Topic perimeter of a cylinder: Welcome to our comprehensive guide on understanding and calculating the perimeter of a cylinder. This article will help you grasp the concepts, learn the formulas, and apply them with confidence. Perfect for students, teachers, and anyone interested in geometry, our step-by-step approach ensures you master the topic with ease.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Perimeter of a Cylinder
- Introduction to Cylinders
- Understanding the Perimeter (Circumference) of a Cylinder's Base
- Formula for Calculating the Circumference of a Cylinder's Base
- Detailed Explanation of the Circumference Formula
- Examples of Calculating the Perimeter of a Cylinder
- Applications of Cylinder Perimeter Calculations
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- FAQs about Cylinder Perimeter
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE:
Understanding the Perimeter of a Cylinder
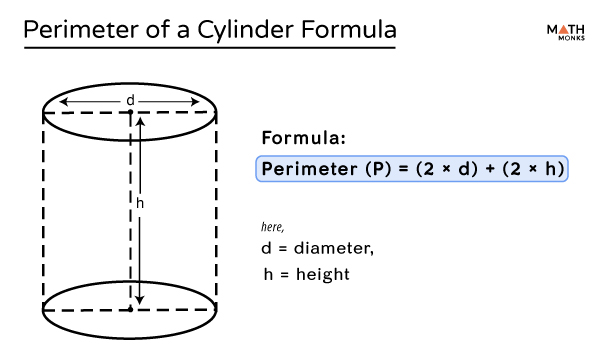
In geometry, the perimeter typically refers to the total distance around the edge of a two-dimensional shape. For a cylinder, which is a three-dimensional object, we can discuss the perimeters of its circular bases. These perimeters are also known as the circumferences of the circles.
Formulas for Calculating the Perimeter (Circumference) of a Cylinder's Base
The perimeter (circumference) of a cylinder's base can be calculated using the following formula:
\[ C = 2 \pi r \]
where:
- \( C \) is the circumference
- \( \pi \) (pi) is approximately 3.14159
- \( r \) is the radius of the base
Detailed Explanation
A cylinder has two circular bases. The formula for the circumference of a circle is used here, and since a cylinder has two identical bases, each with the same radius, we calculate the circumference of one base using the radius \( r \) and the mathematical constant \( \pi \).
Let's consider a cylinder with a radius \( r \) of 5 units:
\[ C = 2 \pi r = 2 \pi \times 5 = 10 \pi \approx 31.42 \, \text{units} \]
Perimeter of the Cylinder's Lateral Surface
The term "perimeter of a cylinder" can also be understood as the perimeter of its lateral surface when unrolled into a rectangle. The width of this rectangle is the circumference of the base, and the height is the height of the cylinder \( h \). However, this is typically referred to as the surface area rather than perimeter.
For clarity, if you unroll the lateral surface of a cylinder, the dimensions of the resulting rectangle would be:
- Width: \( 2 \pi r \) (circumference of the base)
- Height: \( h \) (height of the cylinder)
Summary
In summary, the perimeter (circumference) of a cylinder's base is given by \( 2 \pi r \). This fundamental understanding is essential in various applications, from calculating distances around cylindrical objects to solving complex geometry problems.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Cylinders
A cylinder is a three-dimensional geometric shape with two parallel circular bases connected by a curved surface. Cylinders are commonly found in everyday objects such as cans, tubes, and pipes. They are defined by two main properties: the radius (or diameter) of the base and the height (or length) of the side.
Key characteristics of a cylinder include:
- Base: The flat circular surfaces at the top and bottom of the cylinder.
- Height (h): The perpendicular distance between the bases.
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of the base to its edge.
- Diameter (d): Twice the radius, or the distance across the base through the center.
Mathematically, a cylinder can be represented and analyzed using the following formulas:
| Surface Area | \( A = 2\pi r (r + h) \) |
| Volume | \( V = \pi r^2 h \) |
| Base Circumference | \( C = 2\pi r \) |
The base circumference, also referred to as the perimeter of the base, is a crucial aspect when dealing with cylinders, as it is fundamental in calculating surface area and volume.
In this guide, we will delve into the various aspects of cylinders, focusing particularly on understanding and calculating the perimeter of a cylinder's base. By mastering these concepts, you will gain a solid foundation in geometric calculations involving cylinders.
Understanding the Perimeter (Circumference) of a Cylinder's Base
The perimeter of a cylinder's base, also known as the circumference, is an essential concept in geometry. It is the distance around the edge of the circular base. Understanding the perimeter helps in various calculations, including surface area and volume.
The formula to calculate the circumference of a cylinder's base is derived from the properties of a circle. The key components involved are the radius (\(r\)) and the diameter (\(d\)), which is twice the radius. The formulas are:
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of the base to the edge.
- Diameter (d): The distance across the base through the center, which is \(d = 2r\).
The formula for the circumference (\(C\)) is:
\[
C = 2\pi r
\]
Alternatively, using the diameter, the formula becomes:
\[
C = \pi d
\]
To understand this better, let's break it down step by step:
- Identify the radius or diameter: Measure the distance from the center to the edge of the base to get the radius, or measure across the center to get the diameter.
- Apply the formula: Use either \(C = 2\pi r\) if you have the radius, or \(C = \pi d\) if you have the diameter.
- Calculate the circumference: Multiply the radius by \(2\pi\) or the diameter by \(\pi\) to get the perimeter.
Understanding the perimeter of a cylinder's base is crucial for solving problems related to cylinder measurements. This fundamental concept not only aids in geometry but also in real-life applications where cylindrical shapes are involved.
Formula for Calculating the Circumference of a Cylinder's Base
Calculating the circumference of a cylinder's base is straightforward if you know the radius or diameter of the base. The circumference is the distance around the edge of the circular base and is crucial for various geometric calculations. Here, we will explain the formulas step by step.
Formula Using the Radius
- Step 1: Identify the radius (\(r\)) of the base. The radius is the distance from the center of the base to the edge.
- Step 2: Use the formula for circumference with the radius:
\[
C = 2\pi r
\] - Step 3: Multiply the radius by \(2\pi\) to find the circumference.
Formula Using the Diameter
- Step 1: Identify the diameter (\(d\)) of the base. The diameter is the distance across the base through the center and is twice the radius (\(d = 2r\)).
- Step 2: Use the formula for circumference with the diameter:
\[
C = \pi d
\] - Step 3: Multiply the diameter by \(\pi\) to find the circumference.
Let's summarize the two key formulas for quick reference:
| Using Radius | \( C = 2\pi r \) |
| Using Diameter | \( C = \pi d \) |
Understanding these formulas allows you to easily calculate the circumference of any cylinder's base, whether you have the radius or diameter. These formulas are fundamental in geometry and have numerous practical applications in various fields.
Detailed Explanation of the Circumference Formula
The circumference of a cylinder's base is a crucial measurement that helps in calculating various other properties, such as surface area and volume. Let's delve into the details of the circumference formula to understand its derivation and application.
Understanding the Components
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of the base to its edge. It is a key measurement in determining the size of the circle.
- Diameter (d): The distance across the base, passing through the center. The diameter is twice the radius (\(d = 2r\)).
- Pi (π): A constant approximately equal to 3.14159. It represents the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
Derivation of the Formula
The circumference of a circle (and hence the base of a cylinder) is directly related to its diameter. The relationship can be expressed as:
\[
C = \pi d
\]
Since the diameter is twice the radius (\(d = 2r\)), we can substitute \(2r\) for \(d\) in the formula:
\[
C = \pi (2r) = 2\pi r
\]
This shows that the circumference is twice the product of pi and the radius.
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Measure the Radius or Diameter: Start by measuring the radius (r) or diameter (d) of the base.
- Apply the Formula: Use the appropriate formula based on your measurement.
- If you have the radius: \(C = 2\pi r\)
- If you have the diameter: \(C = \pi d\)
- Calculate the Circumference: Multiply the radius by \(2\pi\) or the diameter by \(\pi\) to get the circumference.
Example Calculation
Let's assume the radius of a cylinder's base is 5 cm. Using the formula \(C = 2\pi r\):
\[
C = 2\pi \times 5 = 10\pi \approx 31.42 \text{ cm}
\]
This detailed explanation shows how the circumference formula is derived and applied, providing a comprehensive understanding for accurate calculations.
Examples of Calculating the Perimeter of a Cylinder
To better understand how to calculate the perimeter (circumference) of a cylinder's base, let's go through some examples. We'll use both the radius and the diameter in our calculations to demonstrate the process clearly.
Example 1: Using the Radius
- Step 1: Identify the radius of the base. Let's assume the radius (\(r\)) is 7 cm.
- Step 2: Apply the formula:
\[
C = 2\pi r
\] - Step 3: Substitute the radius into the formula:
\[
C = 2\pi \times 7 = 14\pi
\] - Step 4: Calculate the value:
\[
C \approx 14 \times 3.14159 \approx 43.98 \text{ cm}
\]
Example 2: Using the Diameter
- Step 1: Identify the diameter of the base. Let's assume the diameter (\(d\)) is 10 cm.
- Step 2: Apply the formula:
\[
C = \pi d
\] - Step 3: Substitute the diameter into the formula:
\[
C = \pi \times 10 = 10\pi
\] - Step 4: Calculate the value:
\[
C \approx 10 \times 3.14159 \approx 31.42 \text{ cm}
\]
Example 3: Practical Application
- Scenario: You have a cylindrical water tank with a radius of 15 cm. You need to find the perimeter of the base to determine the amount of material required to make a circular cover.
- Step 1: Identify the radius (\(r\)) which is 15 cm.
- Step 2: Apply the formula:
\[
C = 2\pi r
\] - Step 3: Substitute the radius into the formula:
\[
C = 2\pi \times 15 = 30\pi
\] - Step 4: Calculate the value:
\[
C \approx 30 \times 3.14159 \approx 94.25 \text{ cm}
\]
These examples illustrate how to calculate the perimeter of a cylinder's base using either the radius or diameter. By following these steps, you can accurately determine the circumference for any cylindrical shape.
Applications of Cylinder Perimeter Calculations
Understanding and calculating the perimeter (circumference) of a cylinder's base has numerous practical applications across various fields. These calculations are essential in both academic and real-world scenarios. Let's explore some of the key applications step by step.
1. Manufacturing and Engineering
- Design and Production: Engineers use perimeter calculations to design cylindrical components such as pipes, tubes, and tanks. Accurate measurements ensure that parts fit correctly and function as intended.
- Material Estimation: Knowing the perimeter helps in estimating the amount of material required for manufacturing cylindrical objects, reducing waste and optimizing costs.
2. Construction and Architecture
- Structural Elements: Architects and builders calculate the perimeter of cylindrical columns and supports to ensure structural integrity and aesthetic design.
- Surface Area Calculations: Perimeter measurements are used to determine the surface area of cylindrical structures, aiding in tasks such as painting, cladding, and insulation.
3. Packaging and Storage
- Container Design: In the packaging industry, calculating the perimeter of cylindrical containers, such as cans and bottles, is crucial for designing labels and packaging materials.
- Volume and Space Utilization: Accurate perimeter calculations help in optimizing storage solutions, ensuring that cylindrical containers fit efficiently within designated spaces.
4. Science and Education
- Academic Exercises: Perimeter calculations are a fundamental part of geometry education, helping students understand the properties of cylinders and other geometric shapes.
- Scientific Research: Scientists use these calculations in experiments and research involving cylindrical shapes, such as test tubes, beakers, and other laboratory equipment.
5. Everyday Applications
- DIY Projects: Home improvement enthusiasts and hobbyists often encounter cylindrical objects in their projects. Knowing how to calculate the perimeter can assist in tasks such as wrapping, fitting, and crafting.
- Measurement and Fitting: Understanding perimeter calculations helps in practical tasks such as measuring ropes, wires, and hoses to fit around cylindrical objects.
These applications highlight the importance of understanding and accurately calculating the perimeter of a cylinder. Whether in professional fields or everyday activities, these skills are invaluable for ensuring precision and efficiency.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Calculating the perimeter (circumference) of a cylinder's base is a straightforward process, but there are common mistakes that can lead to incorrect results. Here, we outline these errors and how to avoid them, ensuring accurate calculations.
1. Confusing Radius and Diameter
- Mistake: Using the diameter value in place of the radius when applying the formula \(C = 2\pi r\).
- Solution: Always double-check whether you have the radius or diameter. Remember, the diameter is twice the radius (\(d = 2r\)). Use the correct formula: \(C = 2\pi r\) for radius and \(C = \pi d\) for diameter.
2. Incorrect Use of Pi (π)
- Mistake: Using an incorrect value for π. The value of π is approximately 3.14159.
- Solution: Use a calculator that has a π function to ensure accuracy, or use the precise value of 3.14159 if calculating manually.
3. Misplacing Decimal Points
- Mistake: Misplacing decimal points when performing multiplication, leading to significant errors in the final result.
- Solution: Pay careful attention to decimal placement in your calculations. Using a calculator can help minimize this risk.
4. Forgetting to Multiply by Two
- Mistake: Forgetting to multiply the radius by two in the formula \(C = 2\pi r\).
- Solution: Recall that the circumference formula \(C = 2\pi r\) explicitly requires multiplying the radius by two.
5. Units of Measurement
- Mistake: Inconsistent units of measurement, such as mixing centimeters with inches, leading to incorrect results.
- Solution: Ensure all measurements are in the same unit before performing calculations. Convert units if necessary to maintain consistency.
6. Overlooking Practical Constraints
- Mistake: Ignoring practical constraints such as material thickness when applying theoretical calculations to real-world scenarios.
- Solution: Consider practical factors such as material thickness and allowances for manufacturing tolerances when using theoretical calculations in real-world applications.
By being aware of these common mistakes and following these solutions, you can ensure accurate and reliable calculations of the perimeter of a cylinder's base. This attention to detail is crucial for both academic exercises and practical applications.
FAQs about Cylinder Perimeter
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about the perimeter of a cylinder to help clarify common doubts and provide detailed insights.
Q1: What is the perimeter of a cylinder?
A1: The term "perimeter" of a cylinder typically refers to the circumference of its circular base. The formula to calculate it is \(C = 2\pi r\) where \(r\) is the radius of the base. If the diameter (\(d\)) is known, the formula \(C = \pi d\) can be used.
Q2: How do you find the circumference if only the diameter is given?
A2: If the diameter (\(d\)) is given, you can use the formula:
\[
C = \pi d
\]
Q3: Can you calculate the perimeter using the height of the cylinder?
A3: No, the height of the cylinder is not used to calculate the circumference of the base. The circumference depends only on the radius or diameter of the base. However, the height is important for calculating the lateral surface area.
Q4: What units should be used for calculating the perimeter?
A4: The units for the perimeter should be the same as the units used for the radius or diameter. For example, if the radius is in centimeters, the circumference will also be in centimeters. Consistency in units is crucial for accurate calculations.
Q5: Is the perimeter of a cylinder's base the same as the lateral surface perimeter?
A5: Yes, the perimeter of the cylinder's base (the circumference) is the same as the lateral surface perimeter. The lateral surface perimeter refers to the distance around the side of the cylinder, which is equal to the base's circumference.
Q6: Why is calculating the perimeter of a cylinder important?
A6: Calculating the perimeter of a cylinder is important for various practical applications, such as determining the amount of material needed for construction, designing cylindrical objects, and performing scientific experiments. It is a fundamental measurement in geometry and engineering.
Q7: Can you explain the formula \(C = 2\pi r\) in simple terms?
A7: The formula \(C = 2\pi r\) means that the circumference (C) of a circle (or the base of a cylinder) is equal to 2 times \(\pi\) (approximately 3.14159) multiplied by the radius (r) of the circle. This formula derives from the relationship between a circle's circumference and its radius.
Q8: How accurate do the calculations need to be?
A8: The accuracy of the calculations depends on the application. For most practical purposes, using \(\pi\) as 3.14159 is sufficiently accurate. For more precise calculations, especially in scientific and engineering contexts, you might use a more accurate value of \(\pi\) or a calculator with a \(\pi\) function.
These FAQs aim to address common questions and provide a deeper understanding of calculating the perimeter of a cylinder, ensuring clarity and precision in both academic and practical applications.

Conclusion
Understanding the perimeter, or more precisely, the circumference of a cylinder's base is essential in both academic and practical applications. By mastering the formula and the concept, you can efficiently tackle various problems involving cylinders.
To summarize:
- The perimeter (circumference) of a cylinder's base is calculated using the formula: \[ C = 2\pi r \] where \( r \) is the radius of the base.
- For the lateral surface, the perimeter is given by the height of the cylinder.
- Applications of these calculations are widespread, from engineering and construction to everyday tasks.
- Common mistakes to avoid include confusing the height with the radius and misapplying the formula for the circumference.
With a clear understanding of these concepts, you can confidently approach problems involving the perimeter of a cylinder. Practice with various examples to reinforce your knowledge and improve your accuracy in calculations. By doing so, you'll develop a solid foundation that will be beneficial in both academic studies and practical situations.
READ MORE:
Chu Vi và Diện Tích Của Kim Tự Tháp, Hình Nón và Hình Trụ