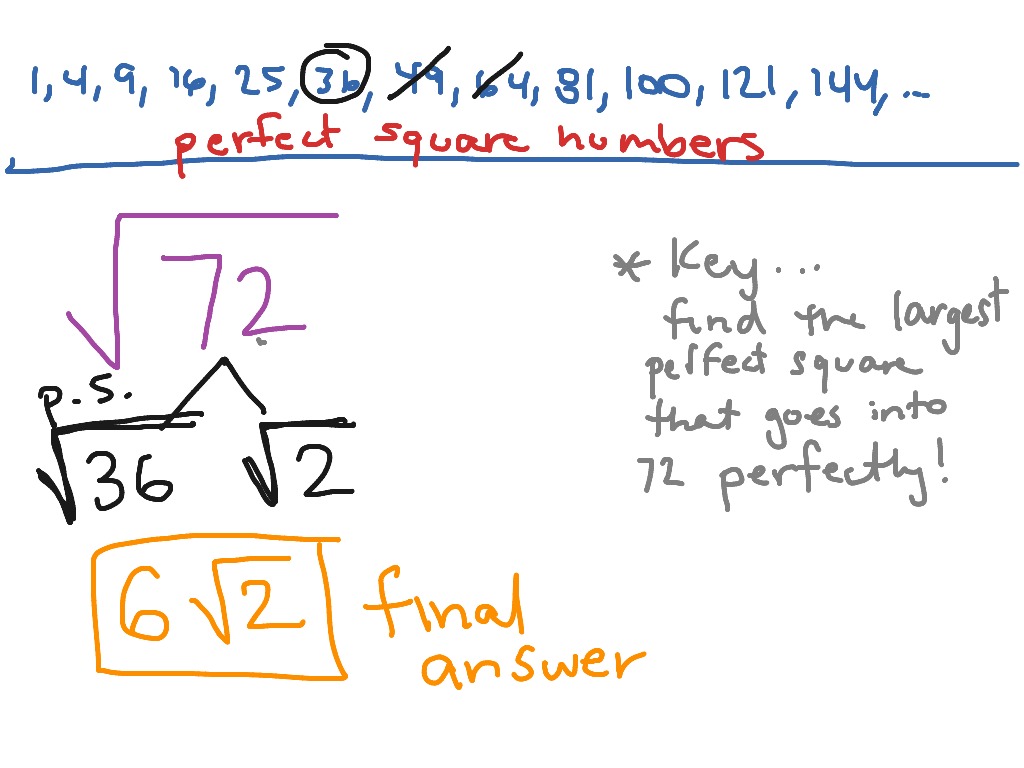Topic simplifying expressions with square roots calculator: Welcome to our comprehensive guide on simplifying expressions with square roots calculator. This article will help you understand the basics, explore step-by-step techniques, and utilize advanced methods to simplify square root expressions effectively. Whether you're a student or a math enthusiast, this guide will enhance your skills and confidence.
Table of Content
- Simplifying Expressions with Square Roots Calculator
- Introduction
- Understanding Square Roots and Radicals
- Step-by-Step Guide to Simplify Square Roots
- Examples of Simplifying Radical Expressions
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Advanced Techniques for Radical Expressions
- Using Online Calculators for Simplifying Expressions
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Additional Resources
- YOUTUBE:
Simplifying Expressions with Square Roots Calculator
Calculators designed to simplify expressions with square roots help users perform mathematical operations involving radicals. These tools can break down complex radical expressions into simpler forms, making calculations easier and more understandable. Below are some examples and features of such calculators:
Basic Rules for Simplifying Square Roots
Examples of Simplification
- Example 1: Simplify
- Example 2: Simplify
Features of Simplifying Radicals Calculators
- Input radical expressions and receive step-by-step simplification.
- Handle both multiplication and division of radicals.
- Provide solutions for addition and subtraction of radical expressions.
- Support for higher-order roots (e.g., cube roots, fourth roots).
Steps for Using a Simplifying Radicals Calculator
- Enter the radical expression into the calculator.
- Select the operation (e.g., simplify, add, multiply).
- View the step-by-step solution provided by the calculator.
Examples from Various Calculators
Different online tools offer similar functionalities:
| Calculator Name | Features |
| Symbolab | Step-by-step solutions, handles various types of expressions, user-friendly interface. |
| Omni Calculator | Supports multiple radical operations, detailed explanations, examples included. |
| MathPortal | Comprehensive radical expression simplification, supports higher-order roots. |
| Calculator Soup | Prime factorization for simplification, shows work and final result. |
Conclusion
Using a calculator to simplify expressions with square roots can save time and reduce errors. These tools are essential for students and professionals dealing with complex mathematical expressions.

READ MORE:
Introduction
Welcome to our detailed guide on simplifying expressions with square roots calculator. Simplifying square roots is an essential skill in algebra and advanced mathematics. This guide will provide you with the fundamental concepts and step-by-step instructions to simplify square root expressions effectively using both manual techniques and online calculators. Whether you are a student or a math enthusiast, this guide will help you understand and master the process.
In this guide, you will learn:
- The basic definitions and properties of square roots and radicals
- The rules for simplifying square roots
- Step-by-step methods for simplifying square root expressions
- Examples to illustrate the simplification process
- Common mistakes to avoid
- Advanced techniques for handling complex radical expressions
- How to use online calculators to simplify square root expressions efficiently
Let’s start by understanding what square roots and radicals are, and why they are important in mathematics.
Understanding Square Roots and Radicals
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For instance, the square root of 9 is 3 because 3 multiplied by 3 equals 9. Square roots are often represented using the radical symbol (√). In mathematical notation, the square root of a number 'x' is written as √x.
Radicals extend the concept of square roots to include roots of any degree, not just squares. The general form of a radical is the nth root of a number, written as √nx or x1/n, where n is the degree of the root. When n is 2, it is specifically called a square root, and when n is 3, it is called a cube root.
Properties of Square Roots and Radicals
- Product Property: √(a * b) = √a * √b
- Quotient Property: √(a / b) = √a / √b
- Power Property: (√a)n = an/2
Examples:
- √16 = 4 because 4 * 4 = 16
- √25 = 5 because 5 * 5 = 25
- √(4 * 9) = √4 * √9 = 2 * 3 = 6
Working with Radicals:
Radicals can often be simplified by factoring out squares. For example:
- √50 can be simplified as √(25 * 2) = √25 * √2 = 5√2
- √72 can be simplified as √(36 * 2) = √36 * √2 = 6√2
Understanding and simplifying radicals is essential for solving equations and expressions that involve roots. Practice with different types of radicals helps in mastering this skill and makes working with complex expressions easier.
Step-by-Step Guide to Simplify Square Roots
Simplifying square roots involves breaking down the number under the square root into its prime factors and simplifying by removing pairs of factors. Follow these steps to simplify square roots:
Step-by-Step Process:
-
Factor the number into prime factors: Decompose the number inside the square root into its prime factors.
- Example: \( 72 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3 \)
-
Identify and group pairs of prime factors: Look for pairs of the same prime factors within the factorization.
- Example: \( 72 = (2 \times 2) \times 2 \times (3 \times 3) \)
-
Move pairs outside the square root: For each pair of prime factors, take one factor out of the square root.
- Example: \( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 2 \times (3 \times 3)} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{2} = 6\sqrt{2} \)
-
Multiply the factors outside the square root: Combine the factors that were taken out of the square root.
- Example: \( \sqrt{72} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{2} = 6\sqrt{2} \)
Additional Examples:
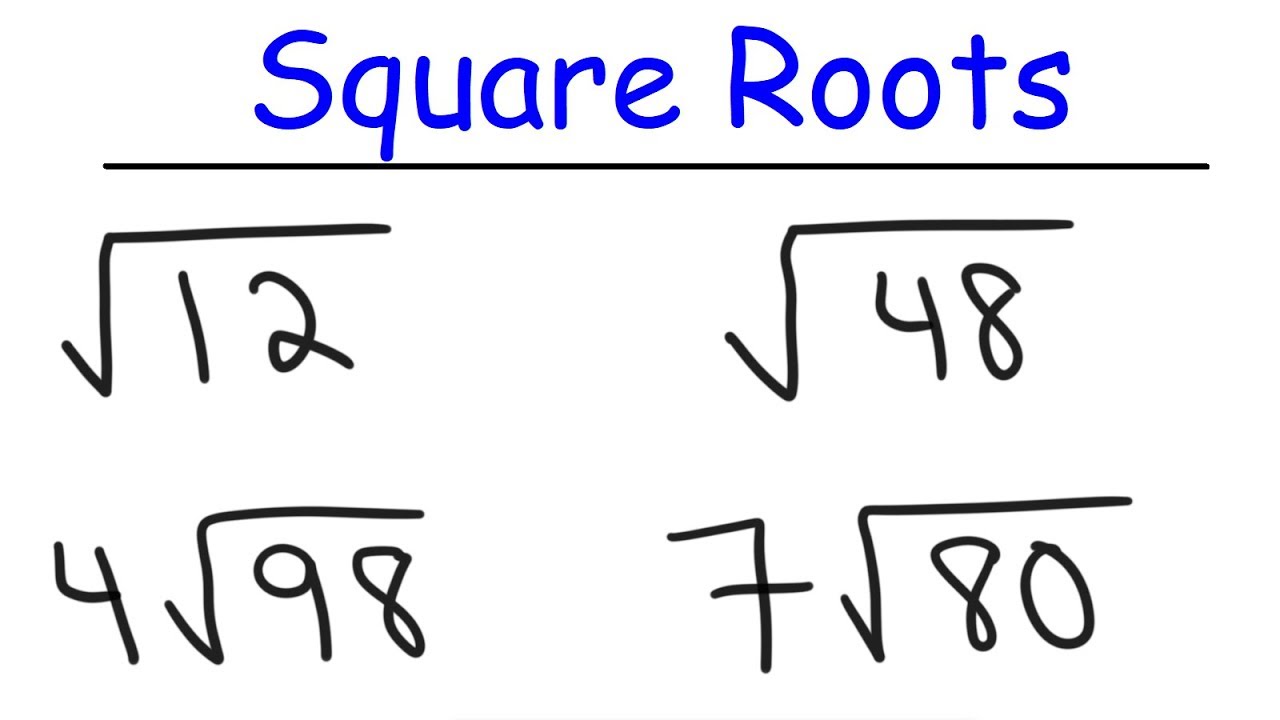
- \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25 \times 2} = \sqrt{25} \times \sqrt{2} = 5\sqrt{2} \)
- \( \sqrt{18} = \sqrt{9 \times 2} = \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{2} = 3\sqrt{2} \)
- \( \sqrt{32} = \sqrt{16 \times 2} = \sqrt{16} \times \sqrt{2} = 4\sqrt{2} \)
- \( \sqrt{98} = \sqrt{49 \times 2} = \sqrt{49} \times \sqrt{2} = 7\sqrt{2} \)
Practicing these steps with different numbers will help you become proficient in simplifying square roots and handling more complex radical expressions.
Examples of Simplifying Radical Expressions
Simplifying radical expressions involves breaking down the numbers into their prime factors and simplifying the radicals by extracting square factors. Below are several examples to illustrate the process:
Example 1: Simplifying \( \sqrt{75} \)
-
Factor the number into prime factors: \( 75 = 3 \times 5 \times 5 \)
-
Group pairs of prime factors: \( 75 = 3 \times (5 \times 5) \)
-
Extract pairs from the square root: \( \sqrt{75} = \sqrt{3 \times (5 \times 5)} = 5\sqrt{3} \)
Example 2: Simplifying \( \sqrt{200} \)
-
Factor the number into prime factors: \( 200 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 5 \times 5 \)
-
Group pairs of prime factors: \( 200 = (2 \times 2) \times 2 \times (5 \times 5) \)
-
Extract pairs from the square root: \( \sqrt{200} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 2 \times (5 \times 5)} = 2 \times 5 \times \sqrt{2} = 10\sqrt{2} \)
Example 3: Simplifying \( \sqrt{245} \)
-
Factor the number into prime factors: \( 245 = 5 \times 7 \times 7 \)
-
Group pairs of prime factors: \( 245 = 5 \times (7 \times 7) \)
-
Extract pairs from the square root: \( \sqrt{245} = \sqrt{5 \times (7 \times 7)} = 7\sqrt{5} \)
Example 4: Simplifying \( \sqrt{360} \)
-
Factor the number into prime factors: \( 360 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3 \times 5 \)
-
Group pairs of prime factors: \( 360 = (2 \times 2) \times 2 \times (3 \times 3) \times 5 \)
-
Extract pairs from the square root: \( \sqrt{360} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 2 \times (3 \times 3) \times 5} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{2 \times 5} = 6\sqrt{10} \)
Example 5: Simplifying \( \sqrt{128} \)
-
Factor the number into prime factors: \( 128 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \)
-
Group pairs of prime factors: \( 128 = (2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) \times 2 \)
-
Extract pairs from the square root: \( \sqrt{128} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) \times 2} = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times \sqrt{2} = 8\sqrt{2} \)
These examples demonstrate the systematic approach to simplifying radical expressions by breaking down the numbers into prime factors and extracting pairs of factors to simplify the square roots.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
When simplifying square roots and radical expressions, there are several common mistakes that students often make. Being aware of these mistakes can help you avoid them and ensure that your work is accurate. Here are some common mistakes to watch out for:
Mistake 1: Incorrectly Pairing Factors
One common mistake is failing to correctly pair the prime factors when simplifying the square root. Make sure to pair the factors accurately.
- Incorrect: \( \sqrt{18} = \sqrt{2 \times 3 \times 3} = 2\sqrt{3} \)
- Correct: \( \sqrt{18} = \sqrt{2 \times 3 \times 3} = 3\sqrt{2} \)
Mistake 2: Ignoring Remaining Factors
Another mistake is ignoring factors that remain inside the square root after simplification.
- Incorrect: \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25} = 5 \)
- Correct: \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25 \times 2} = 5\sqrt{2} \)
Mistake 3: Misapplying the Product Property
Students sometimes misapply the product property of square roots, which states that \( \sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \).
- Incorrect: \( \sqrt{36 \times 4} = 6 \times 4 = 24 \)
- Correct: \( \sqrt{36 \times 4} = \sqrt{36} \times \sqrt{4} = 6 \times 2 = 12 \)
Mistake 4: Misapplying the Quotient Property
Another common error involves misapplying the quotient property, which states that \( \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \).
- Incorrect: \( \sqrt{\frac{9}{16}} = \frac{9}{4} \)
- Correct: \( \sqrt{\frac{9}{16}} = \frac{\sqrt{9}}{\sqrt{16}} = \frac{3}{4} \)
Mistake 5: Forgetting to Simplify Fully
Sometimes, students stop before the expression is fully simplified. Ensure that you simplify the expression as much as possible.
- Incorrect: \( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{36 \times 2} = 6\sqrt{2} \)
- Correct: \( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{36 \times 2} = 6\sqrt{2} \)
Tips for Avoiding Mistakes:
- Double-check your factorization: Ensure that you have correctly factored the number into its prime factors.
- Verify each step: Go through each step methodically to ensure accuracy.
- Practice regularly: The more you practice simplifying square roots, the more familiar you will become with the process.
- Use a calculator: When in doubt, use a square roots calculator to check your work and understand the steps involved.
By being mindful of these common mistakes and following the tips provided, you can improve your ability to simplify square roots and avoid errors in your work.
Advanced Techniques for Radical Expressions
Once you are comfortable with the basic techniques for simplifying square roots, you can move on to more advanced methods for dealing with radical expressions. These techniques involve manipulating and simplifying more complex expressions that contain radicals. Here are some advanced techniques to help you master radical expressions:
1. Rationalizing the Denominator
Rationalizing the denominator involves eliminating radicals from the denominator of a fraction. This is done by multiplying the numerator and the denominator by a suitable radical expression.
- Simple Rationalization: If the denominator is a single square root, multiply the numerator and the denominator by that square root.
- Example: \( \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} = \frac{1 \times \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3} \times \sqrt{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{3} \)
- Complex Rationalization: If the denominator is a binomial expression containing a radical, multiply the numerator and the denominator by the conjugate of the denominator.
- Example: \( \frac{1}{1+\sqrt{2}} = \frac{1 \times (1-\sqrt{2})}{(1+\sqrt{2})(1-\sqrt{2})} = \frac{1-\sqrt{2}}{1-2} = \frac{1-\sqrt{2}}{-1} = -1+\sqrt{2} \)
2. Combining Like Radicals
Combining like radicals is similar to combining like terms in algebra. You can add or subtract radicals that have the same radicand (the number under the square root).
- Example: \( 2\sqrt{3} + 3\sqrt{3} = 5\sqrt{3} \)
- Example: \( 5\sqrt{2} - 2\sqrt{2} = 3\sqrt{2} \)
3. Using the Distributive Property
The distributive property can be used to multiply and factor expressions involving radicals.
- Example: \( \sqrt{2}(3 + \sqrt{5}) = 3\sqrt{2} + \sqrt{10} \)
- Example: \( (\sqrt{3} + 2)^2 = \sqrt{3}^2 + 2 \cdot \sqrt{3} \cdot 2 + 2^2 = 3 + 4\sqrt{3} + 4 = 7 + 4\sqrt{3} \)
4. Solving Radical Equations
Solving equations that involve radicals often requires isolating the radical on one side of the equation and then squaring both sides to eliminate the radical. Be sure to check for extraneous solutions that may arise from squaring.
- Example: Solve \( \sqrt{x+3} = x-3 \)
- Isolate the radical: \( \sqrt{x+3} = x-3 \)
- Square both sides: \( x+3 = (x-3)^2 \)
- Expand and simplify: \( x+3 = x^2 - 6x + 9 \)
- Rearrange to form a quadratic equation: \( x^2 - 7x + 6 = 0 \)
- Factor the quadratic equation: \( (x-6)(x-1) = 0 \)
- Solve for x: \( x = 6 \) or \( x = 1 \)
- Check for extraneous solutions: \( \sqrt{6+3} = 6-3 \) (valid), \( \sqrt{1+3} \neq 1-3 \) (invalid)
- Solution: \( x = 6 \)
By mastering these advanced techniques, you can handle more complex radical expressions with confidence and accuracy.
Using Online Calculators for Simplifying Expressions
Online calculators can be a valuable tool for simplifying expressions with square roots. They provide quick and accurate solutions, and many offer step-by-step explanations to help you understand the process. Here’s a guide on how to effectively use these calculators:
Step-by-Step Guide:
-
Choose a reliable online calculator: There are many online calculators available, so select one that is user-friendly and offers detailed explanations. Some popular options include calculators from educational websites, math help platforms, and standalone calculator tools.
-
Input the expression: Enter the expression you want to simplify into the calculator. Most calculators have a user-friendly interface where you can type or paste the expression directly.
- Example: To simplify \( \sqrt{50} \), type "sqrt(50)" into the calculator.
-
Review the steps: After entering the expression, the calculator will provide the simplified result along with the steps taken to achieve it. Reviewing these steps can help you understand the process and learn how to do it manually.
- Example: The calculator will show that \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25 \times 2} = 5\sqrt{2} \).
-
Check for additional features: Many calculators offer additional features such as the ability to solve equations, factor expressions, and graph functions. Explore these features to get the most out of the tool.
-
Practice with different expressions: Use the calculator to simplify a variety of expressions to gain confidence. Practicing with different numbers and expressions will help reinforce your understanding of the concepts.
Benefits of Using Online Calculators:
- Speed and Accuracy: Online calculators provide quick and accurate results, saving time and reducing errors.
- Learning Tool: Step-by-step explanations help you learn and understand the process of simplifying expressions.
- Accessibility: Most online calculators are free and easily accessible from any device with an internet connection.
- Versatility: Many calculators offer additional functions for solving a wide range of mathematical problems.
Examples:
- Expression: \( \sqrt{72} \)
- Calculator Input: "sqrt(72)"
- Simplified Result: \( 6\sqrt{2} \)
- Expression: \( \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \)
- Calculator Input: "1/sqrt(3)"
- Simplified Result: \( \frac{\sqrt{3}}{3} \)
- Expression: \( \sqrt{18} + \sqrt{32} \)
- Calculator Input: "sqrt(18) + sqrt(32)"
- Simplified Result: \( 3\sqrt{2} + 4\sqrt{2} = 7\sqrt{2} \)
Using online calculators effectively can enhance your understanding of simplifying expressions with square roots and provide a helpful resource for studying and solving mathematical problems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are some frequently asked questions about simplifying expressions with square roots, along with detailed answers to help you understand the concepts better.
Q1: What is the square root of a number?
The square root of a number \( x \) is a number \( y \) such that \( y^2 = x \). For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because \( 3^2 = 9 \).
Q2: How do I simplify a square root?
Simplifying a square root involves expressing it in its simplest radical form. This is done by factoring the number under the square root into its prime factors and then extracting pairs of factors.
- Example: \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25 \times 2} = 5\sqrt{2} \)
Q3: What is a radical expression?
A radical expression is an expression that contains a square root, cube root, or any higher-order root. Simplifying radical expressions involves similar techniques as simplifying square roots.
Q4: Can all square roots be simplified?
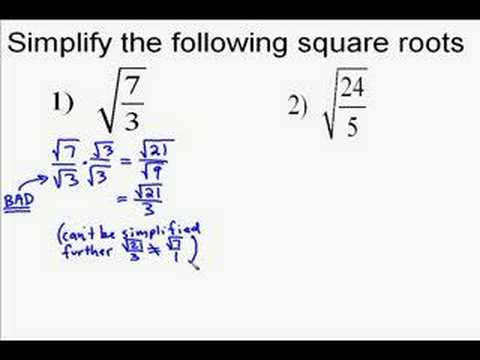
Not all square roots can be simplified. A square root can be simplified if the number under the square root has a perfect square factor other than 1. For example, \( \sqrt{18} \) can be simplified to \( 3\sqrt{2} \), but \( \sqrt{7} \) cannot be simplified further.
Q5: How do I add or subtract square roots?
Square roots can be added or subtracted if they have the same radicand (the number under the square root). This is similar to combining like terms in algebra.
- Example: \( 2\sqrt{3} + 3\sqrt{3} = 5\sqrt{3} \)
- Example: \( 4\sqrt{2} - \sqrt{2} = 3\sqrt{2} \)
Q6: How do I multiply and divide square roots?
To multiply or divide square roots, use the product and quotient properties of square roots:
- Product Property: \( \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} = \sqrt{a \times b} \)
- Quotient Property: \( \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} = \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} \)
Example: \( \sqrt{3} \times \sqrt{12} = \sqrt{36} = 6 \)
Example: \( \frac{\sqrt{20}}{\sqrt{5}} = \sqrt{4} = 2 \)
Q7: What is rationalizing the denominator?
Rationalizing the denominator means eliminating any square roots from the denominator of a fraction. This is done by multiplying both the numerator and the denominator by a suitable radical expression to make the denominator a rational number.
- Example: \( \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} = \frac{1 \times \sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{2}} = \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2} \)
Q8: Are there any tools to help simplify square roots?
Yes, there are many online calculators available that can simplify square roots and provide step-by-step explanations. These tools are helpful for verifying your work and understanding the simplification process.
- Example: Using an online calculator, you can enter \( \sqrt{72} \) and get the simplified result \( 6\sqrt{2} \) along with the steps.
Q9: How do I simplify an expression with multiple square roots?
To simplify an expression with multiple square roots, simplify each square root individually first and then combine the results if possible.
- Example: \( \sqrt{50} + \sqrt{8} = 5\sqrt{2} + 2\sqrt{2} = 7\sqrt{2} \)
Q10: What should I do if I get stuck while simplifying square roots?
If you get stuck, review the basic rules and steps for simplifying square roots, use an online calculator to check your work, and practice with different examples to improve your understanding and skills.
Additional Resources
To further your understanding and mastery of simplifying expressions with square roots, here are some valuable resources that offer tutorials, practice problems, and interactive tools:
Online Calculators
Online calculators are a great way to quickly and accurately simplify square roots and radical expressions. Here are a few reliable ones:
- - A powerful and user-friendly online calculator that can handle complex radical expressions.
- - This calculator not only simplifies radicals but also provides step-by-step solutions and explanations.
- - An advanced computational engine that can simplify expressions and show detailed steps.
Video Tutorials
Visual learners may benefit from video tutorials that walk through the process of simplifying square roots. Here are some useful channels:
- - Offers a comprehensive set of videos on radicals and square roots, including simplification techniques.
- - Provides clear and concise video tutorials on a variety of math topics, including radical expressions.
- - Simplifies math concepts with engaging and easy-to-understand videos.
Interactive Practice
Practicing with interactive problems can help reinforce your skills. Here are some websites that offer practice problems and instant feedback:
- - Provides practice problems on simplifying radicals and offers instant feedback to help you learn from mistakes.
- - An interactive problem solver that allows you to input your own problems and see detailed solutions.
- - Features lessons and interactive quizzes on simplifying square roots and other radical expressions.
Books and Articles
For those who prefer reading, here are some books and articles that provide in-depth explanations and additional practice:
- - A comprehensive guide that covers radicals and other algebraic concepts in an easy-to-understand manner.
- - Offers detailed articles and examples on simplifying radical expressions.
- - Provides lessons and examples on simplifying square roots and other algebraic topics.
By utilizing these resources, you can deepen your understanding of simplifying expressions with square roots and improve your mathematical skills.
Hướng dẫn sử dụng máy tính ClassWiz - Đại số 4-1 Đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai
READ MORE:
Khám phá thủ thuật toán học giúp bạn đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai bằng máy tính TI-84 plus một cách dễ dàng và hiệu quả.
Thủ thuật toán học - đại số với TI-84 plus - đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai