Topic how to find perimeter of a semicircle: Learn how to find the perimeter of a semicircle with our easy step-by-step guide. This article simplifies the process, providing clear instructions and practical examples to help you understand and apply the formula. Whether you're a student or just curious, discover the math behind calculating the perimeter of a semicircle effortlessly.
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Introduction
- Understanding the Semicircle
- Mathematical Definitions
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Formula for the Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Example Calculations
- Using Different Units
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Applications in Real Life
- Practice Problems
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi bán nguyệt bằng phương pháp đơn giản và dễ hiểu.
How to Find the Perimeter of a Semicircle
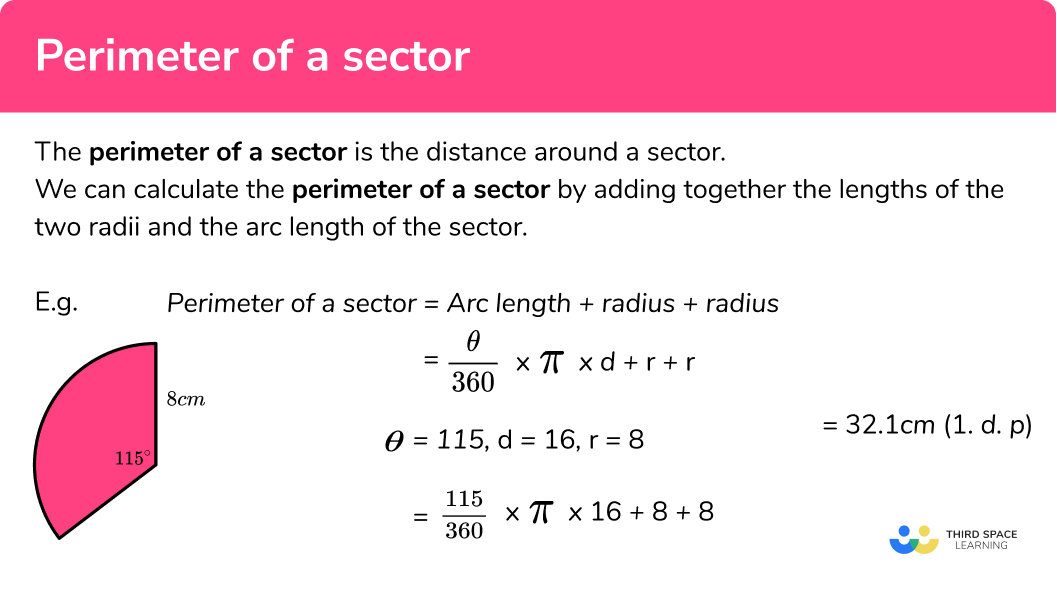
Finding the perimeter of a semicircle involves a few simple steps. A semicircle is half of a circle, so its perimeter includes the curved part (half the circumference of a full circle) and the straight diameter.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Identify the radius (\( r \)) of the semicircle. The radius is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its edge.
- Calculate the circumference of the full circle using the formula:
- Since a semicircle is half of a circle, divide the circumference by 2:
- Add the diameter (\( 2r \)) to the curved part to get the total perimeter of the semicircle:
\[ C = 2 \pi r \]
\[ \text{Curved part of the perimeter} = \frac{1}{2} \times 2 \pi r = \pi r \]
\[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi r + 2r \]
Example Calculation
Let's say the radius (\( r \)) of the semicircle is 5 units. The steps to find the perimeter are as follows:
- Calculate the curved part of the perimeter:
- Add the diameter to the curved part:
- Therefore, the perimeter of the semicircle is:
\[ \pi r = \pi \times 5 = 5\pi \]
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 5\pi + 2 \times 5 = 5\pi + 10 \]
\[ 5\pi + 10 \approx 25.71 \text{ units} \] (using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \))
Summary
The formula to find the perimeter (\( P \)) of a semicircle with radius (\( r \)) is:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
By following the steps outlined above, you can easily calculate the perimeter of any semicircle given its radius.

READ MORE:
Introduction
Calculating the perimeter of a semicircle is a fundamental concept in geometry, combining knowledge of circles and basic arithmetic. A semicircle, being half of a circle, has a unique perimeter calculation that involves both the curved edge and the straight diameter. This guide will walk you through the process, ensuring a clear understanding of the steps involved.
The perimeter of a semicircle consists of:
- The curved part, which is half the circumference of a full circle.
- The straight part, which is the diameter of the semicircle.
By combining these two components, you can easily find the perimeter using the formula:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
Where \( r \) is the radius of the semicircle.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the formula, provide examples, and discuss practical applications to enhance your understanding and proficiency in calculating the perimeter of a semicircle.
Understanding the Semicircle
A semicircle is a two-dimensional geometric shape that represents half of a circle. It is formed by cutting a full circle along its diameter, resulting in a shape that consists of a curved edge and a straight line. The straight line is the diameter, and the curved edge is half of the circle's circumference.
Key components of a semicircle:
- Radius (\( r \)): The distance from the center of the semicircle to any point on its curved edge. It is half the length of the diameter.
- Diameter (\( 2r \)): The straight line that divides the semicircle into two equal halves. It is twice the length of the radius.
- Circumference: The complete distance around a full circle, given by the formula \( 2\pi r \). For a semicircle, this is halved.
To fully understand a semicircle, it is essential to grasp the relationship between these components. The curved part of the perimeter of a semicircle can be calculated by halving the circumference of a full circle:
\[ \text{Curved part} = \frac{1}{2} \times 2\pi r = \pi r \]
The total perimeter of the semicircle includes the curved part and the diameter:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi r + 2r \]
This unique combination of a linear and a curved section is what differentiates the perimeter of a semicircle from other shapes. Understanding these elements and their interplay is crucial for accurate calculation and application in various mathematical and real-world scenarios.
Mathematical Definitions
To understand how to find the perimeter of a semicircle, it's important to first grasp several key mathematical definitions related to circles and semicircles. These terms and formulas form the foundation for the calculation.
- Circle: A two-dimensional shape where all points are equidistant from a central point known as the center. The distance from the center to any point on the circle is the radius.
- Radius (\( r \)): The distance from the center of a circle to any point on its circumference. It is a crucial measurement in calculating the perimeter of a semicircle.
- Diameter (\( 2r \)): A straight line passing through the center of a circle, connecting two points on the circumference. It is twice the length of the radius.
- Circumference (\( C \)): The total distance around a circle. The formula for the circumference of a circle is given by:
- Semicircle: Half of a circle, formed by dividing a circle along its diameter. It includes a curved edge and a straight edge (the diameter).
\[ C = 2\pi r \]
The perimeter (or the total boundary length) of a semicircle combines the length of the curved edge (half the circumference of the full circle) and the straight edge (the diameter). The formula for the perimeter (\( P \)) of a semicircle is:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
Here, \( \pi \) (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159. This formula adds the half-circumference (\( \pi r \)) and the diameter (\( 2r \)) to find the total perimeter.
These mathematical definitions and formulas provide the necessary background to accurately calculate the perimeter of a semicircle, ensuring a clear and comprehensive understanding of the process.
Step-by-Step Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of a semicircle involves combining the length of its curved edge and its diameter. Follow these steps to find the perimeter accurately:
- Identify the radius (\( r \)) of the semicircle:
The radius is the distance from the center of the semicircle to any point on its curved edge. It is a crucial measurement for the calculation.
- Calculate the circumference of the full circle:
Use the formula for the circumference of a full circle:
\[ C = 2\pi r \]
- Find the length of the curved edge of the semicircle:
Since a semicircle is half of a circle, the curved edge is half of the full circle's circumference:
\[ \text{Curved part} = \frac{1}{2} \times 2\pi r = \pi r \]
- Determine the diameter of the semicircle:
The diameter (\( 2r \)) is the straight edge of the semicircle.
- Combine the curved edge and the diameter:
Add the length of the curved edge and the diameter to find the total perimeter:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
Let's consider an example to illustrate the calculation:
Example: Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 4 units.
- Identify the radius: \( r = 4 \) units.
- Calculate the circumference of the full circle:
\[ C = 2\pi \times 4 = 8\pi \] units
- Find the length of the curved edge of the semicircle:
\[ \text{Curved part} = \pi \times 4 = 4\pi \] units
- Determine the diameter:
\[ \text{Diameter} = 2 \times 4 = 8 \] units
- Combine the curved edge and the diameter to find the perimeter:
\[ P = 4\pi + 8 \approx 4 \times 3.14159 + 8 = 12.56636 + 8 = 20.56636 \] units
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any semicircle given its radius.
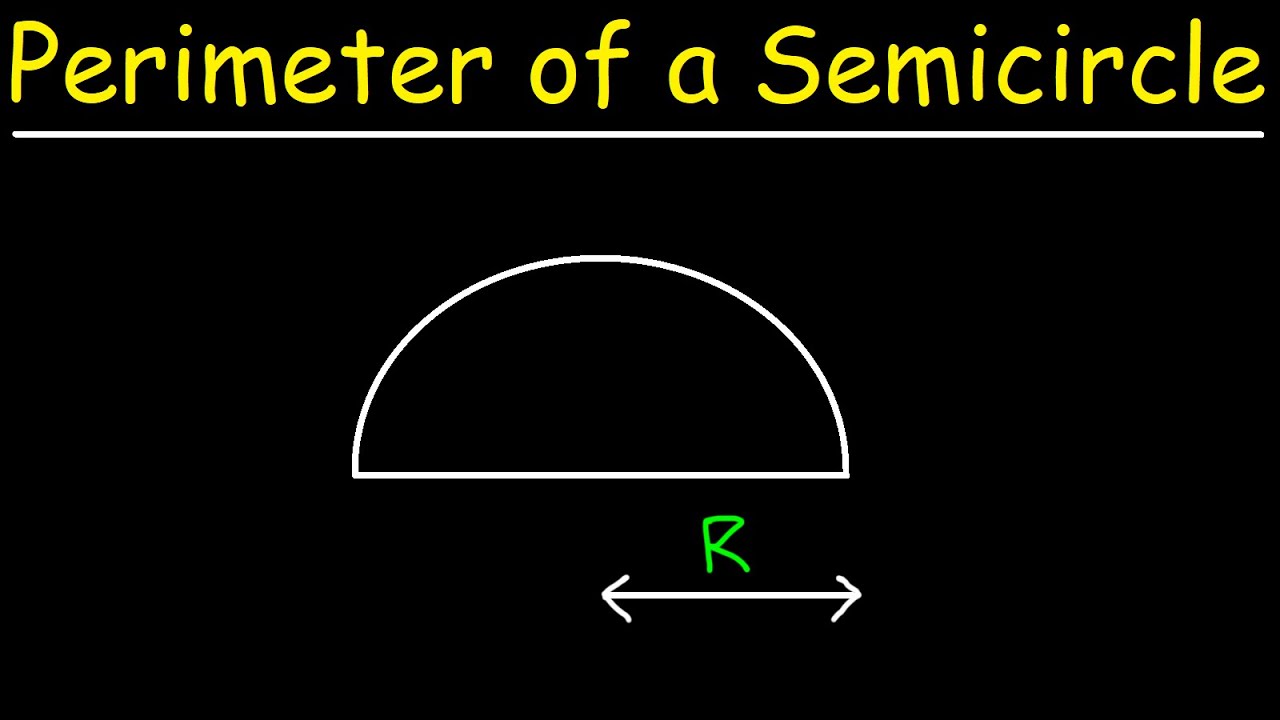
Formula for the Perimeter of a Semicircle
The perimeter of a semicircle is the sum of the length of the curved edge (half the circumference of a full circle) and the diameter of the semicircle. Here is the step-by-step process to derive the formula:
- Start with the formula for the circumference of a full circle, which is \( C = 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius.
- Since a semicircle is half of a circle, the length of the curved edge is half the circumference, or \( \frac{1}{2} \times 2\pi r = \pi r \).
- The diameter \( d \) of the semicircle is twice the radius, so \( d = 2r \).
- Therefore, the perimeter \( P \) of the semicircle is the sum of the curved edge and the diameter: \[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
- Factoring out \( r \), the formula simplifies to: \[ P = r(\pi + 2) \]
This formula can be used directly to find the perimeter if you know the radius or diameter of the semicircle.
Examples
Here are some example calculations:
- Example 1: Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 5 cm.
- Plug the radius into the formula: \( P = r(\pi + 2) \)
- \( P = 5(\pi + 2) \approx 5(3.14 + 2) \approx 5 \times 5.14 = 25.7 \) cm
- The perimeter is approximately 25.7 cm.
- Example 2: Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a diameter of 10 cm.
- First, find the radius: \( r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \) cm
- Plug the radius into the formula: \( P = r(\pi + 2) \)
- \( P = 5(\pi + 2) \approx 5(3.14 + 2) \approx 5 \times 5.14 = 25.7 \) cm
- The perimeter is approximately 25.7 cm.
- Example 3: A semicircle has a perimeter of 27 units. Find the radius.
- Use the formula: \( P = r(\pi + 2) \)
- Substitute the perimeter and solve for \( r \): \( 27 = r(\pi + 2) \)
- \( r = \frac{27}{\pi + 2} \approx \frac{27}{5.14} \approx 5.25 \) units
- The radius is approximately 5.25 units.
Example Calculations
Let's go through a few example problems to understand how to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle.
Example 1: Given Diameter
Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a diameter of 10 cm.
- First, find the radius:
\[
r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \, \text{cm}
\] - Use the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle:
\[
P = r(\pi + 2)
\] - Substitute the radius into the formula:
\[
P = 5(\pi + 2) \approx 5(3.14 + 2) = 5(5.14) = 25.7 \, \text{cm}
\]
Example 2: Given Radius
Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 8 cm.
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle:
\[
P = r(\pi + 2)
\] - Substitute the radius into the formula:
\[
P = 8(\pi + 2) \approx 8(3.14 + 2) = 8(5.14) = 41.12 \, \text{cm}
\]
Example 3: Given Perimeter
A semicircle has a perimeter of 27 cm. Find the radius.
- Use the formula for the perimeter and solve for the radius:
\[
P = r(\pi + 2)
\] - Substitute the perimeter into the formula and solve for \( r \):
\[
27 = r(\pi + 2)
\]\[
r = \frac{27}{\pi + 2} \approx \frac{27}{3.14 + 2} = \frac{27}{5.14} \approx 5.25 \, \text{cm}
\]
Using Different Units
The formula for the perimeter of a semicircle is given by:
P = r(π + 2)
where P is the perimeter and r is the radius.
Let's see how to use this formula with different units of measurement:
Example 1: Using Centimeters
Suppose we have a semicircle with a radius of 10 cm. To find the perimeter, we plug the radius into the formula:
P = 10(π + 2)
Using the approximation
P ≈ 10(3.14 + 2) = 10 × 5.14 = 51.4 \, \text{cm}
Example 2: Using Inches
Consider a semicircle with a radius of 5 inches. The perimeter is calculated as:
P = 5(π + 2)
Using
P ≈ 5(3.14 + 2) = 5 × 5.14 = 25.7 \, \text{inches}
Example 3: Using Meters
If the radius of a semicircle is 0.75 meters, we find the perimeter as follows:
P = 0.75(π + 2)
Using
P ≈ 0.75(3.14 + 2) = 0.75 × 5.14 = 3.855 \, \text{meters}
Example 4: Using Millimeters
For a semicircle with a radius of 200 mm, the perimeter calculation is:
P = 200(π + 2)
With
P ≈ 200(3.14 + 2) = 200 × 5.14 = 1028 \, \text{mm}
These examples illustrate how to apply the perimeter formula for a semicircle using different units of measurement. The key is to consistently use the same unit for both the radius and the calculated perimeter.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When calculating the perimeter of a semicircle, several common mistakes can occur. Here, we identify these mistakes and provide tips on how to avoid them:
- Ignoring the Diameter:
Many people mistakenly consider only the curved part of the semicircle, forgetting to add the diameter to their calculation. Remember, the perimeter of a semicircle is not just the curved part, but also includes the diameter:
\( P = \pi r + d \) where \( d = 2r \)
- Incorrect Use of Pi:
Using an incorrect value for \(\pi\) (pi) can lead to significant errors. Ensure you use \(\pi \approx 3.14\) or the more precise \(\pi \approx 22/7\).
- Wrong Units:
Make sure the units of radius or diameter are consistent throughout the calculation. Mixing units (e.g., using centimeters for radius and meters for diameter) can result in incorrect perimeters.
- Half Circle Assumption:
Assuming the perimeter of a semicircle is half the circumference of a circle is incorrect. The correct formula includes both the curved edge and the diameter:
\( P = \pi r + 2r \)
- Forgetting to Add Diameter in Word Problems:
In word problems, explicitly add the diameter to the curved part of the perimeter. If the problem states the radius or diameter, apply the correct formula directly.
By paying attention to these common mistakes and following the correct steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of a semicircle every time.
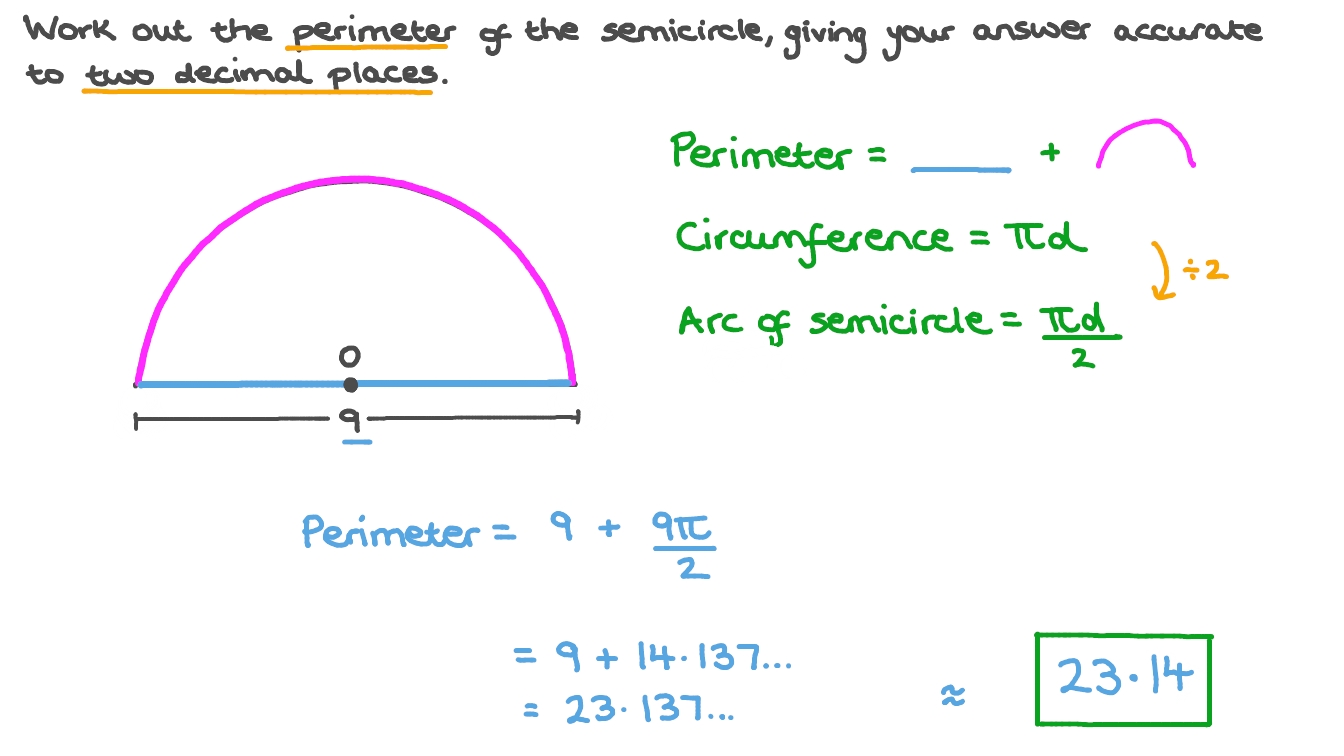
Applications in Real Life
The perimeter of a semicircle finds various practical applications in everyday life. Here are some notable examples:
- Architecture and Construction: Semicircular designs are prevalent in architecture, such as in the construction of archways, tunnels, and domed roofs. The perimeter calculation helps in determining the materials needed for the construction of these structures.
- Gardening: When planning garden layouts, especially those with curved pathways or semi-circular flower beds, knowing the perimeter helps in laying out borders or fencing accurately.
- Furniture Design: Semicircular tables and other furniture pieces are common. Understanding the perimeter is essential for creating precise designs and for determining the amount of material required.
- Road Construction: The design of roundabouts and curved road sections often involves semicircles. Calculating the perimeter is crucial for laying out these road sections and for safety planning.
- Home Décor: Items like semicircular rugs, doormats, and windows utilize the concept of a semicircle. The perimeter calculation helps in accurately fitting these items into specific spaces.
- Sports: Running tracks and certain sports fields incorporate semicircular sections. Knowing the perimeter helps in marking out the tracks and fields correctly.
- Arts and Crafts: Creating semi-circular designs in various craft projects requires precise perimeter measurements to ensure the designs are symmetrical and well-proportioned.
These examples illustrate how the mathematical concept of a semicircle's perimeter is applied in diverse fields, enhancing both functionality and aesthetics in real-world applications.
Practice Problems
Here are some practice problems to help you master the calculation of the perimeter of a semicircle. Follow the steps and use the formula provided earlier.
-
Problem 1: A semicircle has a diameter of 10 cm. Calculate the perimeter.
Solution:
- First, find the radius by dividing the diameter by 2.
- \[ \text{Radius} = \frac{10 \, \text{cm}}{2} = 5 \, \text{cm} \]
- Next, use the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle:
- \[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi \times \text{Radius} + \text{Diameter} \]
- Substitute the values:
- \[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi \times 5 \, \text{cm} + 10 \, \text{cm} \]
- \[ \text{Perimeter} \approx 3.14 \times 5 \, \text{cm} + 10 \, \text{cm} = 15.7 \, \text{cm} + 10 \, \text{cm} = 25.7 \, \text{cm} \]
- Answer: The perimeter is approximately 25.7 cm.
-
Problem 2: Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 7 inches.
Solution:
- First, find the diameter by multiplying the radius by 2.
- \[ \text{Diameter} = 2 \times 7 \, \text{inches} = 14 \, \text{inches} \]
- Next, use the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle:
- \[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi \times \text{Radius} + \text{Diameter} \]
- Substitute the values:
- \[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi \times 7 \, \text{inches} + 14 \, \text{inches} \]
- \[ \text{Perimeter} \approx 3.14 \times 7 \, \text{inches} + 14 \, \text{inches} = 21.98 \, \text{inches} + 14 \, \text{inches} = 35.98 \, \text{inches} \]
- Answer: The perimeter is approximately 35.98 inches.
-
Problem 3: Calculate the perimeter of a semicircle with a diameter of 4 meters.
Solution:
- First, find the radius by dividing the diameter by 2.
- \[ \text{Radius} = \frac{4 \, \text{m}}{2} = 2 \, \text{m} \]
- Next, use the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle:
- \[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi \times \text{Radius} + \text{Diameter} \]
- Substitute the values:
- \[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi \times 2 \, \text{m} + 4 \, \text{m} \]
- \[ \text{Perimeter} \approx 3.14 \times 2 \, \text{m} + 4 \, \text{m} = 6.28 \, \text{m} + 4 \, \text{m} = 10.28 \, \text{m} \]
- Answer: The perimeter is approximately 10.28 meters.
-
Problem 4: A semicircle has a radius of 15 cm. What is its perimeter?
Solution:
- First, find the diameter by multiplying the radius by 2.
- \[ \text{Diameter} = 2 \times 15 \, \text{cm} = 30 \, \text{cm} \]
- Next, use the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle:
- \[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi \times \text{Radius} + \text{Diameter} \]
- Substitute the values:
- \[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi \times 15 \, \text{cm} + 30 \, \text{cm} \]
- \[ \text{Perimeter} \approx 3.14 \times 15 \, \text{cm} + 30 \, \text{cm} = 47.1 \, \text{cm} + 30 \, \text{cm} = 77.1 \, \text{cm} \]
- Answer: The perimeter is approximately 77.1 cm.
-
Problem 5: Determine the perimeter of a semicircle with a diameter of 20 inches.
Solution:
- First, find the radius by dividing the diameter by 2.
- \[ \text{Radius} = \frac{20 \, \text{inches}}{2} = 10 \, \text{inches} \]
- Next, use the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle:
- \[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi \times \text{Radius} + \text{Diameter} \]
- Substitute the values:
- \[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi \times 10 \, \text{inches} + 20 \, \text{inches} \]
- \[ \text{Perimeter} \approx 3.14 \times 10 \, \text{inches} + 20 \, \text{inches} = 31.4 \, \text{inches} + 20 \, \text{inches} = 51.4 \, \text{inches} \]
- Answer: The perimeter is approximately 51.4 inches.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Q1: What is a semicircle?
A semicircle is half of a circle formed by cutting a circle along its diameter. It includes the curved edge (arc) and the straight edge (diameter).
-
Q2: How do you find the perimeter of a semicircle?
The perimeter (P) of a semicircle is given by the formula:
\[
P = \pi r + 2r
\]where \( r \) is the radius of the semicircle.
-
Q3: How do you calculate the area of a semicircle?
The area (A) of a semicircle is calculated using the formula:
\[
A = \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2
\]where \( r \) is the radius of the semicircle.
-
Q4: Is the perimeter of a semicircle half the perimeter of a circle?
No, the perimeter of a semicircle is not simply half the perimeter of a circle. It includes half the circumference of the circle plus the diameter.
-
Q5: What are some practical applications of semicircles?
Semicircles are used in various real-life applications such as in architecture (arches), engineering (bridges), and design (patterns and layouts).
-
Q6: How is the semicircle related to other geometric shapes?
A semicircle is related to a circle as it is half of it. It also forms part of an ellipse when paired with another semicircle.
-
Q7: What is the central angle of a semicircle?
The central angle of a semicircle is always 180 degrees, as it represents half of the 360-degree angle of a full circle.
-
Q8: Can a semicircle be considered a polygon?
No, a semicircle is not considered a polygon because it has a curved edge. Polygons are defined by straight line segments.
-
Q9: How do you derive the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle?
The perimeter of a semicircle is derived by adding half the circumference of the circle (\( \pi r \)) to the diameter (2r):
\[
P = \pi r + 2r
\] -
Q10: How do you find the radius if the perimeter of a semicircle is given?
To find the radius (\( r \)) when the perimeter (\( P \)) is given, use the formula:
\[
P = \pi r + 2r
\]Rearrange the formula to solve for \( r \):
\[
r = \frac{P}{\pi + 2}
\]
Conclusion
The perimeter of a semicircle, though often perceived as challenging, is straightforward with the right understanding and approach. By combining the diameter and half of the circumference, the formula elegantly encapsulates this concept.
Throughout this article, we have explored the geometric and mathematical foundations of the semicircle, leading to the practical application of its perimeter calculation. From understanding the basic definitions to step-by-step calculations and real-life examples, you now have a comprehensive guide to master this topic.
Practicing with various problems and avoiding common mistakes will further solidify your understanding. Remember, the key steps involve:
- Identifying the radius or diameter.
- Applying the formula accurately.
- Ensuring correct unit conversions if necessary.
With these skills, you can confidently tackle any problem related to the perimeter of a semicircle, whether in academic settings or practical applications. Keep practicing and applying these concepts to strengthen your mathematical proficiency.
Mathematics is a field built on clarity and logical progression. By breaking down complex problems into manageable steps, you can achieve a deeper understanding and greater success in your studies. Happy calculating!

Video hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi bán nguyệt bằng phương pháp đơn giản và dễ hiểu.
Cách Tính Chu Vi Bán Nguyệt
READ MORE:
Video từ Corbettmaths hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tính chu vi của một bán nguyệt một cách dễ hiểu và chính xác.
Chu Vi Bán Nguyệt - Corbettmaths