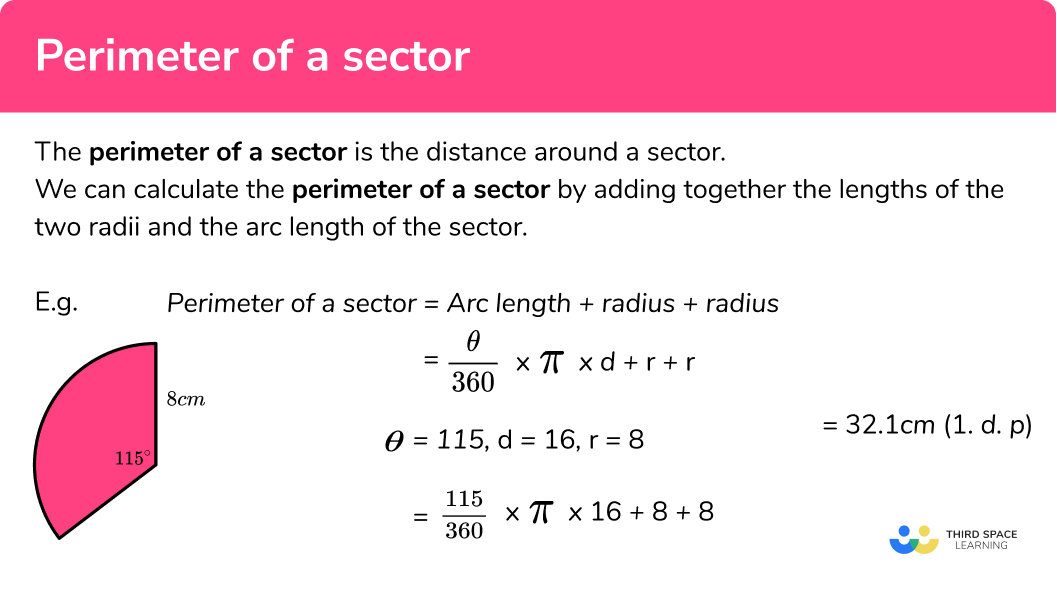
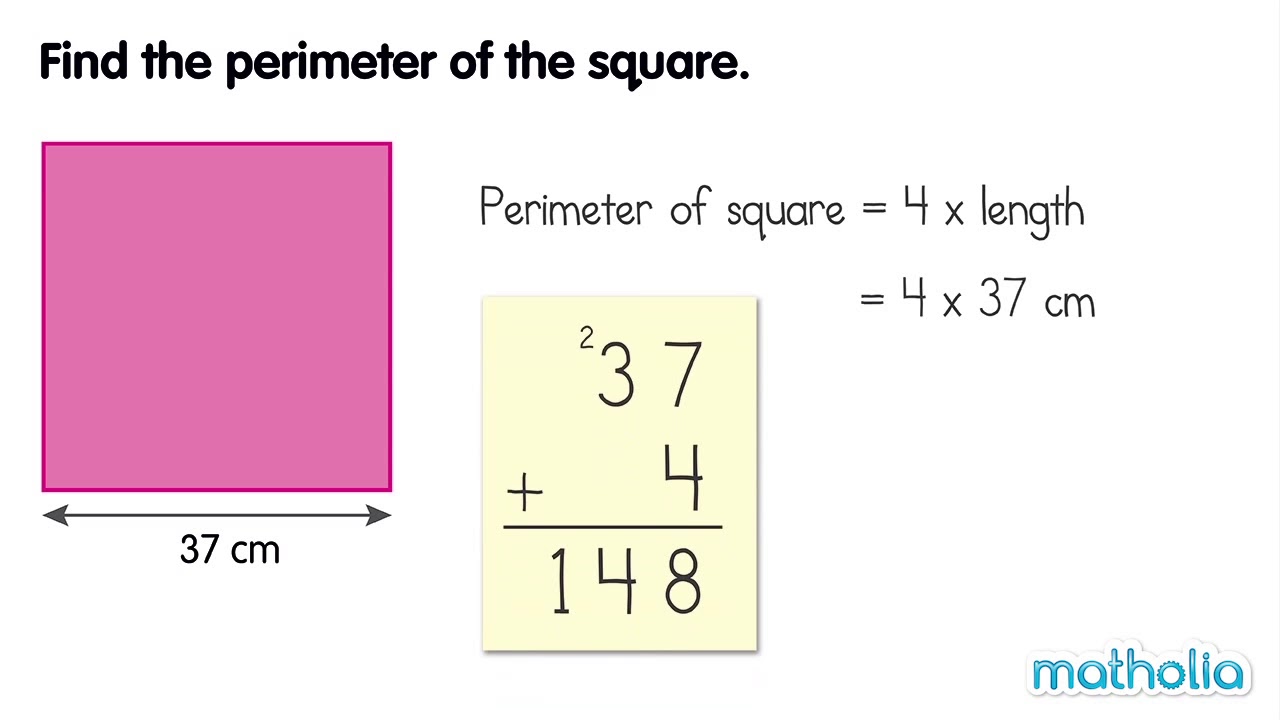
Topic how to figure perimeter of a square: Discover how to figure the perimeter of a square with our easy and accurate calculation guide. Whether you're a student or just curious, this comprehensive article breaks down the steps and provides clear examples to help you understand and master the concept. Start learning today and enhance your geometry skills!
Table of Content
- Understanding the Perimeter of a Square
- Introduction to Perimeter of a Square
- Basic Concept of Perimeter
- Understanding the Geometry of a Square
- Formula for Calculating Perimeter
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Examples of Perimeter Calculation
- Common Mistakes and Tips
- Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
- Advanced Topics and Related Geometric Concepts
- Summary and Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tính chu vi của một hình vuông với Thầy J. Video hữu ích cho người học toán.
Understanding the Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square is the total length of all its four sides. Since all sides of a square are equal in length, calculating the perimeter is straightforward. Here's a step-by-step guide to figure out the perimeter of a square:
Formula for the Perimeter of a Square
The formula to calculate the perimeter (P) of a square is:
where s represents the length of one side of the square.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Measure the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply the length of that side by 4.
This will give you the perimeter of the square.
Example Calculation
Suppose the length of one side of a square is 5 units. Using the formula:
So, the perimeter of the square is 20 units.
Visualization
Here's a simple visual representation of a square with side length s:
| s | ||
| s | s | |
| s | ||
In this diagram, each side of the square is labeled as s, showing that all sides are equal.
Practice Problems
- Find the perimeter of a square with a side length of 7 units.
- If the perimeter of a square is 36 units, what is the length of one side?
Use the formula and steps above to solve these problems and check your answers.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square is a fundamental concept in geometry that refers to the total distance around the square. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter is essential for solving various mathematical problems and real-world applications. This guide will explain the concept in detail and provide a clear, step-by-step method to figure out the perimeter of a square.
A square is a four-sided polygon (quadrilateral) with equal sides and right angles. The perimeter is the sum of all four sides. Since all sides of a square are equal, calculating the perimeter becomes straightforward. Here's a detailed explanation:
- Step 1: Identify the length of one side of the square. Let's denote this length as .
- Step 2: Use the formula for the perimeter of a square:
- Step 3: Multiply the length of one side by 4 to get the perimeter.
For example, if the length of one side of a square is 6 units, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
= 24 units
Thus, the perimeter of a square with side length 6 units is 24 units.
In summary, the perimeter of a square is easily calculated by multiplying the length of one side by four. This simple yet crucial calculation is foundational for many areas of mathematics and practical applications.
Basic Concept of Perimeter
The perimeter of a geometric shape is the total distance around the edge of the shape. It represents the boundary length and is a fundamental concept in geometry. Understanding the perimeter is crucial for various mathematical calculations and real-world applications, such as determining the length of fencing required for a plot of land.
To understand the basic concept of the perimeter, consider the following key points:
- Definition: The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all sides of a polygon. For regular polygons, where all sides are equal, the calculation becomes simpler.
- Units: The perimeter is measured in linear units such as meters, feet, or inches, depending on the units used for the sides of the shape.
- General Formula: For any polygon, the perimeter (P) can be calculated using the formula:
where represents the length of each side.
Let's apply this concept to a square:
- Identify the length of one side of the square. Let’s denote this length as .
- Since a square has four equal sides, its perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all four sides.
- Use the specific formula for the perimeter of a square:
For example, if the length of one side of a square is 5 units, the perimeter is calculated as:
= 20 units
Therefore, the perimeter of a square with side length 5 units is 20 units.
In conclusion, the perimeter is a simple yet essential measurement that helps determine the boundary length of various geometric shapes. For squares, the process is straightforward due to their equal sides, making the perimeter calculation easy and intuitive.
Understanding the Geometry of a Square
The geometry of a square is fundamental in understanding its properties and calculations, such as finding the perimeter. A square is a specific type of quadrilateral with unique characteristics that make it distinct and straightforward to work with. Let's explore the essential aspects of a square's geometry:
- Equal Sides: All four sides of a square are of equal length. This equality simplifies many calculations, including the perimeter, area, and diagonal lengths.
- Right Angles: Each of the four interior angles of a square is a right angle (90 degrees). This property ensures that a square has a regular and symmetrical shape.
- Parallel Sides: Opposite sides of a square are parallel to each other. This means that the top side is parallel to the bottom side, and the left side is parallel to the right side.
- Diagonals: A square has two diagonals that bisect each other at right angles. These diagonals are of equal length and can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem.
To visualize these properties, consider the following diagram of a square with side length :
The diagram shows a square with side length , highlighting its equal sides and right angles. Understanding these basic properties allows us to perform various geometric calculations easily.
Diagonal Length
To calculate the length of a diagonal in a square, we use the Pythagorean theorem. Since a square can be divided into two congruent right-angled triangles by its diagonal, the length of the diagonal () can be found using the formula:
Simplifying this, we get:
For example, if the side length is 4 units, the diagonal length would be:
≈ 5.66 units
Understanding these geometric properties of a square not only helps in calculating the perimeter but also provides a strong foundation for solving more complex geometric problems.
Formula for Calculating Perimeter
The perimeter of a square is the total length of its boundary. Since all sides of a square are equal, the perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides. The formula to calculate the perimeter (P) of a square with side length (a) is:
Here's a step-by-step explanation:
- Identify the length of one side of the square. Let's denote it as a.
- Multiply the length of one side by 4 to get the perimeter.
For example, if the length of one side of the square is 5 cm, then the perimeter would be:
Thus, the perimeter of a square with side length 5 cm is 20 cm.
Alternative Methods
If the length of the side is not directly given, the perimeter can also be calculated using the diagonal or the area of the square:
Using the Diagonal
The diagonal (d) of a square can be related to the side length (a) using the Pythagorean theorem:
Rearranging to find a:
Then, the perimeter can be found using:
Using the Area
If the area (A) of the square is known, the side length can be found using:
Then, the perimeter is:
For example, if the area of the square is 16 cm², then:
The perimeter is:
So, the perimeter of a square with an area of 16 cm² is 16 cm.

Step-by-Step Calculation
To calculate the perimeter of a square, follow these steps:
-
Identify the length of one side of the square. In a square, all four sides are equal in length. Let's denote the side length as s.
-
Use the formula for the perimeter of a square, which is:
\( \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times s \)
-
Substitute the side length into the formula. For example, if the side length of the square is 5 cm:
\( \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times 5 \, \text{cm} = 20 \, \text{cm} \)
-
Write the final answer with the correct units. The perimeter is the total distance around the square, so it will be in the same units as the side length.
Let's go through another example:
-
Given a square with a side length of 8 inches, calculate its perimeter.
-
Using the formula:
\( \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times 8 \, \text{inches} = 32 \, \text{inches} \)
-
The perimeter of the square is 32 inches.
Here is a step-by-step table for visual learners:
| Step | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Identify the side length (s) | 5 cm |
| 2 | Apply the perimeter formula: \( P = 4 \times s \) | \( P = 4 \times 5 \, \text{cm} \) |
| 3 | Calculate the perimeter | \( P = 20 \, \text{cm} \) |
| 4 | Write the final answer with units | 20 cm |
Practice calculating the perimeter with different side lengths to strengthen your understanding!
Examples of Perimeter Calculation
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a square through examples can help solidify the concept. Here are a few detailed examples:
Example 1: Simple Perimeter Calculation
Consider a square with each side measuring 8 meters.
- Step 1: Identify the side length of the square, which is 8 meters.
- Step 2: Use the perimeter formula for a square: \( P = 4 \times \text{side} \).
- Step 3: Substitute the side length into the formula: \( P = 4 \times 8 \).
- Step 4: Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 32 \) meters.
Thus, the perimeter of the square is 32 meters.
Example 2: Finding the Side Length from the Perimeter
A square has a perimeter of 36 inches. Find the length of one side.
- Step 1: Use the perimeter formula \( P = 4 \times \text{side} \).
- Step 2: Substitute the perimeter into the formula: \( 36 = 4 \times \text{side} \).
- Step 3: Solve for the side length: \( \text{side} = \frac{36}{4} \).
- Step 4: Calculate the side length: \( \text{side} = 9 \) inches.
Thus, each side of the square is 9 inches long.
Example 3: Perimeter with Increased Side Length
A square originally has sides of 15 cm. If each side is increased by 5 cm, what is the new perimeter?
- Step 1: Calculate the new side length: \( \text{new side} = 15 + 5 = 20 \) cm.
- Step 2: Use the perimeter formula \( P = 4 \times \text{new side} \).
- Step 3: Substitute the new side length: \( P = 4 \times 20 \).
- Step 4: Calculate the new perimeter: \( P = 80 \) cm.
The new perimeter of the square is 80 cm.
Example 4: Finding Perimeter from Area
A square has an area of 49 square meters. Find its perimeter.
- Step 1: Calculate the side length using the area: \( \text{side} = \sqrt{\text{area}} \).
- Step 2: Substitute the area into the formula: \( \text{side} = \sqrt{49} = 7 \) meters.
- Step 3: Use the perimeter formula \( P = 4 \times \text{side} \).
- Step 4: Substitute the side length into the formula: \( P = 4 \times 7 \).
- Step 5: Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 28 \) meters.
Thus, the perimeter of the square is 28 meters.
These examples illustrate how to apply the perimeter formula in different scenarios, enhancing the understanding of the concept.
Common Mistakes and Tips
Calculating the perimeter of a square might seem straightforward, but there are common mistakes that can occur. Here are some common errors and tips to avoid them:
Common Mistakes
-
Misidentifying the Shape:
Ensure you are working with a square and not another quadrilateral. A square has four equal sides and four right angles. If the sides are not equal, it is not a square.
-
Incorrect Formula:
The perimeter of a square is often confused with the perimeter of other shapes. The correct formula is , where is the length of one side of the square.
-
Arithmetic Errors:
Basic arithmetic mistakes can lead to incorrect calculations. Double-check your multiplication when using the formula .
-
Unit Conversion Errors:
Ensure all measurements are in the same units before calculating the perimeter. Convert units if necessary.
Tips for Accurate Calculation
-
Verify the Shape:
Double-check that all sides are equal and all angles are right angles to confirm the shape is a square.
-
Use the Correct Formula:
Always use the formula . Remember that represents the length of one side of the square.
-
Double-Check Calculations:
Recalculate to verify the accuracy. Simple arithmetic mistakes can often be caught by reviewing your work.
-
Consistent Units:
Ensure that all sides are measured in the same units. Convert if necessary before applying the formula.
-
Practice:
Regular practice with different examples can help solidify your understanding and improve accuracy.
Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
The concept of perimeter, especially that of a square, has numerous practical applications in everyday life. Here are some key examples:
- Gardening and Landscaping: When planning a square garden, the perimeter helps in determining the amount of fencing material required. For instance, if each side of a square garden is 10 meters, the total fencing needed would be 40 meters.
- Home Design and Construction: The perimeter is essential in designing rooms and buildings. For example, when installing baseboards or moldings along the walls of a square room, knowing the perimeter allows for accurate measurement and material estimation.
- Urban Planning: In urban planning, the perimeter of a square plot of land helps in determining the boundary length for walls or roads surrounding the plot. This is crucial for effective space utilization and planning.
- Sports Fields: The design and layout of square sports fields, such as certain playgrounds or tennis courts, rely on the perimeter to ensure proper dimensions and markings for gameplay.
- Art and Craft: Artists and designers use the concept of perimeter when creating frames for square artworks or designing square-shaped crafts, ensuring precision in their creations.
- Fashion Design: Fashion designers use perimeter calculations to measure and cut fabrics accurately when creating square patterns for clothing or accessories.
- Fencing Agricultural Land: Farmers use the perimeter to calculate the length of the fence needed to enclose square plots, helping in budget planning and resource allocation.
Understanding the perimeter of a square is not just an academic exercise but a practical tool that aids in various fields ranging from construction and urban planning to art and sports. Mastery of this concept can lead to more efficient planning and execution of tasks in these areas.
Advanced Topics and Related Geometric Concepts
Understanding the perimeter of a square provides a foundation for exploring more advanced geometric concepts and applications. Here are some key topics and related concepts:
Coordinate Geometry
Coordinate geometry, also known as analytic geometry, involves representing geometric figures and their properties using a coordinate system. For example, the perimeter of a square can be explored within a coordinate plane by determining the coordinates of its vertices and calculating the distances between them using the distance formula.
- Identify the coordinates of the vertices.
- Use the distance formula to find the length of each side: \( d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \).
- Sum the lengths of all four sides to get the perimeter.
Transformations
Transformations in geometry include translations, rotations, reflections, and dilations, which change the position or size of a figure without altering its shape. Studying how the perimeter of a square changes under these transformations can deepen understanding:
- Translation: Moving a square to a different location without changing its size or shape does not affect its perimeter.
- Rotation: Rotating a square around a point maintains its perimeter.
- Reflection: Reflecting a square across an axis preserves its perimeter.
- Dilation: Enlarging or reducing a square changes its side lengths proportionally, and thus its perimeter is scaled by the same factor.
Congruence and Similarity
Two geometric figures are congruent if they have the same shape and size, and similar if they have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. The perimeter plays a crucial role in these concepts:
- Congruent Squares: If two squares are congruent, their perimeters are equal.
- Similar Squares: If two squares are similar, their perimeters are proportional to their corresponding side lengths.
Area and Volume
While the perimeter is the measure of the boundary of a figure, area and volume measure the space within the figure. Understanding these concepts in relation to squares can lead to exploring other shapes and three-dimensional figures:
- Area of a Square: \( A = s^2 \), where \( s \) is the side length.
- Volume of a Cube: A square extended into three dimensions forms a cube, and its volume is \( V = s^3 \).
Applications in Real-Life Problems
Advanced geometric concepts are widely used in various fields such as engineering, architecture, computer graphics, and more. For example:
- Designing and analyzing structures, such as buildings and bridges, involves understanding the geometric properties of shapes.
- In computer graphics, coordinate geometry and transformations are essential for rendering shapes and animations.
- Architects use geometric principles to create aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound designs.
Summary and Conclusion
In this guide, we have explored the concept of the perimeter of a square, which is a fundamental aspect of geometry. Understanding the perimeter is crucial not only for academic purposes but also for practical applications in various fields such as construction, landscaping, and design.
The key points covered include:
- Definition of Perimeter: The perimeter is the total length of the boundary of a shape. For a square, this is calculated by adding up the lengths of all four sides.
- Formula for Perimeter of a Square: The perimeter of a square is given by \( P = 4a \), where \( a \) is the length of one side of the square.
- Step-by-Step Calculation: We provided detailed steps on how to measure the side of a square and use the formula to find the perimeter.
- Examples: Various examples demonstrated how to apply the formula in real-world scenarios, reinforcing the concept through practical application.
- Common Mistakes: Highlighted frequent errors such as incorrect measurement of sides or using wrong units, and provided tips to avoid these mistakes.
- Applications: Discussed how the concept of perimeter is used in different fields, emphasizing its importance in daily life and professional practices.
In conclusion, mastering the calculation of the perimeter of a square not only strengthens your mathematical foundation but also enhances your ability to solve real-world problems. By understanding and applying the concepts discussed, you can confidently handle various geometric tasks. Keep practicing with different examples and exploring advanced topics to deepen your knowledge and skills.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Q: What is the perimeter of a square?
A: The perimeter of a square is the total length around the square, calculated by adding up the lengths of all four sides. Since all sides of a square are equal, the perimeter is four times the length of one side.
-
Q: How do you calculate the perimeter of a square?
A: To calculate the perimeter of a square, use the formula:
where P is the perimeter and s is the length of one side of the square.
-
Q: If the side length of a square is 5 cm, what is its perimeter?
A: Using the formula for the perimeter of a square:
-
Q: Can the perimeter of a square be a negative number?
A: No, the perimeter of a square cannot be negative because it is a measure of length, and lengths cannot be negative.
-
Q: How is the perimeter of a square different from its area?
A: The perimeter of a square is the total distance around its edges, calculated as four times the length of one side. The area of a square, on the other hand, is the measure of the space enclosed within the square, calculated as the length of one side squared.
-
Q: Is the formula for the perimeter of a square the same for all units of measurement?
A: Yes, the formula for the perimeter of a square (P = 4 × s) is the same regardless of the units of measurement. However, ensure that all sides are measured using the same unit.
-
Q: How can I find the perimeter if I only know the area of the square?
A: If you know the area of the square, you can find the side length by taking the square root of the area, and then use that side length to calculate the perimeter. For example, if the area is A:
Then the perimeter is:
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tính chu vi của một hình vuông với Thầy J. Video hữu ích cho người học toán.
Làm thế nào để tìm chu vi của một hình vuông | Toán học với Thầy J
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tìm diện tích và chu vi của một hình vuông. Video hữu ích cho người học toán.
Cách tìm Diện tích và Chu vi của một Hình vuông