Topic how to find perimeter of a cube: Discover the step-by-step method to find the perimeter of a cube in our easy-to-understand guide. Learn the basics of cube geometry, apply simple formulas, and explore practical examples that make calculating the total edge length straightforward and enjoyable. Enhance your mathematical skills with our comprehensive and accessible explanations.
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of a Cube
- Introduction to Perimeter and Edge Length of a Cube
- Understanding Cube Geometry
- Difference Between Perimeter and Total Edge Length
- Formula to Calculate Total Edge Length
- Steps to Calculate Total Edge Length of a Cube
- Example Calculations
- Common Mistakes and Tips
- Practical Applications of Cube Measurements
- Visual Representation and Diagrams
- Additional Resources and Learning Materials
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách tìm diện tích, chu vi và thể tích của hình lập phương. Hướng dẫn chi tiết, dễ hiểu để thu hút người xem.
How to Find the Perimeter of a Cube
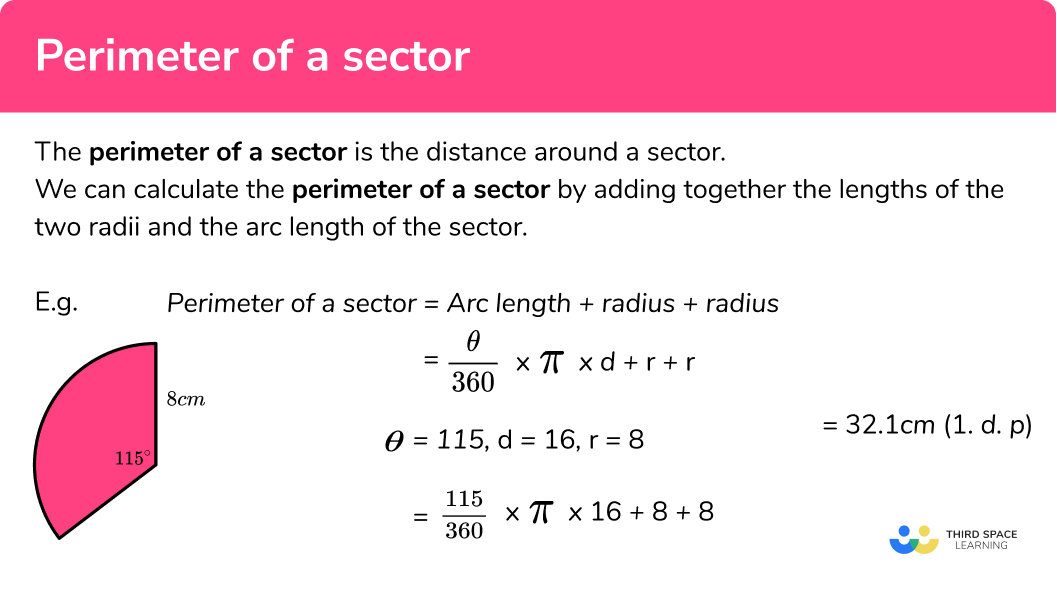
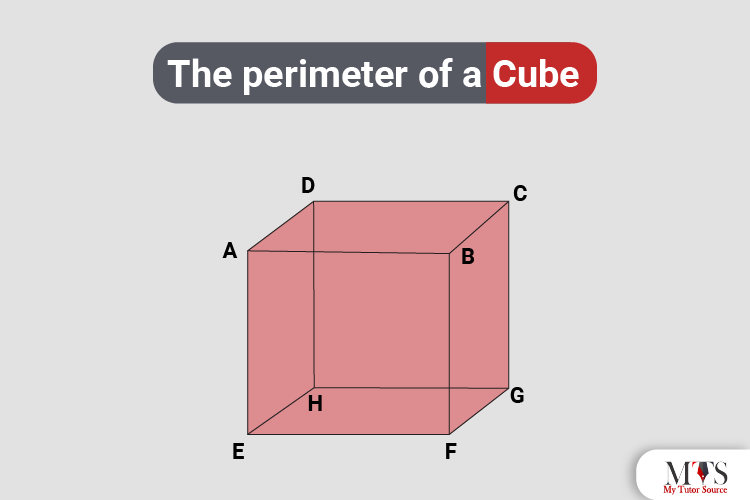
The concept of the perimeter usually applies to 2D shapes, but for a cube, we can discuss the total length of its edges. A cube has 12 edges, all of the same length. Below is a detailed explanation of how to calculate the total edge length of a cube.
Formula
For a cube with edge length a, the total length of all edges is:
Example Calculation
To find the total length of all edges for a cube with edge length 4 units:
Thus, the total length of all edges is 48 units.
Steps to Calculate
- Identify the length of one edge of the cube (a).
- Multiply this length by 12 to get the total length of all edges.
Visual Representation
Here is a simple table to summarize:
| Edge Length (a) | Total Edge Length |
|---|---|
| 1 unit | 12 units |
| 2 units | 24 units |
| 3 units | 36 units |
| 4 units | 48 units |
Additional Information
The term "perimeter" traditionally applies to 2D shapes. For 3D objects like a cube, it is more appropriate to refer to the total length of the edges. Ensure to use the proper terminology in mathematical contexts.
Understanding these principles will help in comprehending the basic properties of geometric shapes and their measurements.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter and Edge Length of a Cube
Understanding the perimeter and edge length of a cube is fundamental in geometry and spatial reasoning. A cube is a three-dimensional shape characterized by six square faces, all of equal size, and 12 straight edges of equal length.
The perimeter of a cube refers to the total length around its outer boundary, while the edge length represents the length of each individual edge. These measurements are crucial in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and mathematics.
In this section, we will delve into the concepts of perimeter and edge length, exploring their significance and applications in real-world scenarios. We will also discuss the relationship between perimeter and edge length in a cube and how to calculate them efficiently.
Understanding Cube Geometry
Cube geometry is a fascinating aspect of mathematics and spatial reasoning. A cube is a three-dimensional shape with six square faces, all of equal size, and 12 straight edges.
Key characteristics of cube geometry include:
- Equal Face Dimensions: Each face of a cube is a perfect square, with all sides having the same length.
- Uniform Edge Length: All 12 edges of a cube have the same length, resulting in uniformity and symmetry.
- Right Angles: The edges of a cube meet at right angles, forming 90-degree angles at each vertex.
- Diagonals: The diagonals of a cube's faces are equal in length and intersect at the center of the cube, forming a perfect cross-section.
Understanding these properties is essential for various applications, including architecture, engineering, and problem-solving in mathematics. By grasping the intricacies of cube geometry, one can unlock the potential for creative solutions and insights into spatial relationships.
Difference Between Perimeter and Total Edge Length
While the perimeter and total edge length are both measurements associated with the boundaries of a cube, they represent distinct concepts:
| Perimeter | Total Edge Length |
| Refers to the total length around the outer boundary of a two-dimensional shape. | Denotes the combined length of all the edges of a three-dimensional object. |
| Applicable to flat, two-dimensional shapes such as squares and rectangles. | Specifically relevant to three-dimensional figures like cubes. |
| Calculated by summing the lengths of all sides of the shape. | Computed by adding the lengths of all individual edges of the object. |
| Measured in linear units, such as inches, centimeters, or meters. | Also measured in linear units, following the same units as perimeter measurement. |
| Used in various contexts, including geometry, perimeter fencing, and area calculations. | Applied in geometry, architecture, engineering, and 3D modeling. |
Understanding the difference between perimeter and total edge length is crucial for accurately describing and analyzing the boundaries of geometric shapes and objects.
Formula to Calculate Total Edge Length
The total edge length of a cube can be determined using a straightforward mathematical formula:
| Formula: | Edge Length = 12 * Length of One Edge |
Where:
- Edge Length: Represents the total length of all edges of the cube.
- Length of One Edge: Indicates the length of a single edge of the cube. Since all edges of a cube are of equal length, this value can be obtained by measuring any one of the edges.
By multiplying the number of edges (which is 12 for a cube) by the length of a single edge, you can compute the total edge length of the cube. This formula simplifies the process of determining the combined length of all edges, providing a quick and efficient method for calculation.
Steps to Calculate Total Edge Length of a Cube
Determine the length of one edge of the cube by measuring any of its edges using a ruler or measuring tape. Ensure accuracy in measurement to obtain precise results.
Multiply the length of one edge by 12. Since a cube has 12 edges, this step accounts for each edge's contribution to the total edge length.
Perform the multiplication to obtain the total edge length of the cube. This value represents the combined length of all edges, providing a comprehensive measure of the cube's boundary.
Example Calculations
Let's consider an example to illustrate the calculation of the total edge length of a cube:
Given: The length of one edge of the cube is 5 centimeters.
Calculation:
Length of One Edge: 5 cmTotal Edge Length: 12 * 5 cm = 60 cmResult: The total edge length of the cube is 60 centimeters.
This example demonstrates how to apply the formula for calculating the total edge length of a cube using a specific edge length. By following these steps, you can easily determine the total edge length for any cube given its edge dimension.
Common Mistakes and Tips
When calculating the total edge length of a cube, it's essential to avoid common mistakes and follow helpful tips to ensure accuracy and efficiency:
Mistake: Incorrectly measuring the length of one edge of the cube can lead to inaccurate calculations.
Tip: Use a reliable measuring tool, such as a ruler or measuring tape, to obtain precise measurements of the cube's edges.
Mistake: Neglecting to multiply the length of one edge by 12 to account for all edges of the cube.
Tip: Remember to apply the formula correctly by multiplying the edge length by 12 to find the total edge length.
Mistake: Failing to convert units consistently when working with different measurement systems.
Tip: Ensure uniformity in units throughout the calculation process, converting measurements if necessary to maintain consistency.
By avoiding these common mistakes and following the provided tips, you can enhance the accuracy and reliability of your calculations when determining the total edge length of a cube.
Practical Applications of Cube Measurements
The measurements of a cube play a significant role in various practical applications across different fields:
Architecture: Architects use cube measurements to design buildings, ensuring structural integrity and optimal use of space.
Construction: Construction workers rely on cube measurements to accurately cut materials and assemble components, contributing to the construction process's efficiency and precision.
Engineering: Engineers utilize cube measurements in designing mechanical components, calculating volumes, and determining load-bearing capacities.
Manufacturing: Manufacturers apply cube measurements in producing standardized components and ensuring product quality and consistency.
3D Modeling and Animation: Professionals in the entertainment industry use cube measurements for creating realistic 3D models and animations in movies, video games, and simulations.
Education: Teachers incorporate cube measurements into educational activities and lessons to enhance students' understanding of geometry and spatial reasoning.
By understanding and applying cube measurements effectively, individuals and organizations can achieve greater precision, efficiency, and innovation in their respective fields.

Visual Representation and Diagrams
Visual representations and diagrams are invaluable tools for understanding the concepts of cube geometry and measurements:
Orthographic Projection: Orthographic drawings provide detailed views of a cube from different angles, allowing for a comprehensive visualization of its dimensions and structure.
Isometric Projection: Isometric drawings depict a cube in three dimensions, showing all three pairs of its parallel faces and illustrating how the edges and vertices are positioned relative to each other.
Interactive Models: Digital simulations and interactive models enable users to manipulate and explore virtual cubes, offering a hands-on approach to learning and experimentation.
Scale Models: Physical scale models of cubes provide a tangible representation of their size and proportions, facilitating tactile learning and visualization.
These visual aids enhance understanding by providing spatial context and allowing learners to observe the relationships between different elements of a cube. Whether through drawings, digital simulations, or physical models, visual representations are essential for grasping the intricacies of cube geometry and measurements.
Additional Resources and Learning Materials
To deepen your understanding of finding the perimeter of a cube, here are some valuable resources and learning materials:
-
Online Tutorials:
- - This tutorial provides a comprehensive overview of cube geometry, including volume and surface area.
- - Learn about the properties of cubes and how to calculate their dimensions.
-
Interactive Simulations:
- - Use this tool to visualize and manipulate a cube to better understand its geometry.
-
Practice Problems:
- - Access practice problems and step-by-step solutions to reinforce your learning.
-
Books:
- Geometry for Dummies - This book provides a user-friendly approach to understanding the basics of geometry, including cubes.
- High School Geometry Unlocked - A comprehensive guide that covers various geometric concepts, including the properties and calculations related to cubes.
-
Educational Videos:
- - Watch videos that explain the process of calculating the perimeter and other related measurements of a cube.
Conclusion
In conclusion, finding the perimeter of a cube is a straightforward process once you understand the basic geometric principles involved. A cube is a three-dimensional shape with six identical square faces, and the perimeter, in this context, refers to the total length of all its edges.
To recap:
- A cube has 12 edges of equal length.
- The formula for the total edge length (or perimeter) of a cube is: where a is the length of one edge.
By applying this formula, you can easily determine the perimeter of any cube given the length of one of its edges. For example, if the edge length is 8 units, the perimeter would be:
.
Understanding these concepts not only helps in solving academic problems but also provides a foundation for more complex geometric and mathematical applications. Keep practicing with different edge lengths to reinforce your understanding.
Video hướng dẫn cách tìm diện tích, chu vi và thể tích của hình lập phương. Hướng dẫn chi tiết, dễ hiểu để thu hút người xem.
Cách Tìm Diện Tích, Chu Vi Và Thể Tích Của Hình Lập Phương
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách tính thể tích, diện tích bề mặt và chu vi của hình lập phương. Hướng dẫn chi tiết, dễ hiểu để thu hút người xem.
Thủ Thuật Toán Học: Cách Tính Thể Tích, Diện Tích Bề Mặt và Chu Vi Của Hình Lập Phương