Topic perimeter octagon: Discover the essential guide to calculating the perimeter of an octagon. This article covers the definition, properties, and types of octagons, along with step-by-step instructions for finding their perimeter. Learn practical applications in architecture, urban planning, and art, and avoid common mistakes with our expert tips. Start mastering octagon perimeter calculations today!
Table of Content
- Calculating the Perimeter of an Octagon
- Introduction to Octagons
- Definition and Properties of an Octagon
- Types of Octagons
- Regular Octagons
- Irregular Octagons
- Formula for Calculating the Perimeter
- Perimeter of a Regular Octagon
- Perimeter of an Irregular Octagon
- Step-by-Step Calculation of the Perimeter
- Measuring the Side Length
- Applying the Perimeter Formula
- Examples of Perimeter Calculations
- Practical Applications of Octagon Perimeter Calculation
- Architectural Design
- Urban Planning
- Art and Decorative Uses
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Frequently Asked Questions
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của hình bát giác một cách dễ dàng và chính xác. Xem video để tìm hiểu thêm về các bước và công thức cần thiết để tính chu vi của hình bát giác.
Calculating the Perimeter of an Octagon
An octagon is an eight-sided polygon. To calculate its perimeter, you need to know the length of one of its sides. The formula for the perimeter \( P \) of a regular octagon (where all sides are of equal length) is:
where \( s \) is the length of one side of the octagon.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Measure the length of one side of the octagon.
- Multiply this length by 8.
- The result is the perimeter of the octagon.
For example, if one side of the octagon is 5 units long, the perimeter would be:
Properties of a Regular Octagon
- All sides are of equal length.
- All interior angles are equal, each measuring 135 degrees.
- The sum of all interior angles is 1080 degrees.
Applications of Octagons
Regular octagons are commonly found in various architectural and design elements, such as:
- Stop signs
- Tile patterns
- Decorative elements in buildings
READ MORE:
Introduction to Octagons
An octagon is a polygon with eight sides and eight angles. Octagons can be classified into two main types: regular and irregular.
- Regular Octagons: All sides and angles are equal. Each interior angle measures 135 degrees.
- Irregular Octagons: The sides and angles can vary in length and measure.
The perimeter of an octagon is the total length around the shape. For a regular octagon, the perimeter \( P \) can be calculated using the formula:
where \( s \) is the length of one side. This formula simplifies the calculation, making it easy to determine the perimeter if you know the side length.
Octagons are often seen in various practical applications, including:
- Architecture: Octagonal shapes are used in building designs and structures.
- Urban Planning: Octagonal layouts are common in traffic signs and street patterns.
- Art and Design: Octagonal patterns are popular in decorative arts and crafts.
Understanding the properties and perimeter calculation of octagons is essential for both practical and theoretical purposes in various fields.
Definition and Properties of an Octagon
An octagon is a geometric figure with eight sides and eight angles. It is a type of polygon and can be either regular or irregular. The term "octagon" is derived from the Greek words "okto" meaning eight and "gonia" meaning angle.
Here are the key properties of an octagon:
- Sides: An octagon has eight sides.
- Angles: An octagon has eight interior angles.
- Sum of Interior Angles: The sum of the interior angles of an octagon is: , calculated using the formula: , where \( n \) is the number of sides (8 in the case of an octagon).
- Each Interior Angle: In a regular octagon, each interior angle measures: , calculated by dividing the sum of the interior angles by 8.
- Exterior Angles: Each exterior angle of a regular octagon measures: , calculated using the formula: .
- Symmetry: A regular octagon has 8 lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry of order 8.
In a regular octagon, all sides are equal in length and all interior angles are equal. In contrast, an irregular octagon does not have equal sides and angles, making the calculation of its perimeter and other properties more complex.
The perimeter of a regular octagon can be easily calculated using the formula:
where \( s \) is the length of one side.
Understanding these properties is fundamental for geometric calculations and practical applications involving octagonal shapes.
Types of Octagons
Octagons are polygons with eight sides and eight angles. There are two main types of octagons:
- Regular Octagons
- Irregular Octagons
Regular Octagons
A regular octagon has all sides of equal length and all interior angles equal. The symmetry and uniformity of regular octagons make them easy to analyze mathematically and visually appealing in design.
The properties of a regular octagon include:
- Each interior angle is \(135^\circ\).
- Each exterior angle is \(45^\circ\).
- It has eight lines of symmetry.
- The formula for the perimeter \(P\) of a regular octagon with side length \(s\) is given by:
\(P = 8s\)
Irregular Octagons
An irregular octagon has sides of different lengths and angles of different measures. These octagons do not have the symmetry of regular octagons, making them more complex to analyze and calculate.
Characteristics of irregular octagons include:
- Not all sides are equal.
- Not all interior angles are equal.
- It may have lines of symmetry, but fewer than eight, depending on the specific shape.
- The perimeter \(P\) of an irregular octagon is the sum of the lengths of all its sides:
\(P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 + s_6 + s_7 + s_8\)
Understanding the types of octagons helps in various applications, from architectural design to solving geometric problems.
Regular Octagons
A regular octagon is a polygon with eight equal sides and eight equal angles. Due to its symmetry and uniformity, a regular octagon has unique properties that simplify the calculation of its perimeter and other geometric characteristics.
Properties of a Regular Octagon
- All sides are of equal length.
- All interior angles are equal, each measuring \(135^\circ\).
- All exterior angles are equal, each measuring \(45^\circ\).
- A regular octagon has eight lines of symmetry.
- It is both cyclic (its vertices can all lie on a single circle) and equilateral (all sides are equal).
Calculating the Perimeter of a Regular Octagon
The perimeter of a regular octagon is straightforward to calculate due to the equal side lengths. The formula for the perimeter \(P\) of a regular octagon with side length \(s\) is:
\(P = 8s\)
Here is a step-by-step process to calculate the perimeter:
- Measure the length of one side of the regular octagon. Let this length be denoted as \(s\).
- Multiply the side length \(s\) by 8 to find the perimeter.
For example, if each side of a regular octagon is 5 units long, the perimeter would be:
\(P = 8 \times 5 = 40\) units
Examples of Regular Octagons in Real Life
- Architectural Designs: Regular octagons are often used in floor plans, window designs, and other architectural elements due to their aesthetic appeal and structural balance.
- Stop Signs: The common stop sign is an example of a regular octagon used in traffic control, where all sides and angles are equal to provide clear and uniform signaling.
- Decorative Patterns: Regular octagons are used in tiling and decorative arts, creating visually pleasing and repetitive patterns.
Understanding and calculating the perimeter of regular octagons is essential in various fields, including geometry, architecture, and design.
Irregular Octagons
An irregular octagon is a polygon with eight sides of varying lengths and eight angles of different measures. Unlike regular octagons, irregular octagons lack symmetry, making the calculation of their perimeter more complex.
Properties of an Irregular Octagon
- Not all sides are of equal length.
- Angles can vary and are not necessarily equal.
- May or may not have lines of symmetry depending on the specific configuration.
- Each irregular octagon is unique in shape and size.
Calculating the Perimeter of an Irregular Octagon
The perimeter of an irregular octagon is the total length around the shape, calculated by summing the lengths of all its sides. The formula for the perimeter \(P\) of an irregular octagon is:
\(P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 + s_6 + s_7 + s_8\)
Here is a step-by-step process to calculate the perimeter:
- Measure the length of each side of the octagon. Let these lengths be \(s_1, s_2, s_3, s_4, s_5, s_6, s_7,\) and \(s_8\).
- Add the lengths of all eight sides to find the perimeter:
\(P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 + s_6 + s_7 + s_8\)
For example, if the side lengths of an irregular octagon are 3, 4, 5, 4, 3, 6, 5, and 4 units, the perimeter would be:
\(P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 4 + 3 + 6 + 5 + 4 = 34\) units
Examples of Irregular Octagons in Real Life
- Custom Architectural Elements: Irregular octagons are used in custom window designs, unique floor plans, and other architectural elements where standard shapes do not fit the design requirements.
- Natural Formations: Certain crystals and organic shapes in nature may form irregular octagonal patterns due to varying environmental factors.
- Art and Sculpture: Artists and sculptors may use irregular octagons to create unique and asymmetrical pieces that stand out visually.
Understanding and calculating the perimeter of irregular octagons is important for precise measurements in various fields, including architecture, art, and engineering.
Formula for Calculating the Perimeter
To calculate the perimeter of an octagon, whether it is regular or irregular, we need to know the lengths of its sides. The formulas vary slightly depending on the type of octagon.
Perimeter of a Regular Octagon
A regular octagon has all eight sides of equal length. The formula for the perimeter (P) of a regular octagon with side length (s) is given by:
Where:
- P is the perimeter of the regular octagon
- s is the length of one side of the octagon
Perimeter of an Irregular Octagon
An irregular octagon has sides of different lengths. To find the perimeter of an irregular octagon, sum the lengths of all its sides. The formula is:
Where:
- P is the perimeter of the irregular octagon
- s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6, s7, s8 are the lengths of each side of the octagon
Perimeter of a Regular Octagon
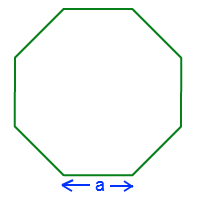
The perimeter of a regular octagon is the total length of its boundary. A regular octagon has all its sides of equal length, denoted as \( a \). To calculate the perimeter, we sum the lengths of all the sides.
The formula to find the perimeter \( P \) of a regular octagon is:
\( P = 8a \)
Here, \( a \) represents the length of one side of the octagon. This formula is straightforward because it involves simply multiplying the side length by 8, given that all sides are equal.
For a step-by-step calculation:
- Measure the length of one side of the regular octagon.
- Multiply this length by 8 to get the perimeter.
For example, if the side length of a regular octagon is 5 cm, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
\( P = 8 \times 5 = 40 \) cm
Thus, the perimeter of the octagon is 40 cm.
Below is a summary table for quick reference:
| Side Length (a) | Perimeter (P) |
|---|---|
| 2 cm | 16 cm |
| 5 cm | 40 cm |
| 10 cm | 80 cm |
This simple formula and method ensure accurate perimeter calculation for any regular octagon.
Perimeter of an Irregular Octagon
An irregular octagon is a polygon with eight sides of varying lengths and angles. Unlike regular octagons, which have equal side lengths and angles, irregular octagons do not follow this uniformity. The calculation of the perimeter of an irregular octagon involves summing the lengths of all its sides.
To calculate the perimeter of an irregular octagon, follow these steps:
- Measure the Length of Each Side: Use a ruler or measuring tape to determine the length of each of the eight sides of the octagon. Label these lengths as \(a_1, a_2, a_3, \ldots, a_8\).
- Add the Lengths Together: Sum all the measured lengths to find the perimeter \(P\). The formula to calculate the perimeter is:
\[
P = a_1 + a_2 + a_3 + a_4 + a_5 + a_6 + a_7 + a_8
\]
For example, if the side lengths of an irregular octagon are as follows: \(a_1 = 3\), \(a_2 = 4\), \(a_3 = 5\), \(a_4 = 6\), \(a_5 = 4\), \(a_6 = 3\), \(a_7 = 6\), and \(a_8 = 5\), then the perimeter \(P\) would be calculated as:
\[
P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 4 + 3 + 6 + 5 = 36
\]
Thus, the perimeter of this irregular octagon is 36 units.
Irregular octagons can vary greatly in shape and size, so accurately measuring each side is crucial for an exact perimeter calculation.

Step-by-Step Calculation of the Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of an octagon involves a few straightforward steps. Below is a detailed guide to help you understand the process, whether the octagon is regular or irregular.
Step 1: Measuring the Side Length
To begin, measure the length of one side of the octagon. This is a crucial step as the accuracy of your measurement will directly impact the precision of the perimeter calculation.
Step 2: Applying the Perimeter Formula
The formula for calculating the perimeter of an octagon depends on whether it is regular or irregular:
For a Regular Octagon:
- Since all sides of a regular octagon are equal, the perimeter (\(P\)) is simply eight times the length of one side (\(s\)).
- The formula is: \( P = 8 \times s \)
For an Irregular Octagon:
- If the octagon is irregular, you need to add up the lengths of all eight sides.
- The formula is: \( P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 + s_6 + s_7 + s_8 \)
Step 3: Examples of Perimeter Calculations
Here are some examples to illustrate the calculation process:
Example 1: Regular Octagon
- Suppose each side of a regular octagon is 5 units.
- Using the formula \( P = 8 \times s \):
- \( P = 8 \times 5 = 40 \) units
Example 2: Irregular Octagon
- Suppose the side lengths of an irregular octagon are 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10 units.
- Using the formula \( P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 + s_6 + s_7 + s_8 \):
- \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9 + 10 = 52 \) units
Step 4: Practical Applications
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of an octagon can be useful in various real-world applications such as architectural design, urban planning, and art. For instance:
- Architectural Design: Accurate perimeter calculations ensure that materials for octagonal structures are correctly estimated.
- Urban Planning: Designing octagonal plots or features requires precise perimeter measurements.
- Art and Decorative Uses: Octagonal frames or tiles need exact perimeter knowledge to fit the intended design space.
Step 5: Avoiding Common Mistakes
- Confusing Perimeter with Area: Remember that perimeter is the total distance around the shape, not the area it encloses.
- Using Different Units: Ensure consistency in the units of measurement.
- Incorrect Side Lengths: Verify the accuracy of side length measurements.
- Rounding Errors: Avoid rounding numbers too early in the calculation process to maintain precision.
Step 6: Tips for Accurate Calculations
- Use precision tools like a ruler or caliper for accurate measurements.
- Double-check your measurements to avoid errors.
- Practice with examples to become familiar with the process.
Measuring the Side Length
Measuring the side length of an octagon is crucial for calculating its perimeter. Here is a step-by-step guide to accurately measure the side length:
Using a Ruler or Measuring Tape
- Place the ruler or measuring tape at one vertex of the octagon.
- Extend it to the next adjacent vertex, ensuring the ruler is straight.
- Record the measurement. This is the side length of the octagon.
Calculating Side Length from the Area
If you know the area of a regular octagon, you can calculate the side length using the following formula:
\[
\text{Length} = \sqrt{\frac{\text{Area}}{2 + 2\sqrt{2}}}
\]
Here's how you can do it step-by-step:
- Simplify the denominator \(2 + 2\sqrt{2}\) to approximately 4.828.
- Divide the area by 4.828.
- Take the square root of the result to get the side length.
Using the Diameter
If you have the diameter (the distance across the octagon through its center), use this method:
- Divide the diameter by 2.41 to find the side length.
For example, if the diameter is 12 inches:
\[
\text{Side Length} = \frac{12}{2.41} \approx 4.98 \text{ inches}
\]
Using Apothem (Inradius)
If you know the apothem (distance from the center to the midpoint of a side), use the formula:
\[
\text{Side Length} = 2 \times \text{Apothem} \times \tan\left(\frac{\pi}{8}\right)
\]
- Calculate \(\tan\left(\frac{\pi}{8}\right)\) which is approximately 0.414.
- Multiply the apothem by 2 and then by 0.414.
Using the Radius (Circumradius)
If you have the circumradius (distance from the center to a vertex), use this formula:
\[
\text{Side Length} = \text{Radius} \times 2 \sin\left(\frac{\pi}{8}\right)
\]
- Calculate \(\sin\left(\frac{\pi}{8}\right)\) which is approximately 0.383.
- Multiply the radius by 2 and then by 0.383.
Examples
Let's see a practical example:
- If the area of the octagon is 100 square units:
- First, divide 100 by 4.828 to get approximately 20.71.
- Then, take the square root of 20.71, which gives approximately 4.55 units for the side length.
- If the apothem is 5 units:
- First, multiply 5 by 2 to get 10.
- Then, multiply 10 by 0.414 to get approximately 4.14 units for the side length.
Applying the Perimeter Formula
To find the perimeter of an octagon, you can apply a simple formula depending on whether the octagon is regular or irregular.
Perimeter of a Regular Octagon
A regular octagon has all eight sides of equal length. The formula for the perimeter (P) is:
Where
Follow these steps:
- Measure the length of one side of the octagon.
- Multiply this length by 8.
For example, if one side is 5 units, the perimeter is:
Perimeter of an Irregular Octagon
An irregular octagon has sides of different lengths. The formula for the perimeter (P) is the sum of the lengths of all sides:
Where
Follow these steps:
- Measure the length of each side of the octagon.
- Add all these lengths together.
For example, if the sides are 3, 4, 5, 4, 3, 6, 5, and 4 units, the perimeter is:
Examples of Perimeter Calculations
Understanding the perimeter calculation of octagons can be enhanced through practical examples. Here are a few examples demonstrating how to calculate the perimeter of both regular and irregular octagons.
Example 1: Regular Octagon
Given a regular octagon with each side length \( a = 5 \, \text{cm} \), we can calculate its perimeter using the formula:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 8 \times a \]
Substitute the given side length into the formula:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 8 \times 5 = 40 \, \text{cm} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of the regular octagon is 40 cm.
Example 2: Irregular Octagon
Consider an irregular octagon with the following side lengths: \( a_1 = 3 \, \text{cm}, a_2 = 4 \, \text{cm}, a_3 = 5 \, \text{cm}, a_4 = 6 \, \text{cm}, a_5 = 7 \, \text{cm}, a_6 = 8 \, \text{cm}, a_7 = 9 \, \text{cm}, a_8 = 10 \, \text{cm} \). The perimeter is the sum of all side lengths:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a_1 + a_2 + a_3 + a_4 + a_5 + a_6 + a_7 + a_8 \]
Substitute the given side lengths into the formula:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9 + 10 = 52 \, \text{cm} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of the irregular octagon is 52 cm.
Example 3: Regular Octagon with Different Units
Let's calculate the perimeter of a regular octagon where each side length is \( a = 2.5 \, \text{m} \):
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 8 \times a \]
Substitute the given side length into the formula:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 8 \times 2.5 = 20 \, \text{m} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of the regular octagon is 20 meters.
Example 4: Irregular Octagon with Mixed Measurements
For an irregular octagon with mixed side lengths \( a_1 = 1.2 \, \text{m}, a_2 = 1.3 \, \text{m}, a_3 = 1.4 \, \text{m}, a_4 = 1.5 \, \text{m}, a_5 = 1.6 \, \text{m}, a_6 = 1.7 \, \text{m}, a_7 = 1.8 \, \text{m}, a_8 = 1.9 \, \text{m} \), the perimeter is calculated as:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a_1 + a_2 + a_3 + a_4 + a_5 + a_6 + a_7 + a_8 \]
Substitute the given side lengths into the formula:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 1.2 + 1.3 + 1.4 + 1.5 + 1.6 + 1.7 + 1.8 + 1.9 = 12.4 \, \text{m} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of the irregular octagon is 12.4 meters.
These examples illustrate the process of calculating the perimeter for both regular and irregular octagons, highlighting the simplicity of the formula for regular octagons and the summation approach for irregular ones.
Practical Applications of Octagon Perimeter Calculation
Understanding the perimeter of an octagon has several practical applications across different fields. Here are some key areas where this knowledge is particularly useful:
-
Architectural Design:
Architects often use octagonal shapes in buildings for aesthetic and structural purposes. Knowing the perimeter helps in the accurate design of floor plans, ensuring the correct dimensions for walls, windows, and other structural elements.
-
Urban Planning:
Urban planners may incorporate octagonal layouts in city designs, such as roundabouts or plazas. Calculating the perimeter is essential for determining the space required and the distribution of infrastructure around these areas.
-
Art and Decoration:
Artists and designers use octagonal shapes in various forms of art and decoration, including mosaics, paintings, and sculptures. Accurate perimeter calculations ensure that these pieces fit their intended spaces perfectly.
-
Sports Facilities:
Some sports, like Mixed Martial Arts (MMA), use octagonal rings. Knowing the perimeter helps in designing these spaces to meet regulatory sizes and provide adequate space for athletes.
-
Game Design:
Board games and puzzles may feature octagonal pieces. Calculating the perimeter ensures that the pieces fit together correctly and that the game functions as intended.
-
Furniture Design:
Designing furniture with octagonal shapes, such as tables or mirrors, requires precise perimeter measurements to ensure all elements align properly and the final product is stable and aesthetically pleasing.
-
Landscaping and Garden Design:
Octagonal patios, gazebos, and garden beds are popular for their visual appeal. Calculating the perimeter helps in estimating the materials needed and ensuring the layout fits within the garden space.
-
Educational Tools:
Teachers use octagonal shapes to help students understand basic geometry concepts. Knowing the perimeter aids in creating educational models and exercises that enhance learning.
These applications demonstrate how the concept of an octagon's perimeter extends beyond theoretical mathematics, influencing various aspects of design, construction, and creativity in the real world.
Architectural Design
The octagonal shape has been a unique and efficient choice in architectural design for centuries. Its use dates back to ancient times, with notable examples like the Tower of the Winds in Athens, Greece, constructed around 300 BCE. In modern architecture, the octagon shape offers several advantages, particularly in residential construction.
Historical Significance
Octagonal architecture gained popularity in the mid-19th century, primarily due to Orson Squire Fowler, who advocated for its benefits in his book "The Octagon House: A Home for All." Fowler highlighted the octagon's ability to enclose more space with less material compared to traditional rectangular or square designs.
Design Benefits
- Increased Interior Space: An octagon encloses approximately 20% more space than a square with the same perimeter, providing more usable interior area and reducing wasted space in corners.
- Energy Efficiency: The shape minimizes the exterior wall length, reducing heat loss and construction material costs. The design also promotes natural ventilation and lighting, enhancing energy efficiency.
- Versatility in Aesthetics: Octagonal homes can feature various facades, from rustic wood to modern glass, and can incorporate elements like wrap-around porches and cupolas, blending functionality with aesthetic appeal.
Modern Applications
Contemporary architects utilize octagonal designs in diverse projects, from single-family homes to community buildings. The flexibility in design allows for innovative use of space, offering a balance of tradition and modernity in architectural projects.
Conclusion
The octagon remains a symbol of architectural ingenuity, providing practical benefits and aesthetic versatility. Its ability to maximize space efficiency and energy performance makes it a valuable design choice in modern construction.
Urban Planning
The perimeter of an octagon plays a significant role in urban planning, contributing to the design and organization of public spaces and infrastructure. Understanding and utilizing the properties of octagons can enhance both the functionality and aesthetic appeal of urban environments.
1. Octagonal Parks and Plazas
Incorporating octagonal shapes in the design of parks and plazas can create visually appealing and efficient public spaces. The symmetry and balance of an octagon allow for a harmonious layout, with pathways and landscaping radiating from the center. This can facilitate smooth pedestrian flow and create focal points for gatherings and activities.
2. Traffic Islands and Roundabouts
Octagonal perimeters are often used in the design of traffic islands and roundabouts. The eight-sided shape provides a balanced approach to managing traffic flow, ensuring that vehicles can navigate the intersection safely and efficiently. The unique geometry of an octagon can help in maximizing space utilization and improving visibility for drivers.
3. Urban Landscaping
Urban planners use octagonal shapes in landscaping projects to add variety and interest to green spaces. For example, octagonal flower beds, fountains, and seating areas can break the monotony of rectangular layouts, offering a refreshing change of scenery. The perimeter calculations help in determining the amount of materials needed for construction and maintenance.
4. Architectural Design
In architecture, octagonal perimeters are used to design unique and iconic structures. Octagonal towers, pavilions, and gazebos can become landmarks within a city, adding to its cultural and historical identity. The precise measurement of the perimeter ensures structural integrity and helps in the accurate placement of architectural elements.
5. Efficient Space Usage
Urban planners leverage the octagon's perimeter to optimize land usage. By dividing larger areas into smaller octagonal sections, planners can create a more organized and efficient layout for residential and commercial developments. This approach helps in maximizing the use of available space while maintaining an aesthetically pleasing environment.
Conclusion
Incorporating octagonal shapes into urban planning provides a blend of functionality, efficiency, and aesthetic appeal. The careful calculation of an octagon's perimeter ensures the accurate implementation of designs, contributing to the overall success of urban development projects.
Art and Decorative Uses
Octagons have a significant presence in art and decorative applications, thanks to their geometric beauty and versatility. Here are some common and creative ways octagons are utilized in art and décor:
-
Wall Art
Octagonal frames and mirrors add a unique and stylish touch to any wall. Their geometric shape can create an eye-catching focal point in a room. These frames are often used for mirrors, photos, and artwork, enhancing the visual interest of the displayed items.
-
Tabletop Decorations
Octagon-shaped coasters, placemats, and table centerpieces are popular choices for adding a decorative element to dining settings. These items can be made from various materials such as wood, glass, or fabric, providing both functionality and aesthetic appeal.
-
Jewelry and Ornaments
Octagons are also used in the design of jewelry and small ornaments. Their symmetrical shape makes them ideal for earrings, pendants, and decorative items like suncatchers and holiday decorations. The faceted edges of octagonal gemstones can reflect light beautifully, enhancing their visual allure.
-
Home Décor
From vintage octagonal shadow boxes to modern led wall clocks, octagon shapes are used in a variety of home décor items. These pieces can add a touch of sophistication and geometric harmony to any interior space.
-
Crafts and DIY Projects
Octagons are a popular shape for various DIY projects. Craft enthusiasts often use octagonal shapes for creating unique and personalized home décor, such as photo frames, decorative boxes, and wall hangings. The geometric simplicity of the octagon lends itself well to creative exploration.
The use of octagons in art and décor demonstrates the timeless appeal of geometric shapes and their ability to enhance both aesthetic and functional elements in everyday objects.
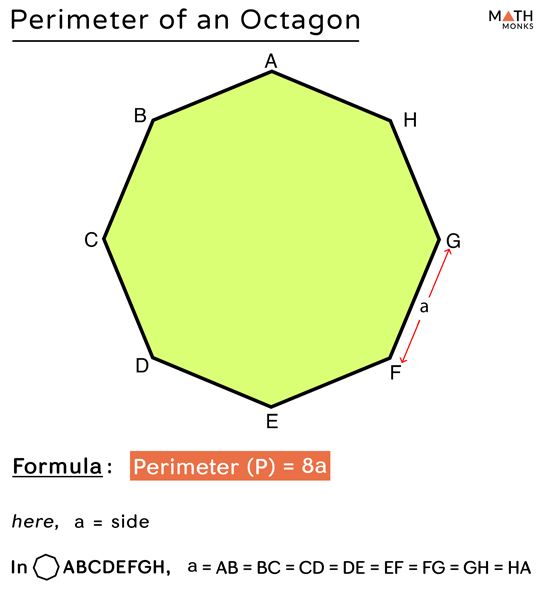
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Calculating the perimeter of an octagon, whether regular or irregular, can sometimes lead to errors if common pitfalls are not addressed. Here are some typical mistakes and how you can avoid them:
- Confusing Regular and Irregular Octagons
Regular octagons have all sides of equal length, while irregular octagons have sides of varying lengths. The formula for the perimeter of a regular octagon is simple:
P = 8s, wheresis the length of one side. For an irregular octagon, you must add the lengths of all eight sides:P = s1 + s2 + s3 + s4 + s5 + s6 + s7 + s8. Ensure you correctly identify the type of octagon you're working with before starting your calculation. - Incorrect Measurement of Side Lengths
Accurate measurement of each side is crucial. For regular octagons, measure one side precisely and use it for all sides. For irregular octagons, measure each side separately. Inaccurate measurements can significantly skew the perimeter calculation.
- Misapplication of Formulas
Using the wrong formula for the type of octagon is a common mistake. Remember, for a regular octagon, use
P = 8s. For an irregular octagon, use the sum of all sides. Double-check which formula applies to your specific octagon. - Neglecting Unit Consistency
Ensure all side lengths are in the same units before summing them. Mixing units (e.g., inches with centimeters) can lead to incorrect results. Convert all measurements to the same unit system before applying the formula.
- Ignoring Decimal Precision
When dealing with measurements that include decimals, maintaining precision is important. Rounding too early in your calculations can result in significant errors. Keep as many decimal places as possible throughout your calculations and only round off the final result if necessary.
- Forgetting to Verify Calculations
Always review your steps and re-check the calculations. Simple arithmetic errors can often go unnoticed but can be easily corrected with a careful second look. Double-checking your work helps ensure the accuracy of the perimeter calculation.
By being mindful of these common mistakes and taking steps to avoid them, you can accurately determine the perimeter of any octagon, whether regular or irregular.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the formula for the perimeter of a regular octagon?
The perimeter
Pof a regular octagon, where all sides are equal in length, is given by the formula:\[ P = 8s \]
Here,
srepresents the length of one side of the octagon. - How do you calculate the perimeter of an irregular octagon?
For an irregular octagon, where the sides are of different lengths, you need to sum the lengths of all eight sides. The formula is:
\[ P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 + s_6 + s_7 + s_8 \]
Here,
s_1, s_2, \dots, s_8are the lengths of the individual sides. - Can I calculate the perimeter if only the area is given?
No, you cannot directly calculate the perimeter of an octagon from its area alone without additional information about the side lengths or the specific type of octagon (regular or irregular). For a regular octagon, you can use the area to find the side length first and then use it to calculate the perimeter.
- Is there a shortcut to find the perimeter if the side length is known?
Yes, for a regular octagon, once you know the length of one side, simply multiply it by 8 to get the perimeter:
\[ P = 8s \]
For example, if one side is 5 cm, the perimeter is \( 8 \times 5 = 40 \) cm.
- How do I ensure accurate measurements for the perimeter calculation?
To ensure accurate measurements, use precise tools for measuring the side lengths, such as a ruler or measuring tape with fine increments. For regular octagons, measuring one side accurately is sufficient. For irregular octagons, measure each side separately and carefully.
- What are the practical applications of knowing the perimeter of an octagon?
Knowing the perimeter of an octagon is useful in various fields such as:
- Architecture: Designing octagonal structures and calculating the materials needed.
- Urban Planning: Planning layouts involving octagonal shapes like parks or plazas.
- Art and Design: Creating octagonal patterns and ensuring correct proportions.
- What common mistakes should I avoid when calculating the perimeter?
Some common mistakes include:
- Using the formula for a regular octagon on an irregular one.
- Incorrectly measuring side lengths.
- Mixing units without proper conversion.
- Rounding off too early in calculations.
- Can I use software or online tools to calculate the perimeter of an octagon?
Yes, there are various online calculators and software tools available that can help you quickly calculate the perimeter of both regular and irregular octagons by inputting the side lengths. These tools are particularly useful for complex shapes or when precision is crucial.
Hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của hình bát giác một cách dễ dàng và chính xác. Xem video để tìm hiểu thêm về các bước và công thức cần thiết để tính chu vi của hình bát giác.
Cách Tìm Chu Vi Của Một Hình Bát Giác - Hướng Dẫn Chi Tiết
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của một hình bát giác đều. Video này cung cấp các bước và công thức chi tiết để bạn có thể tính toán chu vi một cách dễ dàng và chính xác.
Cách Tìm Chu Vi (p) Của Một Hình Bát Giác Đều