Topic how to calculate area from perimeter: Understanding how to calculate area from perimeter is essential for solving various geometric problems. This guide will provide clear steps and examples to help you master the concept. Whether you're dealing with squares, rectangles, circles, or other shapes, knowing the relationship between area and perimeter will enhance your mathematical skills and practical applications.
Table of Content
- How to Calculate Area from Perimeter
- Introduction
- Definitions
- Formulas and Calculations
- Practical Applications
- Advanced Topics
- Practice and Exercises
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- YOUTUBE: Hãy xem cách tính chu vi và diện tích của một hình hợp thành với ví dụ về hình L trong bài giảng này. Hình hợp thành là một khái niệm quan trọng trong hình học, và việc biết cách tính chu vi và diện tích của chúng là rất hữu ích.
How to Calculate Area from Perimeter
Calculating the area of a shape from its perimeter involves different formulas depending on the type of shape. Below, we outline the methods for several common shapes.
Formulas for Common Shapes
-
Rectangle
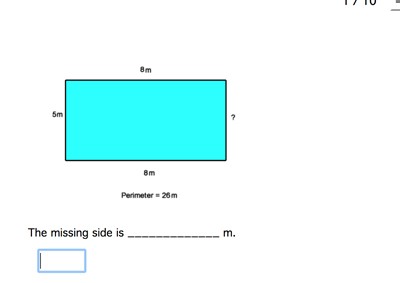
Given a rectangle with a perimeter \( P \) and side lengths \( l \) (length) and \( w \) (width):
- Perimeter formula: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Solve for one variable in terms of the perimeter and the other variable: \( l + w = \frac{P}{2} \)
- If you know the perimeter and one side, you can find the other side.
- Area formula: \( A = l \times w \)
-
Square
For a square with a perimeter \( P \) and side length \( a \):
- Perimeter formula: \( P = 4a \)
- Solve for side length: \( a = \frac{P}{4} \)
- Area formula: \( A = a^2 \)
-
Triangle
For a triangle with a perimeter \( P \) and side lengths \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \):
- Perimeter formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
- If you know the perimeter and two sides, you can find the third side.
- Area formulas vary based on the type of triangle. For example, for a right triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \).
-
Circle
For a circle with a circumference \( C \) and radius \( r \):
- Circumference formula: \( C = 2\pi r \)
- Solve for radius: \( r = \frac{C}{2\pi} \)
- Area formula: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
Example Calculations
| Shape | Perimeter | Calculation | Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Square | 20 units |
|
25 square units |
| Rectangle | 30 units (length = 10 units) |
|
50 square units |
Conclusion
The methods to calculate the area from the perimeter vary depending on the shape. By using the appropriate formulas, you can determine the area once you have the perimeter and necessary dimensions.

READ MORE:
Introduction
Calculating the area from the perimeter can be a useful skill in various fields such as mathematics, architecture, and engineering. Understanding the relationship between these two measurements for different geometric shapes is essential. This guide will provide a step-by-step approach to finding the area from the perimeter for various shapes, including squares, rectangles, circles, and triangles. Each shape has specific formulas that make the process straightforward and easy to follow.
- Square
- Rectangle
- Circle
- Triangle
By mastering these techniques, you can efficiently determine the area when given the perimeter, enhancing your problem-solving skills and mathematical understanding.
Definitions
Understanding how to calculate area from perimeter requires a grasp of basic geometry concepts. Below are the definitions of key terms used in these calculations.
- Area: The area of a shape is the measure of the space inside it. For two-dimensional shapes, this is typically measured in square units (e.g., square meters, square centimeters).
- Perimeter: The perimeter is the total length of all the sides of a shape. It is the distance around the boundary of a shape, measured in linear units (e.g., meters, centimeters).
| Shape | Area Formula | Perimeter Formula |
| Square | A = a^2 | P = 4a |
| Rectangle | A = l × w | P = 2(l + w) |
| Triangle | A = (1/2) × b × h | P = a + b + c |
| Circle | A = πr^2 | P = 2πr |
In these formulas, a represents the side length of a square, l and w are the length and width of a rectangle, b and h are the base and height of a triangle, and r is the radius of a circle.
Formulas and Calculations
To calculate the area from the perimeter, you need specific formulas and calculations based on the shape you are dealing with. Here are detailed steps and examples:
- Rectangle:
- Perimeter: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Area: \( A = l \times w \)
- Example Calculation:
- Given perimeter \( P = 20 \) and length \( l = 6 \), find width \( w \):
- Step 1: \( 20 = 2(6 + w) \)
- Step 2: \( 20 = 12 + 2w \)
- Step 3: \( 8 = 2w \)
- Step 4: \( w = 4 \)
- Area \( A = 6 \times 4 = 24 \)
- Square:
- Perimeter: \( P = 4s \)
- Area: \( A = s^2 \)
- Example Calculation:
- Given perimeter \( P = 16 \), find side \( s \):
- Step 1: \( 16 = 4s \)
- Step 2: \( s = 4 \)
- Area \( A = 4^2 = 16 \)
- Circle:
- Perimeter (Circumference): \( C = 2\pi r \)
- Area: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
- Example Calculation:
- Given circumference \( C = 31.4 \), find radius \( r \):
- Step 1: \( 31.4 = 2\pi r \)
- Step 2: \( r = \frac{31.4}{2\pi} \approx 5 \)
- Area \( A = \pi \times 5^2 \approx 78.5 \)
- Triangle:
- Perimeter: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Area (using Heron's formula):
- Step 1: Calculate semi-perimeter \( s = \frac{P}{2} \)
- Step 2: \( A = \sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \)
- Example Calculation:
- Given sides \( a = 3, b = 4, c = 5 \), find perimeter \( P \):
- Step 1: \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \)
- Step 2: Calculate semi-perimeter \( s = \frac{12}{2} = 6 \)
- Step 3: \( A = \sqrt{6(6-3)(6-4)(6-5)} = \sqrt{6 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1} = \sqrt{36} = 6 \)
Practical Applications
Understanding the relationship between perimeter and area has numerous practical applications in various fields. Here are some examples:
- Architectural Design: Calculating the area from the perimeter helps architects optimize space in building layouts and ensure efficient use of materials.
- Landscaping: Landscapers use these calculations to determine the amount of sod, mulch, or gravel needed for gardens and outdoor spaces.
- Urban Planning: City planners utilize area calculations to design parks, public spaces, and infrastructure while adhering to space constraints.
- Agriculture: Farmers calculate areas to efficiently plan the sowing of crops and the use of irrigation systems.
- Interior Design: Interior designers use area measurements to plan furniture arrangements and the use of space in homes and offices.
By mastering these calculations, professionals across these industries can improve accuracy, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in their projects.

Advanced Topics
Exploring advanced topics in calculating the area from the perimeter involves understanding more complex geometric shapes and their properties. This section delves into various advanced concepts and methodologies used in higher geometry.
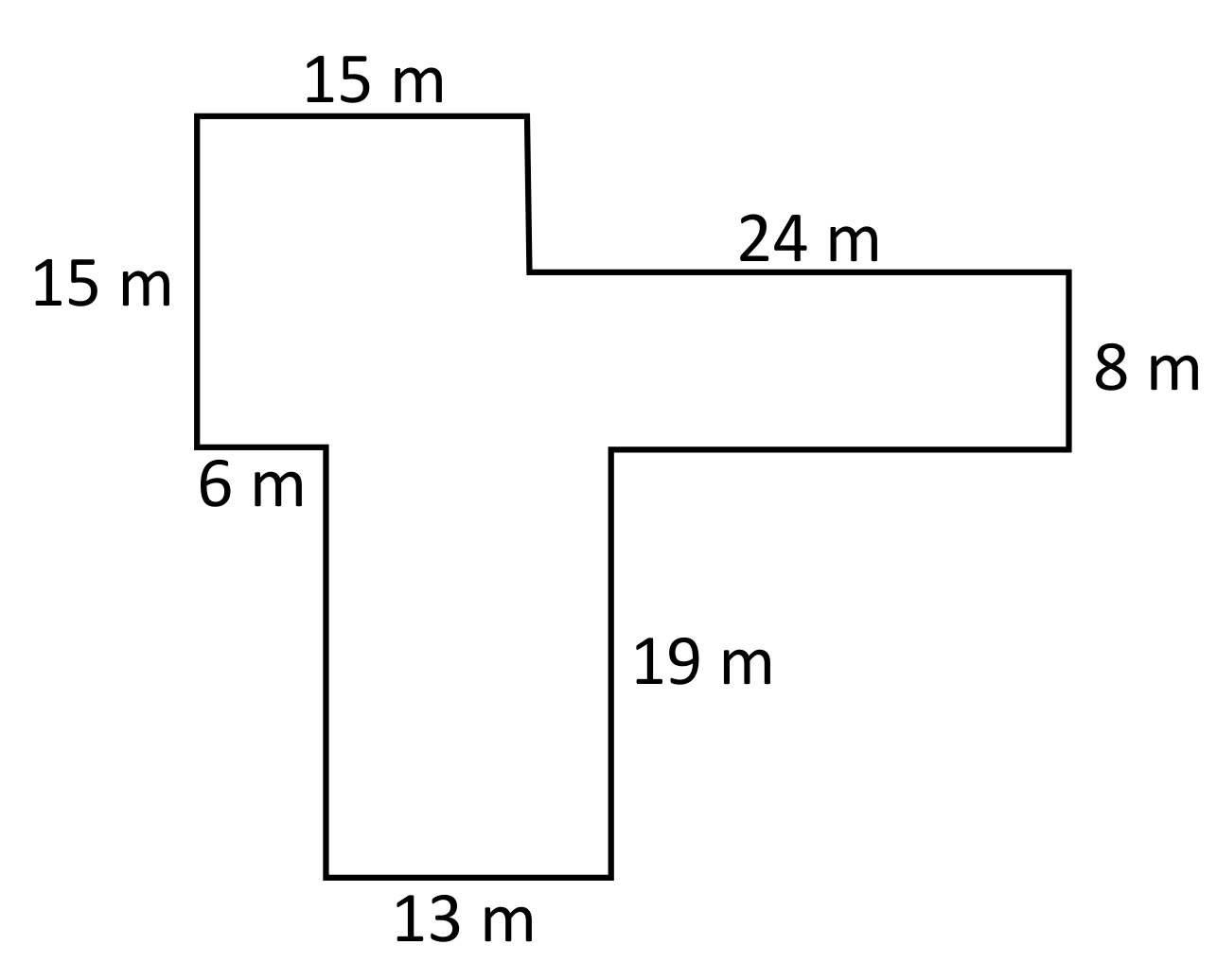
Calculating Area of Irregular Shapes
For irregular shapes, the process often involves breaking the shape down into simpler, regular shapes whose areas can be calculated and then summed up.
- Decomposition Method: Splitting the irregular shape into a combination of rectangles, triangles, or other polygons.
- Integration Method: Using integral calculus to find the area under a curve, suitable for more complex shapes.
Using the Perimeter for Specific Shapes
Certain shapes allow for direct calculation of area from perimeter under specific conditions:
- Circles: For a circle, if the perimeter (circumference) is known, the radius can be found using the formula \( P = 2\pi r \), and subsequently, the area \( A = \pi r^2 \).
- Regular Polygons: For regular polygons (e.g., equilateral triangles, squares), knowing the perimeter can help in finding the side length, which can then be used to find the area.
Advanced Geometric Theorems
Several advanced theorems and principles can be applied to derive area from perimeter:
- Pick's Theorem: Used for finding the area of simple polygons whose vertices are points on a lattice grid.
- Heron's Formula: Applied to find the area of a triangle when the lengths of all three sides are known.
- Brahmagupta's Formula: Used for cyclic quadrilaterals (quadrilaterals inscribed in a circle).
Application in Real-Life Problems
Understanding these advanced topics is essential for solving complex real-life problems, such as architectural design, land surveying, and various fields of engineering:
- Designing structures with specific area requirements while maintaining boundary constraints.
- Calculating land areas for agricultural or development purposes based on perimeter fencing.
Practice and Exercises
To master the concepts of calculating the area from the perimeter, practicing with various exercises is essential. Below are some exercises and practice problems that will help reinforce your understanding:
- Calculate the area of a square with a perimeter of 20 cm.
- Given a rectangle with a perimeter of 30 cm and a length of 10 cm, find the area.
- A triangle has sides measuring 5 cm, 12 cm, and 13 cm. Calculate its perimeter and area.
-
Square Example:
Perimeter: \( P = 4 \times \text{side} \)
If \( P = 20 \, \text{cm} \), then \( \text{side} = \frac{P}{4} = 5 \, \text{cm} \)
Area: \( A = \text{side}^2 = 5^2 = 25 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
-
Rectangle Example:
Perimeter: \( P = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \)
If \( P = 30 \, \text{cm} \) and \( \text{length} = 10 \, \text{cm} \), then
\( 30 = 2 \times (10 + \text{width}) \)
\( \text{width} = \frac{30}{2} - 10 = 5 \, \text{cm} \)
Area: \( A = \text{length} \times \text{width} = 10 \times 5 = 50 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
-
Triangle Example:
Perimeter: \( P = a + b + c = 5 + 12 + 13 = 30 \, \text{cm} \)
Using Heron's formula to find the area:
First, calculate the semi-perimeter: \( s = \frac{P}{2} = 15 \, \text{cm} \)
Area: \( A = \sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} = \sqrt{15(15-5)(15-12)(15-13)} \)
\( A = \sqrt{15 \times 10 \times 3 \times 2} = \sqrt{900} = 30 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
Regular practice with a variety of shapes and sizes will help you become proficient in calculating areas from perimeters. These exercises can be adjusted for different levels of difficulty by changing the dimensions and types of shapes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
How can I calculate the area from the perimeter of a shape?
To calculate the area from the perimeter of a shape, you need additional information about the shape. The perimeter alone does not provide enough information to determine the area of a shape because different shapes with the same perimeter can have different areas. For example, a square and a rectangle can have the same perimeter but different areas. You will typically need either the dimensions of the shape (e.g., length and width for a rectangle) or additional constraints to solve for the area.
Hãy xem cách tính chu vi và diện tích của một hình hợp thành với ví dụ về hình L trong bài giảng này. Hình hợp thành là một khái niệm quan trọng trong hình học, và việc biết cách tính chu vi và diện tích của chúng là rất hữu ích.
Tìm Chu Vi và Diện Tích của Hình Hợp thành | Ví dụ hình L | Hình Học | Toán cùng Thầy J
READ MORE:
Hãy khám phá về diện tích và chu vi trong bài giảng này. Hiểu rõ về cách tính toán diện tích và chu vi của các hình học sẽ giúp bạn áp dụng chúng vào các vấn đề thực tế và tối ưu hóa kết quả.
Diện Tích và Chu Vi