Topic perimeter formula of a pentagon: Understanding the perimeter formula of a pentagon is essential for students and math enthusiasts. This guide simplifies the concept, providing clear steps and examples to calculate the perimeter of both regular and irregular pentagons. Dive in to master this fundamental geometry topic with ease!
Table of Content
- Perimeter Formula of a Pentagon
- Introduction to Pentagon Perimeter
- Regular Pentagon Perimeter Formula
- Irregular Pentagon Perimeter Calculation
- Steps to Calculate Perimeter of a Pentagon
- Examples of Pentagon Perimeter Calculation
- Visual Representations of Pentagons
- Common Mistakes in Pentagon Perimeter Calculations
- Applications of Pentagon Perimeter in Real Life
- Practice Problems for Pentagon Perimeter
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Pentagon Perimeter
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Khám phá cách tính chu vi hình ngũ giác đều và không đều cùng với công thức và ví dụ minh họa.
Perimeter Formula of a Pentagon
The perimeter of a pentagon can be calculated using the following formula:
\[
P = 5 \times a
\]
where:
- P is the perimeter of the pentagon
- a is the length of one side of the pentagon
Types of Pentagons
There are different types of pentagons, and the formula for the perimeter can vary depending on the type:
- Regular Pentagon: All sides and angles are equal. Use the formula \( P = 5 \times a \).
- Irregular Pentagon: Sides and angles are not equal. The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all sides: \[ P = a_1 + a_2 + a_3 + a_4 + a_5 \] where \( a_1, a_2, a_3, a_4, \) and \( a_5 \) are the lengths of the sides.
Example Calculation
For a regular pentagon with a side length of 6 units:
\[
P = 5 \times 6 = 30 \text{ units}
\]
For an irregular pentagon with side lengths of 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8 units:
\[
P = 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 = 30 \text{ units}
\]
Visual Representation
A regular pentagon looks like this:
An irregular pentagon looks like this:
These images are placeholders and should be replaced with actual diagrams of pentagons.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Pentagon Perimeter
A pentagon is a five-sided polygon with various applications in geometry, architecture, and art. Calculating the perimeter of a pentagon involves summing the lengths of its sides. Understanding the perimeter formula is essential for solving geometry problems involving pentagons.
The perimeter of a pentagon can be categorized into two types:
- Regular Pentagon: All sides and angles are equal.
- Irregular Pentagon: Sides and angles are not necessarily equal.
For a regular pentagon, the formula to calculate the perimeter (P) is straightforward:
\[
P = 5 \times a
\]
where:
- P is the perimeter of the pentagon
- a is the length of one side
For an irregular pentagon, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all five sides:
\[
P = a_1 + a_2 + a_3 + a_4 + a_5
\]
where:
- P is the perimeter of the pentagon
- a_1, a_2, a_3, a_4, and a_5 are the lengths of the sides
In summary, whether dealing with a regular or irregular pentagon, calculating the perimeter involves knowing the lengths of the sides and applying the appropriate formula. This foundational knowledge is crucial for more advanced studies in geometry and practical applications.
Regular Pentagon Perimeter Formula
A regular pentagon is a polygon with five equal sides and five equal angles. Calculating the perimeter of a regular pentagon is straightforward due to its symmetrical properties. The perimeter formula for a regular pentagon is derived from the length of one of its sides.
The formula to calculate the perimeter (P) of a regular pentagon is:
\[
P = 5 \times a
\]
where:
- P is the perimeter of the pentagon
- a is the length of one side
To compute the perimeter, follow these simple steps:
- Measure the length of one side of the pentagon.
- Multiply this length by 5, since all sides are equal in a regular pentagon.
For example, if the length of one side of a regular pentagon is 7 units, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
\[
P = 5 \times 7 = 35 \text{ units}
\]
This formula is useful in various applications, including geometry problems, construction projects, and any scenario requiring knowledge of the boundaries of a five-sided shape. By understanding and applying this simple formula, you can easily determine the perimeter of any regular pentagon.
Irregular Pentagon Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of an irregular pentagon involves summing the lengths of all its sides. Unlike a regular pentagon, where all sides are equal, an irregular pentagon has sides of varying lengths. The formula to find the perimeter of an irregular pentagon is:
\( \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d + e \)
where \(a\), \(b\), \(c\), \(d\), and \(e\) are the lengths of the sides of the pentagon.
To calculate the perimeter of an irregular pentagon, follow these steps:
- Measure the lengths of all five sides of the pentagon.
- Write down the length of each side.
- Use the perimeter formula: \( \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d + e \).
- Add the lengths together to get the total perimeter.
Here is an example:
| Side | Length (units) |
|---|---|
| a | 5 |
| b | 7 |
| c | 6 |
| d | 8 |
| e | 4 |
| Total Perimeter | 30 |
So, the perimeter of the irregular pentagon with the given side lengths is 30 units.
Steps to Calculate Perimeter of a Pentagon
Calculating the perimeter of a pentagon involves adding the lengths of all its sides. The method varies slightly depending on whether the pentagon is regular (all sides are equal) or irregular (sides have different lengths).
For a Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon has all sides of equal length. Therefore, the perimeter can be calculated using the formula:
\[ P = 5a \]
where \( P \) is the perimeter and \( a \) is the length of one side.
Steps:
- Identify the length of one side of the pentagon.
- Multiply this length by 5.
- The result is the perimeter of the pentagon.
Example: If each side of the pentagon is 6 units, then the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = 5 \times 6 = 30 \text{ units} \]
For an Irregular Pentagon
An irregular pentagon has sides of different lengths. The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all the sides.
\[ P = a + b + c + d + e \]
where \( a, b, c, d, \) and \( e \) are the lengths of the sides.
Steps:
- Measure the length of each side of the pentagon.
- Add all these lengths together.
- The result is the perimeter of the pentagon.
Example: If the sides of the pentagon are 3 units, 7 units, 8 units, 9 units, and 6 units, then the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = 3 + 7 + 8 + 9 + 6 = 33 \text{ units} \]
Whether dealing with a regular or irregular pentagon, the process involves straightforward arithmetic, making it accessible for various practical applications and educational purposes.

Examples of Pentagon Perimeter Calculation
In this section, we will go through several examples to illustrate how to calculate the perimeter of both regular and irregular pentagons. We will use detailed steps to ensure clarity.
Example 1: Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon has all sides of equal length. Suppose each side of the pentagon is 5 units.
- Identify the length of one side (s):
5units. - Use the perimeter formula for a regular pentagon:
P = 5s. - Calculate the perimeter:
P = 5 \times 5 = 25units.
The perimeter of the regular pentagon is 25 units.
Example 2: Irregular Pentagon
An irregular pentagon has sides of different lengths. Suppose the lengths of the sides are 3 units, 4 units, 5 units, 6 units, and 7 units.
- List the lengths of all sides:
3, 4, 5, 6, 7units. - Add the lengths of the sides:
3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7. - Calculate the perimeter:
P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 25units.
The perimeter of the irregular pentagon is 25 units.
Example 3: Regular Pentagon with Algebraic Side Length
Suppose each side of a regular pentagon is represented by the variable x. If x = 8 units, find the perimeter.
- Identify the length of one side (s):
x = 8units. - Use the perimeter formula for a regular pentagon:
P = 5s. - Substitute
xinto the formula:P = 5 \times 8. - Calculate the perimeter:
P = 40units.
The perimeter of the regular pentagon with side length 8 units is 40 units.
Example 4: Irregular Pentagon with Given Side Lengths
Consider an irregular pentagon with side lengths a = 4, b = 5, c = 7, d = 3, and e = 6 units. Calculate its perimeter.
- List the lengths of all sides:
4, 5, 7, 3, 6units. - Add the lengths of the sides:
4 + 5 + 7 + 3 + 6. - Calculate the perimeter:
P = 4 + 5 + 7 + 3 + 6 = 25units.
The perimeter of the irregular pentagon is 25 units.
Example 5: Real-life Application
A garden in the shape of a regular pentagon has each side measuring 12 meters. Find the total length of the fence needed to enclose the garden.
- Identify the length of one side (s):
12meters. - Use the perimeter formula for a regular pentagon:
P = 5s. - Calculate the perimeter:
P = 5 \times 12 = 60meters.
The total length of the fence needed is 60 meters.
Visual Representations of Pentagons
A pentagon is a five-sided polygon, and it can be either regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles can vary). Visual representations help in understanding the shape and calculating its perimeter.
Below are visual representations of both regular and irregular pentagons:
Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon has equal side lengths and internal angles of 108 degrees each. The visual representation is as follows:

The perimeter \( P \) of a regular pentagon with side length \( s \) is given by:
\( P = 5s \)
Irregular Pentagon
An irregular pentagon has sides and angles of different lengths and measures. Here is an example of an irregular pentagon:

The perimeter \( P \) of an irregular pentagon is the sum of the lengths of its sides:
\( P = a + b + c + d + e \)
where \( a, b, c, d, \) and \( e \) are the lengths of the sides of the pentagon.
Interactive Pentagon Tool
Using an interactive tool can greatly help in visualizing and understanding pentagons. Here are some useful tools:
- - Create and explore pentagons
Drawing a Pentagon
To draw a regular pentagon, you can use the following steps:
- Draw a circle with a compass.
- Mark a point on the circle; this will be one vertex of the pentagon.
- Using a protractor, measure 72-degree increments around the circle and mark the points.
- Connect the points to form a regular pentagon.
For an irregular pentagon, simply connect five points in any order, ensuring they form a closed shape.
Tables of Pentagon Properties
Here is a table summarizing the properties of regular and irregular pentagons:
| Property | Regular Pentagon | Irregular Pentagon |
|---|---|---|
| Sides | Equal | Unequal |
| Angles | 108 degrees each | Varies |
| Symmetry | High symmetry | Low symmetry |
| Formula for Perimeter | \( P = 5s \) | \( P = a + b + c + d + e \) |
These visual representations and tools can aid in the understanding and calculation of the perimeter of pentagons, whether regular or irregular.
Common Mistakes in Pentagon Perimeter Calculations
Calculating the perimeter of a pentagon can be straightforward, but there are several common mistakes that people often make. Here are some of the most frequent errors and how to avoid them:
- Assuming All Pentagons are Regular: A regular pentagon has all sides of equal length, but many pentagons are irregular. Ensure you identify whether the pentagon is regular or irregular before using the formula. For a regular pentagon, use \( P = 5a \) where \( a \) is the side length. For an irregular pentagon, add up all the side lengths individually: \( P = a_1 + a_2 + a_3 + a_4 + a_5 \).
- Incorrectly Measuring Side Lengths: Precision in measuring each side is crucial. Using approximate or incorrect lengths can lead to significant errors in the total perimeter. Always double-check your measurements.
- Confusing Side Length with Apothem or Radius: The side length is not the same as the apothem (a perpendicular line from the center to a side) or the radius (distance from the center to a vertex). Use the correct dimension for perimeter calculations.
- Using Wrong Units: Ensure all side lengths are in the same unit before adding them together. Mixing units (e.g., centimeters and inches) without conversion will lead to incorrect results.
- Forgetting to Add All Sides: In irregular pentagons, it's easy to forget one or more sides. Keep track of each side you measure to ensure all are included in the sum.
- Misinterpreting the Problem: Sometimes problems give indirect information about the sides, such as the perimeter of other shapes or using angles to calculate side lengths. Ensure you interpret the problem correctly and derive the necessary side lengths accurately.
By being aware of these common mistakes, you can ensure more accurate calculations of the perimeter of any pentagon, whether regular or irregular.
Applications of Pentagon Perimeter in Real Life
The perimeter of a pentagon, like other geometric shapes, has numerous practical applications in various fields. Understanding and calculating the perimeter is crucial for efficient resource management, security, and design. Here are some detailed applications:
- Construction and Architecture:
In construction, knowing the perimeter of a pentagon-shaped plot is essential for planning the layout and determining the boundaries. Architects use the perimeter to design buildings and structures, ensuring they fit within specified plots and optimizing the use of space. Accurate perimeter calculations help in estimating the amount of materials needed, such as fencing or wall lengths, to enclose the area effectively.
- Fencing and Landscaping:
When planning to install a fence around a pentagon-shaped garden or property, the perimeter is a key measurement. It helps in determining the total length of the fence required, which is crucial for budgeting and purchasing the correct amount of materials. Landscapers use the perimeter to design aesthetically pleasing and functional garden layouts, ensuring that pathways and borders are properly planned.
- Sports and Recreation:
In sports, the perimeter of playing fields, especially those with non-standard shapes like pentagons, must be accurately measured to meet regulatory standards. This ensures fair play and safety. Additionally, calculating the perimeter is important for installing boundary markers and planning spectator areas.
- Urban Planning:
Urban planners use the concept of perimeter in designing road networks and determining the layout of parks and public spaces. For example, pentagon-shaped parks or plazas require precise perimeter calculations to plan walkways, seating areas, and other amenities efficiently.
- Security and Surveillance:
In security, knowing the perimeter of an area is vital for setting up surveillance systems and patrol routes. Fencing the perimeter of a property helps in preventing unauthorized access and ensuring safety. The perimeter also plays a role in emergency planning, helping to define evacuation routes and secure zones.
Understanding the perimeter of a pentagon is not only a theoretical exercise but also a practical necessity in various real-life scenarios. It aids in making informed decisions, optimizing resource use, and ensuring safety and efficiency in everyday applications.
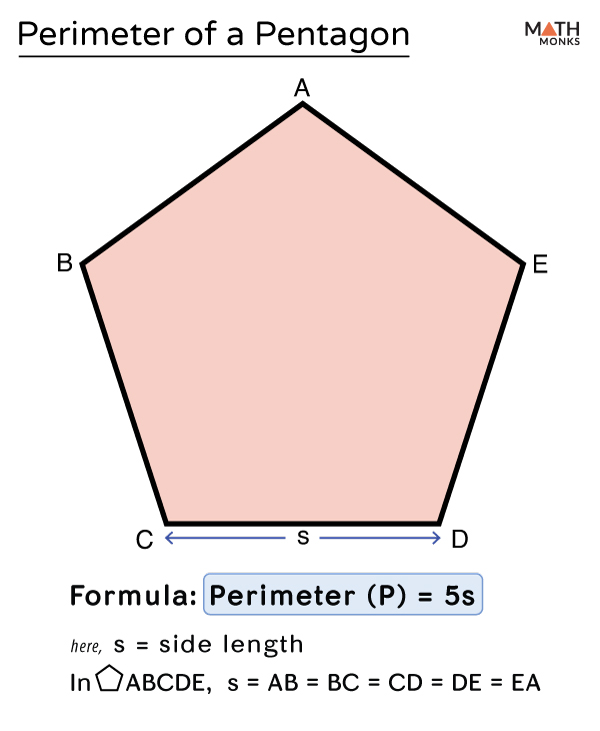
Practice Problems for Pentagon Perimeter
Practicing the calculation of a pentagon's perimeter helps reinforce understanding of both regular and irregular pentagons. Here are several problems to practice:
Problem 1: Regular Pentagon
Given a regular pentagon with each side measuring 8 units, find the perimeter.
- Identify the formula for the perimeter of a regular pentagon: \( P = 5s \).
- Substitute the given side length \( s = 8 \) into the formula: \( P = 5 \times 8 \).
- Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 40 \) units.
Problem 2: Irregular Pentagon
An irregular pentagon has sides measuring 7 units, 5 units, 6 units, 4 units, and 8 units. Find the perimeter.
- List the side lengths: \( a = 7 \), \( b = 5 \), \( c = 6 \), \( d = 4 \), \( e = 8 \).
- Use the formula for the perimeter of an irregular pentagon: \( P = a + b + c + d + e \).
- Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 7 + 5 + 6 + 4 + 8 = 30 \) units.
Problem 3: True or False
Determine if the following statements are true or false:
- The perimeter of a pentagon is the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
- If the side of a regular pentagon is 9 units, then the perimeter of the pentagon is 45 units.
Solutions:
- True: The perimeter of a pentagon is indeed the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
- False: The perimeter of a regular pentagon with each side 9 units is \( 5 \times 9 = 45 \) units, so the statement is true.
Problem 4: Visualization
Visualize and calculate the perimeter of a regular pentagon with each side of 12 units:
| Side Length (s) | Perimeter (P) |
| 12 units | \( P = 5 \times 12 = 60 \) units |
Problem 5: Mixed Practice
Find the perimeter of the following irregular pentagon: 3.5 units, 4.2 units, 5.1 units, 3.8 units, and 4.4 units.
- List the side lengths: \( a = 3.5 \), \( b = 4.2 \), \( c = 5.1 \), \( d = 3.8 \), \( e = 4.4 \).
- Use the formula for the perimeter: \( P = a + b + c + d + e \).
- Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 3.5 + 4.2 + 5.1 + 3.8 + 4.4 = 21 \) units.
Problem 6: Word Problem
A garden is designed in the shape of a regular pentagon with each side measuring 10 meters. What is the total length of the fencing required to enclose the garden?
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a regular pentagon: \( P = 5s \).
- Substitute the side length \( s = 10 \) meters: \( P = 5 \times 10 \).
- Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 50 \) meters.
These practice problems cover a variety of scenarios involving the perimeter of pentagons, providing a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Pentagon Perimeter
-
What is the perimeter of a pentagon?
The perimeter of a pentagon is the total length of its boundary. For a regular pentagon (where all sides are equal), the formula is \( P = 5a \), where \( a \) is the side length. For an irregular pentagon (where sides are of different lengths), the perimeter is the sum of all its sides, \( P = a + b + c + d + e \).
-
How do you find the perimeter of a regular pentagon?
The perimeter of a regular pentagon can be found using the formula \( P = 5a \), where \( a \) is the length of one side. Simply multiply the side length by 5.
-
How do you find the perimeter of an irregular pentagon?
To find the perimeter of an irregular pentagon, add the lengths of all five sides together: \( P = a + b + c + d + e \).
-
Can you find the perimeter of a pentagon using the radius?
Yes, if the pentagon is inscribed in a circle (circumradius), the side length can be calculated using the formula \( a = 2r \times \sin(36^\circ) \), where \( r \) is the radius. Once the side length is found, use the regular pentagon perimeter formula \( P = 5a \).
-
How do you find the perimeter of a pentagon using the apothem?
If the apothem (the perpendicular distance from the center to a side) is given, the side length can be found using \( a = 2 \times \text{apothem} \times \tan(36^\circ) \). After finding the side length, use \( P = 5a \) to find the perimeter.
-
What units are used for the perimeter of a pentagon?
The perimeter is a linear measurement and can be expressed in units such as inches, feet, centimeters, meters, etc.
Conclusion
Understanding the perimeter of a pentagon, whether regular or irregular, is essential for various applications in geometry and real life. A regular pentagon, with all sides equal, has a straightforward formula for its perimeter:
\( P = 5 \times s \)
where \( s \) is the length of one side.
For an irregular pentagon, the perimeter is the sum of all its sides:
\( P = a + b + c + d + e \)
where \( a, b, c, d, \) and \( e \) are the lengths of the sides.
Here are the steps to calculate the perimeter of any pentagon:
- Identify if the pentagon is regular or irregular.
- For a regular pentagon, measure one side and use the formula \( P = 5 \times s \).
- For an irregular pentagon, measure all five sides and sum them up using the formula \( P = a + b + c + d + e \).
- Ensure accuracy in your measurements to avoid errors in the final perimeter calculation.
Common mistakes to avoid include:
- Confusing a regular pentagon with an irregular one, which can lead to incorrect formula application.
- Incorrectly measuring the sides, especially in irregular pentagons where each side can be different.
By mastering these concepts and methods, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any pentagon, aiding in both academic studies and practical applications in fields such as architecture, engineering, and design.
Practice regularly with different examples and problems to solidify your understanding and improve your calculation skills. Visual representations and diagrams can also help in comprehending the geometric properties and perimeter calculations of pentagons.
Remember, the key to success in geometry is a clear understanding of the fundamental concepts and consistent practice. With this knowledge, calculating the perimeter of pentagons will become an easy and routine task.
Khám phá cách tính chu vi hình ngũ giác đều và không đều cùng với công thức và ví dụ minh họa.
Công Thức Chu Vi Hình Ngũ Giác, Chu Vi Cho Ngũ Giác Đều Và Không Đều Cùng Ví Dụ
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi hình ngũ giác với công thức đơn giản và ví dụ minh họa.
Cách Tìm Chu Vi Hình Ngũ Giác
