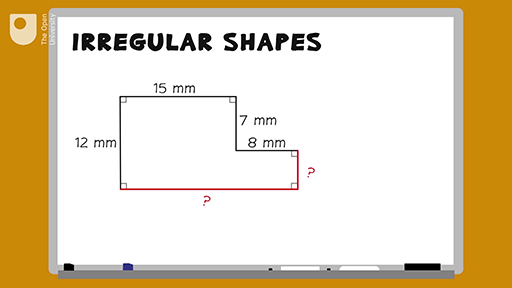
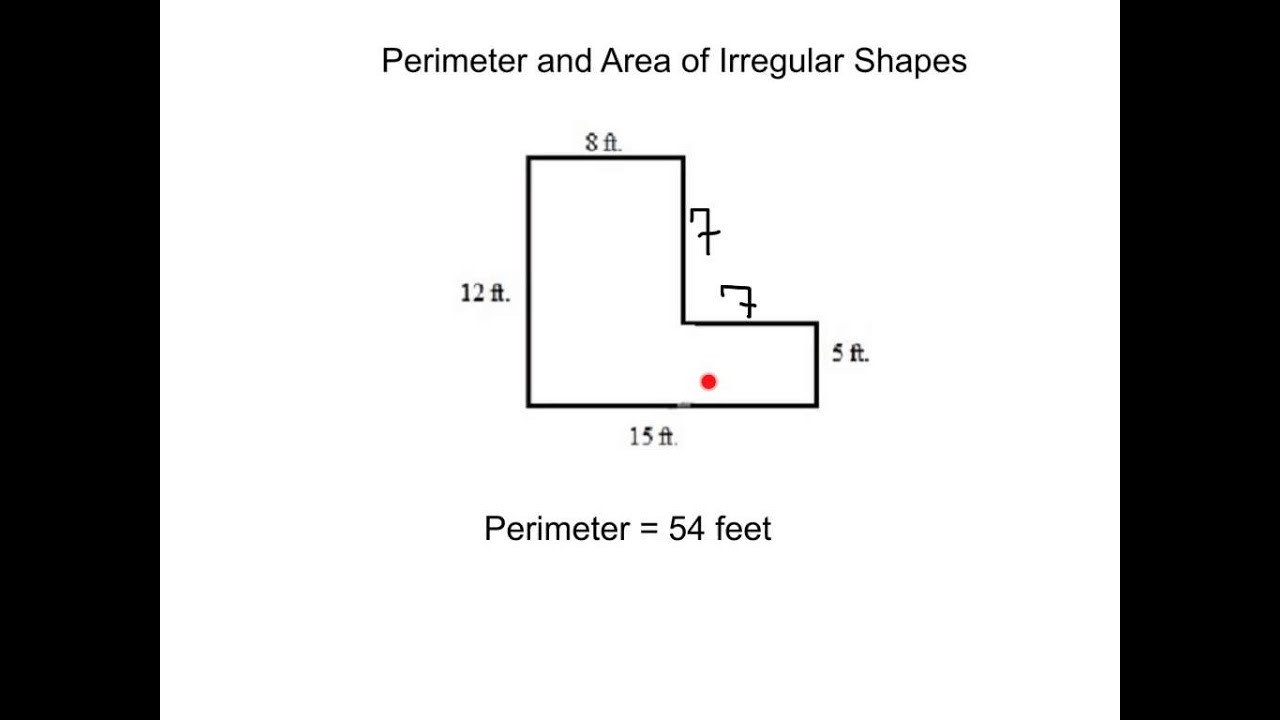
Topic how do i find the perimeter of a pentagon: Discover how to find the perimeter of a pentagon with our comprehensive guide. Learn the formulas and methods to calculate the perimeter for both regular and irregular pentagons, whether using side length, radius, or apothem. Enhance your understanding with practical examples and tips to avoid common mistakes.
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of a Pentagon
- Introduction
- Understanding Pentagons
- Types of Pentagons
- Formulas for Perimeter
- Steps to Calculate Perimeter
- Examples of Perimeter Calculation
- Using Side Length
- Using Radius
- Using Apothem
- Practical Applications
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tính chu vi ngũ giác, bao gồm các loại ngũ giác và công thức cần thiết.
How to Find the Perimeter of a Pentagon
The perimeter of a pentagon is the total length around its five sides. The method to calculate the perimeter depends on whether the pentagon is regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles are not equal).
Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon has five sides of equal length. The formula to find the perimeter (P) is:
\[
P = 5 \times s
\]
where \( s \) is the length of one side.
For example, if the side length of a regular pentagon is 7 cm:
\[
P = 5 \times 7 = 35 \, \text{cm}
\]
Irregular Pentagon
An irregular pentagon has sides of different lengths. To find the perimeter, add the lengths of all five sides:
\[
P = a + b + c + d + e
\]
where \( a, b, c, d, \) and \( e \) are the lengths of the sides.
For example, if the sides of an irregular pentagon are 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 6 cm, and 7 cm:
\[
P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 25 \, \text{cm}
\]
Using the Radius or Apothem
If the radius (r) of the circumscribed circle is known, the side length (s) can be calculated using:
\[
s = 2r \times \sin\left(\frac{180^\circ}{5}\right)
\]
If the apothem (a) is known, the side length (s) can be calculated using:
\[
s = 2a \times \tan\left(\frac{180^\circ}{5}\right)
\]
Once the side length is known, the perimeter is found using \( P = 5 \times s \).
Examples
- For a regular pentagon with a side length of 15 cm:
\[
P = 5 \times 15 = 75 \, \text{cm}
\] - For an irregular pentagon with side lengths of 2.36 cm, 4.01 cm, 3.12 cm, 3.22 cm, and 4.41 cm:
\[
P = 2.36 + 4.01 + 3.12 + 3.22 + 4.41 = 17.12 \, \text{cm}
\]
Knowing how to calculate the perimeter is essential for understanding various geometric properties and solving real-world problems.

READ MORE:
Introduction
Finding the perimeter of a pentagon involves understanding the type of pentagon you are working with. Whether it is a regular pentagon, with all sides of equal length, or an irregular pentagon, with sides of different lengths, the method to calculate the perimeter varies. This guide will walk you through the steps to determine the perimeter for both types of pentagons, using straightforward formulas and practical examples.
Understanding Pentagons
A pentagon is a five-sided polygon with five angles. The name derives from the Greek words 'pente' meaning five and 'gonia' meaning angle. Pentagons can be classified into regular and irregular forms. A regular pentagon has all sides and angles equal, while an irregular pentagon has sides and angles of varying lengths and measures.
The sum of the internal angles in a pentagon is always 540 degrees. In a regular pentagon, each internal angle measures 108 degrees, and each exterior angle measures 72 degrees. A pentagon also has five diagonals.
The formulas for the perimeter and area of a regular pentagon are essential for various geometric calculations. The perimeter (P) of a regular pentagon is calculated using the formula:
\[ P = 5 \times a \]
where 'a' is the side length. The area (A) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ A = \frac{1}{2} \times P \times a \]
where 'P' is the perimeter and 'a' is the apothem, the perpendicular distance from the center to a side.
Understanding these properties and formulas is crucial for solving problems related to pentagons in both academic and real-life applications.
Types of Pentagons
Understanding the different types of pentagons is essential for various mathematical calculations, including finding their perimeter. A pentagon, by definition, is a five-sided polygon. There are two main types of pentagons:
- Regular Pentagon: All five sides and angles are equal. The interior angles are each 108 degrees.
- Irregular Pentagon: The sides and angles are not necessarily equal. Each side and angle can vary in length and degree.
Here is a more detailed breakdown of these types:
| Type | Characteristics |
| Regular Pentagon | Five equal sides and five equal angles. Symmetrical and often used in geometric problems and designs. |
| Irregular Pentagon | Five sides of different lengths and five angles of different measures. More complex to analyze and often found in real-world applications. |
In addition to these primary types, pentagons can also be classified based on the nature of their sides and angles:
- Convex Pentagon: All interior angles are less than 180 degrees, and no sides are indented.
- Concave Pentagon: At least one interior angle is greater than 180 degrees, causing at least one indentation.
Understanding these classifications helps in various geometric calculations and in appreciating the diverse applications of pentagons in both theoretical and practical contexts.
Formulas for Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a pentagon involves determining the sum of the lengths of its sides. There are several formulas you can use depending on the information available:
- Regular Pentagon: If all sides of the pentagon are equal, the perimeter (P) can be calculated using the formula: \( P = 5 \times \text{side length} \).
- Irregular Pentagon: For an irregular pentagon with different side lengths, you'll need to measure each side and then sum them up to find the perimeter.
- Using Apothem: If you know the apothem (distance from the center to a side's midpoint) and the side length, you can use the formula: \( P = 5 \times \text{side length} \).

Steps to Calculate Perimeter
- Identify the type of pentagon: Determine whether the pentagon is regular or irregular.
- Measure the sides: If it's an irregular pentagon, measure the length of each side using a ruler or measuring tape.
- Use a formula: For a regular pentagon, you can use the formula \( P = 5 \times \text{side length} \) to calculate the perimeter.
- Sum the lengths: If it's an irregular pentagon, add up the lengths of all the sides.
Examples of Perimeter Calculation
Here are some examples demonstrating how to calculate the perimeter of pentagons:
- Regular Pentagon: If all sides are equal, let's say each side measures 6 units. Using the formula \( P = 5 \times \text{side length} \), the perimeter would be \( P = 5 \times 6 = 30 \) units.
- Irregular Pentagon: Suppose an irregular pentagon has side lengths of 7, 9, 6, 8, and 5 units. To find the perimeter, add up the lengths of all sides: \( P = 7 + 9 + 6 + 8 + 5 = 35 \) units.
- Using Apothem: If the side length of a regular pentagon is 10 units and the apothem (distance from the center to a side's midpoint) is 7 units, you can use the formula \( P = 5 \times \text{side length} \) to find the perimeter, which equals \( P = 5 \times 10 = 50 \) units.
Using Side Length
To calculate the perimeter of a pentagon using the side length, follow these steps:
- Identify the length of one side of the pentagon.
- Multiply the side length by 5, as a pentagon has five equal sides.
- The result is the perimeter of the pentagon.
Using Radius
To find the perimeter of a regular pentagon using the radius, you can follow these steps:
- Determine the length of the radius, which is the distance from the center to a vertex of the pentagon.
- Multiply the radius by 10, as there are five equal sides in a regular pentagon.
- The result is the perimeter of the pentagon.
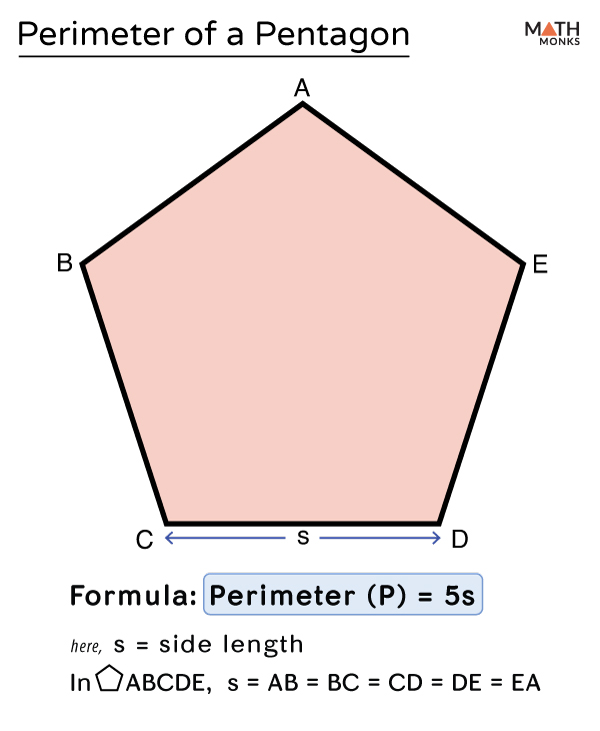
Using Apothem
To calculate the perimeter of a regular pentagon using the apothem, you can follow these steps:
- Determine the length of the apothem, which is the distance from the center to a side's midpoint.
- Multiply the apothem by 10, as there are five equal sides in a regular pentagon.
- The result is the perimeter of the pentagon.
Practical Applications
Understanding how to find the perimeter of a pentagon can be beneficial in various real-life scenarios:
- Construction: Architects and builders use perimeter calculations to determine the amount of material needed for fencing or building foundations.
- Landscaping: Landscapers use perimeter measurements to plan garden beds, walkways, and other outdoor features.
- Geometry: Students and educators use pentagon perimeter calculations to deepen their understanding of geometric principles.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers may incorporate pentagons into their creations, requiring accurate perimeter measurements for proportion and balance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the perimeter of a pentagon, it's important to avoid these common mistakes:
- Incorrect Side Length: Using the wrong length for one or more sides of the pentagon can lead to inaccurate perimeter calculations.
- Skipping Measurement: Neglecting to measure all sides of an irregular pentagon can result in an incomplete or incorrect perimeter.
- Confusing Formulas: Mixing up formulas for regular and irregular pentagons can lead to errors in perimeter calculation.
- Missing Units: Forgetting to include units (e.g., inches, centimeters) in the perimeter measurement can cause confusion or misinterpretation of the result.
Conclusion
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a pentagon is an essential skill in geometry that can be applied in various practical scenarios. Whether you are working with a regular pentagon, where all sides are equal, or an irregular pentagon, knowing the different methods to find the perimeter will help you solve problems accurately and efficiently.
Here is a summary of the key points covered in this guide:
- Understanding Pentagons: A pentagon is a five-sided polygon, and its perimeter is the total length of its sides.
- Types of Pentagons: Pentagons can be regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles can vary).
- Formulas for Perimeter: For regular pentagons, the perimeter can be calculated using the formula , where is the length of one side. For irregular pentagons, the perimeter is the sum of all side lengths.
- Steps to Calculate Perimeter: Measure the length of each side and use the appropriate formula based on the type of pentagon.
- Examples of Perimeter Calculation: Practice with examples helps reinforce the understanding of the formulas and steps involved.
- Using Side Length: Direct measurement of sides simplifies the calculation for both regular and irregular pentagons.
- Using Radius: For regular pentagons inscribed in a circle, the perimeter can be found using trigonometric relationships involving the radius.
- Using Apothem: The apothem can be used in conjunction with side lengths in specific cases to determine the perimeter.
- Practical Applications: Calculating the perimeter of a pentagon is useful in fields such as architecture, engineering, and various design projects.
- Common Mistakes to Avoid: Ensure accurate measurements and correct application of formulas to avoid errors.
By following the guidelines and methods outlined in this article, you can confidently find the perimeter of any pentagon. Continuous practice with different types of pentagons will enhance your skills and understanding of geometric properties and their applications.

Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tính chu vi ngũ giác, bao gồm các loại ngũ giác và công thức cần thiết.
Cách Tìm Chu Vi Ngũ Giác
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tìm chu vi của một ngũ giác, bao gồm các công thức và bước thực hiện cụ thể.
Tìm Chu Vi Ngũ Giác