Topic perimeter diameter calculator: Welcome to our comprehensive guide on using a perimeter diameter calculator. Whether you're a student, teacher, or professional, this tool simplifies the process of calculating perimeters and diameters for various shapes. Discover easy-to-follow formulas, step-by-step instructions, and practical applications to enhance your mathematical skills and accuracy. Let's start calculating!
Table of Content
- Perimeter and Diameter Calculator
- Introduction to Perimeter and Diameter Calculations
- Understanding Perimeter and Diameter
- Perimeter and Diameter Formulas
- Circle Perimeter and Diameter
- Square Perimeter and Diameter
- Rectangle Perimeter and Diameter
- Triangle Perimeter and Diameter
- Polygon Perimeter and Diameter
- Perimeter and Diameter Calculator Tools
- Step-by-Step Calculation Guide
- Common Mistakes and Tips
- Applications in Real Life
- Conclusion and Further Resources
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi hình tròn một cách đơn giản và dễ hiểu, phù hợp cho mọi người học toán và ứng dụng thực tế.
Perimeter and Diameter Calculator
Welcome to the Perimeter and Diameter Calculator. Use this tool to calculate the perimeter and diameter of various geometric shapes. The formulas and detailed steps are provided to help you understand the calculations.
Circle
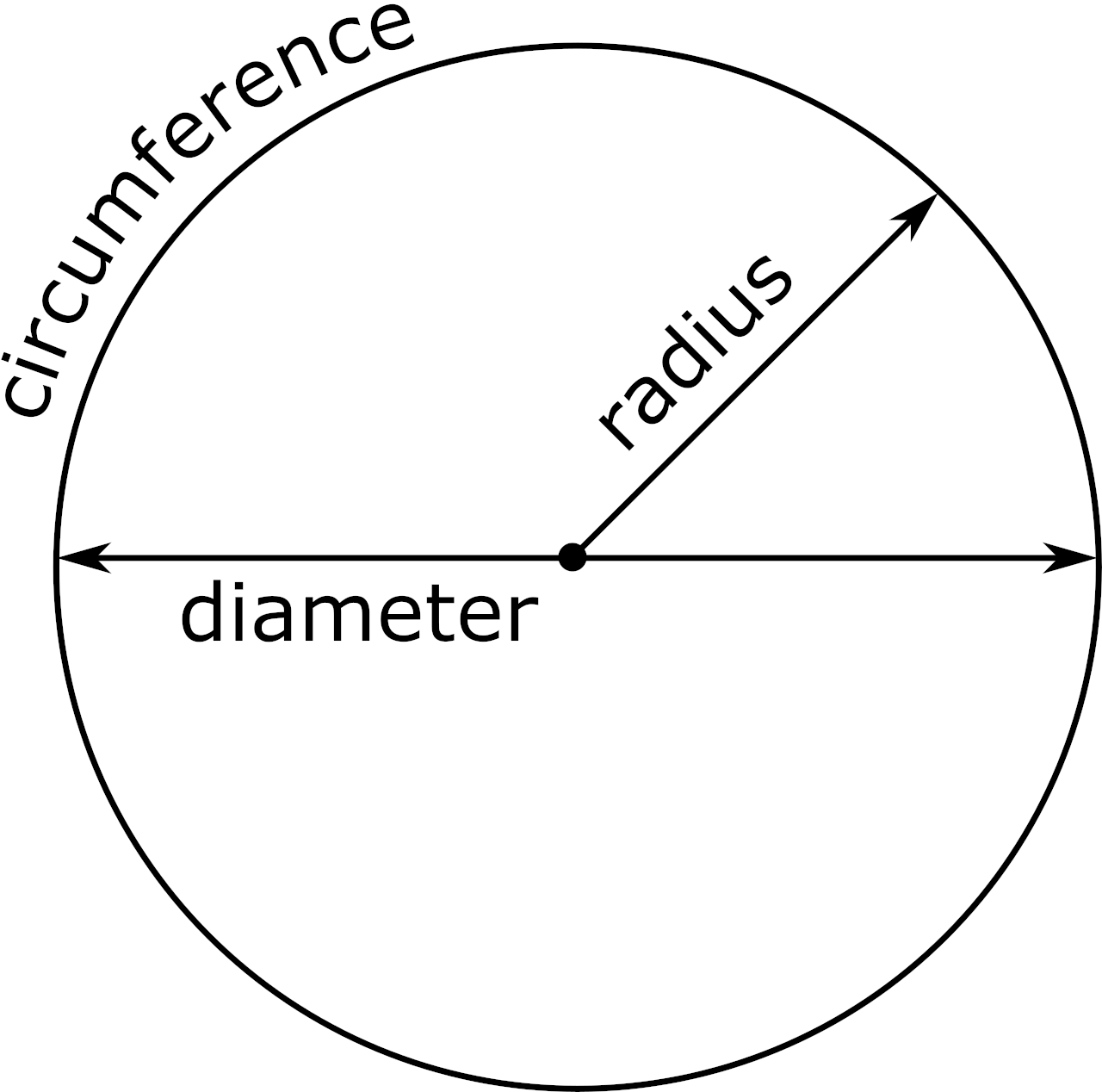
For a circle, you can calculate the perimeter (circumference) and diameter using the radius.
- Perimeter (Circumference) Formula: \( C = 2\pi r \)
- Diameter Formula: \( D = 2r \)
Where \( r \) is the radius of the circle.
Square
For a square, you can calculate the perimeter and the diameter (diagonal).
- Perimeter Formula: \( P = 4s \)
- Diameter (Diagonal) Formula: \( D = s\sqrt{2} \)
Where \( s \) is the side length of the square.
Rectangle
For a rectangle, you can calculate the perimeter and the diameter (diagonal).
- Perimeter Formula: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Diameter (Diagonal) Formula: \( D = \sqrt{l^2 + w^2} \)
Where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width of the rectangle.
Triangle
For a triangle, you can calculate the perimeter. The diameter (circumradius) is only defined for certain triangles.
- Perimeter Formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
Where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
For an equilateral triangle:
- Diameter (Circumradius) Formula: \( D = \frac{a}{\sqrt{3}} \)
Where \( a \) is the side length of the equilateral triangle.
General Polygon
For a regular polygon with \( n \) sides, you can calculate the perimeter.
- Perimeter Formula: \( P = ns \)
Where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the side length of the polygon.
Feel free to use these formulas to calculate the perimeter and diameter of your shapes. Happy calculating!

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter and Diameter Calculations
Calculating the perimeter and diameter of various geometric shapes is a fundamental skill in mathematics, useful in numerous real-life applications. This guide will help you understand the concepts, formulas, and methods needed to accurately determine these measurements.
Perimeter: The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a shape. It is a linear measurement representing the boundary length of two-dimensional figures.
- Circle: The perimeter of a circle, also known as the circumference, is calculated using the formula \( C = 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius.
- Square: For a square, the perimeter is the sum of all four sides, given by \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the side length.
- Rectangle: The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of its three sides, \( P = a + b + c \), where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the side lengths.
- Regular Polygon: For a regular polygon with \( n \) sides of equal length \( s \), the perimeter is \( P = ns \).
Diameter: The diameter is a specific type of distance measurement in circles and some polygons, representing the longest straight line passing through the center of the shape.
- Circle: The diameter of a circle is twice the radius, given by \( D = 2r \).
- Square: The diameter (or diagonal) of a square can be found using \( D = s\sqrt{2} \).
- Rectangle: The diagonal of a rectangle is calculated using the Pythagorean theorem, \( D = \sqrt{l^2 + w^2} \).
- Equilateral Triangle: The circumradius (diameter) of an equilateral triangle is \( D = \frac{a}{\sqrt{3}} \), where \( a \) is the side length.
Understanding these fundamental concepts and formulas will enable you to use perimeter and diameter calculators effectively. These tools are designed to streamline your calculations, providing quick and accurate results for various geometric shapes.
Understanding Perimeter and Diameter
To effectively use a perimeter diameter calculator, it is essential to understand the basic concepts of perimeter and diameter. These measurements are fundamental in geometry, and grasping their definitions and applications will enhance your calculation skills.
Perimeter: The perimeter is the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is a measure of the distance around the shape.
- Circle: The perimeter of a circle, also known as the circumference, is calculated using the formula \( C = 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius. This formula emphasizes the relationship between the circle's radius and its boundary length.
- Square: For a square, the perimeter is the sum of all four equal sides, given by \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the side length. This simple formula highlights the uniformity of a square's sides.
- Rectangle: The perimeter of a rectangle is the sum of its opposite sides, calculated by \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width. This formula reflects the addition of the lengths and widths to determine the boundary.
- Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of its three sides, \( P = a + b + c \), where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the side lengths. This general formula applies to all triangles, regardless of type.
- Regular Polygon: For a regular polygon with \( n \) sides of equal length \( s \), the perimeter is \( P = ns \). This formula is useful for polygons with equal side lengths, such as pentagons, hexagons, and octagons.
Diameter: The diameter is a specific linear measurement that spans the widest point of a shape, passing through its center. It is commonly used in circles and some regular polygons.
- Circle: The diameter of a circle is twice the radius, given by \( D = 2r \). This straightforward relationship makes it easy to convert between radius and diameter.
- Square: The diameter (or diagonal) of a square can be found using the formula \( D = s\sqrt{2} \), where \( s \) is the side length. This formula arises from the Pythagorean theorem applied to the square's diagonal.
- Rectangle: The diagonal of a rectangle is calculated using the Pythagorean theorem, \( D = \sqrt{l^2 + w^2} \). This formula combines the rectangle's length and width to find the diagonal distance.
- Equilateral Triangle: The circumradius (diameter) of an equilateral triangle is \( D = \frac{a}{\sqrt{3}} \), where \( a \) is the side length. This formula provides a way to determine the diameter for triangles with equal sides.
By understanding these fundamental concepts and formulas, you will be better equipped to calculate the perimeter and diameter of various shapes accurately. These measurements are crucial for many practical applications, from simple geometric problems to complex engineering tasks.
Perimeter and Diameter Formulas
Understanding the formulas for calculating perimeter and diameter is essential for accurately measuring various geometric shapes. Below are detailed formulas for common shapes, along with step-by-step explanations to help you apply them effectively.
Circle
- Perimeter (Circumference) Formula: The perimeter of a circle is called the circumference, calculated using the formula: \[ C = 2\pi r \] where \( r \) is the radius of the circle.
- Diameter Formula: The diameter is twice the radius: \[ D = 2r \] This relationship is straightforward and helps in converting between radius and diameter.
Square
- Perimeter Formula: For a square, the perimeter is the sum of all four equal sides: \[ P = 4s \] where \( s \) is the side length of the square.
- Diameter (Diagonal) Formula: The diagonal of a square can be found using the Pythagorean theorem: \[ D = s\sqrt{2} \] This formula highlights the relationship between the side length and the diagonal.
Rectangle
- Perimeter Formula: The perimeter of a rectangle is the sum of its lengths and widths: \[ P = 2(l + w) \] where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width of the rectangle.
- Diameter (Diagonal) Formula: The diagonal is calculated using the Pythagorean theorem: \[ D = \sqrt{l^2 + w^2} \] This formula combines the length and width to determine the diagonal distance.
Triangle
- Perimeter Formula: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of its three sides: \[ P = a + b + c \] where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the side lengths of the triangle.
- Equilateral Triangle Diameter (Circumradius) Formula: For an equilateral triangle, the circumradius (diameter) is: \[ D = \frac{a}{\sqrt{3}} \] where \( a \) is the side length of the triangle.
Regular Polygon
- Perimeter Formula: For a regular polygon with \( n \) sides of equal length \( s \), the perimeter is: \[ P = ns \] This formula applies to polygons such as pentagons, hexagons, and octagons.
By mastering these formulas, you will be able to calculate the perimeter and diameter for a wide range of shapes with confidence and precision. These calculations are foundational in geometry and have practical applications in various fields, from architecture to engineering.
Circle Perimeter and Diameter
The perimeter of a circle is often referred to as the circumference. The diameter is a straight line passing through the center of the circle, connecting two points on its boundary. Understanding these concepts is crucial for various mathematical and practical applications.
Key Concepts and Formulas
- Diameter (D): The distance across the circle through its center.
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of the circle to any point on its boundary. The diameter is twice the radius (D = 2r).
- Circumference (C): The distance around the circle. The formulas to calculate the circumference are:
- \( C = 2\pi r \)
- \( C = \pi D \)
Step-by-Step Calculation Guide
- Measure the radius (r) or diameter (D) of the circle.
- If you have the radius, use the formula \( C = 2\pi r \).
- If you have the diameter, use the formula \( C = \pi D \).
- Plug the value into the appropriate formula.
- Example: For a circle with a radius of 3 cm, the circumference is \( C = 2 \times \pi \times 3 = 6\pi \approx 18.85 \) cm.
- Example: For a circle with a diameter of 4 cm, the circumference is \( C = \pi \times 4 = 4\pi \approx 12.57 \) cm.
- Solve the equation to find the circumference.
Visual Representation
Below is a table that outlines the relationship between radius, diameter, and circumference for various circles:
| Radius (r) | Diameter (D) | Circumference (C) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | \(2\pi\) |
| 2 | 4 | \(4\pi\) |
| 3 | 6 | \(6\pi\) |
| 4 | 8 | \(8\pi\) |
Common Mistakes and Tips
- Misidentifying Radius and Diameter: Remember that the diameter is twice the radius.
- Incorrect Use of Pi: Ensure you are using an accurate value for π (pi), approximately 3.14159.
- Unit Consistency: Maintain consistent units throughout your calculations.
Applications in Real Life
The concepts of circle perimeter (circumference) and diameter are used in various fields, including engineering, architecture, and everyday activities such as crafting and designing objects with circular shapes.
Square Perimeter and Diameter
A square is a special type of polygon with four equal sides and four right angles. Calculating the perimeter and the diameter (also known as the diagonal) of a square is straightforward with the right formulas.
Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square is the total length of all its sides. Since all four sides of a square are equal, the perimeter \( P \) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ P = 4a \]
where \( a \) is the length of one side of the square.
For example, if the side length \( a \) is 5 units, then the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \, \text{units} \]
Diameter (Diagonal) of a Square
The diameter or diagonal of a square is the line segment connecting two opposite corners. It can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem, considering the diagonal as the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle with the two sides of the square as the other two sides. The formula for the diagonal \( d \) is:
\[ d = a\sqrt{2} \]
where \( a \) is the length of one side of the square.
For example, if the side length \( a \) is 5 units, then the diagonal \( d \) is:
\[ d = 5\sqrt{2} \approx 7.07 \, \text{units} \]
Step-by-Step Calculation Guide
- Measure the length of one side of the square.
- Use the formula \( P = 4a \) to calculate the perimeter by multiplying the side length by 4.
- To find the diagonal, use the formula \( d = a\sqrt{2} \). Multiply the side length by the square root of 2.
Example Calculation
Let's consider a square with a side length of 6 units:
- Perimeter: \( P = 4 \times 6 = 24 \, \text{units} \)
- Diagonal: \( d = 6\sqrt{2} \approx 8.49 \, \text{units} \)
Common Mistakes and Tips
- Ensure all sides are equal; otherwise, it's not a square.
- Use a calculator for accurate results when dealing with square roots.
- Remember that the diagonal is longer than any side of the square.
Applications in Real Life
The concepts of square perimeter and diagonal are widely used in various fields, such as architecture, engineering, and design. Understanding these measurements helps in space planning, material estimation, and structural analysis.
Rectangle Perimeter and Diameter
Calculating the perimeter and diameter of a rectangle is straightforward and involves basic arithmetic. A rectangle has four sides with opposite sides being equal in length.
Perimeter of a Rectangle
The perimeter of a rectangle is the total distance around the edge of the rectangle. It can be calculated using the formula:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \]
Where:
- Length (l) is the longer side of the rectangle.
- Width (w) is the shorter side of the rectangle.
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Measure the length of the rectangle.
- Measure the width of the rectangle.
- Add the length and the width together.
- Multiply the result by 2 to get the perimeter.
For example, if the length of the rectangle is 8 units and the width is 5 units:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (8 + 5) = 2 \times 13 = 26 \text{ units} \]
Diameter of a Rectangle
The term "diameter" is not typically used in reference to rectangles. However, the diagonal of a rectangle can be considered analogous to a diameter in some contexts. The diagonal can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem:
\[ \text{Diagonal} = \sqrt{(\text{length}^2 + \text{width}^2)} \]
Where:
- Length (l) is the longer side of the rectangle.
- Width (w) is the shorter side of the rectangle.
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Measure the length of the rectangle.
- Measure the width of the rectangle.
- Square both the length and the width.
- Add the squared values together.
- Take the square root of the sum to get the diagonal.
For example, if the length of the rectangle is 8 units and the width is 5 units:
\[ \text{Diagonal} = \sqrt{(8^2 + 5^2)} = \sqrt{(64 + 25)} = \sqrt{89} \approx 9.43 \text{ units} \]
Summary Table
| Measurement | Formula | Example Calculation (l = 8, w = 5) |
|---|---|---|
| Perimeter | \( 2 \times (l + w) \) | \( 2 \times (8 + 5) = 26 \text{ units} \) |
| Diagonal | \( \sqrt{(l^2 + w^2)} \) | \( \sqrt{(8^2 + 5^2)} \approx 9.43 \text{ units} \) |
Triangle Perimeter and Diameter
The perimeter of a triangle is the total length around the triangle, which can be calculated by summing the lengths of its three sides.
Formula for Perimeter
For a triangle with sides \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \), the perimeter \( P \) is given by:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
Step-by-Step Calculation Guide
- Measure the lengths of all three sides of the triangle.
- Add the lengths of the three sides together using the formula above.
Example Calculation
Consider a triangle with sides \( a = 3 \) units, \( b = 4 \) units, and \( c = 5 \) units:
\[ P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \text{ units} \]
Special Cases
- Equilateral Triangle: All three sides are equal. If each side is \( a \), then:
\[ P = 3a \] - Isosceles Triangle: Two sides are equal. If the equal sides are \( a \) and the base is \( b \), then:
\[ P = 2a + b \]
Diameter Equivalent in Triangles
In the context of a triangle, there isn't a direct "diameter" equivalent as in circles. However, if you consider the circumcircle (the circle that passes through all three vertices of the triangle), the diameter \( D \) of the circumcircle can be related to the triangle's sides using the formula:
\[ D = \frac{a \cdot b \cdot c}{2 \cdot A} \]
where \( A \) is the area of the triangle, which can be calculated using Heron's formula:
\[ A = \sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \]
with \( s \) being the semi-perimeter:
\[ s = \frac{a + b + c}{2} \]
Example Calculation for Diameter
For a triangle with sides \( a = 3 \), \( b = 4 \), and \( c = 5 \) units:
- Calculate the semi-perimeter:
\[ s = \frac{3 + 4 + 5}{2} = 6 \] - Calculate the area using Heron's formula:
\[ A = \sqrt{6(6-3)(6-4)(6-5)} = \sqrt{6 \cdot 3 \cdot 2 \cdot 1} = \sqrt{36} = 6 \] - Calculate the diameter of the circumcircle:
\[ D = \frac{3 \cdot 4 \cdot 5}{2 \cdot 6} = \frac{60}{12} = 5 \text{ units} \]
Conclusion
Understanding the perimeter and equivalent diameter in the context of triangles is crucial for various applications in geometry. Using the formulas provided, one can easily calculate these properties for any given triangle.
Polygon Perimeter and Diameter
Calculating the perimeter of a polygon involves summing the lengths of all its sides. Polygons can be regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles are not equal). Here's a detailed guide to understanding and calculating the perimeter and diameter of polygons:
Perimeter of a Regular Polygon
A regular polygon has all sides of equal length. The formula to calculate the perimeter (P) of a regular polygon is:
\(P = n \times a\)
where:
- \(n\) = number of sides
- \(a\) = length of one side
Perimeter of an Irregular Polygon
For an irregular polygon, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all sides. The formula is:
\(P = a_1 + a_2 + a_3 + \ldots + a_n\)
where \(a_1, a_2, a_3, \ldots, a_n\) are the lengths of the sides of the polygon.
Calculating the Diameter of a Polygon
While the term "diameter" is more commonly associated with circles, for polygons, especially regular polygons, the diameter can refer to the longest distance between two vertices. This is often called the "circumcircle diameter" and can be calculated for regular polygons using the formula:
\(D = \frac{a}{\sin(\pi/n)}\)
where:
- \(a\) = length of one side
- \(n\) = number of sides
Example Calculations
Let's consider a few examples to illustrate these calculations:
Example 1: Perimeter of a Regular Hexagon
- Number of sides (\(n\)) = 6
- Length of one side (\(a\)) = 5 cm
- Perimeter (\(P\)) = \(6 \times 5 = 30\) cm
- Diameter (\(D\)) = \(\frac{5}{\sin(\pi/6)} = 10\) cm
Example 2: Perimeter of an Irregular Quadrilateral
- Lengths of sides: \(a_1 = 4\) cm, \(a_2 = 5\) cm, \(a_3 = 6\) cm, \(a_4 = 7\) cm
- Perimeter (\(P\)) = \(4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 22\) cm
Using Perimeter and Diameter Calculator Tools
To make these calculations easier, you can use online perimeter and diameter calculators. These tools allow you to input the necessary values and obtain results quickly, which is particularly useful for complex shapes or when precision is required.
Conclusion
Understanding the formulas and methods for calculating the perimeter and diameter of polygons is essential for various applications in geometry, engineering, and real-life scenarios. Whether dealing with regular or irregular polygons, the key is to know the dimensions and apply the appropriate formulas. For more accurate and complex calculations, leveraging online calculators can save time and ensure precision.

Perimeter and Diameter Calculator Tools
There are many online tools available to help you calculate the perimeter and diameter of various geometric shapes. These tools are designed to be user-friendly and provide accurate results quickly. Here, we will discuss some of the most popular and useful perimeter and diameter calculator tools, how to use them, and what features they offer.
1. Omni Calculator
Omni Calculator offers a comprehensive perimeter calculator that can handle various shapes such as circles, triangles, rectangles, and more. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to use it:
- Visit the website.
- Select the shape for which you need to calculate the perimeter.
- Input the necessary dimensions (e.g., radius for circles, side lengths for polygons).
- Click "Calculate" to get the perimeter.
This calculator also provides formulas used for the calculations, ensuring transparency and educational value.
2. Calculator Soup
Calculator Soup provides a versatile circle calculator that can compute the radius, diameter, circumference, and area of a circle. Here's how to use it:
- Go to the .
- Choose the calculation type from the dropdown menu (e.g., find diameter, circumference, and area given the radius).
- Enter the known value (e.g., radius) into the appropriate field.
- Press "Calculate" to see the results along with the formulas used.
This tool also allows you to adjust the value of π and change the units of measurement, adding flexibility to your calculations.
3. Calculator.io
Calculator.io offers an intuitive circle calculator that helps you find the radius, diameter, circumference, and area of a circle based on any one of these values. Follow these steps:
- Navigate to the .
- Select the known characteristic (e.g., radius) from the dropdown menu.
- Input the value into the corresponding field.
- Click "Calculate" to get the remaining characteristics.
This calculator simplifies the process with a clear interface and provides precise results quickly.
4. Common Features of Calculator Tools
- User-Friendly Interface: Most calculators have a straightforward design, making them easy to use even for beginners.
- Multiple Calculation Options: They can handle various inputs and provide outputs for radius, diameter, circumference, and area.
- Formula Display: Many tools show the formulas used, helping users understand the calculation process.
- Unit Conversion: Some calculators allow you to change the units of measurement to suit your needs.
Conclusion
Using online perimeter and diameter calculator tools can save time and ensure accuracy in your calculations. Whether you are a student, teacher, or professional, these tools are valuable resources for quickly obtaining geometric measurements. Explore the recommended calculators and find the one that best suits your needs.
Step-by-Step Calculation Guide
Calculating the perimeter and diameter of various shapes involves understanding and applying specific formulas. Below is a detailed guide to help you through the process for different geometric shapes.
Circle
- Perimeter (Circumference): Use the formula
C = 2πrwhereris the radius of the circle.- Measure the radius of the circle.
- Multiply the radius by 2.
- Multiply the result by π (approximately 3.14159).
- Diameter: Use the formula
D = 2r.- Measure the radius of the circle.
- Multiply the radius by 2 to get the diameter.
Square
- Perimeter: Use the formula
P = 4awhereais the side length of the square.- Measure the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply the side length by 4 to get the perimeter.
- Diameter: Use the formula
D = a√2.- Measure the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply the side length by √2 (approximately 1.414).
Rectangle
- Perimeter: Use the formula
P = 2(l + w)wherelis the length andwis the width of the rectangle.- Measure the length and width of the rectangle.
- Add the length and the width.
- Multiply the sum by 2 to get the perimeter.
- Diameter (Diagonal): Use the formula
D = √(l² + w²).- Measure the length and width of the rectangle.
- Square the length and the width.
- Add the squared values.
- Take the square root of the sum to get the diagonal.
Triangle
- Perimeter: Use the formula
P = a + b + cwherea,b, andcare the lengths of the sides of the triangle.- Measure the lengths of all three sides of the triangle.
- Add the lengths of the three sides to get the perimeter.
- Diameter: Typically, triangles do not have a diameter, but you can calculate the circumcircle diameter for an equilateral triangle using the formula
D = a√3whereais the side length.- Measure the side length of the equilateral triangle.
- Multiply the side length by √3 (approximately 1.732).
Polygon
- Perimeter: Use the formula
P = n × swherenis the number of sides andsis the length of one side.- Measure the length of one side of the polygon.
- Multiply the side length by the number of sides to get the perimeter.
- Diameter (Circumradius): For regular polygons, use the formula
D = 2RwhereRis the circumradius.- Calculate or measure the circumradius.
- Multiply the circumradius by 2 to get the diameter.
Common Mistakes and Tips
Calculating the perimeter and diameter of various shapes can sometimes lead to common mistakes. Here are some typical errors and tips to help you avoid them:
-
Misidentifying Shape Dimensions:
Ensure you correctly identify the dimensions of the shape. For example, for a rectangle, distinguish between length and width, and for a circle, ensure you are measuring the radius or diameter correctly.
-
Incorrect Formula Usage:
Using the wrong formula is a frequent error. Always double-check the formula before performing calculations. Here are the correct formulas:
- Perimeter of a Circle (Circumference): \( P = 2\pi r \) or \( P = \pi d \)
- Diameter of a Circle: \( D = 2r \)
- Perimeter of a Square: \( P = 4a \)
- Perimeter of a Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Perimeter of a Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Perimeter of a Polygon: Sum of all sides
-
Unit Conversion Errors:
Ensure all measurements are in the same units before performing calculations. Convert units if necessary to avoid errors.
-
Rounding Errors:
Be careful with rounding intermediate values in calculations. It's better to round off only the final result to maintain accuracy.
-
Neglecting to Double-check Work:
Always recheck your calculations to ensure there are no mistakes. Simple arithmetic errors can lead to incorrect results.
Here are some additional tips to improve your calculation accuracy:
-
Use a Calculator:
Using a reliable calculator can minimize manual calculation errors, especially for complex shapes.
-
Visualize the Shape:
Drawing the shape and labeling all dimensions can help ensure you use the correct measurements in your calculations.
-
Practice Regularly:
Regular practice can help you become more familiar with the formulas and reduce the likelihood of errors.
-
Understand the Concepts:
Understanding the underlying geometric concepts can help you apply the correct formulas and make sense of the calculations.
-
Refer to Reliable Resources:
When in doubt, refer to textbooks, educational websites, or instructional videos to clarify concepts and formulas.
Applications in Real Life
The concepts of perimeter and diameter are not confined to the realms of geometry and mathematics but find practical applications in various aspects of our daily lives. Here are some common applications:
-
Construction and Architecture
Understanding perimeter is crucial in construction for determining the boundaries of plots, planning the layout of buildings, and ensuring accurate measurements for building materials. For example, calculating the perimeter helps in estimating the amount of fencing needed to enclose a property, ensuring that adequate materials are procured.
-
Fencing and Landscaping
When installing fences around gardens or properties, knowing the perimeter is essential. It allows homeowners to purchase the correct amount of materials, preventing both shortages and excess. For instance, if a garden measures 20 feet by 30 feet, the perimeter calculation ensures that 100 feet of fencing is ordered.
-
Sports and Recreational Areas
In sports, the perimeter is used to define the dimensions of playing fields, tracks, and courts. This ensures that all areas meet regulatory standards and provide fair play conditions. For example, the perimeter of a basketball court is used to lay out the boundaries and ensure the court is constructed to standard dimensions.
-
Urban Planning and Infrastructure
Urban planners use perimeter calculations to design efficient road networks and plan the layout of city blocks. This ensures optimal use of space and resources, contributing to well-organized urban environments. The perimeter measurements also aid in the planning of utilities and public services within these areas.
-
Home Improvement
For home improvement projects such as installing moldings, picture frames, or tiling, calculating the perimeter is vital. For example, when adding tiles to a room, knowing the perimeter helps determine the number of tiles needed to cover the edges seamlessly.
-
Surveying and Land Measurement
Surveyors use perimeter calculations to determine property boundaries and create accurate maps. This is important for legal documentation and resolving property disputes. For instance, the perimeter of a plot of land defines its exact boundaries, which is crucial for ownership and development purposes.
-
Gardening and Agriculture
In gardening, the perimeter helps in planning garden beds and installing irrigation systems. For agricultural purposes, understanding the perimeter of fields assists in the efficient layout of crops and the management of resources like water and fertilizers.
Overall, a solid understanding of perimeter and diameter is not only helpful in academic settings but also essential for practical applications in real life, ensuring functionality, aesthetics, and safety in our everyday activities.

Conclusion and Further Resources
Understanding the calculations of perimeter and diameter is fundamental in various fields such as geometry, architecture, engineering, and everyday problem-solving. This guide has provided you with essential formulas, practical applications, common mistakes to avoid, and tips to enhance your calculation accuracy.
To sum up, the key points covered include:
- Formulas: Knowing the basic formulas for calculating the perimeter and diameter of different shapes such as circles, squares, rectangles, triangles, and polygons.
- Common Mistakes: Recognizing common errors like incorrect units and misapplying formulas, and tips on how to avoid them.
- Applications: Practical uses of these calculations in real life, from simple tasks like garden planning to complex engineering projects.
- Tools: Utilizing various online calculators to simplify and verify your calculations.
For those looking to dive deeper into the subject, here are some valuable resources and tools:
- - A tool to quickly calculate the circumference of a circle.
- - Helps in calculating the diameter from various inputs like radius, circumference, or area.
- - Useful for calculating the perimeter of various geometric shapes.
- - Offers in-depth tutorials and exercises on geometric calculations.
- - Provides explanations and interactive tools for learning about circles.
With these resources, you can continue to explore and master the concepts of perimeter and diameter calculations. Remember, practice and the right tools are key to becoming proficient in these essential mathematical skills.
Video hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi hình tròn một cách đơn giản và dễ hiểu, phù hợp cho mọi người học toán và ứng dụng thực tế.
Cách Tính Chu Vi Hình Tròn
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi hình tròn từ đường kính một cách đơn giản và dễ hiểu, giúp bạn nắm vững kiến thức toán học cơ bản.
Cách Tính Chu Vi Hình Tròn Từ Đường Kính