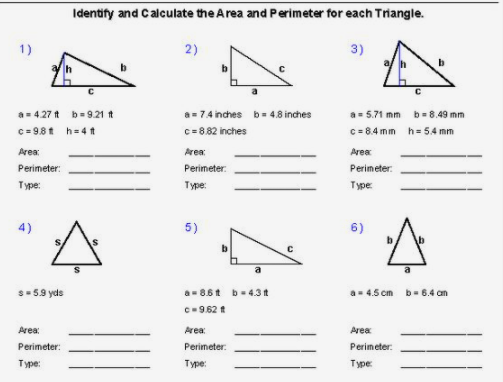
Topic perimeter of polygon calculator: Discover the easiest way to calculate the perimeter of any polygon with our Perimeter of Polygon Calculator. Whether you're dealing with regular or irregular polygons, our guide provides clear instructions, formulas, and examples to help you master perimeter calculations effortlessly. Simplify your geometry homework and projects with our comprehensive tool.
Table of Content
- Perimeter of Polygon Calculator
- Perimeter of Polygon Calculator
- Introduction to Polygon Perimeters
- Introduction to Polygon Perimeters
- Understanding Polygons
- Understanding Polygons
- Basic Concepts of Perimeter Calculation
- Basic Concepts of Perimeter Calculation
- Formulas for Perimeter Calculation
- Formulas for Perimeter Calculation
- Regular vs. Irregular Polygons
- Regular vs. Irregular Polygons
- Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Perimeters
- Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Perimeters
- Examples of Perimeter Calculations
- Examples of Perimeter Calculations
- Online Perimeter Calculators
- Online Perimeter Calculators
- Benefits of Using Online Calculators
- Benefits of Using Online Calculators
- Applications of Perimeter Calculations
- Applications of Perimeter Calculations
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Tips for Accurate Perimeter Calculation
- Tips for Accurate Perimeter Calculation
- FAQs on Perimeter Calculation
- FAQs on Perimeter Calculation
- Additional Resources
- Additional Resources
- Conclusion
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách tìm diện tích của đa giác đều khi biết bán kính. Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ và dễ dàng áp dụng công thức tính toán trong thực tế.
Perimeter of Polygon Calculator
A polygon is a two-dimensional geometric figure with straight sides. The perimeter of a polygon is the total length of its sides. Calculating the perimeter of a polygon involves summing the lengths of all its sides.
How to Calculate the Perimeter
To calculate the perimeter of a polygon, follow these steps:
- Identify the lengths of all the sides of the polygon.
- Sum the lengths of all the sides.
Formula for Regular Polygons
For a regular polygon (where all sides and angles are equal), the formula to calculate the perimeter is simpler:
\[
P = n \times s
\]
where:
- \(P\) is the perimeter
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s\) is the length of one side
Perimeter of an Irregular Polygon
For an irregular polygon (where sides and angles can vary), the perimeter is calculated by summing the length of each side individually:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i
\]
where:
- \(s_i\) is the length of the \(i\)-th side
Example Calculation
Consider a pentagon with sides of lengths 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, and 3 cm:
\[
P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 4 + 3 = 19 \text{ cm}
\]
The perimeter of this pentagon is 19 cm.
Using an Online Calculator
Online calculators can simplify the process of finding the perimeter of a polygon. These calculators typically require you to input the number of sides and the length of each side (for irregular polygons) or just the number of sides and one side length (for regular polygons). The calculator will then compute the perimeter for you.
Benefits of Using a Perimeter Calculator
- Time-saving: Quickly calculates the perimeter without manual computation.
- Accuracy: Reduces the chances of errors in calculations.
- Convenience: Easy to use, especially for complex polygons with many sides.

READ MORE:
Perimeter of Polygon Calculator
A polygon is a two-dimensional geometric figure with straight sides. The perimeter of a polygon is the total length of its sides. Calculating the perimeter of a polygon involves summing the lengths of all its sides.
How to Calculate the Perimeter
To calculate the perimeter of a polygon, follow these steps:
- Identify the lengths of all the sides of the polygon.
- Sum the lengths of all the sides.
Formula for Regular Polygons
For a regular polygon (where all sides and angles are equal), the formula to calculate the perimeter is simpler:
\[
P = n \times s
\]
where:
- \(P\) is the perimeter
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s\) is the length of one side
Perimeter of an Irregular Polygon
For an irregular polygon (where sides and angles can vary), the perimeter is calculated by summing the length of each side individually:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i
\]
where:
- \(s_i\) is the length of the \(i\)-th side
Example Calculation
Consider a pentagon with sides of lengths 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, and 3 cm:
\[
P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 4 + 3 = 19 \text{ cm}
\]
The perimeter of this pentagon is 19 cm.
Using an Online Calculator
Online calculators can simplify the process of finding the perimeter of a polygon. These calculators typically require you to input the number of sides and the length of each side (for irregular polygons) or just the number of sides and one side length (for regular polygons). The calculator will then compute the perimeter for you.
Benefits of Using a Perimeter Calculator
- Time-saving: Quickly calculates the perimeter without manual computation.
- Accuracy: Reduces the chances of errors in calculations.
- Convenience: Easy to use, especially for complex polygons with many sides.

Introduction to Polygon Perimeters
A polygon is a closed, two-dimensional shape with straight sides. The perimeter of a polygon is the total distance around the shape, calculated by summing the lengths of all its sides. This measurement is crucial in various fields, including mathematics, engineering, and architecture.
Polygons can be regular or irregular:
- Regular Polygons: All sides and angles are equal. Examples include equilateral triangles and squares.
- Irregular Polygons: Sides and angles can vary in length and size. Examples include scalene triangles and trapezoids.
Calculating the perimeter of a polygon involves different steps depending on whether the polygon is regular or irregular.
For Regular Polygons
Use the formula:
\[
P = n \times s
\]
where:
- \(P\) is the perimeter
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s\) is the length of one side
For Irregular Polygons
Sum the lengths of all sides:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i
\]
where:
- \(P\) is the perimeter
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s_i\) is the length of the \(i\)-th side
Let's consider an example for better understanding:
Example: Calculate the perimeter of a pentagon with side lengths 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, and 3 cm.
\[
P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 4 + 3 = 19 \text{ cm}
\]
The perimeter of this pentagon is 19 cm.
Using an online perimeter calculator can significantly simplify these calculations, ensuring accuracy and saving time. These tools are especially useful for complex polygons with many sides or varying lengths.
Introduction to Polygon Perimeters
A polygon is a closed, two-dimensional shape with straight sides. The perimeter of a polygon is the total distance around the shape, calculated by summing the lengths of all its sides. This measurement is crucial in various fields, including mathematics, engineering, and architecture.
Polygons can be regular or irregular:
- Regular Polygons: All sides and angles are equal. Examples include equilateral triangles and squares.
- Irregular Polygons: Sides and angles can vary in length and size. Examples include scalene triangles and trapezoids.
Calculating the perimeter of a polygon involves different steps depending on whether the polygon is regular or irregular.
For Regular Polygons
Use the formula:
\[
P = n \times s
\]
where:
- \(P\) is the perimeter
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s\) is the length of one side
For Irregular Polygons
Sum the lengths of all sides:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i
\]
where:
- \(P\) is the perimeter
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s_i\) is the length of the \(i\)-th side
Let's consider an example for better understanding:
Example: Calculate the perimeter of a pentagon with side lengths 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, and 3 cm.
\[
P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 4 + 3 = 19 \text{ cm}
\]
The perimeter of this pentagon is 19 cm.
Using an online perimeter calculator can significantly simplify these calculations, ensuring accuracy and saving time. These tools are especially useful for complex polygons with many sides or varying lengths.
Understanding Polygons
Polygons are fundamental shapes in geometry, characterized by straight sides that form a closed figure. The term "polygon" comes from the Greek words "poly," meaning "many," and "gon," meaning "angle." Polygons can be classified based on the number of sides they have and whether their sides and angles are equal.
Types of Polygons
Polygons are broadly categorized into two types:
- Regular Polygons: All sides and angles are equal. Examples include the equilateral triangle, square, and regular pentagon.
- Irregular Polygons: Sides and angles are not equal. Examples include the scalene triangle and irregular quadrilateral.
Classification by Number of Sides
Polygons are also classified by the number of sides they have:
- Triangle: 3 sides
- Quadrilateral: 4 sides
- Pentagon: 5 sides
- Hexagon: 6 sides
- Heptagon: 7 sides
- Octagon: 8 sides
- Nonagon: 9 sides
- Decagon: 10 sides
Properties of Polygons
Polygons have several key properties:
- Sides: The straight line segments that form the polygon.
- Vertices: The points where two sides meet.
- Angles: The angles formed by two adjacent sides.
- Diagonals: Line segments connecting non-adjacent vertices.
Sum of Interior Angles
The sum of the interior angles of a polygon depends on the number of sides (\(n\)) and can be calculated using the formula:
\[
\text{Sum of Interior Angles} = (n - 2) \times 180^\circ
\]
For example, in a hexagon (\(n = 6\)):
\[
\text{Sum of Interior Angles} = (6 - 2) \times 180^\circ = 720^\circ
\]
Perimeter of Polygons
The perimeter of a polygon is the total length of its sides. For regular polygons, the perimeter (\(P\)) is given by:
\[
P = n \times s
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s\) is the length of one side
For irregular polygons, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all sides:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s_i\) is the length of the \(i\)-th side
Understanding these properties and classifications is essential for accurately calculating the perimeter and other characteristics of polygons.
Understanding Polygons
Polygons are fundamental shapes in geometry, characterized by straight sides that form a closed figure. The term "polygon" comes from the Greek words "poly," meaning "many," and "gon," meaning "angle." Polygons can be classified based on the number of sides they have and whether their sides and angles are equal.
Types of Polygons
Polygons are broadly categorized into two types:
- Regular Polygons: All sides and angles are equal. Examples include the equilateral triangle, square, and regular pentagon.
- Irregular Polygons: Sides and angles are not equal. Examples include the scalene triangle and irregular quadrilateral.
Classification by Number of Sides
Polygons are also classified by the number of sides they have:
- Triangle: 3 sides
- Quadrilateral: 4 sides
- Pentagon: 5 sides
- Hexagon: 6 sides
- Heptagon: 7 sides
- Octagon: 8 sides
- Nonagon: 9 sides
- Decagon: 10 sides
Properties of Polygons
Polygons have several key properties:
- Sides: The straight line segments that form the polygon.
- Vertices: The points where two sides meet.
- Angles: The angles formed by two adjacent sides.
- Diagonals: Line segments connecting non-adjacent vertices.
Sum of Interior Angles
The sum of the interior angles of a polygon depends on the number of sides (\(n\)) and can be calculated using the formula:
\[
\text{Sum of Interior Angles} = (n - 2) \times 180^\circ
\]
For example, in a hexagon (\(n = 6\)):
\[
\text{Sum of Interior Angles} = (6 - 2) \times 180^\circ = 720^\circ
\]
Perimeter of Polygons
The perimeter of a polygon is the total length of its sides. For regular polygons, the perimeter (\(P\)) is given by:
\[
P = n \times s
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s\) is the length of one side
For irregular polygons, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all sides:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s_i\) is the length of the \(i\)-th side
Understanding these properties and classifications is essential for accurately calculating the perimeter and other characteristics of polygons.
Basic Concepts of Perimeter Calculation
The perimeter of a polygon is the total length of its sides. Calculating the perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry, essential for various applications in science, engineering, and everyday life.
Step-by-Step Calculation
To calculate the perimeter of a polygon, follow these steps:
- Identify all the sides of the polygon.
- Measure the length of each side.
- Sum the lengths of all the sides to get the perimeter.
Formula for Regular Polygons
For regular polygons, where all sides are equal, the formula to calculate the perimeter (\(P\)) is:
\[
P = n \times s
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s\) is the length of one side
For example, for a square with a side length of 5 cm:
\[
P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ cm}
\]
Formula for Irregular Polygons
For irregular polygons, where sides can have different lengths, the perimeter is calculated by summing the lengths of all the sides:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s_i\) is the length of the \(i\)-th side
For example, for a polygon with side lengths of 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, and 3 cm:
\[
P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 4 + 3 = 19 \text{ cm}
\]
Special Cases
Some polygons have specific names and properties that can simplify the perimeter calculation:
- Triangle: The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of its three sides.
- Quadrilateral: The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of its four sides.
- Polygon with equal sides: For any polygon where all sides are equal, multiply the number of sides by the length of one side.
Using a Perimeter Calculator
Online perimeter calculators can automate these steps, making it easy to find the perimeter quickly and accurately. Simply input the number of sides and their lengths, and the calculator will provide the perimeter.
Understanding these basic concepts and formulas allows you to calculate the perimeter of any polygon, whether regular or irregular, with confidence and ease.
Basic Concepts of Perimeter Calculation
The perimeter of a polygon is the total length of its sides. Calculating the perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry, essential for various applications in science, engineering, and everyday life.
Step-by-Step Calculation
To calculate the perimeter of a polygon, follow these steps:
- Identify all the sides of the polygon.
- Measure the length of each side.
- Sum the lengths of all the sides to get the perimeter.
Formula for Regular Polygons
For regular polygons, where all sides are equal, the formula to calculate the perimeter (\(P\)) is:
\[
P = n \times s
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s\) is the length of one side
For example, for a square with a side length of 5 cm:
\[
P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ cm}
\]
Formula for Irregular Polygons
For irregular polygons, where sides can have different lengths, the perimeter is calculated by summing the lengths of all the sides:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s_i\) is the length of the \(i\)-th side
For example, for a polygon with side lengths of 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, and 3 cm:
\[
P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 4 + 3 = 19 \text{ cm}
\]
Special Cases
Some polygons have specific names and properties that can simplify the perimeter calculation:
- Triangle: The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of its three sides.
- Quadrilateral: The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of its four sides.
- Polygon with equal sides: For any polygon where all sides are equal, multiply the number of sides by the length of one side.
Using a Perimeter Calculator
Online perimeter calculators can automate these steps, making it easy to find the perimeter quickly and accurately. Simply input the number of sides and their lengths, and the calculator will provide the perimeter.
Understanding these basic concepts and formulas allows you to calculate the perimeter of any polygon, whether regular or irregular, with confidence and ease.
Formulas for Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of a polygon involves using specific formulas depending on whether the polygon is regular or irregular. Understanding these formulas allows for accurate and efficient perimeter calculations.
Perimeter of Regular Polygons
For regular polygons, where all sides and angles are equal, the formula to calculate the perimeter (\(P\)) is straightforward:
\[
P = n \times s
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s\) is the length of one side
Example:
For a hexagon with each side measuring 6 cm:
\[
P = 6 \times 6 = 36 \text{ cm}
\]
Perimeter of Irregular Polygons
For irregular polygons, where sides can have different lengths, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all the sides:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s_i\) is the length of the \(i\)-th side
Example:
For a polygon with side lengths of 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, and 3 cm:
\[
P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 4 + 3 = 19 \text{ cm}
\]
Special Formulas for Common Polygons
- Triangle: The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of its three sides: \[ P = a + b + c \] where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the side lengths.
- Rectangle: The perimeter is calculated by: \[ P = 2(l + w) \] where \(l\) is the length and \(w\) is the width.
- Square: The perimeter is four times the length of one side: \[ P = 4s \] where \(s\) is the side length.
- Regular Pentagon: The perimeter is five times the length of one side: \[ P = 5s \] where \(s\) is the side length.
Using Online Calculators
Online perimeter calculators can automate these calculations, ensuring accuracy and saving time. Users simply need to input the number of sides and the length of each side (for irregular polygons) or just the side length (for regular polygons), and the calculator will compute the perimeter.
Understanding and using these formulas will help in accurately determining the perimeter of various polygons, whether regular or irregular, enhancing both mathematical understanding and practical application.

Formulas for Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of a polygon involves using specific formulas depending on whether the polygon is regular or irregular. Understanding these formulas allows for accurate and efficient perimeter calculations.
Perimeter of Regular Polygons
For regular polygons, where all sides and angles are equal, the formula to calculate the perimeter (\(P\)) is straightforward:
\[
P = n \times s
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s\) is the length of one side
Example:
For a hexagon with each side measuring 6 cm:
\[
P = 6 \times 6 = 36 \text{ cm}
\]
Perimeter of Irregular Polygons
For irregular polygons, where sides can have different lengths, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all the sides:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s_i\) is the length of the \(i\)-th side
Example:
For a polygon with side lengths of 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, and 3 cm:
\[
P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 4 + 3 = 19 \text{ cm}
\]
Special Formulas for Common Polygons
- Triangle: The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of its three sides: \[ P = a + b + c \] where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the side lengths.
- Rectangle: The perimeter is calculated by: \[ P = 2(l + w) \] where \(l\) is the length and \(w\) is the width.
- Square: The perimeter is four times the length of one side: \[ P = 4s \] where \(s\) is the side length.
- Regular Pentagon: The perimeter is five times the length of one side: \[ P = 5s \] where \(s\) is the side length.
Using Online Calculators
Online perimeter calculators can automate these calculations, ensuring accuracy and saving time. Users simply need to input the number of sides and the length of each side (for irregular polygons) or just the side length (for regular polygons), and the calculator will compute the perimeter.
Understanding and using these formulas will help in accurately determining the perimeter of various polygons, whether regular or irregular, enhancing both mathematical understanding and practical application.

Regular vs. Irregular Polygons
Polygons are geometric shapes with multiple sides. They can be classified into two main categories: regular and irregular polygons. Understanding the differences between these two types is essential for accurate perimeter calculations and other geometric applications.
Regular Polygons
Regular polygons have all sides and angles equal. This uniformity simplifies calculations and provides unique geometric properties.
- Properties:
- All sides are of equal length.
- All interior angles are equal.
- They are highly symmetrical.
- Examples:
- Equilateral triangle (3 sides)
- Square (4 sides)
- Regular pentagon (5 sides)
- Regular hexagon (6 sides)
The perimeter of a regular polygon can be calculated using the formula:
\[
P = n \times s
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s\) is the length of one side
Irregular Polygons
Irregular polygons have sides and angles of different lengths and sizes. These polygons lack the symmetry found in regular polygons, making their properties more complex.
- Properties:
- Sides can be of different lengths.
- Interior angles can vary.
- They lack uniformity and symmetry.
- Examples:
- Scalene triangle (3 sides of different lengths)
- Irregular quadrilateral (4 sides of different lengths)
- Irregular pentagon (5 sides of different lengths)
The perimeter of an irregular polygon is calculated by summing the lengths of all its sides:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s_i\) is the length of the \(i\)-th side
Comparison Table
| Feature | Regular Polygons | Irregular Polygons |
|---|---|---|
| Sides | Equal length | Different lengths |
| Angles | Equal | Varying |
| Symmetry | Highly symmetrical | Lacks symmetry |
| Perimeter Calculation | \[ P = n \times s \] | \[ P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i \] |
Understanding whether a polygon is regular or irregular is crucial for applying the correct formulas and achieving accurate geometric calculations.
Regular vs. Irregular Polygons
Polygons are geometric shapes with multiple sides. They can be classified into two main categories: regular and irregular polygons. Understanding the differences between these two types is essential for accurate perimeter calculations and other geometric applications.
Regular Polygons
Regular polygons have all sides and angles equal. This uniformity simplifies calculations and provides unique geometric properties.
- Properties:
- All sides are of equal length.
- All interior angles are equal.
- They are highly symmetrical.
- Examples:
- Equilateral triangle (3 sides)
- Square (4 sides)
- Regular pentagon (5 sides)
- Regular hexagon (6 sides)
The perimeter of a regular polygon can be calculated using the formula:
\[
P = n \times s
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s\) is the length of one side
Irregular Polygons
Irregular polygons have sides and angles of different lengths and sizes. These polygons lack the symmetry found in regular polygons, making their properties more complex.
- Properties:
- Sides can be of different lengths.
- Interior angles can vary.
- They lack uniformity and symmetry.
- Examples:
- Scalene triangle (3 sides of different lengths)
- Irregular quadrilateral (4 sides of different lengths)
- Irregular pentagon (5 sides of different lengths)
The perimeter of an irregular polygon is calculated by summing the lengths of all its sides:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s_i\) is the length of the \(i\)-th side
Comparison Table
| Feature | Regular Polygons | Irregular Polygons |
|---|---|---|
| Sides | Equal length | Different lengths |
| Angles | Equal | Varying |
| Symmetry | Highly symmetrical | Lacks symmetry |
| Perimeter Calculation | \[ P = n \times s \] | \[ P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i \] |
Understanding whether a polygon is regular or irregular is crucial for applying the correct formulas and achieving accurate geometric calculations.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Perimeters
Calculating the perimeter of a polygon involves summing the lengths of all its sides. Follow this step-by-step guide to accurately determine the perimeter of both regular and irregular polygons.
Step 1: Identify the Type of Polygon
Determine whether the polygon is regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles vary).
Step 2: List the Side Lengths
Measure and list the lengths of all the sides of the polygon. Ensure that each side is measured accurately.
Step 3: Apply the Appropriate Formula
Use the correct formula based on the type of polygon:
For Regular Polygons
Use the formula:
\[
P = n \times s
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s\) is the length of one side
For Irregular Polygons
Sum the lengths of all sides:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s_i\) is the length of the \(i\)-th side
Step 4: Calculate the Perimeter
Perform the arithmetic to find the perimeter.
Example for a regular pentagon with each side measuring 5 cm:
\[
P = 5 \times 5 = 25 \text{ cm}
\]
Example for an irregular polygon with side lengths 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, and 3 cm:
\[
P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 4 + 3 = 19 \text{ cm}
\]
Step 5: Double-Check Measurements and Calculations
Review your measurements and calculations to ensure accuracy. Small errors in measurement can lead to incorrect perimeter values.
Using Online Perimeter Calculators
For convenience, use an online perimeter calculator. These tools can quickly compute the perimeter by simply inputting the number of sides and their respective lengths.
Steps to use an online calculator:
- Go to a reliable perimeter calculator website.
- Select the type of polygon (regular or irregular).
- Enter the number of sides.
- Input the length of each side (for irregular polygons) or the length of one side (for regular polygons).
- Click on the "Calculate" button to get the perimeter.
Understanding these steps and using the right tools will help you accurately calculate the perimeter of any polygon, ensuring precision in your geometric tasks.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Perimeters
Calculating the perimeter of a polygon involves summing the lengths of all its sides. Follow this step-by-step guide to accurately determine the perimeter of both regular and irregular polygons.
Step 1: Identify the Type of Polygon
Determine whether the polygon is regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles vary).
Step 2: List the Side Lengths
Measure and list the lengths of all the sides of the polygon. Ensure that each side is measured accurately.
Step 3: Apply the Appropriate Formula
Use the correct formula based on the type of polygon:
For Regular Polygons
Use the formula:
\[
P = n \times s
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s\) is the length of one side
For Irregular Polygons
Sum the lengths of all sides:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i
\]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides
- \(s_i\) is the length of the \(i\)-th side
Step 4: Calculate the Perimeter
Perform the arithmetic to find the perimeter.
Example for a regular pentagon with each side measuring 5 cm:
\[
P = 5 \times 5 = 25 \text{ cm}
\]
Example for an irregular polygon with side lengths 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, and 3 cm:
\[
P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 4 + 3 = 19 \text{ cm}
\]
Step 5: Double-Check Measurements and Calculations
Review your measurements and calculations to ensure accuracy. Small errors in measurement can lead to incorrect perimeter values.
Using Online Perimeter Calculators
For convenience, use an online perimeter calculator. These tools can quickly compute the perimeter by simply inputting the number of sides and their respective lengths.
Steps to use an online calculator:
- Go to a reliable perimeter calculator website.
- Select the type of polygon (regular or irregular).
- Enter the number of sides.
- Input the length of each side (for irregular polygons) or the length of one side (for regular polygons).
- Click on the "Calculate" button to get the perimeter.
Understanding these steps and using the right tools will help you accurately calculate the perimeter of any polygon, ensuring precision in your geometric tasks.
Examples of Perimeter Calculations
Understanding the process of perimeter calculation through examples can help solidify the concepts. Here are several examples illustrating how to calculate the perimeter of different types of polygons.
Example 1: Perimeter of a Regular Hexagon
A regular hexagon has six equal sides. If each side is 7 cm long, the perimeter (\(P\)) is calculated as follows:
\[
P = n \times s = 6 \times 7 = 42 \text{ cm}
\]
Example 2: Perimeter of a Square
A square has four equal sides. If each side is 5 cm long, the perimeter is:
\[
P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ cm}
\]
Example 3: Perimeter of an Irregular Quadrilateral
An irregular quadrilateral has sides of different lengths: 4 cm, 6 cm, 7 cm, and 5 cm. The perimeter is found by summing the lengths of all sides:
\[
P = 4 + 6 + 7 + 5 = 22 \text{ cm}
\]
Example 4: Perimeter of a Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon has five equal sides. If each side is 8 cm long, the perimeter is:
\[
P = 5 \times 8 = 40 \text{ cm}
\]
Example 5: Perimeter of an Irregular Hexagon
An irregular hexagon has sides of 3 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, 6 cm, 2 cm, and 7 cm. The perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of all the sides:
\[
P = 3 + 5 + 4 + 6 + 2 + 7 = 27 \text{ cm}
\]
Step-by-Step Calculation for Irregular Polygon
Consider a polygon with sides of different lengths: 3 cm, 5 cm, 7 cm, 5 cm, and 6 cm. To calculate the perimeter:
- List the lengths of all sides:
- Side 1: 3 cm
- Side 2: 5 cm
- Side 3: 7 cm
- Side 4: 5 cm
- Side 5: 6 cm
- Sum the lengths of all sides:
\[
P = 3 + 5 + 7 + 5 + 6 = 26 \text{ cm}
\]
Using an Online Calculator for Perimeter Calculation
Online calculators can simplify these calculations. For example, to calculate the perimeter of an irregular polygon:
- Enter the number of sides.
- Input the length of each side.
- Click the "Calculate" button to get the perimeter.
This method ensures accuracy and saves time, especially for polygons with many sides.
These examples highlight the straightforward process of calculating the perimeter for various polygons, whether regular or irregular.
Examples of Perimeter Calculations
Understanding the process of perimeter calculation through examples can help solidify the concepts. Here are several examples illustrating how to calculate the perimeter of different types of polygons.
Example 1: Perimeter of a Regular Hexagon
A regular hexagon has six equal sides. If each side is 7 cm long, the perimeter (\(P\)) is calculated as follows:
\[
P = n \times s = 6 \times 7 = 42 \text{ cm}
\]
Example 2: Perimeter of a Square
A square has four equal sides. If each side is 5 cm long, the perimeter is:
\[
P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ cm}
\]
Example 3: Perimeter of an Irregular Quadrilateral
An irregular quadrilateral has sides of different lengths: 4 cm, 6 cm, 7 cm, and 5 cm. The perimeter is found by summing the lengths of all sides:
\[
P = 4 + 6 + 7 + 5 = 22 \text{ cm}
\]
Example 4: Perimeter of a Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon has five equal sides. If each side is 8 cm long, the perimeter is:
\[
P = 5 \times 8 = 40 \text{ cm}
\]
Example 5: Perimeter of an Irregular Hexagon
An irregular hexagon has sides of 3 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, 6 cm, 2 cm, and 7 cm. The perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of all the sides:
\[
P = 3 + 5 + 4 + 6 + 2 + 7 = 27 \text{ cm}
\]
Step-by-Step Calculation for Irregular Polygon
Consider a polygon with sides of different lengths: 3 cm, 5 cm, 7 cm, 5 cm, and 6 cm. To calculate the perimeter:
- List the lengths of all sides:
- Side 1: 3 cm
- Side 2: 5 cm
- Side 3: 7 cm
- Side 4: 5 cm
- Side 5: 6 cm
- Sum the lengths of all sides:
\[
P = 3 + 5 + 7 + 5 + 6 = 26 \text{ cm}
\]
Using an Online Calculator for Perimeter Calculation
Online calculators can simplify these calculations. For example, to calculate the perimeter of an irregular polygon:
- Enter the number of sides.
- Input the length of each side.
- Click the "Calculate" button to get the perimeter.
This method ensures accuracy and saves time, especially for polygons with many sides.
These examples highlight the straightforward process of calculating the perimeter for various polygons, whether regular or irregular.
Online Perimeter Calculators
Online perimeter calculators are powerful tools designed to simplify the process of calculating the perimeter of various polygons. These calculators are particularly useful for students, engineers, architects, and anyone needing quick and accurate perimeter measurements. Below, we provide an overview of how to use these calculators and the benefits they offer.
How to Use Online Perimeter Calculators
- Select the Shape: Choose the type of polygon you need to calculate the perimeter for. Common options include triangles, rectangles, pentagons, hexagons, and other regular and irregular polygons.
- Input the Dimensions: Enter the required dimensions. For regular polygons, this typically includes the length of one side. For irregular polygons, you will need to enter the lengths of all sides.
- Calculate: Click the calculate button to get the perimeter. The calculator will use the appropriate formula based on the polygon type and provided dimensions.
- Review the Result: The calculator will display the perimeter, often along with a visual representation of the polygon and the applied formula.
Benefits of Using Online Perimeter Calculators
- Accuracy: These tools eliminate human error, ensuring precise perimeter calculations.
- Convenience: Accessible from any device with internet connectivity, making them perfect for use on-the-go.
- Speed: Quickly calculate perimeters without manual computations, saving time and effort.
- Educational Value: Many calculators provide step-by-step explanations and visual aids, helping users understand the calculation process.
Examples of Popular Online Perimeter Calculators
- Calculator.net: Offers a versatile polygon perimeter calculator that handles both regular and irregular polygons.
- Mathsisfun.com: Provides a user-friendly interface with educational explanations for each calculation.
- Symbolab: Features an advanced calculator that also supports various mathematical operations and conversions.
Step-by-Step Example: Calculating the Perimeter of a Hexagon
Let’s consider a hexagon with each side measuring 5 units:
- Select the Shape: Choose "Hexagon" from the shape options.
- Input the Dimensions: Enter the side length, which is 5 units.
- Calculate: Click the calculate button. The formula for the perimeter of a regular hexagon \(P = 6 \times \text{side length}\) will be applied.
- Review the Result: The calculator displays the perimeter: \(P = 6 \times 5 = 30\) units.
Conclusion
Online perimeter calculators are indispensable tools for anyone needing accurate and fast perimeter measurements. By understanding how to use these calculators and leveraging their benefits, users can enhance their efficiency and accuracy in various applications.

Online Perimeter Calculators
Online perimeter calculators are powerful tools designed to simplify the process of calculating the perimeter of various polygons. These calculators are particularly useful for students, engineers, architects, and anyone needing quick and accurate perimeter measurements. Below, we provide an overview of how to use these calculators and the benefits they offer.
How to Use Online Perimeter Calculators
- Select the Shape: Choose the type of polygon you need to calculate the perimeter for. Common options include triangles, rectangles, pentagons, hexagons, and other regular and irregular polygons.
- Input the Dimensions: Enter the required dimensions. For regular polygons, this typically includes the length of one side. For irregular polygons, you will need to enter the lengths of all sides.
- Calculate: Click the calculate button to get the perimeter. The calculator will use the appropriate formula based on the polygon type and provided dimensions.
- Review the Result: The calculator will display the perimeter, often along with a visual representation of the polygon and the applied formula.
Benefits of Using Online Perimeter Calculators
- Accuracy: These tools eliminate human error, ensuring precise perimeter calculations.
- Convenience: Accessible from any device with internet connectivity, making them perfect for use on-the-go.
- Speed: Quickly calculate perimeters without manual computations, saving time and effort.
- Educational Value: Many calculators provide step-by-step explanations and visual aids, helping users understand the calculation process.
Examples of Popular Online Perimeter Calculators
- Calculator.net: Offers a versatile polygon perimeter calculator that handles both regular and irregular polygons.
- Mathsisfun.com: Provides a user-friendly interface with educational explanations for each calculation.
- Symbolab: Features an advanced calculator that also supports various mathematical operations and conversions.
Step-by-Step Example: Calculating the Perimeter of a Hexagon
Let’s consider a hexagon with each side measuring 5 units:
- Select the Shape: Choose "Hexagon" from the shape options.
- Input the Dimensions: Enter the side length, which is 5 units.
- Calculate: Click the calculate button. The formula for the perimeter of a regular hexagon \(P = 6 \times \text{side length}\) will be applied.
- Review the Result: The calculator displays the perimeter: \(P = 6 \times 5 = 30\) units.
Conclusion
Online perimeter calculators are indispensable tools for anyone needing accurate and fast perimeter measurements. By understanding how to use these calculators and leveraging their benefits, users can enhance their efficiency and accuracy in various applications.

Benefits of Using Online Calculators
Online perimeter calculators offer a range of benefits that make them an essential tool for students, educators, professionals, and anyone interested in geometry. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Accuracy: Online calculators provide precise calculations, reducing the risk of human error. They use advanced algorithms to ensure the results are accurate, even for complex shapes.
- Convenience: These calculators are available 24/7 and can be accessed from any device with an internet connection. This makes them a convenient option for quick calculations anytime and anywhere.
- Time-saving: By automating the calculation process, online calculators save time. Users can quickly obtain results without manually performing each step of the calculation.
- User-friendly: Most online calculators are designed with a user-friendly interface that makes them easy to use. They often include clear instructions and examples to guide users through the process.
- Educational Value: These tools can serve as educational resources, helping users to understand the principles behind the calculations. They often include explanations and visual aids that enhance learning.
- Versatility: Online calculators can handle a wide range of shapes and formulas, from simple polygons to complex irregular shapes. They often include additional features such as area calculation and conversion between different units of measurement.
- Cost-effective: Many online calculators are free to use, providing a cost-effective solution compared to purchasing specialized software or tools.
Overall, online perimeter calculators are valuable tools that enhance accuracy, efficiency, and understanding in mathematical calculations. Whether for educational purposes or practical applications, they offer significant benefits that make perimeter calculations easier and more reliable.
Benefits of Using Online Calculators
Online perimeter calculators offer a range of benefits that make them an essential tool for students, educators, professionals, and anyone interested in geometry. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Accuracy: Online calculators provide precise calculations, reducing the risk of human error. They use advanced algorithms to ensure the results are accurate, even for complex shapes.
- Convenience: These calculators are available 24/7 and can be accessed from any device with an internet connection. This makes them a convenient option for quick calculations anytime and anywhere.
- Time-saving: By automating the calculation process, online calculators save time. Users can quickly obtain results without manually performing each step of the calculation.
- User-friendly: Most online calculators are designed with a user-friendly interface that makes them easy to use. They often include clear instructions and examples to guide users through the process.
- Educational Value: These tools can serve as educational resources, helping users to understand the principles behind the calculations. They often include explanations and visual aids that enhance learning.
- Versatility: Online calculators can handle a wide range of shapes and formulas, from simple polygons to complex irregular shapes. They often include additional features such as area calculation and conversion between different units of measurement.
- Cost-effective: Many online calculators are free to use, providing a cost-effective solution compared to purchasing specialized software or tools.
Overall, online perimeter calculators are valuable tools that enhance accuracy, efficiency, and understanding in mathematical calculations. Whether for educational purposes or practical applications, they offer significant benefits that make perimeter calculations easier and more reliable.
Applications of Perimeter Calculations
Perimeter calculations are essential in various fields and practical applications. Below are some key areas where understanding and calculating the perimeter of polygons is crucial:
- Architecture and Construction: In building design and construction, determining the perimeter of a plot or a structure is fundamental. It helps in planning the amount of materials needed for fencing, flooring, and other construction purposes.
- Landscaping: When designing gardens, parks, or any outdoor space, knowing the perimeter helps in planning pathways, borders, and the distribution of plants and decorations.
- Interior Design: Calculating the perimeter of rooms and spaces allows for accurate placement of furniture, carpeting, and other interior elements.
- Urban Planning: Urban planners use perimeter calculations for zoning, planning public spaces, and ensuring efficient use of land within cities and towns.
- Sports: In sports, the perimeter of fields, tracks, and courts is measured to ensure they meet regulatory standards. For instance, the perimeter of a basketball court or a running track must be precise for fair play.
- Education: Teaching perimeter calculations helps students understand basic geometry and its real-world applications. It's a fundamental concept in mathematics education.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers often calculate perimeters when creating frames, patterns, and other geometric art pieces to ensure accuracy and proportion.
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing, especially in the production of items like carpets, tiles, and metal sheets, knowing the perimeter is necessary for cutting materials to the correct size.
- Agriculture: Farmers and agriculturists measure the perimeter of fields to plan irrigation systems, planting strategies, and fencing for livestock.
Understanding the perimeter of polygons is not just an academic exercise but a practical skill that finds application in numerous professional and everyday contexts. Accurate perimeter calculations ensure efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and adherence to standards in various fields.
Applications of Perimeter Calculations
Perimeter calculations are essential in various fields and practical applications. Below are some key areas where understanding and calculating the perimeter of polygons is crucial:
- Architecture and Construction: In building design and construction, determining the perimeter of a plot or a structure is fundamental. It helps in planning the amount of materials needed for fencing, flooring, and other construction purposes.
- Landscaping: When designing gardens, parks, or any outdoor space, knowing the perimeter helps in planning pathways, borders, and the distribution of plants and decorations.
- Interior Design: Calculating the perimeter of rooms and spaces allows for accurate placement of furniture, carpeting, and other interior elements.
- Urban Planning: Urban planners use perimeter calculations for zoning, planning public spaces, and ensuring efficient use of land within cities and towns.
- Sports: In sports, the perimeter of fields, tracks, and courts is measured to ensure they meet regulatory standards. For instance, the perimeter of a basketball court or a running track must be precise for fair play.
- Education: Teaching perimeter calculations helps students understand basic geometry and its real-world applications. It's a fundamental concept in mathematics education.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers often calculate perimeters when creating frames, patterns, and other geometric art pieces to ensure accuracy and proportion.
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing, especially in the production of items like carpets, tiles, and metal sheets, knowing the perimeter is necessary for cutting materials to the correct size.
- Agriculture: Farmers and agriculturists measure the perimeter of fields to plan irrigation systems, planting strategies, and fencing for livestock.
Understanding the perimeter of polygons is not just an academic exercise but a practical skill that finds application in numerous professional and everyday contexts. Accurate perimeter calculations ensure efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and adherence to standards in various fields.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the perimeter of polygons, several common mistakes can occur. Understanding these errors can help you avoid them and ensure accurate calculations.
- Incorrect Measurement Units: Always ensure that all side lengths are measured in the same units. Mixing units can lead to incorrect perimeter calculations.
- Omitting Sides: It's easy to overlook a side, especially in polygons with many sides. Double-check that you have accounted for all sides.
- Misidentifying Polygon Type: Confusing regular polygons (where all sides and angles are equal) with irregular polygons can lead to incorrect use of formulas. Use the appropriate formula for the type of polygon.
- Incorrect Formula Application: Ensure you are using the correct formula for the perimeter based on the polygon type. For regular polygons, the formula is \( P = n \times s \), where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the side length. For irregular polygons, add up the lengths of all sides.
- Calculation Errors: Double-check arithmetic operations to avoid simple mistakes. Use a calculator to ensure accuracy.
- Assuming Measurements: Ensure all side lengths are measured accurately. Avoid guessing or assuming measurements.
- Not Accounting for Units in Final Answer: Always include the measurement unit in your final answer to clearly convey the perimeter.
- Ignoring Decimal Precision: When dealing with decimal lengths, ensure precision in measurement and calculation. Round off only in the final step if required.
By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can improve the accuracy of your perimeter calculations and avoid potential errors.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the perimeter of polygons, several common mistakes can occur. Understanding these errors can help you avoid them and ensure accurate calculations.
- Incorrect Measurement Units: Always ensure that all side lengths are measured in the same units. Mixing units can lead to incorrect perimeter calculations.
- Omitting Sides: It's easy to overlook a side, especially in polygons with many sides. Double-check that you have accounted for all sides.
- Misidentifying Polygon Type: Confusing regular polygons (where all sides and angles are equal) with irregular polygons can lead to incorrect use of formulas. Use the appropriate formula for the type of polygon.
- Incorrect Formula Application: Ensure you are using the correct formula for the perimeter based on the polygon type. For regular polygons, the formula is \( P = n \times s \), where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the side length. For irregular polygons, add up the lengths of all sides.
- Calculation Errors: Double-check arithmetic operations to avoid simple mistakes. Use a calculator to ensure accuracy.
- Assuming Measurements: Ensure all side lengths are measured accurately. Avoid guessing or assuming measurements.
- Not Accounting for Units in Final Answer: Always include the measurement unit in your final answer to clearly convey the perimeter.
- Ignoring Decimal Precision: When dealing with decimal lengths, ensure precision in measurement and calculation. Round off only in the final step if required.
By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can improve the accuracy of your perimeter calculations and avoid potential errors.
Tips for Accurate Perimeter Calculation
Accurately calculating the perimeter of a polygon involves several key steps and considerations. Here are some tips to help ensure precision in your calculations:
- Use Precise Measurements: Ensure that all side lengths are measured accurately. Use a reliable ruler or measuring tape and, if possible, measure more than once to confirm the lengths.
- Maintain Consistent Units: Always use the same unit of measurement for all sides. Convert units if necessary to maintain consistency throughout your calculations.
- Double-Check Your Polygon Type: Identify whether the polygon is regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles are not necessarily equal). Use the appropriate formula based on the polygon type.
- Apply the Correct Formula: For regular polygons, use the formula \( P = n \times s \), where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the length of each side. For irregular polygons, sum the lengths of all sides: \[ P = s_1 + s_2 + \ldots + s_n \]
- Use a Calculator for Accuracy: Use a calculator to ensure accuracy in your arithmetic operations. This helps minimize errors due to manual calculations.
- Verify Each Step: Check your work at each step of the calculation. Verify that you have included all sides and that each arithmetic operation is correct.
- Consider Decimal Precision: When dealing with decimals, maintain precision throughout your calculations. Avoid rounding until the final step to ensure accuracy.
- Document Measurements and Calculations: Keep a record of all measurements and steps taken during your calculations. This helps in verifying your work and identifying any potential errors.
- Review Your Final Answer: After completing your calculations, review the final answer to ensure it makes sense. Check that the unit of measurement is included and correct.
- Use Online Tools: Utilize online perimeter calculators to cross-check your manual calculations. These tools can provide quick and accurate results.
By following these tips, you can achieve accurate and reliable perimeter calculations for any polygon.

Tips for Accurate Perimeter Calculation
Accurately calculating the perimeter of a polygon involves several key steps and considerations. Here are some tips to help ensure precision in your calculations:
- Use Precise Measurements: Ensure that all side lengths are measured accurately. Use a reliable ruler or measuring tape and, if possible, measure more than once to confirm the lengths.
- Maintain Consistent Units: Always use the same unit of measurement for all sides. Convert units if necessary to maintain consistency throughout your calculations.
- Double-Check Your Polygon Type: Identify whether the polygon is regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles are not necessarily equal). Use the appropriate formula based on the polygon type.
- Apply the Correct Formula: For regular polygons, use the formula \( P = n \times s \), where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the length of each side. For irregular polygons, sum the lengths of all sides: \[ P = s_1 + s_2 + \ldots + s_n \]
- Use a Calculator for Accuracy: Use a calculator to ensure accuracy in your arithmetic operations. This helps minimize errors due to manual calculations.
- Verify Each Step: Check your work at each step of the calculation. Verify that you have included all sides and that each arithmetic operation is correct.
- Consider Decimal Precision: When dealing with decimals, maintain precision throughout your calculations. Avoid rounding until the final step to ensure accuracy.
- Document Measurements and Calculations: Keep a record of all measurements and steps taken during your calculations. This helps in verifying your work and identifying any potential errors.
- Review Your Final Answer: After completing your calculations, review the final answer to ensure it makes sense. Check that the unit of measurement is included and correct.
- Use Online Tools: Utilize online perimeter calculators to cross-check your manual calculations. These tools can provide quick and accurate results.
By following these tips, you can achieve accurate and reliable perimeter calculations for any polygon.

FAQs on Perimeter Calculation
Here are some frequently asked questions about calculating the perimeter of polygons:
- What is a polygon?
A polygon is a 2D shape with straight sides. Examples include triangles, quadrilaterals, and pentagons.
- How do you calculate the perimeter of a polygon?
To calculate the perimeter of a polygon, add up the lengths of all its sides:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = \sum \text{length of all sides} \]
- What is the perimeter of a regular polygon?
For a regular polygon (all sides and angles are equal), the perimeter can be calculated by multiplying the length of one side by the number of sides:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = \text{Number of sides} \times \text{Length of one side} \]
- Can a polygon have curved sides?
No, by definition, a polygon must have straight sides.
- What is the smallest possible polygon?
The smallest possible polygon is a triangle, which has three sides.
- How is the perimeter of a polygon used in real life?
The perimeter can be used for various practical applications such as determining the amount of fencing needed for a field or the length of wire needed to enclose a certain area.
- Is there a difference in calculating the perimeter for regular and irregular polygons?
The method is the same—sum up the lengths of all sides. However, for regular polygons, you can also multiply the length of one side by the number of sides.
- Can I calculate the perimeter if I only know the lengths of some sides?
No, to calculate the perimeter accurately, you need to know the lengths of all sides.
- Can I calculate the perimeter of a polygon with an unlimited number of sides?
A polygon with an unlimited number of sides approximates a circle. The perimeter calculation for such shapes would follow the circumference formula:
\[ C = 2\pi r \]
- What factors can affect the accuracy of perimeter calculations?
Measurement errors and rounding errors can affect the accuracy of perimeter calculations.
FAQs on Perimeter Calculation
Here are some frequently asked questions about calculating the perimeter of polygons:
- What is a polygon?
A polygon is a 2D shape with straight sides. Examples include triangles, quadrilaterals, and pentagons.
- How do you calculate the perimeter of a polygon?
To calculate the perimeter of a polygon, add up the lengths of all its sides:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = \sum \text{length of all sides} \]
- What is the perimeter of a regular polygon?
For a regular polygon (all sides and angles are equal), the perimeter can be calculated by multiplying the length of one side by the number of sides:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = \text{Number of sides} \times \text{Length of one side} \]
- Can a polygon have curved sides?
No, by definition, a polygon must have straight sides.
- What is the smallest possible polygon?
The smallest possible polygon is a triangle, which has three sides.
- How is the perimeter of a polygon used in real life?
The perimeter can be used for various practical applications such as determining the amount of fencing needed for a field or the length of wire needed to enclose a certain area.
- Is there a difference in calculating the perimeter for regular and irregular polygons?
The method is the same—sum up the lengths of all sides. However, for regular polygons, you can also multiply the length of one side by the number of sides.
- Can I calculate the perimeter if I only know the lengths of some sides?
No, to calculate the perimeter accurately, you need to know the lengths of all sides.
- Can I calculate the perimeter of a polygon with an unlimited number of sides?
A polygon with an unlimited number of sides approximates a circle. The perimeter calculation for such shapes would follow the circumference formula:
\[ C = 2\pi r \]
- What factors can affect the accuracy of perimeter calculations?
Measurement errors and rounding errors can affect the accuracy of perimeter calculations.
Additional Resources
For those looking to delve deeper into the topic of polygon perimeter calculations, the following resources provide comprehensive information, tools, and references:
-
Online Perimeter Calculators
- : An easy-to-use tool that calculates the perimeter of regular polygons based on the number of sides and side length.
- : Offers a wide range of perimeter calculators for different shapes, including polygons, circles, ellipses, and more.
- : Provides formulas and calculators for finding the perimeter of various shapes, including squares, rectangles, trapezoids, and more.
- : A versatile tool for calculating the perimeter of regular and irregular polygons.
-
Educational Articles and Tutorials
- : An educational resource explaining the concept of perimeter with interactive examples and exercises.
- : Video tutorials and practice exercises on perimeter calculations for various geometric shapes.
- : Detailed explanations and interactive diagrams for understanding perimeter concepts.
-
Mathematical Tools and References
- : A powerful computational tool for calculating the perimeter of complex shapes using Wolfram's computational engine.
- : A graphing tool that can help visualize and calculate the perimeters of geometric shapes.
- : Offers step-by-step solutions for perimeter calculations and other geometric problems.
These resources provide a solid foundation for understanding and calculating the perimeter of various polygons, whether for academic purposes or practical applications.
Additional Resources
For those looking to delve deeper into the topic of polygon perimeter calculations, the following resources provide comprehensive information, tools, and references:
-
Online Perimeter Calculators
- : An easy-to-use tool that calculates the perimeter of regular polygons based on the number of sides and side length.
- : Offers a wide range of perimeter calculators for different shapes, including polygons, circles, ellipses, and more.
- : Provides formulas and calculators for finding the perimeter of various shapes, including squares, rectangles, trapezoids, and more.
- : A versatile tool for calculating the perimeter of regular and irregular polygons.
-
Educational Articles and Tutorials
- : An educational resource explaining the concept of perimeter with interactive examples and exercises.
- : Video tutorials and practice exercises on perimeter calculations for various geometric shapes.
- : Detailed explanations and interactive diagrams for understanding perimeter concepts.
-
Mathematical Tools and References
- : A powerful computational tool for calculating the perimeter of complex shapes using Wolfram's computational engine.
- : A graphing tool that can help visualize and calculate the perimeters of geometric shapes.
- : Offers step-by-step solutions for perimeter calculations and other geometric problems.
These resources provide a solid foundation for understanding and calculating the perimeter of various polygons, whether for academic purposes or practical applications.
Conclusion
Understanding and calculating the perimeter of a polygon is fundamental in geometry, whether for academic purposes, practical applications in construction, or various other fields. The ability to accurately determine the perimeter helps in resource estimation, design planning, and ensuring structural integrity.
In this guide, we've explored different methods and formulas for calculating the perimeter of both regular and irregular polygons. Utilizing online perimeter calculators can significantly simplify these calculations, providing quick and precise results. These tools are particularly useful for handling complex shapes and large datasets, saving time and reducing the potential for human error.
To recap:
- For regular polygons, the perimeter is calculated by multiplying the number of sides by the length of one side.
- For irregular polygons, sum the lengths of all individual sides to find the perimeter.
- Ensure accurate measurements of side lengths to avoid errors in calculation.
We also discussed the benefits of using online calculators, including their ease of use, speed, and accuracy. Such tools often come with additional features like unit conversions and error-checking mechanisms, which further enhance their utility.
By understanding the fundamental concepts and leveraging available resources, anyone can efficiently and accurately calculate the perimeter of any polygon, whether simple or complex. This knowledge is not only crucial for mathematical accuracy but also for practical applications in various professional fields.
We hope this guide has provided valuable insights and practical tips to help you master perimeter calculations. Happy calculating!
Conclusion
Understanding and calculating the perimeter of a polygon is fundamental in geometry, whether for academic purposes, practical applications in construction, or various other fields. The ability to accurately determine the perimeter helps in resource estimation, design planning, and ensuring structural integrity.
In this guide, we've explored different methods and formulas for calculating the perimeter of both regular and irregular polygons. Utilizing online perimeter calculators can significantly simplify these calculations, providing quick and precise results. These tools are particularly useful for handling complex shapes and large datasets, saving time and reducing the potential for human error.
To recap:
- For regular polygons, the perimeter is calculated by multiplying the number of sides by the length of one side.
- For irregular polygons, sum the lengths of all individual sides to find the perimeter.
- Ensure accurate measurements of side lengths to avoid errors in calculation.
We also discussed the benefits of using online calculators, including their ease of use, speed, and accuracy. Such tools often come with additional features like unit conversions and error-checking mechanisms, which further enhance their utility.
By understanding the fundamental concepts and leveraging available resources, anyone can efficiently and accurately calculate the perimeter of any polygon, whether simple or complex. This knowledge is not only crucial for mathematical accuracy but also for practical applications in various professional fields.
We hope this guide has provided valuable insights and practical tips to help you master perimeter calculations. Happy calculating!
Hướng dẫn cách tìm diện tích của đa giác đều khi biết bán kính. Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ và dễ dàng áp dụng công thức tính toán trong thực tế.
Tìm Diện Tích Đa Giác Đều Dựa Trên Bán Kính
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi của đa giác nội tiếp. Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ và dễ dàng áp dụng công thức tính toán trong thực tế.
Tìm Chu Vi của Đa Giác Nội Tiếp