Topic how to perimeter of a circle: Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a circle is essential for students and professionals alike. This guide will walk you through the key concepts, formulas, and steps needed to accurately determine the perimeter using both the radius and diameter. Master these calculations and apply them confidently in various practical scenarios.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Perimeter of a Circle
- Introduction
- What is the Perimeter of a Circle?
- Understanding Key Terms
- Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating the Perimeter
- Example Calculations
- Using the Radius
- Using the Diameter
- Practical Applications
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Summary and Conclusion
- YOUTUBE:
Understanding the Perimeter of a Circle
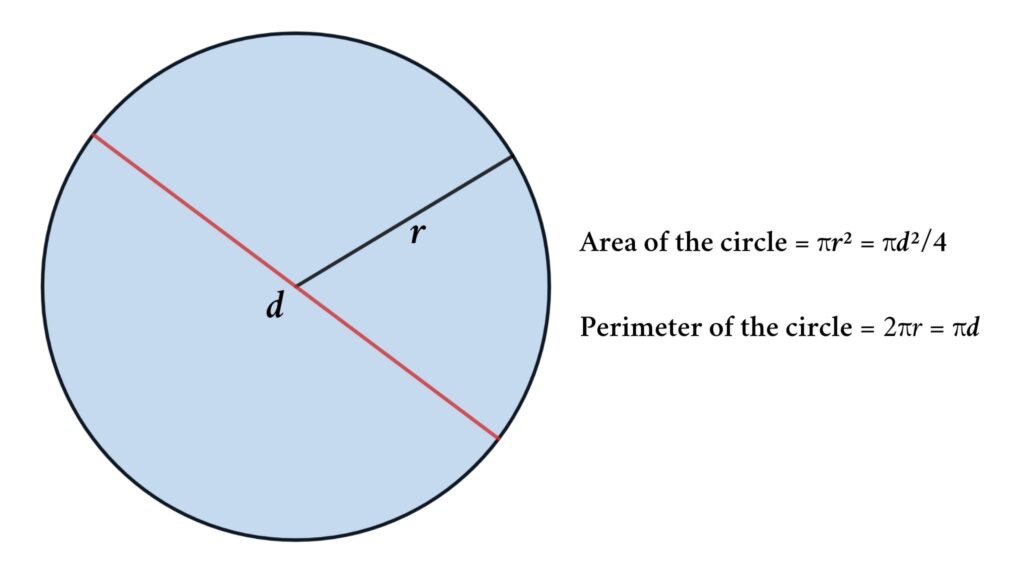
The perimeter of a circle, also known as the circumference, is the distance around the circle. Calculating the perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry and is essential for understanding various aspects of circular shapes.
Formula for the Perimeter of a Circle
The formula to calculate the perimeter (circumference) of a circle is given by:
\[
C = 2 \pi r
\]
where:
- C is the circumference of the circle.
- r is the radius of the circle.
- \(\pi\) (pi) is a constant approximately equal to 3.14159.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of a Circle
- Measure the radius of the circle. The radius is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its edge.
- Multiply the radius by 2 to get the diameter. This is because the diameter is twice the radius. \[ d = 2r \]
- Multiply the diameter by \(\pi\) to get the circumference. \[ C = \pi d \]
Example Calculation
Let's calculate the perimeter of a circle with a radius of 5 units:
- Radius \( r = 5 \) units
- Diameter \( d = 2 \times 5 = 10 \) units
- Circumference \( C = \pi \times 10 \approx 31.4159 \) units
Therefore, the perimeter (circumference) of a circle with a radius of 5 units is approximately 31.4159 units.
Using Diameter to Calculate the Perimeter
If you know the diameter of the circle directly, you can use a simplified version of the formula:
\[
C = \pi d
\]
where d is the diameter of the circle.
For example, if the diameter of a circle is 8 units, the perimeter would be:
- Diameter \( d = 8 \) units
- Circumference \( C = \pi \times 8 \approx 25.1327 \) units
Thus, the perimeter of a circle with a diameter of 8 units is approximately 25.1327 units.
Summary
To summarize, the perimeter of a circle is calculated using the formula \( C = 2 \pi r \) or \( C = \pi d \), depending on whether you know the radius or the diameter. Understanding and applying this formula allows you to determine the distance around any circular shape efficiently.

READ MORE:
Introduction
The perimeter of a circle, also known as the circumference, is a fundamental concept in geometry that is essential for various fields, including engineering, architecture, and everyday problem-solving. Calculating the perimeter involves understanding key mathematical principles and using specific formulas.
In this article, we will cover the following:
- Definition of the perimeter (circumference) of a circle
- Key terms and concepts
- Formulas for calculating the perimeter using the radius and diameter
- Step-by-step instructions for performing the calculations
- Example problems to illustrate the process
- Practical applications of calculating the perimeter
- Common mistakes to avoid
- Frequently asked questions
By the end of this guide, you will have a thorough understanding of how to accurately calculate the perimeter of a circle and apply this knowledge confidently in various scenarios.
What is the Perimeter of a Circle?
The perimeter of a circle, more commonly referred to as the circumference, is the distance around the outer edge of the circle. It is a crucial concept in geometry and can be used in various practical applications. The circumference is directly related to the radius and diameter of the circle.
To understand the perimeter of a circle, you need to be familiar with the following key terms:
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of the circle to any point on its boundary.
- Diameter (d): The distance across the circle, passing through the center. It is twice the length of the radius (d = 2r).
- Pi (π): A mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159, representing the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
The formula for calculating the perimeter (circumference) of a circle is:
- Using the radius: \( C = 2\pi r \)
- Using the diameter: \( C = \pi d \)
Where:
- \( C \) = Circumference
- \( r \) = Radius
- \( d \) = Diameter
- \( \pi \) = Pi, approximately 3.14159
Understanding these terms and formulas will allow you to accurately calculate the perimeter of any circle, which is an essential skill in both academic and real-world contexts.
Understanding Key Terms
To effectively calculate the perimeter of a circle, it's crucial to understand several key terms used in the process. Below are some essential terms and their definitions:
- Circle: A shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the center.
- Center: The point inside the circle that is equidistant from all points on the circle.
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference. It is half the diameter.
- Diameter (d): The distance across the circle through its center. It is twice the radius.
- Circumference: The total distance around the circle, also known as the perimeter of the circle.
- Pi (π): A mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159, representing the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
Below is a table summarizing these key terms and their symbols:
| Term | Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Radius | r | The distance from the center to any point on the circle |
| Diameter | d | The distance across the circle through its center (d = 2r) |
| Circumference | C | The perimeter of the circle (C = 2πr or C = πd) |
| Pi | π | A constant approximately equal to 3.14159 |
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating the Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter, or circumference, of a circle is a straightforward process when you follow these detailed steps. Whether you start with the radius or the diameter, the steps below will guide you through the calculation:
Step 1: Identify the Given Measurement
Determine if you have been provided with the radius (\( r \)) or the diameter (\( d \)) of the circle. The formulas for the perimeter differ based on this initial information.
- If you have the radius, proceed with the formula \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \pi r \).
- If you have the diameter, use the formula \( \text{Perimeter} = \pi d \).
Step 2: Apply the Formula
Using the appropriate formula, substitute the given measurement into the equation:
- If you have the radius:
- Multiply the radius by 2.
- Then multiply the result by \( \pi \) (approximately 3.14159).
- The formula is \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \pi r \).
- If you have the diameter:
- Simply multiply the diameter by \( \pi \) (approximately 3.14159).
- The formula is \( \text{Perimeter} = \pi d \).
Step 3: Perform the Calculation
Use a calculator to ensure accuracy, especially for \( \pi \). You can use either the approximate value of \( \pi \) (3.14159) or the \( \pi \) button on your calculator:
- Example with Radius: If the radius \( r \) is 5 units, the calculation is:
- Perimeter = \( 2 \times 3.14159 \times 5 \)
- Perimeter ≈ 31.4159 units
- Example with Diameter: If the diameter \( d \) is 10 units, the calculation is:
- Perimeter = \( 3.14159 \times 10 \)
- Perimeter ≈ 31.4159 units
Step 4: Review and Interpret the Result
Ensure that your final answer is reasonable. The perimeter should be a positive value that reflects the total distance around the circle.
To summarize, follow these steps carefully:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Identify the given measurement (radius or diameter). |
| 2 | Apply the correct formula. |
| 3 | Perform the calculation using \( \pi \). |
| 4 | Review and interpret the result. |
By following these steps, you can accurately determine the perimeter of any circle.

Example Calculations
To better understand how to calculate the perimeter of a circle, let's look at a few example calculations using both the radius and the diameter.
Example 1: Using the Radius
Suppose we have a circle with a radius (\( r \)) of 7 units. We will use the formula:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \pi r \]
- Substitute the radius:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \pi \times 7 \]
- Multiply the radius by 2:
\[ 2 \times 7 = 14 \]
- Multiply the result by \( \pi \) (using \( \pi \approx 3.14159 \)):
\[ 14 \times 3.14159 \approx 43.98226 \]
- Thus, the perimeter of the circle is approximately:
\[ \text{Perimeter} \approx 43.98226 \text{ units} \]
Example 2: Using the Diameter
Next, consider a circle with a diameter (\( d \)) of 12 units. We will use the formula:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi d \]
- Substitute the diameter:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi \times 12 \]
- Multiply the diameter by \( \pi \):
\[ 12 \times 3.14159 \approx 37.69908 \]
- Thus, the perimeter of the circle is approximately:
\[ \text{Perimeter} \approx 37.69908 \text{ units} \]
Example 3: Large Circle Using the Radius
For a larger circle with a radius (\( r \)) of 15 units, the calculation follows the same steps:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \pi r \]
- Substitute the radius:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \pi \times 15 \]
- Multiply the radius by 2:
\[ 2 \times 15 = 30 \]
- Multiply the result by \( \pi \):
\[ 30 \times 3.14159 \approx 94.2477 \]
- Thus, the perimeter of the circle is approximately:
\[ \text{Perimeter} \approx 94.2477 \text{ units} \]
Summary of Examples
In summary, these examples illustrate the straightforward process of calculating the perimeter of a circle using either the radius or the diameter. Below is a quick reference table summarizing these calculations:
| Example | Given | Calculation | Perimeter (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Radius \( r = 7 \) units | \[ 2 \pi \times 7 \] | 43.98226 units |
| 2 | Diameter \( d = 12 \) units | \[ \pi \times 12 \] | 37.69908 units |
| 3 | Radius \( r = 15 \) units | \[ 2 \pi \times 15 \] | 94.2477 units |
By practicing these calculations, you can easily determine the perimeter of any circle.
Using the Radius
When calculating the perimeter of a circle, using the radius is a common and straightforward approach. The radius is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its edge. Here's a detailed step-by-step guide on how to calculate the perimeter using the radius.
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Identify the Radius:
Determine the radius (\( r \)) of your circle. This is usually provided in the problem or can be measured if dealing with a physical circle.
- Recall the Formula:
The formula to calculate the perimeter (\( P \)) using the radius is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \pi r \]
where \( \pi \) (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
- Substitute the Radius:
Plug the given radius into the formula. For example, if the radius is 5 units, you substitute \( r \) with 5:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times \pi \times 5 \]
- Multiply the Radius by 2:
First, multiply the radius by 2:
\[ 2 \times 5 = 10 \]
- Multiply by \( \pi \):
Next, multiply the result by \( \pi \):
\[ 10 \times 3.14159 \approx 31.4159 \]
- Interpret the Result:
The result is the perimeter of the circle. In this example, the perimeter is approximately 31.4159 units.
Example Calculation
Let's consider a practical example to solidify our understanding:
Example: Calculate the perimeter of a circle with a radius of 8 units.
- Identify the radius: \( r = 8 \) units.
- Apply the formula: \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \pi r \).
- Substitute the radius: \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times \pi \times 8 \).
- Multiply the radius by 2: \( 2 \times 8 = 16 \).
- Multiply by \( \pi \): \( 16 \times 3.14159 \approx 50.2655 \).
- Result: The perimeter of the circle is approximately 50.2655 units.
Quick Reference Table
Here's a quick reference for different radii:
| Radius (\( r \)) | Calculation | Perimeter (approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| 3 units | \( 2 \times 3.14159 \times 3 \) | 18.8495 units |
| 6 units | \( 2 \times 3.14159 \times 6 \) | 37.6991 units |
| 10 units | \( 2 \times 3.14159 \times 10 \) | 62.8318 units |
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of a circle using its radius. This method is efficient and widely applicable in various practical scenarios.
Using the Diameter
Calculating the perimeter of a circle using the diameter is a simple and direct method. The diameter is the distance across the circle, passing through its center, and it is twice the radius. Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide on how to calculate the perimeter using the diameter.
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Identify the Diameter:
Determine the diameter (\( d \)) of the circle. This value might be given directly or you might need to measure it. The diameter is the longest straight line that can be drawn within the circle, passing through the center from one edge to the opposite edge.
- Recall the Formula:
The formula to calculate the perimeter (\( P \)) using the diameter is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi d \]
where \( \pi \) (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
- Substitute the Diameter:
Insert the given diameter into the formula. For example, if the diameter is 10 units, you substitute \( d \) with 10:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi \times 10 \]
- Multiply by \( \pi \):
Multiply the diameter by \( \pi \). Using the approximate value of \( \pi \) (3.14159), the calculation is:
\[ 10 \times 3.14159 \approx 31.4159 \]
- Interpret the Result:
The result is the perimeter of the circle. In this example, the perimeter is approximately 31.4159 units.
Example Calculation
Let’s go through an example to see how this method works in practice:
Example: Calculate the perimeter of a circle with a diameter of 15 units.
- Identify the diameter: \( d = 15 \) units.
- Apply the formula: \( \text{Perimeter} = \pi d \).
- Substitute the diameter: \( \text{Perimeter} = \pi \times 15 \).
- Multiply by \( \pi \): \( 15 \times 3.14159 \approx 47.12385 \).
- Result: The perimeter of the circle is approximately 47.12385 units.
Quick Reference Table
Here’s a quick reference for various diameters and their corresponding perimeters:
| Diameter (\( d \)) | Calculation | Perimeter (approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| 4 units | \( \pi \times 4 \) | 12.5664 units |
| 8 units | \( \pi \times 8 \) | 25.1327 units |
| 20 units | \( \pi \times 20 \) | 62.8318 units |
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of a circle when you know its diameter. This method is useful in various practical applications where the diameter is easily measured or given.
Practical Applications
The perimeter of a circle, also known as the circumference, has numerous practical applications in various fields. Here are some common examples:
- Engineering and Construction: Engineers and architects often need to calculate the circumference of circular components, such as pipes, columns, and roundabouts, to ensure accurate measurements and proper fitting.
- Agriculture: Farmers might use the circumference to determine the area of circular plots of land or to calculate the length of fencing required to enclose a circular field.
- Sports: The design and layout of running tracks, basketball courts, and other sports facilities often involve circles and curves, requiring precise calculations of their perimeters.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturers need to know the circumference of circular objects like wheels, gears, and cylindrical containers to maintain quality control and consistency in production.
- Urban Planning: City planners use the circumference to design roundabouts, fountains, and other circular structures in public spaces.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers often incorporate circular shapes into their work, requiring accurate measurements to achieve the desired aesthetic effects.
Here are a few step-by-step examples to illustrate these applications:
- Example 1: Calculating the Perimeter of a Circular Garden Bed
- Determine the radius of the garden bed. For example, let’s say the radius is 5 meters.
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a circle: \( C = 2\pi r \).
- Substitute the radius into the formula: \( C = 2 \times \pi \times 5 \).
- Calculate the perimeter: \( C \approx 2 \times 3.14159 \times 5 \approx 31.42 \) meters.
- Example 2: Designing a Circular Running Track
- Measure the diameter of the track. Suppose the diameter is 400 meters.
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a circle using the diameter: \( C = \pi d \).
- Substitute the diameter into the formula: \( C = 3.14159 \times 400 \).
- Calculate the perimeter: \( C \approx 1256.64 \) meters.
- Example 3: Planning a Circular Water Fountain
- Determine the radius of the fountain. Assume the radius is 2 meters.
- Use the formula: \( C = 2\pi r \).
- Substitute the radius: \( C = 2 \times \pi \times 2 \).
- Calculate the perimeter: \( C \approx 2 \times 3.14159 \times 2 \approx 12.57 \) meters.
By understanding and applying the formula for the perimeter of a circle, one can solve real-world problems effectively and accurately across various disciplines.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the perimeter, or more accurately, the circumference of a circle, there are several common mistakes that can lead to inaccuracies. Here are some of the most frequent errors and tips on how to avoid them:
-
Confusing Perimeter and Circumference:
One of the most common mistakes is using the terms "perimeter" and "circumference" interchangeably. The perimeter refers to the distance around any two-dimensional shape, while the circumference specifically refers to the distance around a circle.
-
Forgetting to Include π (Pi):
When calculating the circumference, it's crucial to include π (pi). The formula for the circumference is \( C = 2\pi r \) or \( C = \pi d \), where \( r \) is the radius and \( d \) is the diameter of the circle. Forgetting to multiply by π will result in a significant error.
-
Using Incorrect Units:
Ensure that all measurements are in the same unit before performing calculations. Mixing units (e.g., inches with centimeters) without proper conversion can lead to incorrect results.
-
Incorrect Use of Diameter and Radius:
Confusion often arises between the diameter and radius. Remember that the diameter is twice the radius (\( d = 2r \)). Ensure you are using the correct value in the formula.
-
Rounding Errors:
When working with π, rounding too early in your calculations can lead to inaccuracies. Use more decimal places of π (3.14159...) during calculations and round off only the final result.
By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can improve the accuracy of your calculations. Always double-check your formulas, units, and calculations to ensure correctness.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the formula for the perimeter of a circle?
The formula for the perimeter (circumference) of a circle is \(C = 2\pi r\) if the radius \(r\) is known, or \(C = \pi d\) if the diameter \(d\) is known.
-
How do I calculate the radius if I know the circumference?
To calculate the radius \(r\) from the circumference \(C\), use the formula \(r = \frac{C}{2\pi}\).
-
How do I calculate the diameter if I know the circumference?
To calculate the diameter \(d\) from the circumference \(C\), use the formula \(d = \frac{C}{\pi}\).
-
What is the perimeter of a semi-circle?
The perimeter of a semi-circle is given by the formula \(\text{Perimeter} = \pi r + 2r\), where \(r\) is the radius of the circle.
-
What common mistakes should I avoid when calculating the perimeter of a circle?
Common mistakes include using the wrong value for \(\pi\), confusing the radius with the diameter, and arithmetic errors during calculations. Always double-check your values and units.
-
Can the perimeter formula be used for other shapes?
The specific formulas \(C = 2\pi r\) and \(C = \pi d\) are unique to circles. Other shapes have their own perimeter formulas based on their geometry.
-
What practical applications does calculating the perimeter of a circle have?
Calculating the perimeter of a circle is useful in various fields such as engineering, architecture, and any context involving circular objects, like wheels, circular tracks, and pipes.
Summary and Conclusion
Calculating the perimeter of a circle, also known as the circumference, is a fundamental concept in geometry. Understanding this concept is essential for solving various mathematical problems and has practical applications in numerous fields. Here's a summary of what we've covered:
- Introduction: An overview of the importance of knowing how to calculate the perimeter of a circle.
- Definition: The perimeter or circumference of a circle is the distance around the circle.
- Key Terms: Important terms include radius, diameter, and pi (π).
- Formula: The formula for the perimeter of a circle is \(C = 2\pi r\) or \(C = \pi d\), where \(C\) is the circumference, \(r\) is the radius, and \(d\) is the diameter.
- Step-by-Step Guide: A detailed, step-by-step process to calculate the perimeter using both the radius and the diameter.
- Example Calculations: Practical examples demonstrating how to use the formulas.
- Using the Radius: Calculating the perimeter when the radius is known.
- Using the Diameter: Calculating the perimeter when the diameter is known.
- Practical Applications: Real-world uses of calculating the perimeter of a circle.
- Common Mistakes: Common errors to avoid when calculating the perimeter.
- Frequently Asked Questions: Answers to common questions about the perimeter of a circle.
In conclusion, calculating the perimeter of a circle is a straightforward process once you understand the basic concepts and formulas. By following the steps outlined and being mindful of common mistakes, you can accurately determine the circumference for any given circle. Whether you're a student, teacher, or professional, this knowledge is invaluable in both academic and practical scenarios.
Remember, the key formulas are:
- Using the radius: \(C = 2\pi r\)
- Using the diameter: \(C = \pi d\)
With these tools at your disposal, you are well-equipped to tackle any problem involving the perimeter of a circle. Keep practicing, and soon calculating the circumference will become second nature.
Cách Tính Chu Vi Hình Tròn Từ Đường Kính