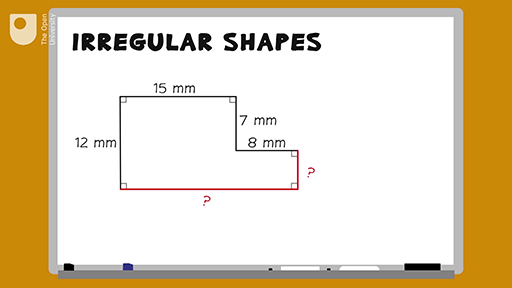
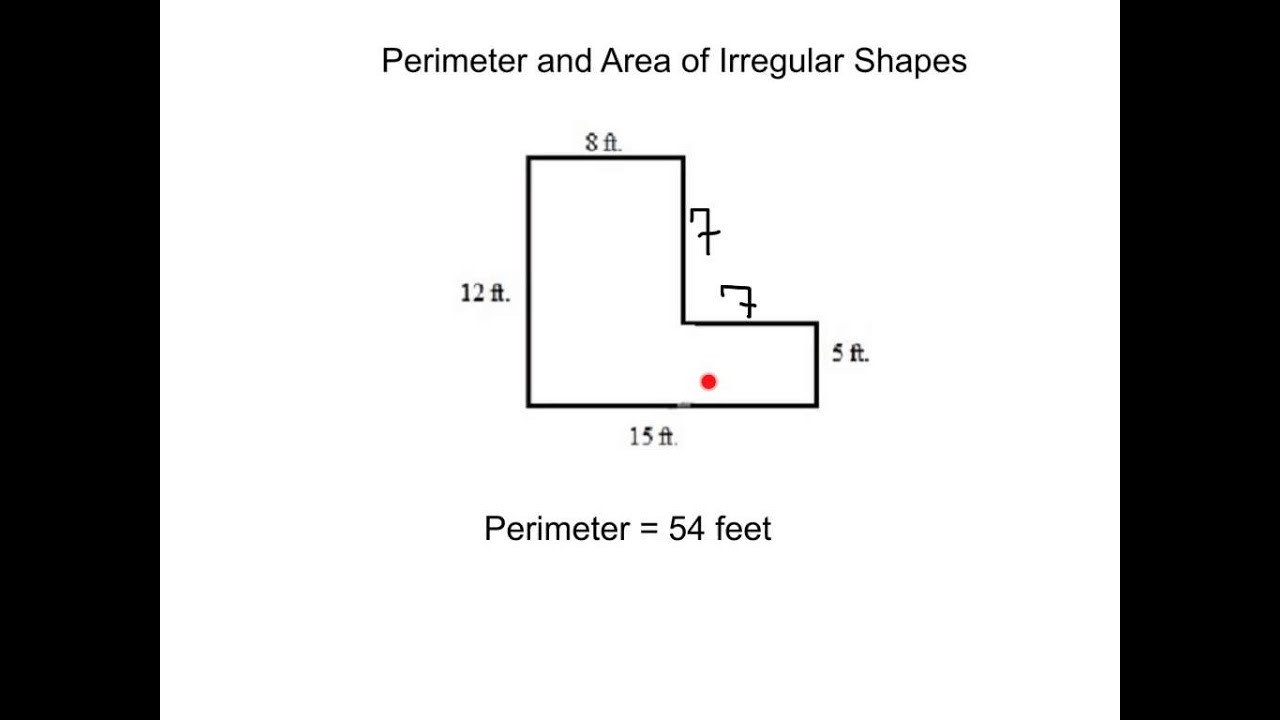
Topic finding area and perimeter of irregular shapes: Unlock the secrets to accurately finding the area and perimeter of irregular shapes with our detailed guide. Whether you're a student, teacher, or geometry enthusiast, this article provides step-by-step methods, practical examples, and useful tips to master these essential geometry skills. Start your journey to geometric precision today!
Table of Content
- Area and Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
- Introduction to Irregular Shapes
- Understanding Irregular Shapes
- Basic Geometry Concepts
- Types of Irregular Shapes
- Tools and Materials Needed
- Measuring Irregular Shapes
- Methods for Finding Area
- Calculating Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
- Practical Applications
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Advanced Techniques
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Conclusion and Summary
- Further Reading and Resources
- YOUTUBE:
Area and Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
Irregular shapes can pose a challenge when it comes to calculating their area and perimeter. Here's a synthesis of information on how to approach this:
1. Break It Down into Smaller Shapes
One approach is to break down the irregular shape into smaller, simpler shapes such as rectangles, triangles, or circles. Then, calculate the area and perimeter of each smaller shape separately and add them up.
2. Approximation Methods
For very irregular shapes, approximation methods like the grid method or using a series of rectangles with progressively smaller widths can be employed. While not as precise as other methods, they can provide a reasonable estimate.
3. Calculating Area
To calculate the area of irregular shapes, various formulas can be used depending on the shape. For example:
- - For triangles: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- - For circles: \( \text{Area} = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \)
- - For irregular polygons: methods such as the shoelace formula or breaking it down into triangles can be used.
4. Calculating Perimeter
The perimeter of an irregular shape is the total length of its boundary. This can be calculated by adding up the lengths of all its sides. For complex shapes, this may involve breaking it down into simpler components and summing up their perimeters.
5. Use of Technology
Various software tools and apps are available that can assist in calculating the area and perimeter of irregular shapes. These tools often allow you to input the coordinates or draw the shape, and then automatically compute its properties.
6. Practice and Visualization
Practicing with different irregular shapes and visualizing how they can be broken down into simpler components can improve your ability to calculate their area and perimeter accurately.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Irregular Shapes
Irregular shapes, unlike regular polygons, do not have equal sides or angles. These shapes often appear in real-life scenarios, making it essential to understand how to calculate their area and perimeter accurately. Irregular shapes can be complex, but by breaking them down into smaller, more manageable sections, you can determine their measurements with precision.
Here is a step-by-step guide to understanding and measuring irregular shapes:
- Identify the Shape: Look at the shape and identify its irregularity. Note the lengths of sides and angles if available.
- Divide into Simpler Shapes: Break down the irregular shape into simpler shapes such as triangles, rectangles, and trapezoids. This decomposition makes it easier to calculate the area and perimeter.
- Calculate the Area: Use appropriate formulas for each of the simpler shapes and sum their areas.
- Triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Rectangle: \( A = \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
- Trapezoid: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times (\text{base}_1 + \text{base}_2) \times \text{height} \)
- Calculate the Perimeter: Add up the lengths of all the sides of the irregular shape. For shapes broken into simpler components, sum the perimeters of these components.
- Use Graph Paper or Software: For highly irregular shapes, graph paper can help estimate the area by counting squares. Software tools can also provide precise measurements using digital methods.
Understanding irregular shapes enhances your spatial awareness and geometric problem-solving skills. Practice with different shapes to master these calculations.
Understanding Irregular Shapes
Irregular shapes are figures that do not conform to standard geometric rules. Unlike regular polygons, they have sides and angles of varying lengths and degrees, making their measurement more complex. To effectively work with irregular shapes, it's crucial to understand their properties and characteristics.
Here is a detailed approach to understanding irregular shapes:
- Identify Key Features: Examine the shape to identify its sides, angles, and any notable features. This initial analysis helps in planning how to break down the shape for measurement.
- Classification: Determine if the shape can be classified under any specific types of irregular shapes, such as polygons with unequal sides, composite shapes, or natural forms.
- Breaking Down the Shape: Decompose the irregular shape into simpler components. Common methods include:
- Triangulation: Dividing the shape into multiple triangles, which can be easily measured.
- Rectangular Approximation: Using rectangles to approximate the areas of parts of the shape.
- Polygonal Approximation: Approximating the shape with a polygon whose sides closely follow the outline of the irregular shape.
- Calculating Area: For each of the simpler shapes obtained:
- Triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Rectangle: \( A = \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
- Trapezoid: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times (\text{base}_1 + \text{base}_2) \times \text{height} \)
- Calculating Perimeter: Measure the length of each side of the shape and sum them up. If the shape is decomposed into simpler shapes, ensure all external sides are included in the total perimeter.
- Using Technology: Employ digital tools and software for precise measurement and visualization of complex irregular shapes. These tools can provide more accurate results, especially for highly irregular or intricate shapes.
By breaking down and analyzing the components of irregular shapes, you can accurately determine their area and perimeter. This methodical approach simplifies the process and enhances your geometric skills.
Basic Geometry Concepts
Understanding basic geometry concepts is crucial for accurately finding the area and perimeter of irregular shapes. These foundational concepts provide the tools needed to break down and analyze complex figures.
Here are key geometry concepts to master:
- Points and Lines:
- Point: A point represents a precise location in space with no dimensions, often labeled with a letter.
- Line: A line is a straight one-dimensional figure that extends infinitely in both directions, defined by two points.
- Line Segment: A part of a line bounded by two distinct endpoints.
- Angles:
- Angle: Formed by two rays (sides) with a common endpoint (vertex). Measured in degrees.
- Types of Angles:
- Acute: Less than 90°
- Right: Exactly 90°
- Obtuse: Greater than 90° but less than 180°
- Straight: Exactly 180°
- Polygons:
- Polygon: A closed figure with three or more straight sides. Examples include triangles, rectangles, and pentagons.
- Regular Polygon: All sides and angles are equal.
- Irregular Polygon: Sides and angles are not equal.
- Perimeter:
- Definition: The perimeter is the total length of all the sides of a polygon.
- Calculation: Sum the lengths of all sides.
\( P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} \text{side}_i \)
- Area:
- Definition: The area is the measure of the space inside a two-dimensional shape.
- Basic Formulas:
- Triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Rectangle: \( A = \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
- Circle: \( A = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \)
- Decomposition:
- Definition: Breaking down complex shapes into simpler components (triangles, rectangles, etc.) for easier calculation.
- Method: Identify simpler shapes within the irregular shape and use known formulas to calculate the area and perimeter of each component.
Mastering these basic geometry concepts provides a solid foundation for tackling more complex problems, such as finding the area and perimeter of irregular shapes. Practice applying these concepts to build confidence and accuracy in your calculations.
Types of Irregular Shapes
Irregular shapes come in various forms, each with unique characteristics that require different approaches for measuring area and perimeter. Understanding the types of irregular shapes helps in selecting the right methods for their calculation.
Here are the common types of irregular shapes:
- Irregular Polygons:
- Definition: Polygons with sides and angles of different lengths and measures.
- Examples:
- Irregular Triangles: Triangles where no sides are equal.
- Irregular Quadrilaterals: Four-sided polygons with unequal sides, such as trapezoids and kites.
- Irregular Pentagons: Five-sided polygons with varying side lengths and angles.
- Composite Shapes:
- Definition: Shapes that are a combination of two or more simple shapes (e.g., triangles, rectangles, circles).
- Examples:
- Shape Combinations: A shape that combines a rectangle and a semicircle.
- Complex Figures: L-shaped or T-shaped figures formed by combining multiple rectangles or other polygons.
- Natural Irregular Shapes:
- Definition: Shapes found in nature that do not have regular geometric properties.
- Examples:
- Leaf Shapes: Leaves with varied edges and contours.
- Rocks and Stones: Irregularly shaped rocks with no definite geometric pattern.
- Lakes and Ponds: Bodies of water with irregular shorelines.
To effectively work with these types of irregular shapes, follow these steps:
- Identify the Shape Type: Determine which category the irregular shape belongs to (polygon, composite, or natural).
- Break Down the Shape: Decompose the shape into simpler components if possible, using triangles, rectangles, and circles.
- Apply Appropriate Formulas: Use known formulas for the simpler shapes to calculate the area and perimeter.
- Triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Rectangle: \( A = \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
- Circle (for composite shapes): \( A = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \)
- Sum the Measurements: Add the areas of all the simpler shapes to find the total area. For the perimeter, add the lengths of all the outer sides.
Understanding the different types of irregular shapes and their properties allows for more accurate and efficient calculation of their area and perimeter.
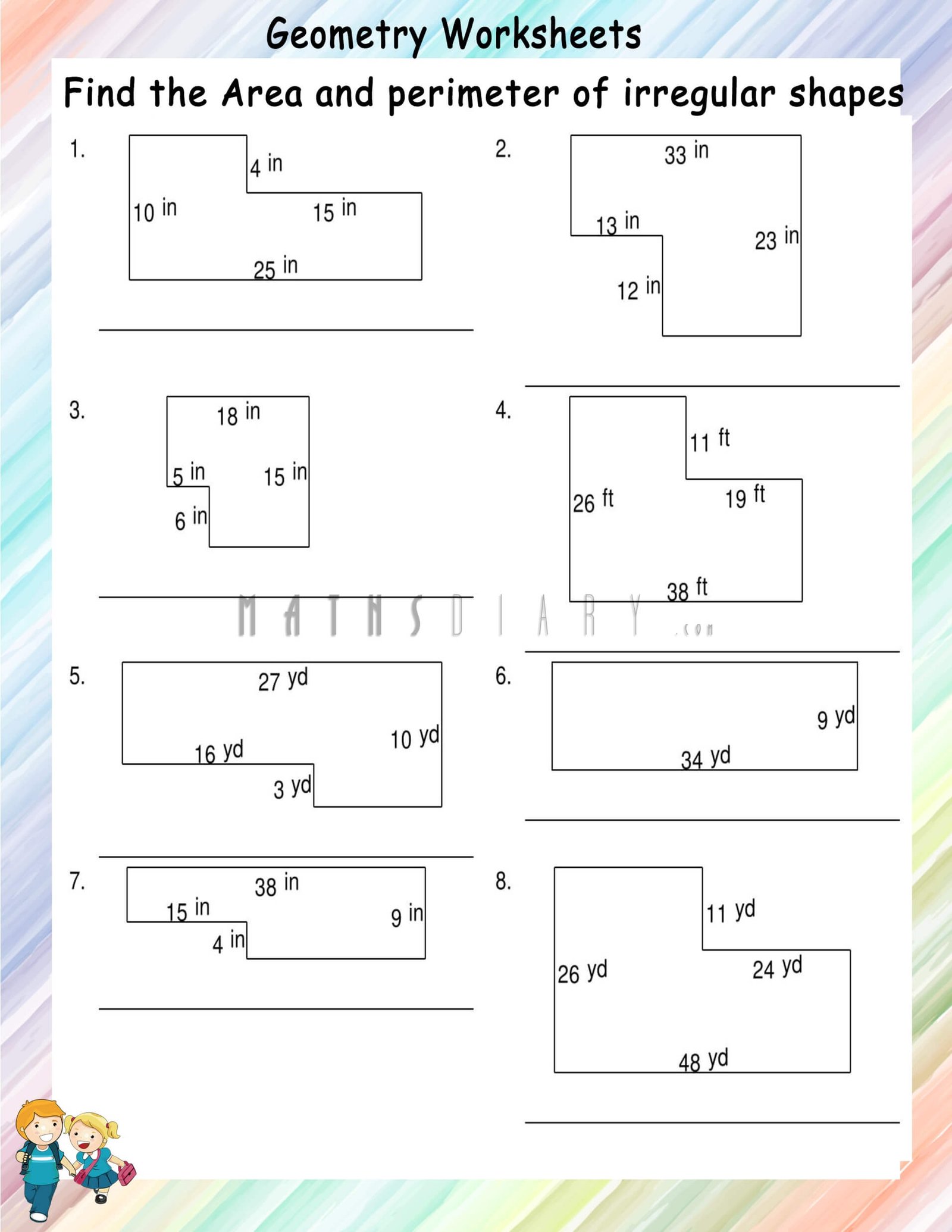
Tools and Materials Needed
When embarking on the journey of finding the area and perimeter of irregular shapes, having the right tools and materials is essential for accurate measurements and calculations. Here's a comprehensive list of what you'll need:
- Measuring tape or ruler: For measuring the dimensions of the irregular shape.
- Graph paper: Useful for sketching the irregular shape and facilitating calculations, especially when using the graph paper method.
- Calculator: Necessary for performing complex calculations, especially when employing advanced techniques like the calculus approach.
- Pencil and eraser: Essential for drawing and making adjustments to sketches.
- Compass: Helpful for drawing circles or arcs that may be present in the irregular shape.
- Protractor: Useful for measuring angles in the irregular shape, particularly when using the coordinate geometry method.
- String: Used in the string method for calculating perimeter, where it is wrapped around the irregular shape to measure its boundary.
- Scissors: Required for cutting string in the string method.
- Computer or mobile device with internet access: Beneficial for utilizing software tools for advanced techniques and accessing further reading and resources.
Measuring Irregular Shapes
Measuring irregular shapes can be a bit more challenging than measuring regular shapes due to their non-uniformity. However, with the right techniques and tools, it can be done accurately. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Identify the Shape: Before measuring, identify the type of irregular shape you're dealing with. Is it a polygon, a curved shape, or a combination of both?
- Break It Down: If the irregular shape is complex, consider breaking it down into simpler shapes that you can measure more easily. For example, you might decompose it into rectangles, triangles, or circles.
- Use a Measuring Tape or Ruler: For linear measurements, use a measuring tape or ruler to measure the lengths of the sides or segments of the shape.
- Estimate Curved Sections: If the shape has curved sections, you may need to estimate their lengths using a flexible measuring tape or by comparing them to straight segments of known lengths.
- Apply Geometric Formulas: Once you have the measurements, apply the appropriate geometric formulas to calculate the area and perimeter of each component shape. For example, for a rectangle, the area is calculated by multiplying its length by its width.
- Sum Up: Finally, sum up the areas and perimeters of all the component shapes to find the total area and perimeter of the irregular shape.
By following these steps and using precision in measurements, you can accurately determine the area and perimeter of irregular shapes, opening doors to various applications in fields such as architecture, engineering, and design.
Methods for Finding Area
When it comes to determining the area of irregular shapes, several methods can be employed, each suited to different scenarios. Here are some effective techniques:
- Using Graph Paper: Sketch the irregular shape on graph paper and count the number of squares it covers. Each square represents a unit area, and by counting the squares, you can approximate the total area.
- Decomposition Method: Break down the irregular shape into simpler, regular shapes (like triangles, rectangles, or circles) whose areas can be easily calculated. Then, sum up the areas of these component shapes to find the total area.
- Using Coordinate Geometry: If the irregular shape can be represented by coordinates on a graph, you can use geometric formulas to calculate its area. For example, you can apply the shoelace formula to find the area of a polygon with vertices given by coordinates.
- Trapezoidal Rule: Approximate the irregular shape by a series of trapezoids whose areas can be easily calculated. Then, sum up the areas of these trapezoids to estimate the total area.
- Calculus Approach: For more complex shapes, you can use calculus techniques such as integration to find the area under a curve. This method is particularly useful when dealing with curved or irregular boundaries.
By utilizing these methods, you can accurately determine the area of irregular shapes, enabling precise calculations and analysis in various fields such as mathematics, engineering, and architecture.
Calculating Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
Measuring the perimeter of irregular shapes involves determining the total length of their boundaries. Here are some methods to accomplish this:
- Summing Side Lengths: Measure each side of the irregular shape using a ruler or measuring tape, then sum up these lengths to find the perimeter.
- Using String Method: Take a piece of string and wrap it around the boundary of the irregular shape, making sure it follows the shape's contours. Then, measure the length of the string to determine the perimeter.
By employing these techniques, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of irregular shapes, which is crucial for various applications in fields such as geometry, architecture, and land surveying.

Practical Applications
The knowledge of finding the area and perimeter of irregular shapes has numerous practical applications across various fields. Here are some notable ones:
- Architecture and Construction: Architects and civil engineers often need to calculate the area and perimeter of irregularly shaped plots of land for designing buildings and infrastructure.
- Land Surveying: Surveyors use these calculations to define property boundaries, assess land for development, and create accurate maps.
- Geography and Cartography: Geographers and cartographers employ these concepts to measure the area and perimeter of geographic features like lakes, forests, and mountain ranges.
- Physics and Engineering: In physics and engineering, understanding irregular shapes' dimensions is crucial for designing components, analyzing structures' strength, and determining material quantities.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers use these calculations to create aesthetically pleasing compositions, determine canvas sizes, and plan spatial arrangements.
- Biology and Ecology: Biologists and ecologists measure the area and perimeter of habitats, study population distributions, and assess ecological impacts.
These practical applications highlight the importance of mastering the techniques for finding the area and perimeter of irregular shapes, as they are fundamental skills with broad relevance across numerous disciplines.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
While finding the area and perimeter of irregular shapes, it's common to encounter certain pitfalls. Here's how to steer clear of them:
- Incorrect Measurements: Ensure precision in measurements to avoid inaccuracies in the final calculations. Double-check measurements and use appropriate tools for accurate results.
- Ignoring Curved Sections: Neglecting to account for curved sections can lead to significant errors in area and perimeter calculations. Take special care to measure and include these sections accurately.
- Improper Decomposition: When decomposing irregular shapes into simpler components, ensure that the chosen shapes accurately represent the original shape. Incorrect decomposition can result in incorrect area and perimeter calculations.
- Forgetting Units: Always include units (such as square units for area and linear units for perimeter) in your calculations and final results to provide context and clarity.
- Overlooking Adjustments: In methods like the string method or using graph paper, failing to make necessary adjustments for scale or grid size can lead to inaccuracies. Be mindful of any adjustments needed in your calculations.
By being vigilant and mindful of these common mistakes, you can ensure accurate and reliable calculations when finding the area and perimeter of irregular shapes, leading to better outcomes in various applications.
Advanced Techniques
For those seeking to delve deeper into the intricacies of finding the area and perimeter of irregular shapes, several advanced techniques offer sophisticated solutions:
- Using Software Tools: Utilize specialized software applications designed for geometric calculations. These tools offer advanced algorithms and visualization features to accurately determine the area and perimeter of complex irregular shapes.
- 3D Irregular Shapes: Extend your understanding to three-dimensional irregular shapes, where calculating volume and surface area becomes paramount. Advanced techniques such as integration in calculus can be applied to determine these properties.
By exploring these advanced techniques, enthusiasts and professionals can push the boundaries of their knowledge and capabilities in analyzing irregular shapes, unlocking new insights and possibilities in diverse fields.
Examples and Practice Problems
Practice makes perfect when it comes to mastering the concepts of finding the area and perimeter of irregular shapes. Here are some examples and practice problems to sharpen your skills:
- Example 1: Calculate the area and perimeter of a irregular polygon with given side lengths and angles.
- Example 2: Determine the area and perimeter of a irregular shape composed of rectangles and triangles.
- Practice Problem 1: Given the dimensions of a irregular shape, find its area using the decomposition method.
- Practice Problem 2: Using the trapezoidal rule, estimate the area of a irregular shape with curved boundaries.
- Practice Problem 3: Measure the perimeter of a irregular shape using the string method and compare it with other methods for validation.
By working through these examples and practice problems, you'll gain confidence and proficiency in tackling various irregular shapes, preparing you for real-world applications and challenges.
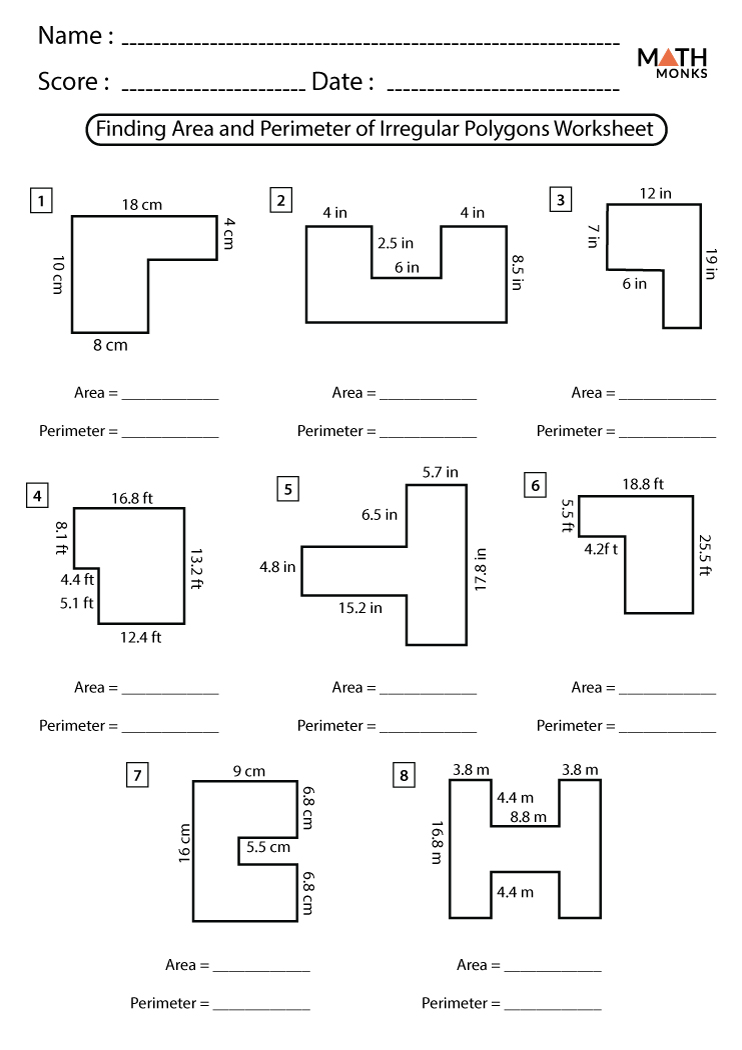
Conclusion and Summary
In conclusion, the ability to find the area and perimeter of irregular shapes is a valuable skill with broad applications across various fields. Throughout this guide, we've explored numerous methods, techniques, and practical considerations for accurately calculating these properties.
From basic geometry concepts to advanced calculus approaches, there are multiple tools and strategies available to tackle irregular shapes effectively. By understanding the nuances of measurement, decomposition, and calculation, individuals can navigate the complexities of irregular shapes with confidence and precision.
Moreover, practicing with examples and solving problems enhances proficiency and fosters a deeper understanding of the concepts involved. Whether you're an architect designing buildings, a biologist studying ecosystems, or a student learning mathematical principles, mastering the fundamentals of irregular shapes is essential for success.
In summary, by honing your skills in finding the area and perimeter of irregular shapes, you equip yourself with valuable knowledge that can be applied in diverse contexts, driving innovation, problem-solving, and creativity.
Further Reading and Resources
For those looking to delve deeper into the methods and techniques for finding the area and perimeter of irregular shapes, the following resources provide comprehensive guides, examples, and practice problems:
-
This resource explains various methods for calculating the area of irregular shapes, including unit squares and decomposing shapes into regular polygons. It also offers practice problems and visual examples.
-
Cuemath provides detailed explanations and solved examples for calculating the area of irregular shapes. It covers techniques such as using unit squares and decomposing complex shapes into simpler ones.
-
K5 Learning offers a step-by-step guide for finding the area of irregular shapes, complete with examples and visual aids to help students understand the process.
-
Math is Fun provides an easy-to-understand guide on how to calculate the area of irregular shapes, with interactive tools and examples to enhance learning.
-
IXL offers lessons and practice problems on calculating the area of irregular shapes, making it a great resource for students looking to improve their skills through practice.
These resources should provide a solid foundation and additional practice for mastering the techniques of finding the area and perimeter of irregular shapes. Whether you're a student, teacher, or just looking to refresh your knowledge, these guides will be invaluable.
Diện tích và Chu vi của Hình dạng Bất thường - Rất nhiều Ví dụ!
READ MORE:
Tìm Chu vi và Diện tích của Hình dạng Kết hợp | Ví dụ Hình L | Hình học | Toán với Thầy J