Topic simplify the square root of 12: Understanding how to simplify the square root of 12 is an essential skill in mathematics. This guide will walk you through easy steps to break down and simplify \(\sqrt{12}\) using prime factorization. Mastering this technique will enhance your problem-solving abilities and build a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Table of Content
- Simplifying the Square Root of 12
- Introduction to Simplifying Square Roots
- Understanding Prime Factorization
- Step-by-Step Process to Simplify the Square Root of 12
- Detailed Example: Simplifying \(\sqrt{12}\)
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Practice Problems and Solutions
- Applications of Simplified Square Roots in Real Life
- FAQs about Simplifying Square Roots
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 12 (√12) để giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về quá trình này.
Simplifying the Square Root of 12
To simplify the square root of 12, we need to find the prime factorization of 12 and then simplify it by grouping the prime factors into pairs. Here are the steps:
Step-by-Step Solution:
- Prime factorize 12:
- 12 can be written as 4 × 3
- 4 can be further factorized into 2 × 2
- So, the prime factorization of 12 is 2 × 2 × 3
- Write the square root of 12 using its prime factors:
\(\sqrt{12} = \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 3}\)
- Group the prime factors into pairs:
\(\sqrt{12} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 3}\)
- Take the square root of the pair of 2's and simplify:
\(\sqrt{12} = 2 \times \sqrt{3}\)
Simplified Form:
The simplified form of \(\sqrt{12}\) is \(2 \sqrt{3}\).
Summary:
By following these steps, we have simplified \(\sqrt{12}\) to \(2 \sqrt{3}\).

READ MORE:
Introduction to Simplifying Square Roots
Simplifying square roots is a fundamental skill in algebra and higher-level mathematics. It involves breaking down a square root into its simplest form, which can make calculations easier and results more understandable. Here’s a step-by-step approach to simplify square roots, using the example of \(\sqrt{12}\).
- Prime Factorization: Begin by finding the prime factors of the number under the square root.
- For 12, the prime factors are 2, 2, and 3, because \(12 = 2 \times 2 \times 3\).
- Group the Prime Factors: Identify pairs of prime factors.
- In \(\sqrt{12}\), we have a pair of 2’s and a single 3.
- Simplify the Square Root: Take the square root of the pairs and move them outside the radical.
- \(\sqrt{12} = \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 3} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 3} = 2\sqrt{3}\)
This process shows that \(\sqrt{12}\) simplifies to \(2\sqrt{3}\). By learning how to simplify square roots, you can make complex calculations more manageable and enhance your understanding of mathematical principles.
Understanding Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is the process of breaking down a composite number into its prime factors, which are numbers that are only divisible by 1 and themselves. This technique is crucial for simplifying square roots and understanding the structure of numbers. Here’s a detailed guide on prime factorization:
- Identify the Composite Number:
First, choose the composite number you want to factorize. For example, let's use 12.
- Start with the Smallest Prime Number:
Begin dividing the number by the smallest prime number, which is 2.
- \(12 \div 2 = 6\)
- Continue Dividing:
Repeat the process with the quotient obtained, until you cannot divide evenly by 2 anymore.
- \(6 \div 2 = 3\)
- \(3\) is a prime number and cannot be divided by 2, so we stop here.
- List the Prime Factors:
The prime factors of 12 are the prime numbers you used for division and the final quotient, which are:
- \(2, 2, 3\)
To summarize, the prime factorization of 12 is \(2 \times 2 \times 3\) or \(2^2 \times 3\). Understanding this process is essential for simplifying square roots and solving various mathematical problems efficiently.
Step-by-Step Process to Simplify the Square Root of 12
Simplifying the square root of 12 involves breaking down the number into its prime factors and then simplifying the expression. Follow these detailed steps to understand the process:
- Find the Prime Factors:
First, determine the prime factors of 12. The prime factors of 12 are 2 and 3.
- Start with 12: \(12 = 2 \times 6\)
- Then factor 6: \(6 = 2 \times 3\)
- So, \(12 = 2 \times 2 \times 3\)
- Write the Square Root Expression:
Express the square root of 12 using its prime factors:
\(\sqrt{12} = \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 3}\)
- Group the Prime Factors:
Group the prime factors into pairs. In this case, \(2 \times 2\) forms a pair:
\(\sqrt{12} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 3}\)
- Simplify the Square Root:
Take the square root of the pair and move it outside the radical:
\(\sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 3} = 2 \sqrt{3}\)
Therefore, the simplified form of \(\sqrt{12}\) is \(2 \sqrt{3}\). This step-by-step process makes it clear how to break down and simplify square roots effectively.
Detailed Example: Simplifying \(\sqrt{12}\)
Simplifying the square root of 12 can be done by following a clear, step-by-step process. Let's go through a detailed example to illustrate this:
- Prime Factorization:
First, find the prime factors of 12:
- 12 can be factorized into \(2 \times 6\)
- 6 can be further factorized into \(2 \times 3\)
- So, \(12 = 2 \times 2 \times 3\)
- Express the Square Root:
Write the square root of 12 using its prime factors:
\(\sqrt{12} = \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 3}\)
- Group the Factors:
Group the factors into pairs wherever possible:
\(\sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 3} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 3}\)
- Simplify the Expression:
Take the square root of the pair and place it outside the radical:
\(\sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 3} = 2 \sqrt{3}\)
- Final Simplified Form:
The simplified form of \(\sqrt{12}\) is \(2 \sqrt{3}\).
By following these steps, we have simplified \(\sqrt{12}\) to \(2 \sqrt{3}\), demonstrating the process in a clear and detailed manner.
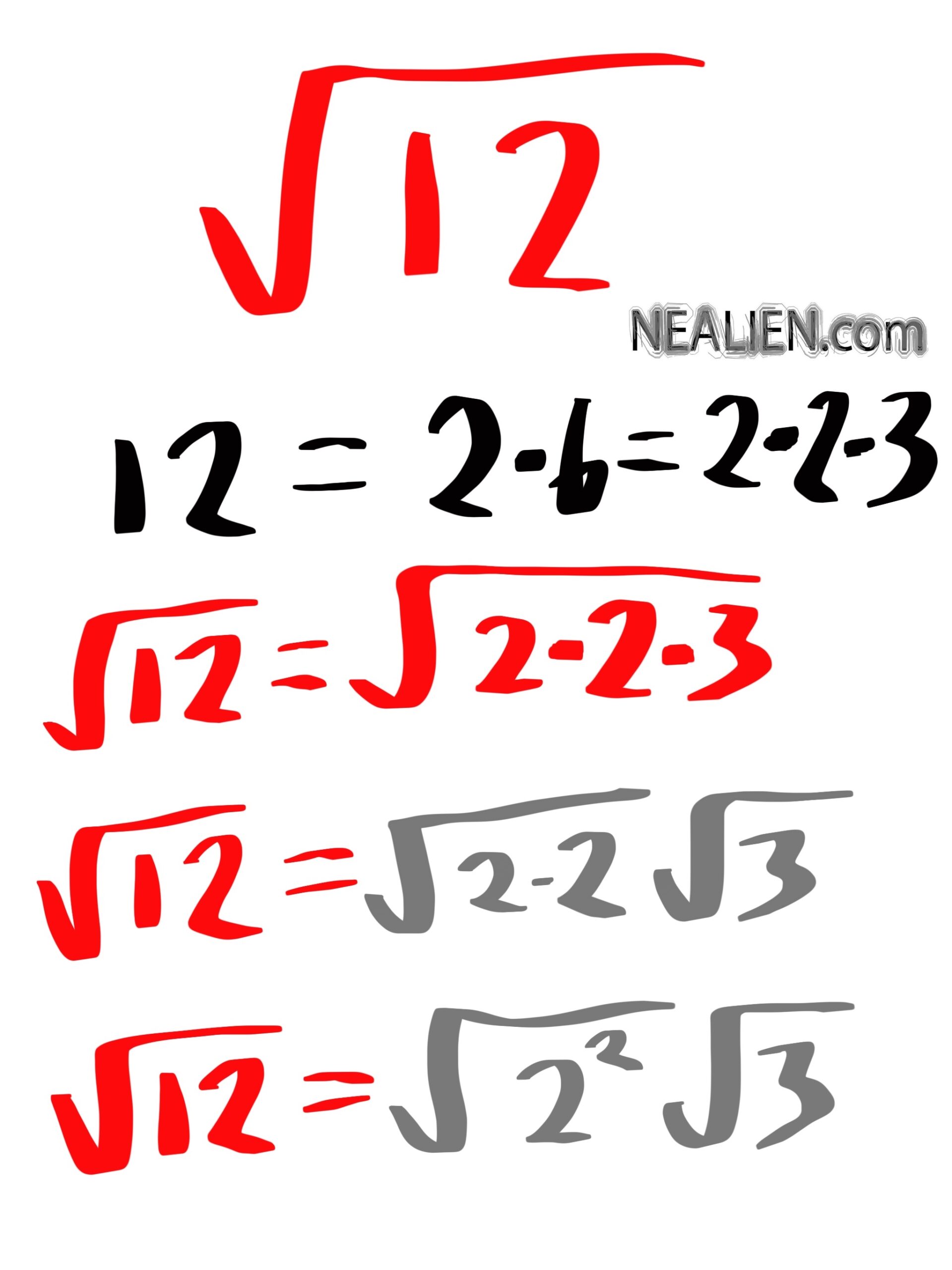
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When simplifying square roots, especially \(\sqrt{12}\), it's easy to make mistakes. Here are some common errors to watch out for and tips to avoid them:
- Not Finding All Prime Factors:
Ensure you factorize the number completely into its prime factors. Missing any factors will lead to incorrect simplification.
- Example Mistake: \(12 = 2 \times 6\) and stopping here.
- Correct: \(12 = 2 \times 2 \times 3\).
- Incorrect Grouping of Factors:
Make sure to group factors correctly. Only pairs of the same number can be simplified outside the square root.
- Example Mistake: Grouping \(2 \times 3\) together.
- Correct: Grouping \(2 \times 2\) together.
- Forgetting to Simplify Completely:
After taking out the pairs, ensure the remaining number under the square root is simplified as much as possible.
- Example Mistake: Leaving the expression as \(\sqrt{4 \times 3}\).
- Correct: Simplifying to \(2\sqrt{3}\).
- Incorrect Arithmetic:
Double-check your arithmetic operations when factorizing and simplifying.
- Example Mistake: Incorrect multiplication or division during factorization.
- Tip: Verify each step carefully.
By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can ensure accurate simplification of \(\sqrt{12}\) and other square roots.
Practice Problems and Solutions
Practicing the simplification of square roots helps reinforce understanding and accuracy. Below are several practice problems along with their solutions to help you master the concept.
Practice Problems
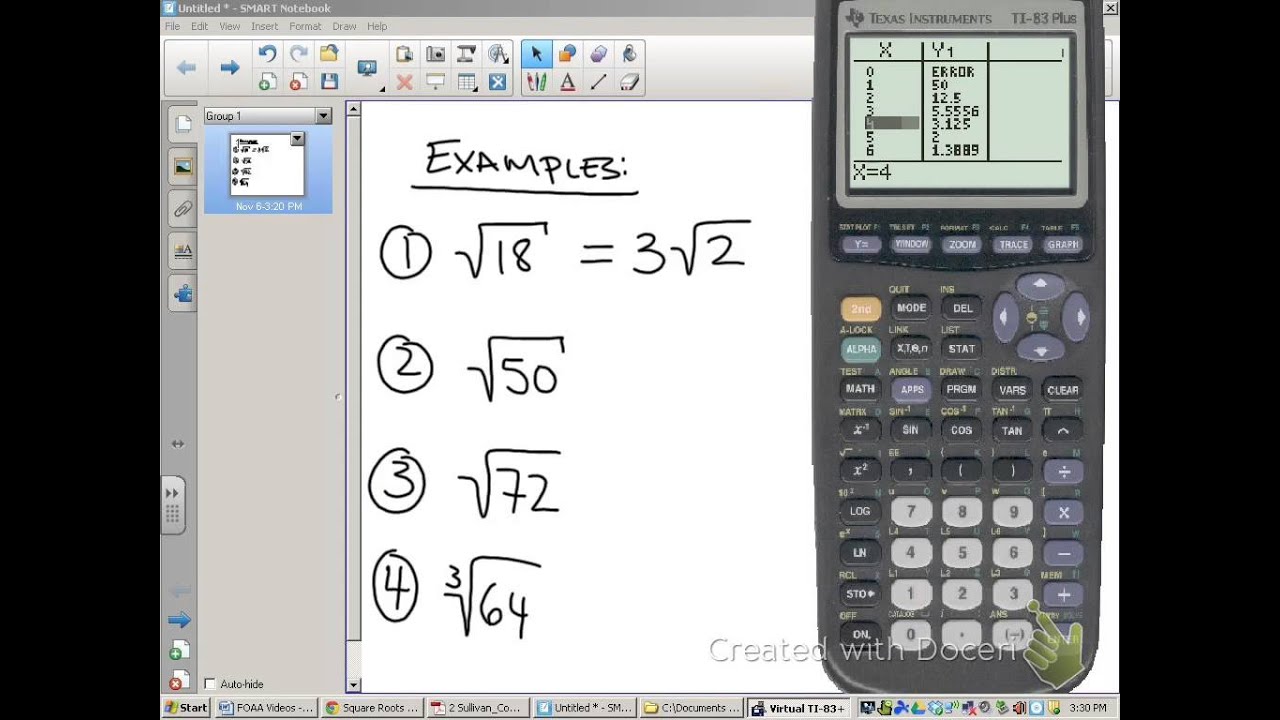
- Simplify \(\sqrt{18}\)
- Simplify \(\sqrt{50}\)
- Simplify \(\sqrt{72}\)
- Simplify \(\sqrt{45}\)
- Simplify \(\sqrt{27}\)
Solutions
- Simplify \(\sqrt{18}\):
Prime factors of 18: \(18 = 2 \times 3 \times 3\)
\(\sqrt{18} = \sqrt{2 \times 3 \times 3} = \sqrt{(3 \times 3) \times 2} = 3 \sqrt{2}\)
- Simplify \(\sqrt{50}\):
Prime factors of 50: \(50 = 2 \times 5 \times 5\)
\(\sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5 \times 5} = \sqrt{(5 \times 5) \times 2} = 5 \sqrt{2}\)
- Simplify \(\sqrt{72}\):
Prime factors of 72: \(72 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3\)
\(\sqrt{72} = \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3) \times 2} = 2 \times 3 \sqrt{2} = 6 \sqrt{2}\)
- Simplify \(\sqrt{45}\):
Prime factors of 45: \(45 = 3 \times 3 \times 5\)
\(\sqrt{45} = \sqrt{3 \times 3 \times 5} = \sqrt{(3 \times 3) \times 5} = 3 \sqrt{5}\)
- Simplify \(\sqrt{27}\):
Prime factors of 27: \(27 = 3 \times 3 \times 3\)
\(\sqrt{27} = \sqrt{3 \times 3 \times 3} = \sqrt{(3 \times 3) \times 3} = 3 \sqrt{3}\)
By practicing these problems and understanding the solutions, you can become proficient in simplifying square roots and apply this knowledge to more complex mathematical tasks.
Applications of Simplified Square Roots in Real Life
Simplifying square roots is not just a mathematical exercise; it has practical applications in various real-life scenarios. Understanding how to simplify square roots can help in diverse fields such as engineering, physics, architecture, and everyday problem-solving. Here are some key applications:
- Engineering and Construction:
Engineers and architects often use simplified square roots when dealing with measurements and dimensions. For instance, when calculating the diagonal of a square or rectangle, the Pythagorean theorem is used, which involves square roots.
- Example: To find the diagonal of a square with a side length of 6 units, you calculate \(\sqrt{6^2 + 6^2} = \sqrt{72} = 6\sqrt{2}\).
- Physics:
In physics, square roots are used in formulas involving areas, volumes, and distances. Simplifying these roots can make calculations more manageable.
- Example: Calculating the root mean square speed of gas molecules involves square roots. Simplifying the root helps in understanding the speed distribution.
- Finance:
Square roots are used in financial models to calculate standard deviation and other statistical measures. Simplifying these roots aids in clearer financial analysis.
- Example: The standard deviation formula involves the square root of the variance. Simplifying the square root provides a clearer measure of data spread.
- Art and Design:
Artists and designers use square roots to maintain proportions and symmetry. Understanding and simplifying square roots help in creating aesthetically pleasing designs.
- Example: The golden ratio, often used in art, involves square roots. Simplifying these helps in accurately applying the ratio.
- Everyday Problem-Solving:
Simplifying square roots can be useful in daily tasks such as calculating distances, areas, and volumes for home projects or navigation.
- Example: Finding the shortest path or diagonal distance between two points on a grid involves simplifying square roots.
By understanding how to simplify square roots, you can enhance your problem-solving skills and apply mathematical concepts to real-world situations effectively.
FAQs about Simplifying Square Roots
Here are some frequently asked questions about simplifying square roots:
- What is simplifying a square root?
Simplifying a square root involves expressing it in the simplest radical form. This means rewriting the square root such that there are no perfect square factors under the radical sign.
- Why simplify square roots?
Simplifying square roots can make them easier to work with in mathematical calculations and can help in recognizing patterns and relationships between numbers.
- How do you simplify \(\sqrt{12}\)?
To simplify \(\sqrt{12}\), follow these steps:
- Find the prime factors of 12: \(12 = 2 \times 2 \times 3\).
- Group the factors into pairs of the same number: \(12 = 2^2 \times 3\).
- Take the square root of each pair: \(\sqrt{12} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 3} = 2\sqrt{3}\).
Thus, \(\sqrt{12} = 2\sqrt{3}\).
- What are some common mistakes to avoid when simplifying square roots?
Common mistakes include:
- Forgetting to pair all the factors.
- Not fully factorizing the number under the square root.
- Incorrectly simplifying the radical expression.
- Can all square roots be simplified?
No, not all square roots can be simplified. Only square roots of numbers with perfect square factors can be simplified. For example, \(\sqrt{13}\) cannot be simplified because 13 is a prime number.
- What are the benefits of using simplified square roots in real life?
Using simplified square roots can make complex calculations more manageable and can be useful in various fields such as engineering, physics, and architecture where precise measurements are crucial.

Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we have delved into the process of simplifying the square root of 12. By following the method of prime factorization, we discovered that \(\sqrt{12}\) can be simplified to \(2\sqrt{3}\). This transformation allows for easier handling and application in various mathematical contexts.
Here are the key steps we covered:
- Prime Factorization: Breaking down 12 into its prime factors, which are \(2 \times 2 \times 3\).
- Grouping Factors: Identifying pairs of factors to simplify under the radical sign, resulting in \(2\sqrt{3}\).
Understanding these steps not only helps in simplifying square roots but also builds a strong foundation for tackling more complex mathematical problems. Simplifying square roots is a fundamental skill in algebra that can be applied to real-life situations, such as calculating dimensions in geometry or solving physics problems involving roots.
By practicing and mastering this process, you will enhance your problem-solving abilities and mathematical confidence. Always remember, the essence of simplifying square roots lies in making the numbers more manageable while retaining their exact values in a simpler form.
Keep practicing with various square roots, and explore different methods to strengthen your understanding. Whether you are a student, educator, or math enthusiast, the knowledge of simplifying square roots is a valuable tool in your mathematical toolkit.
Thank you for exploring this guide. We hope it has been informative and helpful in your learning journey.
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 12 (√12) để giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về quá trình này.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 12: Sqrt(12)
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn chi tiết cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 12 (√12) từng bước một, giúp bạn hiểu rõ quá trình này.
Căn Bậc Hai của 12 = ? Hãy Đơn Giản Hóa Từng Bước