Topic spell perimeter: Welcome to our comprehensive guide on spell perimeter, where we delve into the definition, importance, and methods of calculating perimeter. Whether you're dealing with regular or irregular polygons, circles, or ellipses, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and tools you need for accurate perimeter calculations.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Perimeter
- Understanding the Perimeter
- Introduction to Spell Perimeter
- Introduction to Spell Perimeter
- Definition and Importance of Perimeter in Geometry
- Definition and Importance of Perimeter in Geometry
- Calculating Perimeter: Basic Formulas and Methods
- Calculating Perimeter: Basic Formulas and Methods
- Spell Perimeter for Different Shapes
- Spell Perimeter for Different Shapes
- Perimeter of Regular Polygons
- Perimeter of Regular Polygons
- Perimeter of Irregular Polygons
- Perimeter of Irregular Polygons
- Perimeter of Circles and Ellipses
- Perimeter of Circles and Ellipses
- Practical Applications of Perimeter Calculations
- Practical Applications of Perimeter Calculations
- Common Mistakes in Calculating Perimeter
- Common Mistakes in Calculating Perimeter
- Tips and Tricks for Accurate Perimeter Calculation
- Tips and Tricks for Accurate Perimeter Calculation
- Advanced Perimeter Calculation Techniques
- Advanced Perimeter Calculation Techniques
- Interactive Tools for Learning and Practicing Perimeter
- Interactive Tools for Learning and Practicing Perimeter
- Educational Resources and Worksheets for Perimeter
- Educational Resources and Worksheets for Perimeter
- Conclusion: Mastering Perimeter Calculations
- Conclusion: Mastering Perimeter Calculations
- YOUTUBE:
Understanding the Perimeter
The perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry that represents the total length around a two-dimensional shape. It is the sum of the lengths of all sides of the figure. The formula for calculating the perimeter depends on the type of shape.
Perimeter Formulas for Common Shapes
- Rectangle: The perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is calculated using the formula: \[ P = 2(l + w) \] where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Square: The perimeter \( P \) of a square is: \[ P = 4s \] where \( s \) is the side length.
- Triangle: The perimeter \( P \) of a triangle is the sum of its three sides: \[ P = a + b + c \] where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle (Circumference): The perimeter (circumference) \( C \) of a circle is given by: \[ C = 2\pi r \] where \( r \) is the radius.
Example Calculations
Here are some example calculations for the perimeter of different shapes:
- For a rectangle with a length of 5 units and a width of 3 units: \[ P = 2(5 + 3) = 2 \times 8 = 16 \text{ units} \]
- For a square with a side length of 4 units: \[ P = 4 \times 4 = 16 \text{ units} \]
- For a triangle with sides of lengths 3 units, 4 units, and 5 units: \[ P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \text{ units} \]
- For a circle with a radius of 7 units: \[ C = 2\pi \times 7 \approx 2 \times 3.14 \times 7 \approx 43.96 \text{ units} \]
Applications of Perimeter
Understanding and calculating the perimeter is useful in various real-world applications, including:
- Fencing a yard or garden
- Framing a picture or a painting
- Bordering a fabric or any material in tailoring
- Planning the layout of a track or a field
Knowing how to calculate the perimeter can help in efficient planning and resource management in these and other scenarios.

READ MORE:
Understanding the Perimeter
The perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry that represents the total length around a two-dimensional shape. It is the sum of the lengths of all sides of the figure. The formula for calculating the perimeter depends on the type of shape.
Perimeter Formulas for Common Shapes
- Rectangle: The perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is calculated using the formula: \[ P = 2(l + w) \] where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Square: The perimeter \( P \) of a square is: \[ P = 4s \] where \( s \) is the side length.
- Triangle: The perimeter \( P \) of a triangle is the sum of its three sides: \[ P = a + b + c \] where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle (Circumference): The perimeter (circumference) \( C \) of a circle is given by: \[ C = 2\pi r \] where \( r \) is the radius.
Example Calculations
Here are some example calculations for the perimeter of different shapes:
- For a rectangle with a length of 5 units and a width of 3 units: \[ P = 2(5 + 3) = 2 \times 8 = 16 \text{ units} \]
- For a square with a side length of 4 units: \[ P = 4 \times 4 = 16 \text{ units} \]
- For a triangle with sides of lengths 3 units, 4 units, and 5 units: \[ P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \text{ units} \]
- For a circle with a radius of 7 units: \[ C = 2\pi \times 7 \approx 2 \times 3.14 \times 7 \approx 43.96 \text{ units} \]
Applications of Perimeter
Understanding and calculating the perimeter is useful in various real-world applications, including:
- Fencing a yard or garden
- Framing a picture or a painting
- Bordering a fabric or any material in tailoring
- Planning the layout of a track or a field
Knowing how to calculate the perimeter can help in efficient planning and resource management in these and other scenarios.

Introduction to Spell Perimeter
The perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry, representing the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of various shapes is essential for solving many practical problems in mathematics and real-life applications. In this guide, we will explore the concept of perimeter in detail, including basic definitions, formulas for different shapes, and step-by-step methods to ensure accurate calculations.
To calculate the perimeter, you simply add the lengths of all the sides of a polygon. For more complex shapes like circles, the perimeter (also called the circumference) involves specific formulas. Here are the key formulas you will need:
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \) where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Square: \( P = 4a \) where \( a \) is the side length.
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \) where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the side lengths.
- Circle: \( P = 2\pi r \) where \( r \) is the radius.
These basic formulas cover the most common shapes. For irregular polygons, the perimeter is simply the sum of all side lengths. Mastery of these calculations is not only useful for academic purposes but also for practical tasks such as fencing a garden, framing a picture, or any activity that involves outlining a shape.
Introduction to Spell Perimeter
The perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry, representing the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of various shapes is essential for solving many practical problems in mathematics and real-life applications. In this guide, we will explore the concept of perimeter in detail, including basic definitions, formulas for different shapes, and step-by-step methods to ensure accurate calculations.
To calculate the perimeter, you simply add the lengths of all the sides of a polygon. For more complex shapes like circles, the perimeter (also called the circumference) involves specific formulas. Here are the key formulas you will need:
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \) where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Square: \( P = 4a \) where \( a \) is the side length.
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \) where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the side lengths.
- Circle: \( P = 2\pi r \) where \( r \) is the radius.
These basic formulas cover the most common shapes. For irregular polygons, the perimeter is simply the sum of all side lengths. Mastery of these calculations is not only useful for academic purposes but also for practical tasks such as fencing a garden, framing a picture, or any activity that involves outlining a shape.
Definition and Importance of Perimeter in Geometry
In geometry, the perimeter is defined as the total length of the boundary of a closed plane figure. The concept of perimeter is fundamental in understanding the properties and measurements of various geometric shapes. It plays a crucial role in both theoretical mathematics and practical applications.
The importance of the perimeter can be highlighted through its various applications:
- Architectural Design: In construction and architecture, knowing the perimeter helps in calculating the amount of materials needed for building the boundaries of structures such as fences, walls, and roofs.
- Landscaping: The perimeter is used to design and layout gardens, parks, and other outdoor spaces, ensuring proper allocation of space and resources.
- Sports: In sports, the perimeter defines the boundaries of playing fields and courts, essential for fair play and rule enforcement.
- Education: Understanding perimeter is a foundational skill in mathematics education, helping students develop problem-solving abilities and spatial awareness.
Mathematically, the perimeter of a polygon is the sum of the lengths of its sides. For example:
- For a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \), the perimeter \( P \) is given by: \[ P = 2(l + w) \]
- For a triangle with sides \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \), the perimeter \( P \) is: \[ P = a + b + c \]
- For a circle with radius \( r \), the perimeter (circumference) \( C \) is: \[ C = 2\pi r \]
Understanding the perimeter and its calculation methods enables accurate measurement and efficient design in various fields. Its relevance extends beyond pure geometry into everyday applications, making it a vital concept in both education and professional practices.
Definition and Importance of Perimeter in Geometry
In geometry, the perimeter is defined as the total length of the boundary of a closed plane figure. The concept of perimeter is fundamental in understanding the properties and measurements of various geometric shapes. It plays a crucial role in both theoretical mathematics and practical applications.
The importance of the perimeter can be highlighted through its various applications:
- Architectural Design: In construction and architecture, knowing the perimeter helps in calculating the amount of materials needed for building the boundaries of structures such as fences, walls, and roofs.
- Landscaping: The perimeter is used to design and layout gardens, parks, and other outdoor spaces, ensuring proper allocation of space and resources.
- Sports: In sports, the perimeter defines the boundaries of playing fields and courts, essential for fair play and rule enforcement.
- Education: Understanding perimeter is a foundational skill in mathematics education, helping students develop problem-solving abilities and spatial awareness.
Mathematically, the perimeter of a polygon is the sum of the lengths of its sides. For example:
- For a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \), the perimeter \( P \) is given by: \[ P = 2(l + w) \]
- For a triangle with sides \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \), the perimeter \( P \) is: \[ P = a + b + c \]
- For a circle with radius \( r \), the perimeter (circumference) \( C \) is: \[ C = 2\pi r \]
Understanding the perimeter and its calculation methods enables accurate measurement and efficient design in various fields. Its relevance extends beyond pure geometry into everyday applications, making it a vital concept in both education and professional practices.
Calculating Perimeter: Basic Formulas and Methods
Calculating the perimeter involves adding the lengths of all the sides of a shape. Here are the basic formulas and methods for different shapes:
- Rectangle: The perimeter \(P\) is given by \(P = 2(l + w)\), where \(l\) is the length and \(w\) is the width.
- Square: The perimeter \(P\) is given by \(P = 4s\), where \(s\) is the side length.
- Triangle: The perimeter \(P\) is given by \(P = a + b + c\), where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle: The perimeter, also known as the circumference \(C\), is given by \(C = 2\pi r\), where \(r\) is the radius.
- Regular Polygon: The perimeter \(P\) is given by \(P = n \times s\), where \(n\) is the number of sides and \(s\) is the length of one side.
Let's break down the steps for calculating the perimeter:
- Identify the shape of the object.
- Measure the length of each side (or use the given lengths).
- Apply the appropriate formula based on the shape.
- Add the lengths of all the sides to find the total perimeter.
For irregular shapes, simply sum the lengths of all the sides. Practice using these formulas and steps to become proficient in calculating perimeters for various shapes.
Calculating Perimeter: Basic Formulas and Methods
Calculating the perimeter involves adding the lengths of all the sides of a shape. Here are the basic formulas and methods for different shapes:
- Rectangle: The perimeter \(P\) is given by \(P = 2(l + w)\), where \(l\) is the length and \(w\) is the width.
- Square: The perimeter \(P\) is given by \(P = 4s\), where \(s\) is the side length.
- Triangle: The perimeter \(P\) is given by \(P = a + b + c\), where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle: The perimeter, also known as the circumference \(C\), is given by \(C = 2\pi r\), where \(r\) is the radius.
- Regular Polygon: The perimeter \(P\) is given by \(P = n \times s\), where \(n\) is the number of sides and \(s\) is the length of one side.
Let's break down the steps for calculating the perimeter:
- Identify the shape of the object.
- Measure the length of each side (or use the given lengths).
- Apply the appropriate formula based on the shape.
- Add the lengths of all the sides to find the total perimeter.
For irregular shapes, simply sum the lengths of all the sides. Practice using these formulas and steps to become proficient in calculating perimeters for various shapes.
Spell Perimeter for Different Shapes
Understanding how to spell and calculate the perimeter for different shapes is crucial in geometry. The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a shape. Here, we will explore how to determine the perimeter for various common shapes.
- Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its sides. For a triangle with sides \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \), the perimeter \( P \) is given by:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
- Square
The perimeter of a square is four times the length of one side. For a square with side length \( a \), the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = 4a \]
- Rectangle
The perimeter of a rectangle is the sum of twice the width and twice the length. For a rectangle with width \( w \) and length \( l \), the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = 2w + 2l \]
- Circle
The perimeter of a circle is known as the circumference. It is calculated using the radius \( r \) and the constant \( \pi \) (pi). The formula is:
\[ P = 2\pi r \]
- Regular Polygon
For a regular polygon (a polygon with all sides and angles equal), the perimeter is the product of the number of sides \( n \) and the length of one side \( a \). The formula is:
\[ P = n \times a \]
By mastering these formulas, you can easily calculate the perimeter of various shapes, which is an essential skill in geometry.

Spell Perimeter for Different Shapes
Understanding how to spell and calculate the perimeter for different shapes is crucial in geometry. The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a shape. Here, we will explore how to determine the perimeter for various common shapes.
- Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its sides. For a triangle with sides \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \), the perimeter \( P \) is given by:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
- Square
The perimeter of a square is four times the length of one side. For a square with side length \( a \), the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = 4a \]
- Rectangle
The perimeter of a rectangle is the sum of twice the width and twice the length. For a rectangle with width \( w \) and length \( l \), the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = 2w + 2l \]
- Circle
The perimeter of a circle is known as the circumference. It is calculated using the radius \( r \) and the constant \( \pi \) (pi). The formula is:
\[ P = 2\pi r \]
- Regular Polygon
For a regular polygon (a polygon with all sides and angles equal), the perimeter is the product of the number of sides \( n \) and the length of one side \( a \). The formula is:
\[ P = n \times a \]
By mastering these formulas, you can easily calculate the perimeter of various shapes, which is an essential skill in geometry.

Perimeter of Regular Polygons
The perimeter of a regular polygon can be calculated easily due to its symmetrical properties. A regular polygon has all sides of equal length and all interior angles equal. The formula to determine the perimeter (\(P\)) of a regular polygon is:
\[ P = n \times s \]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides.
- \(s\) is the length of one side.
Below are the steps to calculate the perimeter for different regular polygons:
- Identify the number of sides: Count the number of sides (\(n\)) of the polygon.
- Measure the side length: Measure the length (\(s\)) of one side of the polygon.
- Apply the formula: Multiply the number of sides (\(n\)) by the side length (\(s\)) to get the perimeter (\(P\)).
Here are some examples:
| Shape | Number of Sides (\(n\)) | Side Length (\(s\)) | Perimeter (\(P\)) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equilateral Triangle | 3 | \(a\) | \(3a\) |
| Square | 4 | \(a\) | \(4a\) |
| Regular Pentagon | 5 | \(a\) | \(5a\) |
| Regular Hexagon | 6 | \(a\) | \(6a\) |
By following these steps and using the provided formula, you can easily calculate the perimeter of any regular polygon.
Perimeter of Regular Polygons
The perimeter of a regular polygon can be calculated easily due to its symmetrical properties. A regular polygon has all sides of equal length and all interior angles equal. The formula to determine the perimeter (\(P\)) of a regular polygon is:
\[ P = n \times s \]
where:
- \(n\) is the number of sides.
- \(s\) is the length of one side.
Below are the steps to calculate the perimeter for different regular polygons:
- Identify the number of sides: Count the number of sides (\(n\)) of the polygon.
- Measure the side length: Measure the length (\(s\)) of one side of the polygon.
- Apply the formula: Multiply the number of sides (\(n\)) by the side length (\(s\)) to get the perimeter (\(P\)).
Here are some examples:
| Shape | Number of Sides (\(n\)) | Side Length (\(s\)) | Perimeter (\(P\)) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equilateral Triangle | 3 | \(a\) | \(3a\) |
| Square | 4 | \(a\) | \(4a\) |
| Regular Pentagon | 5 | \(a\) | \(5a\) |
| Regular Hexagon | 6 | \(a\) | \(6a\) |
By following these steps and using the provided formula, you can easily calculate the perimeter of any regular polygon.
Perimeter of Irregular Polygons
Calculating the perimeter of irregular polygons involves summing the lengths of all the sides of the polygon. Unlike regular polygons, irregular polygons do not have equal side lengths or equal angles. To find the perimeter, follow these steps:
- Identify all the side lengths of the polygon.
- Add the lengths of all the sides together using the formula:
\[ P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} a_i \] where \( P \) is the perimeter, \( n \) is the number of sides, and \( a_i \) represents the length of each side.
For example, consider a pentagon with side lengths of 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 6 cm, and 7 cm:
- Sum of the sides: \( 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 25 \) cm.
- Therefore, the perimeter \( P \) is 25 cm.
Using this method, you can find the perimeter of any irregular polygon by ensuring all sides are measured accurately and then summed.
Perimeter of Irregular Polygons
Calculating the perimeter of irregular polygons involves summing the lengths of all the sides of the polygon. Unlike regular polygons, irregular polygons do not have equal side lengths or equal angles. To find the perimeter, follow these steps:
- Identify all the side lengths of the polygon.
- Add the lengths of all the sides together using the formula:
\[ P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} a_i \] where \( P \) is the perimeter, \( n \) is the number of sides, and \( a_i \) represents the length of each side.
For example, consider a pentagon with side lengths of 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 6 cm, and 7 cm:
- Sum of the sides: \( 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 25 \) cm.
- Therefore, the perimeter \( P \) is 25 cm.
Using this method, you can find the perimeter of any irregular polygon by ensuring all sides are measured accurately and then summed.
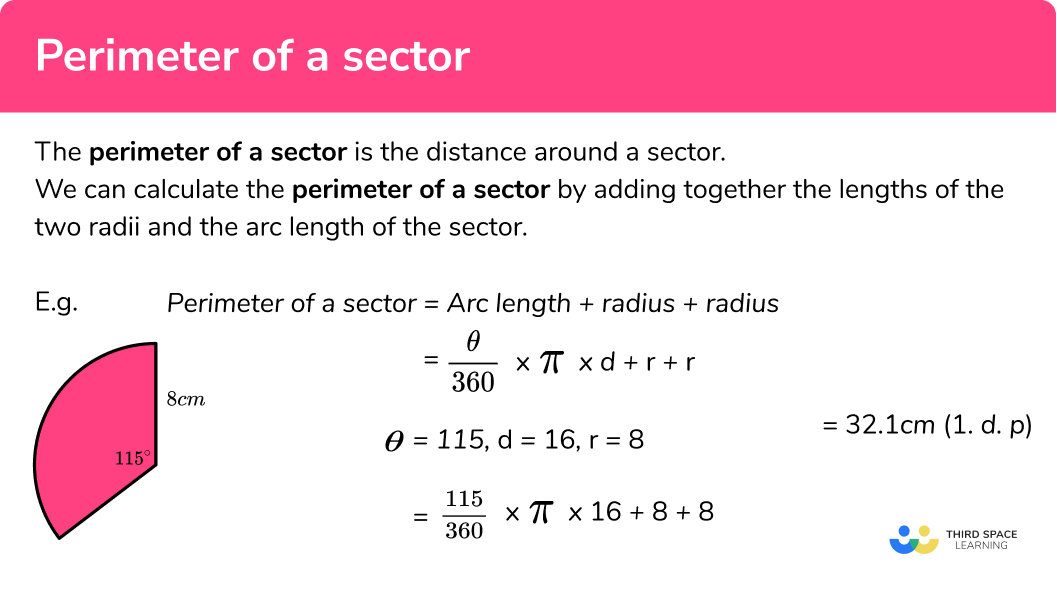
Perimeter of Circles and Ellipses
The perimeter, also known as the circumference, of a circle is a fundamental concept in geometry. Calculating the perimeter of circles and ellipses involves understanding their unique properties and applying specific formulas. Below are detailed explanations and methods for calculating the perimeter of these shapes.
Perimeter of a Circle
The perimeter (circumference) of a circle is calculated using the following formula:
\[ C = 2\pi r \]
where:
- C is the circumference
- r is the radius of the circle
- \(\pi\) (pi) is a constant approximately equal to 3.14159
For example, if a circle has a radius of 5 units, its circumference is:
\[ C = 2 \times 3.14159 \times 5 \approx 31.4159 \text{ units} \]
Perimeter of an Ellipse
The perimeter of an ellipse is more complex to calculate than that of a circle. An ellipse has two radii: the semi-major axis (a) and the semi-minor axis (b). While there is no simple exact formula for the perimeter of an ellipse, it can be approximated using various methods. One commonly used approximation is given by Ramanujan's formula:
\[ P \approx \pi \left[ 3(a + b) - \sqrt{(3a + b)(a + 3b)} \right] \]
where:
- P is the perimeter
- a is the semi-major axis
- b is the semi-minor axis
For example, if an ellipse has a semi-major axis of 6 units and a semi-minor axis of 4 units, its approximate perimeter is:
\[ P \approx 3.14159 \left[ 3(6 + 4) - \sqrt{(3 \times 6 + 4)(6 + 3 \times 4)} \right] \]
\[ P \approx 3.14159 \left[ 30 - \sqrt{58} \right] \]
\[ P \approx 3.14159 \left[ 30 - 7.6158 \right] \]
\[ P \approx 3.14159 \times 22.3842 \]
\[ P \approx 70.403 \text{ units} \]
Practical Tips
- For circles, always ensure you have an accurate measure of the radius to calculate the perimeter precisely.
- For ellipses, using approximation formulas is generally sufficient for practical purposes, but for high precision, numerical methods or specialized software might be necessary.
Interactive Tools
Several online tools and calculators can help you easily compute the perimeter of circles and ellipses. These tools often allow you to input the required measurements and provide quick, accurate results.
- Circle Perimeter Calculators
- Ellipse Perimeter Calculators
Understanding the perimeter of circles and ellipses is crucial for various applications in geometry, engineering, and everyday problem-solving. With the formulas and methods outlined above, you can confidently approach perimeter calculations for these shapes.
Perimeter of Circles and Ellipses
The perimeter, also known as the circumference, of a circle is a fundamental concept in geometry. Calculating the perimeter of circles and ellipses involves understanding their unique properties and applying specific formulas. Below are detailed explanations and methods for calculating the perimeter of these shapes.
Perimeter of a Circle
The perimeter (circumference) of a circle is calculated using the following formula:
\[ C = 2\pi r \]
where:
- C is the circumference
- r is the radius of the circle
- \(\pi\) (pi) is a constant approximately equal to 3.14159
For example, if a circle has a radius of 5 units, its circumference is:
\[ C = 2 \times 3.14159 \times 5 \approx 31.4159 \text{ units} \]
Perimeter of an Ellipse
The perimeter of an ellipse is more complex to calculate than that of a circle. An ellipse has two radii: the semi-major axis (a) and the semi-minor axis (b). While there is no simple exact formula for the perimeter of an ellipse, it can be approximated using various methods. One commonly used approximation is given by Ramanujan's formula:
\[ P \approx \pi \left[ 3(a + b) - \sqrt{(3a + b)(a + 3b)} \right] \]
where:
- P is the perimeter
- a is the semi-major axis
- b is the semi-minor axis
For example, if an ellipse has a semi-major axis of 6 units and a semi-minor axis of 4 units, its approximate perimeter is:
\[ P \approx 3.14159 \left[ 3(6 + 4) - \sqrt{(3 \times 6 + 4)(6 + 3 \times 4)} \right] \]
\[ P \approx 3.14159 \left[ 30 - \sqrt{58} \right] \]
\[ P \approx 3.14159 \left[ 30 - 7.6158 \right] \]
\[ P \approx 3.14159 \times 22.3842 \]
\[ P \approx 70.403 \text{ units} \]
Practical Tips
- For circles, always ensure you have an accurate measure of the radius to calculate the perimeter precisely.
- For ellipses, using approximation formulas is generally sufficient for practical purposes, but for high precision, numerical methods or specialized software might be necessary.
Interactive Tools
Several online tools and calculators can help you easily compute the perimeter of circles and ellipses. These tools often allow you to input the required measurements and provide quick, accurate results.
- Circle Perimeter Calculators
- Ellipse Perimeter Calculators
Understanding the perimeter of circles and ellipses is crucial for various applications in geometry, engineering, and everyday problem-solving. With the formulas and methods outlined above, you can confidently approach perimeter calculations for these shapes.
Practical Applications of Perimeter Calculations
Understanding and calculating perimeter is crucial in various practical applications. Here are some common scenarios where perimeter calculations are used:
-
Construction and Architecture:
When constructing buildings, accurate perimeter measurements are essential for laying foundations, planning walls, and ensuring that structures fit within designated land areas. For example, the perimeter of a plot of land needs to be calculated to determine the amount of fencing required.
-
Interior Design:
Interior designers use perimeter calculations to plan the layout of rooms, ensuring that furniture fits properly and optimizing space usage. For instance, calculating the perimeter of a room helps in determining the length of baseboards and crown molding needed.
-
Landscaping:
In landscaping, perimeter calculations are used to outline garden beds, patios, and walkways. This ensures that materials such as edging, mulch, and paving stones are purchased in the correct amounts.
-
Sports Fields:
Designing sports fields and courts requires accurate perimeter measurements to comply with regulations. For example, the perimeter of a soccer field is necessary to plan the placement of boundary lines and goal posts.
-
Fabric and Sewing Projects:
In sewing, calculating the perimeter of fabric pieces helps in cutting patterns and determining the amount of trim or ribbon needed to decorate the edges of garments or quilts.
-
Event Planning:
For events, such as weddings or outdoor festivals, perimeter calculations help in setting up tents, stages, and fencing to designate areas for guests and activities.
-
Education:
Teaching students to calculate perimeter helps them understand geometric properties and prepares them for real-world applications. Perimeter problems are common in math curricula to develop spatial awareness and problem-solving skills.
By understanding the perimeter and how to calculate it, individuals can effectively plan and execute various tasks, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in both personal and professional projects.

Practical Applications of Perimeter Calculations
Understanding and calculating perimeter is crucial in various practical applications. Here are some common scenarios where perimeter calculations are used:
-
Construction and Architecture:
When constructing buildings, accurate perimeter measurements are essential for laying foundations, planning walls, and ensuring that structures fit within designated land areas. For example, the perimeter of a plot of land needs to be calculated to determine the amount of fencing required.
-
Interior Design:
Interior designers use perimeter calculations to plan the layout of rooms, ensuring that furniture fits properly and optimizing space usage. For instance, calculating the perimeter of a room helps in determining the length of baseboards and crown molding needed.
-
Landscaping:
In landscaping, perimeter calculations are used to outline garden beds, patios, and walkways. This ensures that materials such as edging, mulch, and paving stones are purchased in the correct amounts.
-
Sports Fields:
Designing sports fields and courts requires accurate perimeter measurements to comply with regulations. For example, the perimeter of a soccer field is necessary to plan the placement of boundary lines and goal posts.
-
Fabric and Sewing Projects:
In sewing, calculating the perimeter of fabric pieces helps in cutting patterns and determining the amount of trim or ribbon needed to decorate the edges of garments or quilts.
-
Event Planning:
For events, such as weddings or outdoor festivals, perimeter calculations help in setting up tents, stages, and fencing to designate areas for guests and activities.
-
Education:
Teaching students to calculate perimeter helps them understand geometric properties and prepares them for real-world applications. Perimeter problems are common in math curricula to develop spatial awareness and problem-solving skills.
By understanding the perimeter and how to calculate it, individuals can effectively plan and execute various tasks, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in both personal and professional projects.

Common Mistakes in Calculating Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of various shapes is a fundamental skill in geometry, but it's easy to make mistakes. Here are some common errors to watch out for, along with tips on how to avoid them:
-
Forgetting to Include All Sides:
One of the most common mistakes is neglecting to account for all sides of the shape. Always double-check that you've included every side in your calculations.
-
Misidentifying Sides:
Another frequent error is misidentifying the lengths of sides, especially in irregular shapes. Carefully label each side to ensure accuracy.
-
Using Incorrect Units:
Ensure that all measurements are in the same unit before adding them together. Mixing units (e.g., inches and centimeters) will lead to incorrect results.
-
Confusing Perimeter with Area:
Perimeter and area are different concepts. The perimeter is the total length around a shape, while the area is the amount of space inside the shape. Make sure to use the correct formulas for each calculation.
-
Double-Counting Sides:
In complex shapes, it's easy to count the same side more than once. Carefully trace the outline of the shape to avoid this mistake.
Examples of Common Mistakes and How to Correct Them
-
Rectangle Perimeter:
For a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \), the perimeter \( P \) is given by \( P = 2(l + w) \). A common mistake is to use only one dimension (e.g., calculating \( P = l + w \)).
-
Irregular Polygon Perimeter:
When calculating the perimeter of an irregular polygon, ensure all sides are measured and summed correctly. Break down the shape into smaller parts if necessary and sum the perimeters of those parts.
-
Circle Perimeter (Circumference):
The perimeter of a circle is called the circumference, calculated as \( C = 2\pi r \) where \( r \) is the radius. A common mistake is to use the diameter instead of the radius, leading to an incorrect result of \( C = \pi d \) instead of \( C = 2\pi r \).
Tips to Avoid Common Mistakes
-
Double-Check Your Work:
Always review your calculations to ensure that all sides are included and correctly measured.
-
Consistent Units:
Use the same units throughout your calculations. Convert measurements to the same unit before summing them.
-
Clear Labeling:
Label each side of the shape clearly to avoid confusion and ensure accuracy in your calculations.
-
Use a Checklist:
Create a checklist of steps for each type of shape to ensure you don't miss any sides or make other common errors.
Common Mistakes in Calculating Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of various shapes is a fundamental skill in geometry, but it's easy to make mistakes. Here are some common errors to watch out for, along with tips on how to avoid them:
-
Forgetting to Include All Sides:
One of the most common mistakes is neglecting to account for all sides of the shape. Always double-check that you've included every side in your calculations.
-
Misidentifying Sides:
Another frequent error is misidentifying the lengths of sides, especially in irregular shapes. Carefully label each side to ensure accuracy.
-
Using Incorrect Units:
Ensure that all measurements are in the same unit before adding them together. Mixing units (e.g., inches and centimeters) will lead to incorrect results.
-
Confusing Perimeter with Area:
Perimeter and area are different concepts. The perimeter is the total length around a shape, while the area is the amount of space inside the shape. Make sure to use the correct formulas for each calculation.
-
Double-Counting Sides:
In complex shapes, it's easy to count the same side more than once. Carefully trace the outline of the shape to avoid this mistake.
Examples of Common Mistakes and How to Correct Them
-
Rectangle Perimeter:
For a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \), the perimeter \( P \) is given by \( P = 2(l + w) \). A common mistake is to use only one dimension (e.g., calculating \( P = l + w \)).
-
Irregular Polygon Perimeter:
When calculating the perimeter of an irregular polygon, ensure all sides are measured and summed correctly. Break down the shape into smaller parts if necessary and sum the perimeters of those parts.
-
Circle Perimeter (Circumference):
The perimeter of a circle is called the circumference, calculated as \( C = 2\pi r \) where \( r \) is the radius. A common mistake is to use the diameter instead of the radius, leading to an incorrect result of \( C = \pi d \) instead of \( C = 2\pi r \).
Tips to Avoid Common Mistakes
-
Double-Check Your Work:
Always review your calculations to ensure that all sides are included and correctly measured.
-
Consistent Units:
Use the same units throughout your calculations. Convert measurements to the same unit before summing them.
-
Clear Labeling:
Label each side of the shape clearly to avoid confusion and ensure accuracy in your calculations.
-
Use a Checklist:
Create a checklist of steps for each type of shape to ensure you don't miss any sides or make other common errors.
Tips and Tricks for Accurate Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of various shapes accurately requires attention to detail and the right strategies. Here are some useful tips and tricks to ensure precision in your perimeter calculations:
- Understand the Shape: Clearly identify the shape you are working with. Different shapes have different formulas for perimeter calculation. For instance:
- Square: \( P = 4s \) where \( s \) is the length of a side.
- Rectangle: \( P = 2l + 2w \) where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Circle: \( P = 2\pi r \) where \( r \) is the radius.
- Use Accurate Measurements: Ensure that you measure all sides precisely. Inaccurate measurements can lead to significant errors in the final calculation.
- Break Down Complex Shapes: For irregular or complex shapes, break them down into simpler components (like rectangles, triangles, or circles). Calculate the perimeter of each component and then sum them up.
Example: An L-shaped figure can be divided into two rectangles. Calculate the perimeter of each rectangle and then add them together, ensuring shared sides are not double-counted.
- Double-Check Calculations: Always recheck your calculations to avoid mistakes. This includes verifying each step and the final addition of all sides.
- Use Graph Paper: When dealing with irregular shapes, drawing them on graph paper can help in visualizing and measuring sides accurately.
- Estimate and Round: If precise tools are not available, round measurements to the nearest whole number to simplify calculations. However, be aware that this can introduce slight errors.
- Use Technology: Utilize calculators or computer software designed for geometric calculations. These tools can help minimize human error and speed up the process.
- Practice Mental Math: Strengthening mental arithmetic skills can be beneficial, especially when calculating perimeters without a calculator.
By applying these tips and tricks, you can achieve more accurate and efficient perimeter calculations, whether for simple or complex shapes.
Tips and Tricks for Accurate Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of various shapes accurately requires attention to detail and the right strategies. Here are some useful tips and tricks to ensure precision in your perimeter calculations:
- Understand the Shape: Clearly identify the shape you are working with. Different shapes have different formulas for perimeter calculation. For instance:
- Square: \( P = 4s \) where \( s \) is the length of a side.
- Rectangle: \( P = 2l + 2w \) where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Circle: \( P = 2\pi r \) where \( r \) is the radius.
- Use Accurate Measurements: Ensure that you measure all sides precisely. Inaccurate measurements can lead to significant errors in the final calculation.
- Break Down Complex Shapes: For irregular or complex shapes, break them down into simpler components (like rectangles, triangles, or circles). Calculate the perimeter of each component and then sum them up.
Example: An L-shaped figure can be divided into two rectangles. Calculate the perimeter of each rectangle and then add them together, ensuring shared sides are not double-counted.
- Double-Check Calculations: Always recheck your calculations to avoid mistakes. This includes verifying each step and the final addition of all sides.
- Use Graph Paper: When dealing with irregular shapes, drawing them on graph paper can help in visualizing and measuring sides accurately.
- Estimate and Round: If precise tools are not available, round measurements to the nearest whole number to simplify calculations. However, be aware that this can introduce slight errors.
- Use Technology: Utilize calculators or computer software designed for geometric calculations. These tools can help minimize human error and speed up the process.
- Practice Mental Math: Strengthening mental arithmetic skills can be beneficial, especially when calculating perimeters without a calculator.
By applying these tips and tricks, you can achieve more accurate and efficient perimeter calculations, whether for simple or complex shapes.
Advanced Perimeter Calculation Techniques
Calculating the perimeter of simple shapes is straightforward, but advanced techniques are required for complex and irregular shapes. Here are some advanced methods for accurately determining the perimeter:
- Using Calculus: For curves and irregular shapes, calculus provides a precise method to calculate perimeter through the concept of arc length. The formula for arc length in Cartesian coordinates is:
\[
L = \int_a^b \sqrt{1 + \left(\frac{dy}{dx}\right)^2} \, dx
\] - Parametric Equations: When the shape is defined parametrically by functions \(x(t)\) and \(y(t)\), the perimeter can be calculated using:
\[
L = \int_a^b \sqrt{\left(\frac{dx}{dt}\right)^2 + \left(\frac{dy}{dt}\right)^2} \, dt
\] - Polar Coordinates: For shapes defined in polar coordinates, where \(r = f(\theta)\), the arc length is given by:
\[
L = \int_a^b \sqrt{r^2 + \left(\frac{dr}{d\theta}\right)^2} \, d\theta
\] - Approximation Methods: When exact calculations are difficult, approximation methods such as:
- Dividing the shape into simpler components (e.g., triangles, rectangles) and summing their perimeters.
- Using numerical integration techniques to estimate the perimeter of a complex curve.
Advanced perimeter calculations are crucial in fields such as engineering, architecture, and computer graphics, where precision is essential. By mastering these techniques, you can tackle a wide range of practical and theoretical problems with confidence.
Advanced Perimeter Calculation Techniques
Calculating the perimeter of simple shapes is straightforward, but advanced techniques are required for complex and irregular shapes. Here are some advanced methods for accurately determining the perimeter:
- Using Calculus: For curves and irregular shapes, calculus provides a precise method to calculate perimeter through the concept of arc length. The formula for arc length in Cartesian coordinates is:
\[
L = \int_a^b \sqrt{1 + \left(\frac{dy}{dx}\right)^2} \, dx
\] - Parametric Equations: When the shape is defined parametrically by functions \(x(t)\) and \(y(t)\), the perimeter can be calculated using:
\[
L = \int_a^b \sqrt{\left(\frac{dx}{dt}\right)^2 + \left(\frac{dy}{dt}\right)^2} \, dt
\] - Polar Coordinates: For shapes defined in polar coordinates, where \(r = f(\theta)\), the arc length is given by:
\[
L = \int_a^b \sqrt{r^2 + \left(\frac{dr}{d\theta}\right)^2} \, d\theta
\] - Approximation Methods: When exact calculations are difficult, approximation methods such as:
- Dividing the shape into simpler components (e.g., triangles, rectangles) and summing their perimeters.
- Using numerical integration techniques to estimate the perimeter of a complex curve.
Advanced perimeter calculations are crucial in fields such as engineering, architecture, and computer graphics, where precision is essential. By mastering these techniques, you can tackle a wide range of practical and theoretical problems with confidence.
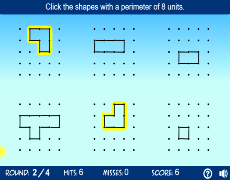
Interactive Tools for Learning and Practicing Perimeter
Interactive tools are a fantastic way to enhance understanding and engagement when learning how to calculate the perimeter of various shapes. Here are some effective tools and activities that can help students practice perimeter calculations:
-
PhET Interactive Simulations:
PhET offers a variety of simulations that allow students to visually and interactively explore perimeter calculations. One such simulation, "Area Builder," helps students understand the relationship between area and perimeter through interactive play and experimentation.
-
Teach Starter Digital Activities:
Teach Starter provides a range of interactive perimeter activities. For example, their "Calculate the Perimeter Interactive Activity" includes drag-and-drop exercises, multiple-choice questions, and true/false assessments to help students practice perimeter calculations in a digital format. These activities are designed to be used in both classroom settings and for individual learning.
-
Online Perimeter Calculators:
There are various online calculators available that allow students to input dimensions and instantly receive perimeter calculations. These tools are great for quick checks and to reinforce manual calculations done by students.
-
Interactive Whiteboard Tools:
Many educational platforms offer interactive whiteboard tools where teachers can demonstrate perimeter calculations live. Students can participate by coming up to the board to solve problems or by using personal devices to interact with the lesson.
These tools not only make learning more engaging but also provide instant feedback, which is crucial for effective learning. By incorporating interactive activities and simulations into perimeter lessons, teachers can help students develop a deeper understanding and appreciation of geometric concepts.

Interactive Tools for Learning and Practicing Perimeter
Interactive tools are a fantastic way to enhance understanding and engagement when learning how to calculate the perimeter of various shapes. Here are some effective tools and activities that can help students practice perimeter calculations:
-
PhET Interactive Simulations:
PhET offers a variety of simulations that allow students to visually and interactively explore perimeter calculations. One such simulation, "Area Builder," helps students understand the relationship between area and perimeter through interactive play and experimentation.
-
Teach Starter Digital Activities:
Teach Starter provides a range of interactive perimeter activities. For example, their "Calculate the Perimeter Interactive Activity" includes drag-and-drop exercises, multiple-choice questions, and true/false assessments to help students practice perimeter calculations in a digital format. These activities are designed to be used in both classroom settings and for individual learning.
-
Online Perimeter Calculators:
There are various online calculators available that allow students to input dimensions and instantly receive perimeter calculations. These tools are great for quick checks and to reinforce manual calculations done by students.
-
Interactive Whiteboard Tools:
Many educational platforms offer interactive whiteboard tools where teachers can demonstrate perimeter calculations live. Students can participate by coming up to the board to solve problems or by using personal devices to interact with the lesson.
These tools not only make learning more engaging but also provide instant feedback, which is crucial for effective learning. By incorporating interactive activities and simulations into perimeter lessons, teachers can help students develop a deeper understanding and appreciation of geometric concepts.

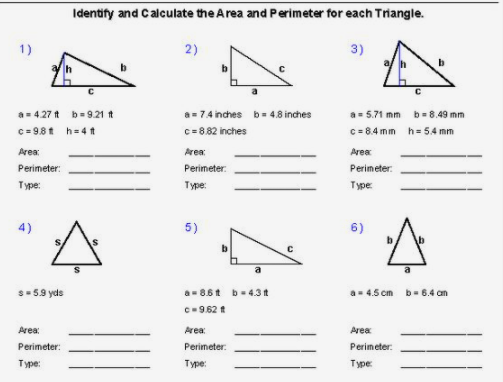
Educational Resources and Worksheets for Perimeter
Educational resources and worksheets are essential for reinforcing students' understanding of perimeter calculations. Below are some valuable resources and types of worksheets available for educators and students:
-
Printable Perimeter Worksheets:
Websites like Education.com and Math Worksheets 4 Kids offer a variety of printable worksheets tailored to different grade levels. These worksheets cover topics such as:
- Perimeter using grids
- Perimeter of squares, rectangles, and triangles
- Perimeter of parallelograms, trapezoids, and rhombuses
- Perimeter of kites and quadrilaterals
- Circumference of circles
- Perimeter of polygons
-
Interactive Digital Worksheets:
Platforms like Twinkl and Quizizz provide interactive digital worksheets that can be used for online learning. These resources often include engaging activities, instant feedback, and adaptive learning paths to cater to individual student needs.
-
Comprehensive Lesson Plans:
Educational websites offer complete lesson plans that integrate perimeter worksheets with hands-on activities and assessments. These plans are designed to be easy to follow and align with curriculum standards, ensuring a structured approach to learning perimeter.
-
Customized Worksheets:
Tools like Common Core Sheets allow teachers to create customized perimeter worksheets that match their specific teaching goals and the unique needs of their students. This flexibility helps in addressing diverse learning paces and styles.
By leveraging these educational resources and worksheets, educators can provide varied and comprehensive practice opportunities, helping students master the concept of perimeter through consistent and structured learning experiences.
Educational Resources and Worksheets for Perimeter
Educational resources and worksheets are essential for reinforcing students' understanding of perimeter calculations. Below are some valuable resources and types of worksheets available for educators and students:
-
Printable Perimeter Worksheets:
Websites like Education.com and Math Worksheets 4 Kids offer a variety of printable worksheets tailored to different grade levels. These worksheets cover topics such as:
- Perimeter using grids
- Perimeter of squares, rectangles, and triangles
- Perimeter of parallelograms, trapezoids, and rhombuses
- Perimeter of kites and quadrilaterals
- Circumference of circles
- Perimeter of polygons
-
Interactive Digital Worksheets:
Platforms like Twinkl and Quizizz provide interactive digital worksheets that can be used for online learning. These resources often include engaging activities, instant feedback, and adaptive learning paths to cater to individual student needs.
-
Comprehensive Lesson Plans:
Educational websites offer complete lesson plans that integrate perimeter worksheets with hands-on activities and assessments. These plans are designed to be easy to follow and align with curriculum standards, ensuring a structured approach to learning perimeter.
-
Customized Worksheets:
Tools like Common Core Sheets allow teachers to create customized perimeter worksheets that match their specific teaching goals and the unique needs of their students. This flexibility helps in addressing diverse learning paces and styles.
By leveraging these educational resources and worksheets, educators can provide varied and comprehensive practice opportunities, helping students master the concept of perimeter through consistent and structured learning experiences.
Conclusion: Mastering Perimeter Calculations
Mastering perimeter calculations is a fundamental skill in geometry that has wide-ranging applications in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and everyday problem-solving. By understanding and practicing the principles of perimeter, students and professionals can enhance their spatial awareness and mathematical proficiency.
The journey to mastering perimeter calculations involves:
- Grasping Basic Concepts: Starting with simple shapes such as rectangles, squares, and triangles helps in building a strong foundation.
- Applying Formulas Accurately: Memorizing and accurately applying perimeter formulas for different shapes, including circles and ellipses, is crucial.
- Practicing with Real-World Examples: Engaging with practical problems enhances understanding and retention of concepts.
- Utilizing Advanced Techniques: Learning to handle composite shapes and applying calculus for complex figures broadens one's skill set.
- Leveraging Educational Resources: Utilizing worksheets, interactive tools, and online platforms such as Khan Academy aids in continuous learning and practice.
Regular practice and the use of varied resources, including interactive tools and educational worksheets, can significantly improve one's ability to calculate perimeters accurately. Embracing challenges and advancing to more complex problems encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
By mastering perimeter calculations, individuals not only excel in academic settings but also gain practical skills applicable in various professional fields, enhancing their overall mathematical literacy and confidence.
Conclusion: Mastering Perimeter Calculations
Mastering perimeter calculations is a fundamental skill in geometry that has wide-ranging applications in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and everyday problem-solving. By understanding and practicing the principles of perimeter, students and professionals can enhance their spatial awareness and mathematical proficiency.
The journey to mastering perimeter calculations involves:
- Grasping Basic Concepts: Starting with simple shapes such as rectangles, squares, and triangles helps in building a strong foundation.
- Applying Formulas Accurately: Memorizing and accurately applying perimeter formulas for different shapes, including circles and ellipses, is crucial.
- Practicing with Real-World Examples: Engaging with practical problems enhances understanding and retention of concepts.
- Utilizing Advanced Techniques: Learning to handle composite shapes and applying calculus for complex figures broadens one's skill set.
- Leveraging Educational Resources: Utilizing worksheets, interactive tools, and online platforms such as Khan Academy aids in continuous learning and practice.
Regular practice and the use of varied resources, including interactive tools and educational worksheets, can significantly improve one's ability to calculate perimeters accurately. Embracing challenges and advancing to more complex problems encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
By mastering perimeter calculations, individuals not only excel in academic settings but also gain practical skills applicable in various professional fields, enhancing their overall mathematical literacy and confidence.
Chu vi là gì? - Hình học cho trẻ em
READ MORE:
Chữ cái quyến rũ & Bùa chú chu vi