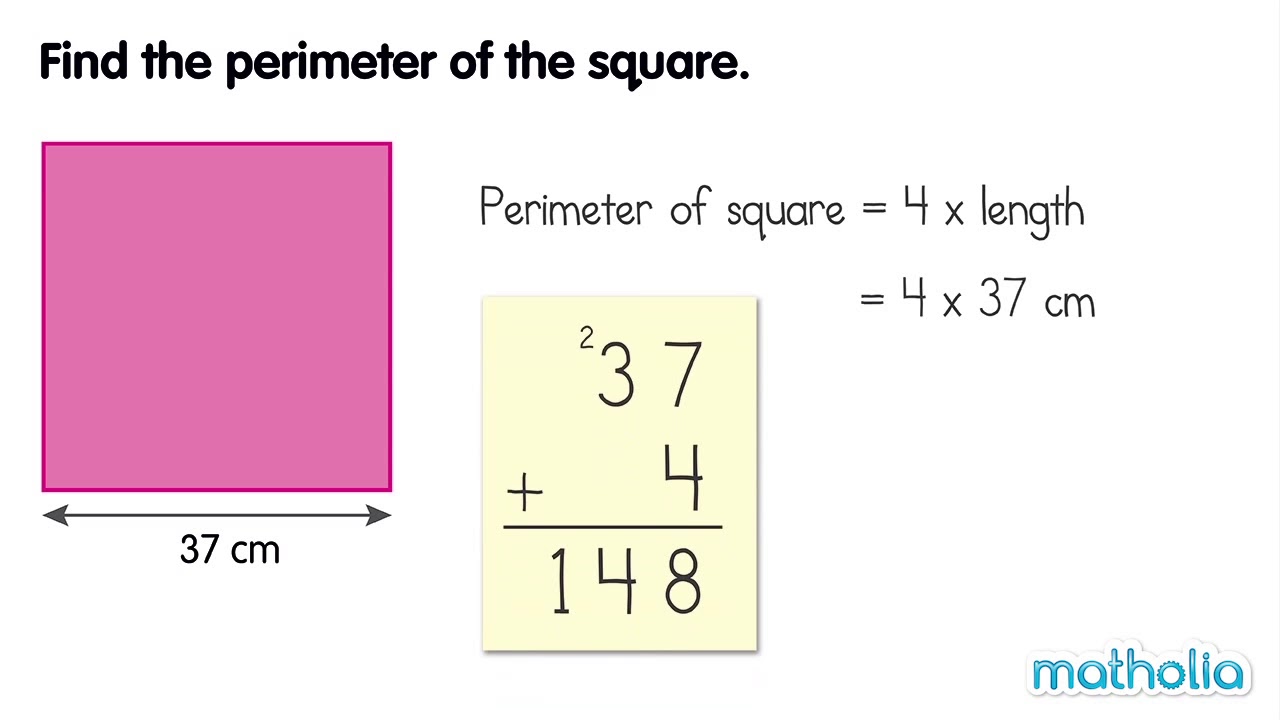
Topic how to get a perimeter of a square: Discover the easiest way to calculate the perimeter of a square with our straightforward guide. Whether you're a student, teacher, or just curious, our step-by-step instructions and examples will help you understand and apply the formula effortlessly. Perfect for all levels, this article ensures you grasp the concept quickly and accurately.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Perimeter of a Square
- Introduction to Perimeter of a Square
- Definition of a Square
- Understanding the Perimeter
- Basic Formula for Perimeter of a Square
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Examples of Perimeter Calculation
- Using Side Length to Find Perimeter
- Real-World Applications
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Practice Problems
- Advanced Concepts
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE:
Understanding the Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square is the total length of all its four sides. Since a square has four equal sides, calculating the perimeter is straightforward.
Formula for the Perimeter of a Square
The formula to find the perimeter \(P\) of a square is:
\[
P = 4 \times s
\]
where \(s\) is the length of one side of the square.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Measure the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply this length by 4.
Example Calculation
Consider a square with each side measuring 5 units. Using the formula:
\[
P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ units}
\]
Visual Representation
Imagine a square where each side is labeled as \(s\). The perimeter would be the sum of all four sides:
- Side 1: \(s\)
- Side 2: \(s\)
- Side 3: \(s\)
- Side 4: \(s\)
Therefore, \(P = s + s + s + s = 4s\).
Summary
To find the perimeter of a square, simply multiply the length of one of its sides by 4. This simple formula applies universally to all squares, making it easy to compute the perimeter given any side length.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square is a fundamental geometric concept that refers to the total distance around the square. To calculate the perimeter, you need to understand the properties of a square and the relevant mathematical formula.
A square is a four-sided polygon, also known as a quadrilateral, where all sides have equal length and all angles are right angles (90 degrees). Given these properties, calculating the perimeter becomes straightforward.
The formula for the perimeter \( P \) of a square is given by:
\[
P = 4 \times s
\]
where \( s \) is the length of one side of the square.
To calculate the perimeter, follow these steps:
- Measure the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply the length of the side by 4.
For example, if one side of the square is 5 units long, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
\[
P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ units}
\]
Understanding the perimeter of a square is essential for solving various mathematical problems and real-life applications such as determining the length of fencing required to enclose a square garden.
Definition of a Square
A square is a special type of quadrilateral, characterized by its four equal sides and four right angles. This geometric shape is both a rectangle and a rhombus, possessing unique properties that distinguish it from other polygons.
Key properties of a square include:
- All four sides are of equal length.
- All four angles are right angles (90 degrees).
- Opposite sides are parallel.
- The diagonals of a square are equal in length and bisect each other at right angles.
To illustrate, consider a square with side length \( s \). The properties can be summarized as follows:
| Property | Value |
| Side Length | \( s \) |
| Perimeter | \( 4s \) |
| Area | \( s^2 \) |
| Diagonal | \( s\sqrt{2} \) |
The equal length of the sides and angles ensures the symmetry and uniformity of the square, making it a fundamental shape in geometry. Understanding these properties is crucial for various mathematical calculations and applications.
Understanding the Perimeter
The perimeter of a geometric shape is the total distance around its edges. For a square, the perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides. Given the properties of a square, where all sides are equal, this calculation becomes straightforward.
To understand the concept better, consider the following:
- A square has four equal sides.
- The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of these sides.
The formula for the perimeter \( P \) of a square is:
\[
P = 4 \times s
\]
where \( s \) represents the length of one side of the square.
Here is a step-by-step approach to finding the perimeter:
- Measure the length of one side: Determine the length of one side of the square. This can be done using a ruler or any other measuring tool.
- Multiply by four: Since all four sides of a square are equal, multiply the length of the measured side by four.
- Express the result: The product obtained from the multiplication is the perimeter of the square.
For example, if one side of the square is 7 units long, the calculation of the perimeter would be:
\[
P = 4 \times 7 = 28 \text{ units}
\]
Understanding the perimeter is essential for various practical applications, such as determining the amount of material needed to frame a square picture or the length of fencing required to enclose a square garden.
Basic Formula for Perimeter of a Square
The basic formula for calculating the perimeter of a square is straightforward due to the equal length of all four sides. The perimeter is the total distance around the square, which can be found using a simple multiplication.
The formula for the perimeter \( P \) of a square is given by:
\[
P = 4 \times s
\]
where \( s \) is the length of one side of the square.
To apply this formula, follow these steps:
- Determine the length of one side: Measure or identify the length of one side of the square. This measurement is crucial as it is used in the formula.
- Multiply by four: Since a square has four equal sides, multiply the length of the side by four to get the total perimeter.
For example, if the side length \( s \) is 6 units, the perimeter calculation would be:
\[
P = 4 \times 6 = 24 \text{ units}
\]
This formula is essential in various practical situations, such as determining the amount of trim needed for a square window or the length of a border required to surround a square garden bed. By understanding and applying this basic formula, you can easily solve perimeter-related problems involving squares.

Step-by-Step Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of a square is a simple process that can be broken down into clear steps. Here is a detailed, step-by-step guide to help you understand and perform this calculation:
- Identify the length of one side: Determine the length of one side of the square. This measurement can be obtained using a ruler or other measuring tools. Let's denote this length as \( s \).
- Write down the formula: The formula for the perimeter \( P \) of a square is:
\[
P = 4 \times s
\] - Substitute the side length into the formula: Replace the variable \( s \) in the formula with the actual length of the side you have measured.
- For example, if the side length \( s \) is 8 units, the formula becomes:
\[
P = 4 \times 8
\]
- For example, if the side length \( s \) is 8 units, the formula becomes:
- Perform the multiplication: Multiply the side length by 4 to find the perimeter.
- Continuing the example, you get:
\[
P = 4 \times 8 = 32 \text{ units}
\]
- Continuing the example, you get:
- Express the result: State the calculated perimeter clearly, including the appropriate unit of measurement.
- In this case, the perimeter of the square is 32 units.
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any square. This method is useful in various practical applications, such as determining the length of materials needed for construction or crafting projects.
Examples of Perimeter Calculation
To calculate the perimeter of a square, you need to know the length of one of its sides. The formula for the perimeter P of a square with side length s is given by:
\( P = 4s \)
Here are some examples to illustrate how to use this formula:
Example 1
Consider a square with a side length of 5 cm.
Using the formula:
\( P = 4 \times 5 \)
Therefore, the perimeter of the square is 20 cm.
Example 2
Now, let's take a square with a side length of 12 inches.
Using the formula:
\( P = 4 \times 12 \)
So, the perimeter of the square is 48 inches.
Example 3
Let's calculate the perimeter of a square where the side length is 7 meters.
Using the formula:
\( P = 4 \times 7 \)
This gives a perimeter of 28 meters.
Example 4
For a square with a side length of 9.5 feet:
Using the formula:
\( P = 4 \times 9.5 \)
The perimeter of the square is 38 feet.
Example 5
Consider a square with a side length of 3.75 yards.
Using the formula:
\( P = 4 \times 3.75 \)
Therefore, the perimeter of the square is 15 yards.
These examples demonstrate that regardless of the unit of measurement, you can always find the perimeter of a square by multiplying the side length by 4.
Using Side Length to Find Perimeter
To find the perimeter of a square, you simply need to know the length of one of its sides. The formula to calculate the perimeter (P) of a square is given by:
\[
P = 4 \times \text{side}
\]
Here is a step-by-step explanation:
Identify the length of one side of the square. Let's denote this length as \( s \).
Multiply the length of the side by 4. This is because a square has four equal sides.
For example, if the side length \( s \) is 5 units, the perimeter can be calculated as follows:
\[
P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ units}
\]
Below are a few more detailed examples:
-
Example 1: A square has a side length of 8 meters. Calculate its perimeter.
\[
P = 4 \times 8 = 32 \text{ meters}
\] -
Example 2: If a square has a side length of 15 centimeters, what is the perimeter?
\[
P = 4 \times 15 = 60 \text{ centimeters}
\] -
Example 3: The side length of a square garden is 12 feet. Determine the total perimeter of the garden.
\[
P = 4 \times 12 = 48 \text{ feet}
\]
These examples illustrate how simple it is to calculate the perimeter of a square once you know the length of one side.
It's important to ensure that all sides are measured in the same units to avoid errors in calculation. This method is applicable for any square, regardless of its size, as long as the side length is known.
Real-World Applications
The concept of perimeter is widely used in various real-world applications, aiding in practical and efficient problem-solving in everyday scenarios. Here are some examples:
-
Construction and Architecture:
In the construction of homes and buildings, knowing the perimeter is essential for planning the layout and ensuring accurate measurements. For example, determining the perimeter of a plot of land helps in deciding the amount of fencing or boundary walls needed. Additionally, the perimeter of rooms guides the amount of materials required for finishing work such as moldings, baseboards, and decorative trims.
-
Gardening:
When planning a garden, calculating the perimeter is crucial for installing fences to protect plants from animals. For instance, if a rectangular garden measures 20 feet by 30 feet, the perimeter would be:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (20 \, \text{ft} + 30 \, \text{ft}) = 100 \, \text{ft}
\]Thus, 100 feet of fencing material is required to enclose the garden.
-
Interior Design:
In interior design, perimeter calculations help in determining the lengths of borders or trims needed for rooms. For example, the perimeter of a room helps in estimating the length of wallpaper borders or paint required to cover the walls.
-
Surveying and Land Measurement:
Surveyors use perimeter calculations to define property boundaries and create accurate maps. For instance, the perimeter of an irregularly shaped plot can be calculated by summing the lengths of all its sides, ensuring precise land measurement and ownership delineation.
-
Sports Fields:
In designing sports fields, such as basketball courts or soccer fields, knowing the perimeter is important for marking boundaries and installing appropriate fencing or barriers.
-
Manufacturing:
In manufacturing, perimeter calculations are used to determine the lengths of materials needed for production processes. For example, calculating the perimeter of a piece of fabric helps in cutting the correct length for garments or other textile products.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the perimeter of a square, several common mistakes can occur. Understanding and avoiding these mistakes can help ensure accurate results. Here are some of the most frequent errors and how to avoid them:
-
Confusing Perimeter with Area:
One of the most common mistakes is confusing the perimeter of a square with its area. Remember, the perimeter is the total distance around the square, calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides. The area, on the other hand, measures the space within the square and is calculated by squaring the side length.
-
Incorrect Formula Application:
Ensure you use the correct formula for the perimeter. The perimeter (P) of a square is calculated using the formula \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the length of one side of the square. Applying this formula incorrectly can lead to wrong results.
-
Ignoring Units of Measurement:
Always include and consistently use units of measurement. For example, if the side length is given in meters, the perimeter should also be expressed in meters. Failing to do so can result in incorrect interpretations of the measurements.
-
Using Mixed Units:
Make sure all side lengths are in the same units before calculating the perimeter. If side lengths are given in different units (e.g., some in centimeters and others in inches), convert them to a common unit before performing calculations.
-
Calculation Errors:
Simple arithmetic mistakes can occur when adding side lengths or multiplying the side length by four. Double-check your calculations to avoid such errors.
-
Incorrect Addition of Side Lengths:
Since a square has four equal sides, you can either add all four sides or multiply one side by four. Ensure you follow this correctly: \( s + s + s + s \) or \( 4s \).
By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of a square and avoid common pitfalls.
Practice Problems
Practicing problems is essential for mastering the calculation of the perimeter of a square. Below are a series of practice problems designed to test your understanding and help you apply the concepts learned.
-
Find the perimeter of a square with a side length of 5 cm.
Solution:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{side} = 4 \times 5 \, \text{cm} = 20 \, \text{cm}
\] -
A square has a perimeter of 36 inches. What is the length of one side?
Solution:
\[
\text{Side length} = \frac{\text{Perimeter}}{4} = \frac{36 \, \text{inches}}{4} = 9 \, \text{inches}
\] -
The side of a square garden is 12 meters. Calculate the perimeter of the garden.
Solution:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{side} = 4 \times 12 \, \text{m} = 48 \, \text{m}
\] -
A square field has a perimeter of 200 meters. Find the length of each side of the field.
Solution:
\[
\text{Side length} = \frac{\text{Perimeter}}{4} = \frac{200 \, \text{m}}{4} = 50 \, \text{m}
\] -
If the side length of a square is increased by 3 cm, and the new perimeter is 32 cm, what was the original side length?
Solution:
Let the original side length be \( s \) cm.
New side length = \( s + 3 \) cm.
\[
4 \times (s + 3) = 32
\]\[
s + 3 = 8 \quad \Rightarrow \quad s = 5 \, \text{cm}
\]
These problems should help you practice the calculation of the perimeter of a square and improve your problem-solving skills. Make sure to verify your answers and understand the steps involved in each calculation.
Advanced Concepts
The perimeter of a square is a fundamental concept in geometry, but there are advanced ways to understand and calculate it, especially in relation to other geometric properties and in different contexts.
1. Using the Diagonal
In some cases, you might know the length of the diagonal of the square instead of the side length. The relationship between the side length (\(a\)) and the diagonal (\(d\)) is given by the Pythagorean theorem:
To find the perimeter from the diagonal, you can rearrange this formula to solve for \(a\):
Then, the perimeter (\(P\)) is:
2. Using the Area
Another advanced concept is calculating the perimeter when only the area (\(A\)) of the square is known. The area of a square is given by:
To find the side length from the area, you take the square root:
Then, the perimeter is:
3. Perimeter in Relation to Other Quadrilaterals
When comparing the perimeter of a square to other quadrilaterals with the same area, the square has the smallest perimeter. This property is crucial in optimization problems where you need to minimize the boundary length for a given enclosed area.
For any quadrilateral with an area (\(A\)) and perimeter (\(P\)), the inequality holds:
The equality occurs only for a square, highlighting its efficiency in enclosing space.
4. Practical Applications
- Urban Planning: Minimizing fencing costs by using squares for gardens and parks.
- Material Usage: Designing square-shaped objects to reduce material wastage in manufacturing.
- Engineering: Understanding stress distribution in square vs. rectangular beams.
By understanding these advanced concepts, you can apply the knowledge of the perimeter of a square in various mathematical and real-world scenarios.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the formula for the perimeter of a square?
The perimeter of a square is given by the formula \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the length of one side of the square.
-
How do you find the perimeter of a square if you know the side length?
To find the perimeter, multiply the length of one side by 4. For example, if the side length is 5 cm, the perimeter is \( 4 \times 5 = 20 \) cm.
-
Can you find the perimeter if the diagonal length is given?
Yes, if the diagonal \( d \) of a square is known, the side length \( s \) can be found using \( s = \frac{d}{\sqrt{2}} \). Then, use the formula \( P = 4s \) to find the perimeter.
Example: If the diagonal is 10 cm, \( s = \frac{10}{\sqrt{2}} \approx 7.07 \) cm. Thus, the perimeter is \( 4 \times 7.07 \approx 28.28 \) cm.
-
What are common mistakes to avoid when calculating the perimeter of a square?
- Ensure you are multiplying the side length by 4, not 2.
- Do not confuse the perimeter with the area, which uses a different formula (\( s^2 \)).
- When given the diagonal, make sure to use the correct formula to find the side length first.
-
How is the perimeter used in real-life applications?
The perimeter of a square is useful for determining the amount of material needed for fencing, framing, or any scenario requiring the boundary length of a square.
Conclusion
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a square is a fundamental mathematical skill with practical applications in various fields. The basic formula, \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the length of one side, allows for quick and efficient calculations. By mastering this concept, you can solve problems related to design, construction, and everyday measurements with confidence.
Throughout this guide, we have explored different methods for determining the perimeter, whether the side length, diagonal, or area is known. We have also delved into advanced concepts and addressed common mistakes to ensure a comprehensive understanding.
With practice, these calculations become second nature, enabling you to apply your knowledge effectively in real-world scenarios. Whether you're a student, professional, or hobbyist, the ability to accurately determine the perimeter of a square will serve you well in numerous contexts.
Keep practicing with the provided problems and explore further applications to solidify your understanding. Remember, mathematics is a skill that improves with practice and application. Happy calculating!
Cách Tìm Chu Vi Hình Vuông | Toán Học với Thầy J
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách tính diện tích và chu vi của hình vuông, giải thích chi tiết từng bước một để người xem dễ dàng hiểu và áp dụng.
Cách tìm Diện tích và Chu vi của Hình vuông