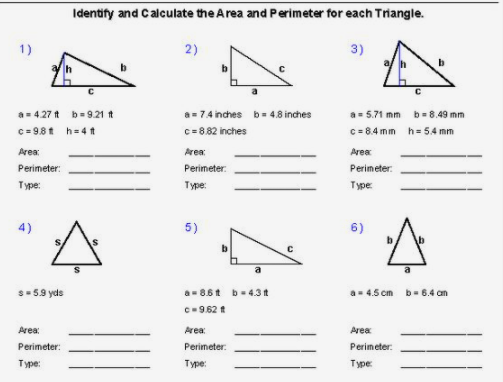
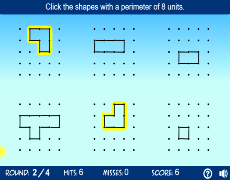
Topic perimeter practice problems: Welcome to our comprehensive guide on perimeter practice problems! This article is designed to help you master the concept of perimeter through a variety of practice problems, formulas, and interactive exercises. Whether you are a student, teacher, or simply looking to improve your math skills, this guide will provide you with the tools you need.
Table of Content
- Perimeter Practice Problems
- Introduction to Perimeter
- Understanding Perimeter
- Perimeter Formulas for Different Shapes
- Perimeter Practice Worksheets and Problems
- Interactive Perimeter Exercises
- Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
- Common Challenges in Solving Perimeter Problems
- Advanced Perimeter Problems
- Perimeter and Area: Integrated Practice
- YOUTUBE: Video này sẽ hướng dẫn bạn cách tìm chu vi của các hình học khác nhau, rất hữu ích cho việc luyện tập các bài toán về chu vi.
Perimeter Practice Problems
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of various shapes is essential for students learning geometry. Here, you'll find practice problems, exercises, and worksheets that will help enhance your understanding of perimeter calculations.
Perimeter Formulas
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Square: \( P = 4s \)
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Circle (Circumference): \( C = 2 \pi r \)
Example Problems
- Rectangle: A rectangle has a length of 7 cm and a width of 3 cm. Calculate its perimeter.
Solution: \( P = 2(7 + 3) = 2 \times 10 = 20 \) cm
- Square: Each side of a square is 5 cm. Find the perimeter.
Solution: \( P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \) cm
- Triangle: A triangle has sides of lengths 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm. Determine its perimeter.
Solution: \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \) cm
- Circle: A circle has a radius of 4 cm. What is its circumference?
Solution: \( C = 2 \pi \times 4 = 8 \pi \) cm
Perimeter Word Problems
- A garden is in the shape of a rectangle with a length of 15 meters and a width of 10 meters. How much fencing is needed to enclose the garden?
- A square playground has a side length of 20 meters. Calculate the perimeter of the playground.
- The perimeter of a triangle is 24 cm. If two sides are 9 cm and 7 cm, find the length of the third side.
- Find the circumference of a circular park with a diameter of 14 meters.
Interactive Exercises
To practice more problems and test your understanding, visit the following resources:

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter
Perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a two-dimensional shape. It is an important concept in geometry, used in various real-life applications such as fencing a yard, framing a picture, or designing a garden.
To understand perimeter better, let's start with the basics:
- Definition: The perimeter of a shape is the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
- Formula for Common Shapes:
- Rectangle: \(P = 2(l + w)\), where \(l\) is the length and \(w\) is the width.
- Square: \(P = 4s\), where \(s\) is the side length.
- Triangle: \(P = a + b + c\), where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the side lengths.
- Circle (Circumference): \(P = 2\pi r\), where \(r\) is the radius.
Let's illustrate the concept with an example:
| Shape | Dimensions | Perimeter Calculation |
| Rectangle | Length = 5 units, Width = 3 units | \(P = 2(5 + 3) = 2 \times 8 = 16\) units |
| Square | Side = 4 units | \(P = 4 \times 4 = 16\) units |
| Triangle | Sides = 3 units, 4 units, 5 units | \(P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12\) units |
| Circle | Radius = 3 units | \(P = 2\pi \times 3 \approx 18.85\) units |
By practicing perimeter calculations, you can improve your understanding and ability to solve geometry problems efficiently. In the following sections, we will explore more examples, worksheets, and interactive exercises to enhance your perimeter skills.
Understanding Perimeter
Understanding perimeter involves recognizing it as a measurement of the total distance around the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is a fundamental concept in geometry, essential for solving various real-life and mathematical problems. Here's a step-by-step breakdown to help you grasp this concept:
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding Perimeter:
- Identify the Shape: Determine the type of shape you are dealing with (e.g., rectangle, square, triangle, circle).
- Measure the Sides: Measure or obtain the length of each side of the shape. For polygons, this involves multiple sides, while for circles, you'll need the radius or diameter.
- Use the Appropriate Formula: Apply the correct perimeter formula based on the shape. Here are some common formulas:
- Rectangle: \(P = 2(l + w)\)
- Square: \(P = 4s\)
- Triangle: \(P = a + b + c\)
- Circle (Circumference): \(P = 2\pi r\)
- Sum the Sides: For polygons, add up the lengths of all sides. For circles, calculate the circumference using the formula.
- Interpret the Result: The final value represents the perimeter, which is the total distance around the shape.
Let's take a look at some examples to solidify our understanding:
| Shape | Dimensions | Perimeter Calculation |
| Rectangle | Length = 7 units, Width = 4 units | \(P = 2(7 + 4) = 2 \times 11 = 22\) units |
| Square | Side = 6 units | \(P = 4 \times 6 = 24\) units |
| Triangle | Sides = 3 units, 5 units, 7 units | \(P = 3 + 5 + 7 = 15\) units |
| Circle | Radius = 5 units | \(P = 2\pi \times 5 \approx 31.42\) units |
By following these steps and practicing various problems, you can develop a strong understanding of how to calculate the perimeter of different shapes. This skill is not only useful in academic settings but also in everyday situations where measuring boundaries is required.
Perimeter Formulas for Different Shapes
Calculating the perimeter of various shapes involves using specific formulas tailored to each geometric figure. Here are the perimeter formulas for some common shapes:
1. Rectangle:
The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by adding together the lengths of all four sides. Since opposite sides of a rectangle are equal, the formula is:
\( P = 2(l + w) \)
- l = length
- w = width
Example: If the length of a rectangle is 8 units and the width is 3 units, the perimeter is:
\( P = 2(8 + 3) = 2 \times 11 = 22 \) units
2. Square:
The perimeter of a square is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by 4, since all sides are equal:
\( P = 4s \)
- s = side length
Example: If the side length of a square is 5 units, the perimeter is:
\( P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \) units
3. Triangle:
The perimeter of a triangle is found by adding the lengths of all three sides:
\( P = a + b + c \)
- a, b, c = lengths of the three sides
Example: If a triangle has sides of 6 units, 7 units, and 8 units, the perimeter is:
\( P = 6 + 7 + 8 = 21 \) units
4. Circle (Circumference):
The perimeter of a circle, known as the circumference, is calculated using the radius or diameter:
\( P = 2\pi r \) or \( P = \pi d \)
- r = radius
- d = diameter
Example: If the radius of a circle is 4 units, the perimeter (circumference) is:
\( P = 2\pi \times 4 \approx 25.13 \) units
5. Regular Polygon:
The perimeter of a regular polygon (a polygon with all sides and angles equal) is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by the total number of sides:
\( P = n \times s \)
- n = number of sides
- s = side length
Example: If a regular hexagon (6 sides) has a side length of 3 units, the perimeter is:
\( P = 6 \times 3 = 18 \) units
These formulas provide a foundation for calculating the perimeter of various shapes. Practicing these calculations can enhance your understanding and ability to apply these formulas effectively.
Perimeter Practice Worksheets and Problems
Practicing perimeter calculations is essential for mastering this fundamental geometry concept. Below are a variety of worksheets and problems designed to enhance your understanding and skills:
Worksheets
These worksheets cover different shapes and difficulty levels to ensure comprehensive practice:
- Basic Perimeter Worksheets: Simple problems involving rectangles, squares, and triangles. Suitable for beginners.
- Calculate the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 7 units and a width of 4 units.
- Find the perimeter of a square with a side length of 5 units.
- Determine the perimeter of a triangle with sides of 3 units, 4 units, and 5 units.
- Intermediate Perimeter Worksheets: More complex shapes and composite figures.
- Calculate the perimeter of an L-shaped figure with given side lengths.
- Find the perimeter of a regular pentagon with each side measuring 6 units.
- Determine the perimeter of a trapezoid with sides of 8 units, 5 units, 7 units, and 5 units.
- Advanced Perimeter Worksheets: Challenging problems involving circles, polygons, and irregular shapes.
- Calculate the circumference of a circle with a radius of 5 units.
- Find the perimeter of a regular octagon with each side measuring 4 units.
- Determine the perimeter of an irregular shape by adding the lengths of its sides.
Practice Problems
Work through these problems step-by-step to build your perimeter calculation skills:
- Problem 1: A rectangular garden has a length of 12 meters and a width of 8 meters. What is the perimeter of the garden?
Solution: Use the formula \( P = 2(l + w) \). Therefore, \( P = 2(12 + 8) = 2 \times 20 = 40 \) meters.
- Problem 2: A square playground has a side length of 15 meters. What is the perimeter of the playground?
Solution: Use the formula \( P = 4s \). Therefore, \( P = 4 \times 15 = 60 \) meters.
- Problem 3: A triangular field has sides measuring 9 meters, 12 meters, and 15 meters. What is the perimeter of the field?
Solution: Use the formula \( P = a + b + c \). Therefore, \( P = 9 + 12 + 15 = 36 \) meters.
- Problem 4: A circular fountain has a radius of 7 meters. What is the perimeter (circumference) of the fountain?
Solution: Use the formula \( P = 2\pi r \). Therefore, \( P = 2 \pi \times 7 \approx 44 \) meters.
- Problem 5: An irregular pentagon has side lengths of 5 units, 7 units, 6 units, 8 units, and 10 units. What is the perimeter of the pentagon?
Solution: Add the lengths of all the sides. Therefore, \( P = 5 + 7 + 6 + 8 + 10 = 36 \) units.
By completing these worksheets and problems, you will gain confidence and proficiency in calculating the perimeter of various shapes, preparing you for more advanced geometry challenges.

Interactive Perimeter Exercises
Interactive exercises provide a dynamic way to practice and understand perimeter calculations. Below are various interactive activities designed to enhance your learning experience:
Online Perimeter Calculators
Use online tools to calculate the perimeter of different shapes by entering the required dimensions. These calculators provide instant feedback and step-by-step solutions.
- Rectangle Perimeter Calculator: Input length and width to find the perimeter.
- Circle Circumference Calculator: Enter the radius or diameter to calculate the circumference.
- Polygon Perimeter Calculator: Provide the number of sides and the side length for regular polygons.
Interactive Geometry Software
Geometry software allows you to draw shapes and measure their perimeters dynamically. Examples include:
- Geogebra: Create and manipulate geometric shapes to see how changes in dimensions affect the perimeter.
- Desmos: Use the geometry tools to construct shapes and calculate their perimeters.
Perimeter Games and Quizzes
Engage in fun games and quizzes to test your perimeter skills. These activities offer a playful way to practice while receiving instant feedback.
- Perimeter Matching Game: Match shapes with their correct perimeters.
- Perimeter Quiz: Answer multiple-choice questions on perimeter calculations to test your knowledge.
Step-by-Step Interactive Problems
Work through problems interactively, receiving hints and solutions at each step. Here's an example exercise:
- Problem: A rectangle has a length of 10 units and a width of 4 units. Calculate its perimeter.
Step 1: Identify the formula: \( P = 2(l + w) \).
Step 2: Substitute the given values: \( l = 10 \) and \( w = 4 \).
Step 3: Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 2(10 + 4) = 2 \times 14 = 28 \) units.
- Problem: A circle has a diameter of 14 units. Calculate its circumference.
Step 1: Identify the formula: \( P = \pi d \) or \( P = 2\pi r \).
Step 2: Use the diameter for the calculation: \( d = 14 \).
Step 3: Calculate the circumference: \( P = \pi \times 14 \approx 44 \) units.
Interactive Perimeter Challenges
Participate in challenges where you compete against others or against the clock to solve perimeter problems.
- Time Trials: Solve as many perimeter problems as you can within a set time limit.
- Competition Mode: Compete with peers to see who can correctly calculate the perimeter of shapes the fastest.
These interactive exercises provide engaging ways to deepen your understanding of perimeter calculations, offering immediate feedback and a variety of learning modalities.
Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
Perimeter calculations are not just academic exercises; they have numerous practical applications in everyday life. Here are some common real-life scenarios where understanding and calculating the perimeter is essential:
Fencing and Bordering
One of the most common applications of perimeter is in fencing properties or gardens. Knowing the perimeter helps in determining the amount of fencing material needed.
- Example: To fence a rectangular garden measuring 20 meters by 15 meters, you need:
\( P = 2(l + w) = 2(20 + 15) = 2 \times 35 = 70 \) meters of fencing material.
Home Improvement and Decoration
Perimeter is crucial in various home improvement projects, such as installing baseboards, crown molding, or wallpaper borders.
- Example: To install baseboards around a rectangular room measuring 12 feet by 10 feet:
\( P = 2(l + w) = 2(12 + 10) = 2 \times 22 = 44 \) feet of baseboard is required.
Construction and Landscaping
Construction projects often require precise perimeter measurements for planning and budgeting purposes, including the layout of foundations and the creation of landscaped areas.
- Example: To lay a walkway around a circular garden with a radius of 5 meters:
\( P = 2\pi r = 2 \pi \times 5 \approx 31.42 \) meters of paving material is needed.
Fashion and Textiles
Designers and tailors use perimeter calculations to determine the lengths of trims, laces, and other decorative elements required for clothing and accessories.
- Example: To add lace around the edge of a square tablecloth with a side length of 1.5 meters:
\( P = 4s = 4 \times 1.5 = 6 \) meters of lace is needed.
Sports and Recreation
In sports, perimeter measurements are used to set up courts, tracks, and fields. This ensures that all dimensions meet official regulations.
- Example: To mark the boundary of a standard tennis court, which is 23.77 meters long and 8.23 meters wide:
\( P = 2(l + w) = 2(23.77 + 8.23) = 2 \times 32 = 64 \) meters of boundary marking material is required.
Packaging and Shipping
Perimeter calculations help in determining the amount of material needed to wrap or package items, which is crucial for shipping and storage.
- Example: To wrap a rectangular box measuring 30 cm by 20 cm:
\( P = 2(l + w) = 2(30 + 20) = 2 \times 50 = 100 \) cm of wrapping material is required.
Understanding perimeter and its practical applications can greatly benefit various aspects of daily life, from home improvement projects to professional tasks in fields such as construction and design. Practicing perimeter problems helps in developing the necessary skills to apply these concepts effectively in real-world scenarios.
Common Challenges in Solving Perimeter Problems
Solving perimeter problems can sometimes present challenges, especially for those new to geometry. Here are some common difficulties and tips on how to overcome them:
1. Misunderstanding the Shape
One of the initial challenges is correctly identifying the shape and its properties. Different shapes have different formulas for calculating the perimeter.
- Tip: Carefully examine the shape and ensure you understand whether it is a rectangle, square, triangle, circle, or a more complex figure. Labeling sides and using diagrams can help.
2. Incorrectly Applying Formulas
Another common issue is using the wrong formula or misapplying the correct formula. Each shape has a specific formula based on its properties.
- Tip: Memorize the perimeter formulas for basic shapes and practice applying them to different problems. For example, the formula for a rectangle is \( P = 2(l + w) \), while for a circle, it is \( P = 2\pi r \) or \( P = \pi d \).
3. Arithmetic Errors
Simple arithmetic errors can lead to incorrect results, especially when adding multiple side lengths or dealing with fractions and decimals.
- Tip: Double-check your calculations at each step. Use a calculator for complex arithmetic to minimize errors.
4. Dealing with Composite Shapes
Composite shapes, which are made up of multiple basic shapes, can be particularly challenging. It’s essential to correctly break down the shape into manageable parts.
- Tip: Divide the composite shape into simpler shapes, calculate the perimeter of each part separately, and then sum these perimeters. Ensure you don’t double-count any shared sides.
5. Handling Irregular Shapes
Irregular shapes without a clear formula can be confusing. These shapes require adding all the side lengths manually.
- Tip: Carefully measure or identify each side length and add them together. For complex irregular shapes, consider using a perimeter tracing tool or software.
6. Overlooking Units of Measurement
Forgetting to convert or consistently use units can lead to incorrect answers, especially in mixed-unit problems.
- Tip: Always check the units of each side length and convert them if necessary before performing any calculations. Ensure your final answer is in the correct unit.
7. Misinterpreting Problem Statements
Sometimes the problem statement can be misleading or complex, causing confusion about what is being asked.
- Tip: Read the problem statement carefully, possibly multiple times, and break it down into smaller parts. Look for keywords that indicate specific operations or shapes.
8. Visualizing the Problem
Struggling to visualize the geometric figures can make it difficult to understand the problem and apply the correct methods.
- Tip: Drawing the shape and labeling its sides can significantly aid in visualization and understanding. Use graph paper for more accuracy if needed.
By recognizing these common challenges and applying the provided tips, you can improve your ability to solve perimeter problems effectively and accurately. Practice regularly with a variety of problems to build confidence and proficiency in these skills.
Advanced Perimeter Problems
Advanced perimeter problems often involve more complex shapes and require a deeper understanding of geometric principles. Here are some challenging perimeter problems to test your skills:
Problem 1: Perimeter of a Composite Shape
Consider an L-shaped figure composed of two rectangles. The larger rectangle has a length of 10 units and a width of 6 units, while the smaller rectangle has a length of 4 units and a width of 2 units.
- Step 1: Draw and label the L-shaped figure, noting the shared sides.
- Step 2: Calculate the perimeter of the composite shape by adding the outer edges:
\( P = 10 + 6 + 6 + 4 + 4 + 2 = 32 \) units
Problem 2: Perimeter of a Regular Polygon
Find the perimeter of a regular hexagon with a side length of 8 units.
- Step 1: Identify the formula for the perimeter of a regular polygon: \( P = n \times s \).
- Step 2: Substitute the number of sides (n = 6) and the side length (s = 8):
\( P = 6 \times 8 = 48 \) units
Problem 3: Perimeter of a Circle Sector
Calculate the perimeter of a sector of a circle with a radius of 7 units and a central angle of 90 degrees.
- Step 1: Find the length of the arc using the formula \( \text{Arc Length} = \frac{\theta}{360} \times 2\pi r \):
\( \text{Arc Length} = \frac{90}{360} \times 2\pi \times 7 = \frac{1}{4} \times 14\pi = 3.5\pi \approx 11 \) units
- Step 2: Add the two radii to the arc length to find the perimeter:
\( P = 2 \times 7 + 11 = 14 + 11 = 25 \) units
Problem 4: Perimeter of an Ellipse
Approximate the perimeter of an ellipse with a major axis of 10 units and a minor axis of 6 units using the formula \( P \approx \pi [3(a + b) - \sqrt{(3a + b)(a + 3b)}] \), where \( a \) is the semi-major axis and \( b \) is the semi-minor axis.
- Step 1: Identify the semi-major axis (\( a = 5 \) units) and the semi-minor axis (\( b = 3 \) units).
- Step 2: Substitute the values into the formula:
\( P \approx \pi [3(5 + 3) - \sqrt{(3 \times 5 + 3)(5 + 3 \times 3)}] = \pi [3 \times 8 - \sqrt{(15 + 3)(5 + 9)}] = \pi [24 - \sqrt{18 \times 14}] \)
\( P \approx \pi [24 - \sqrt{252}] = \pi [24 - 15.87] = \pi \times 8.13 \approx 25.54 \) units
Problem 5: Perimeter of an Irregular Shape
Determine the perimeter of an irregular pentagon with side lengths of 5 units, 7 units, 8 units, 6 units, and 9 units.
- Step 1: Add the lengths of all the sides:
\( P = 5 + 7 + 8 + 6 + 9 = 35 \) units
These advanced problems require careful attention to detail and a solid understanding of geometric principles. Practice solving these problems to enhance your perimeter calculation skills and prepare for more complex geometric challenges.
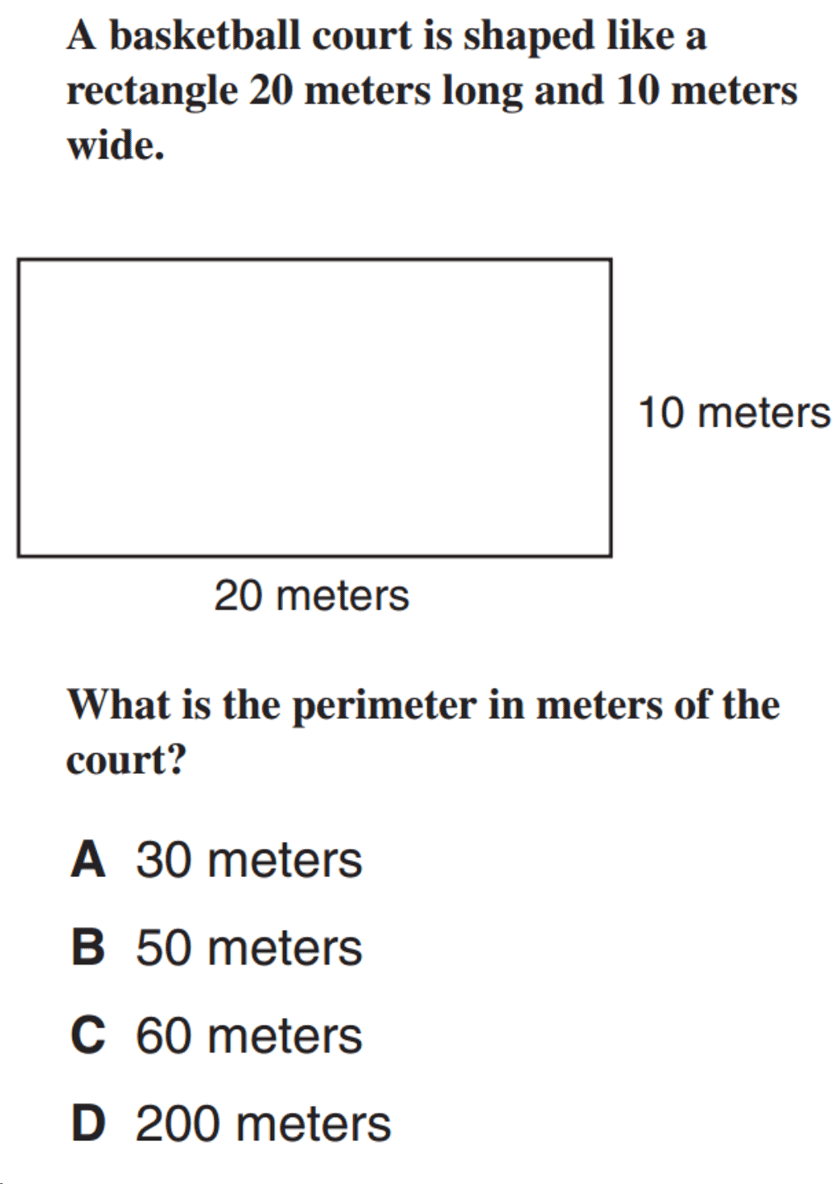
Perimeter and Area: Integrated Practice
Understanding the relationship between perimeter and area is crucial in geometry. These integrated practice problems will help you develop a comprehensive understanding of both concepts.
Problem 1: Rectangle
Given a rectangle with a length of 12 units and a width of 5 units, find both the perimeter and the area.
- Step 1: Calculate the perimeter using the formula \( P = 2(l + w) \):
\( P = 2(12 + 5) = 2 \times 17 = 34 \) units
- Step 2: Calculate the area using the formula \( A = l \times w \):
\( A = 12 \times 5 = 60 \) square units
Problem 2: Circle
Given a circle with a radius of 7 units, find both the circumference (perimeter) and the area.
- Step 1: Calculate the circumference using the formula \( C = 2\pi r \):
\( C = 2\pi \times 7 \approx 44 \) units
- Step 2: Calculate the area using the formula \( A = \pi r^2 \):
\( A = \pi \times 7^2 = \pi \times 49 \approx 154 \) square units
Problem 3: Triangle
Given a right triangle with legs of 6 units and 8 units, find both the perimeter and the area.
- Step 1: Find the hypotenuse using the Pythagorean theorem \( c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \):
\( c = \sqrt{6^2 + 8^2} = \sqrt{36 + 64} = \sqrt{100} = 10 \) units
- Step 2: Calculate the perimeter by adding all the sides:
\( P = 6 + 8 + 10 = 24 \) units
- Step 3: Calculate the area using the formula \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times base \times height \):
\( A = \frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 8 = 24 \) square units
Problem 4: Composite Shape
Given a shape composed of a rectangle and a semicircle, where the rectangle has a length of 10 units and a width of 4 units, and the semicircle has a diameter equal to the width of the rectangle, find both the perimeter and the area.
- Step 1: Calculate the perimeter of the rectangle (excluding the width where the semicircle is attached):
\( P_{\text{rectangle}} = 2(l + w) - w = 2(10 + 4) - 4 = 28 \) units
- Step 2: Calculate the perimeter of the semicircle using \( \frac{1}{2} \times 2\pi r + w \) (to account for the straight edge):
\( P_{\text{semicircle}} = \pi r + w = \pi \times 2 + 4 \approx 6.28 + 4 = 10.28 \) units
- Step 3: Add both perimeters to find the total perimeter:
\( P_{\text{total}} = 28 + 10.28 = 38.28 \) units
- Step 4: Calculate the area of the rectangle:
\( A_{\text{rectangle}} = l \times w = 10 \times 4 = 40 \) square units
- Step 5: Calculate the area of the semicircle using \( \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 \):
\( A_{\text{semicircle}} = \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 = \frac{1}{2} \pi \times 2^2 = 2\pi \approx 6.28 \) square units
- Step 6: Add both areas to find the total area:
\( A_{\text{total}} = 40 + 6.28 = 46.28 \) square units
Practicing problems that integrate both perimeter and area calculations helps in developing a holistic understanding of geometric properties and enhances problem-solving skills.
Video này sẽ hướng dẫn bạn cách tìm chu vi của các hình học khác nhau, rất hữu ích cho việc luyện tập các bài toán về chu vi.
Tìm Chu Vi
READ MORE:
Video này sẽ hướng dẫn bạn cách tính chu vi của các hình học khác nhau một cách dễ hiểu và thú vị, rất phù hợp cho việc luyện tập các bài toán về chu vi.
Toán Học Vui - Chu Vi