Topic find the perimeter of the quadrilateral: Learn how to find the perimeter of a quadrilateral with our easy-to-follow guide. Whether dealing with squares, rectangles, or irregular shapes, this article provides formulas, examples, and practical tips to master perimeter calculations. Perfect for students and educators alike, discover the fundamental techniques for calculating the perimeter of any quadrilateral.
Table of Content
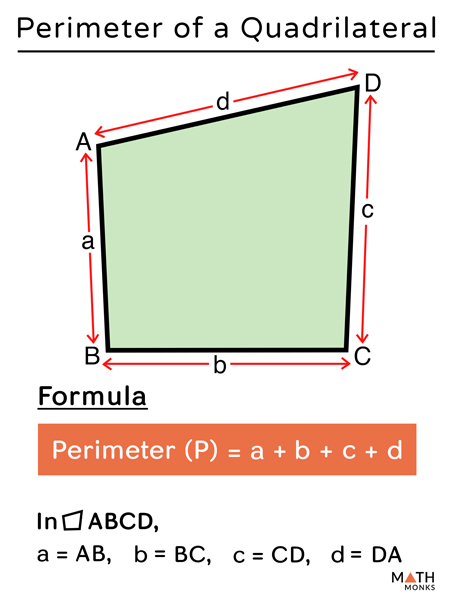
Perimeter of a Quadrilateral
The perimeter of a quadrilateral is the total length of its boundary. This can be calculated by adding the lengths of all its four sides. The general formula for the perimeter \(P\) of a quadrilateral with sides \(a\), \(b\), \(c\), and \(d\) is:
\[
P = a + b + c + d
\]
Examples
- Example 1: Find the perimeter of a kite with adjacent sides of 7 units and 13 units.
Since a kite has two pairs of equal adjacent sides, the perimeter is calculated as:
\[
P = 7 + 7 + 13 + 13 = 40 \text{ units}
\] - Example 2: Find the perimeter of a trapezoid with sides 4 units, 6 units, 7 units, and 9 units.
The perimeter is calculated by summing all the sides:
\[
P = 4 + 6 + 7 + 9 = 26 \text{ units}
\]
Special Cases
- Square:
All sides are equal. If \(a\) is the length of one side, the perimeter is:
\[
P = 4a
\] - Rectangle:
Opposite sides are equal. If \(l\) is the length and \(w\) is the width, the perimeter is:
\[
P = 2(l + w)
\]
Finding the Perimeter with Coordinates
When the coordinates of a quadrilateral's vertices are known, the distance formula is used to calculate the side lengths. For vertices \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\), the distance \(d\) is given by:
\[
d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}
\]
Sum the lengths of all sides to get the perimeter.
Practice Problems
- Find the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 10 units and a width of 5 units.
- Calculate the perimeter of a quadrilateral with sides 3 units, 5 units, 7 units, and 9 units.
- Given a quadrilateral with vertices at \((0, 0)\), \((0, 4)\), \((3, 0)\), and \((3, 4)\), find its perimeter.
For more information and examples, visit educational websites like Cuemath, Tutors.com, and Vedantu.
READ MORE:
Introduction
To find the perimeter of a quadrilateral, you need to sum the lengths of all four of its sides. This principle applies to all types of quadrilaterals, including rectangles, squares, trapezoids, and irregular quadrilaterals. The formula to calculate the perimeter is straightforward: \( P = a + b + c + d \), where \( a, b, c, \) and \( d \) are the lengths of the sides. Below, we outline the steps and provide examples to help you understand how to find the perimeter of different types of quadrilaterals.
- Identify and measure all four sides of the quadrilateral.
- Apply the perimeter formula: \( P = a + b + c + d \).
- Add the side lengths to get the total perimeter.
Let's look at some specific examples:
- For a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \), the perimeter is calculated as \( P = 2(l + w) \).
- For a square with side length \( s \), the perimeter is \( P = 4s \).
- For a trapezoid with sides \( a, b, c, \) and \( d \), the perimeter is \( P = a + b + c + d \).
- For an irregular quadrilateral, simply add the lengths of all four sides.
By following these steps, you can easily find the perimeter of any quadrilateral, ensuring accurate results whether you are dealing with simple or complex shapes.
Basic Formula
The perimeter of a quadrilateral is the total distance around the shape, which can be calculated by summing the lengths of all its sides. The basic formula for finding the perimeter of a quadrilateral is:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d
\]
where \(a\), \(b\), \(c\), and \(d\) are the lengths of the sides of the quadrilateral.
For specific types of quadrilaterals, the formula can be simplified. Here are some examples:
- Square: All sides are equal, so the formula becomes \(4a\).
- Rectangle: Opposite sides are equal, so the formula is \(2(l + w)\), where \(l\) is the length and \(w\) is the width.
- Rhombus: All sides are equal, so the formula is \(4a\).
- Parallelogram: Opposite sides are equal, so the formula is \(2(a + b)\).
For irregular quadrilaterals, where all sides have different lengths, the general formula is used. If the coordinates of the vertices are known, the perimeter can be calculated using the distance formula for each side:
\[
D = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}
\]
Summing the distances for all four sides gives the perimeter.
For example, if the coordinates of the quadrilateral are \((x_1, y_1)\), \((x_2, y_2)\), \((x_3, y_3)\), and \((x_4, y_4)\), you would calculate:
- \(D_{12} = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}\)
- \(D_{23} = \sqrt{(x_3 - x_2)^2 + (y_3 - y_2)^2}\)
- \(D_{34} = \sqrt{(x_4 - x_3)^2 + (y_4 - y_3)^2}\)
- \(D_{41} = \sqrt{(x_1 - x_4)^2 + (y_1 - y_4)^2}\)
Then, the perimeter \(P\) is the sum of these distances:
\[
P = D_{12} + D_{23} + D_{34} + D_{41}
\]
This method ensures accurate calculation of the perimeter for any quadrilateral, whether it is regular or irregular.
Finding the Perimeter of Special Quadrilaterals
Special quadrilaterals, such as squares, rectangles, rhombuses, trapezoids, and kites, each have unique properties that simplify the process of finding their perimeter. Below are step-by-step methods to determine the perimeter for each type:
- Square:
A square has four equal sides. To find the perimeter, multiply the length of one side by four.
Formula: \( P = 4a \)
- Rectangle:
A rectangle has opposite sides that are equal. The perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides.
Formula: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Rhombus:
A rhombus has four sides of equal length. The perimeter is simply four times the length of one side.
Formula: \( P = 4a \)
- Trapezoid:
A trapezoid has one pair of parallel sides. To find the perimeter, add the lengths of all four sides.
Formula: \( P = a + b + c + d \)
- Kite:
A kite has two pairs of adjacent sides that are equal. The perimeter is the sum of all side lengths.
Formula: \( P = 2(a + b) \)
Cách xác định chu vi của tứ giác bằng công thức khoảng cách của bốn điểm