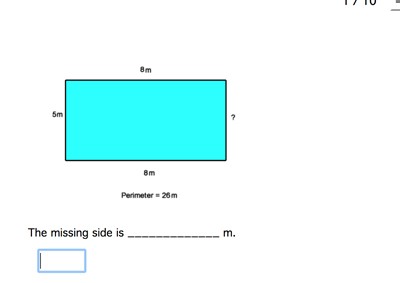
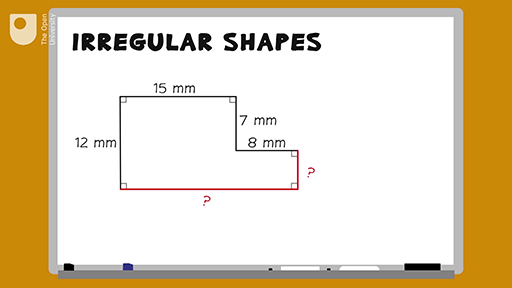
Topic how do you find the perimeter of an irregular shape: Understanding how to find the perimeter of an irregular shape is crucial for various real-life applications. This guide will walk you through the steps and methods to accurately calculate the perimeter of any irregular shape, ensuring you have the skills needed for both simple and complex figures. Let's dive into the world of geometry and uncover the secrets to mastering perimeter calculations!
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of an Irregular Shape
- Introduction
- Definition of Perimeter
- Steps to Calculate Perimeter
- Formulas for Different Shapes
- Examples
- Common Mistakes and Tips
- Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
- Practice Problems
- Frequently Asked Questions
- YOUTUBE: Khám phá cách tính diện tích và chu vi của các hình dạng bất quy tắc với video này. Hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu giúp bạn nắm bắt khái niệm một cách nhanh chóng.
How to Find the Perimeter of an Irregular Shape
To find the perimeter of an irregular shape, you simply need to add up the lengths of all its sides. Unlike regular shapes, irregular shapes do not have equal side lengths or angles. Below, we explain the process and provide examples to help you understand.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Measure the length of each side of the irregular shape.
- Add the lengths of all the sides together.
Example Calculation
Consider an irregular pentagon with the following side lengths:
- Side A: 7 units
- Side B: 8 units
- Side C: 3 units
- Side D: 5 units
The perimeter of this irregular pentagon is calculated as:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 7 + 8 + 3 + 5 = 23 \text{ units} \]
Real-World Applications
Finding the perimeter is useful in various real-life scenarios such as:
- Fencing a garden
- Framing a picture
- Installing baseboards around a room
Additional Examples
Let's consider another example with a more complex shape:
An irregular hexagon with the following side lengths:
- Side 1: 13 meters
- Side 2: 13 meters
- Side 3: 2 meters
- Side 4: 8 meters
- Side 5: 9 meters
The perimeter is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 13 + 13 + 2 + 8 + 9 = 45 \text{ meters} \]
Tips for Accurate Calculation
- Start at one corner and move systematically around the shape.
- Cross off each side length as you add it to avoid counting any side more than once.
- Use number bonds or pair sides that add up to easier sums for simpler calculations.
Conclusion
Calculating the perimeter of an irregular shape involves adding the lengths of all its sides. By following the steps outlined and practicing with different examples, you can accurately determine the perimeter of any irregular shape.
READ MORE:
Introduction
Finding the perimeter of an irregular shape is a fundamental skill in geometry that involves calculating the total length around a shape with sides of varying lengths. This process can be applied to a wide range of shapes encountered in both academic settings and real-life applications. By understanding the steps and methods to determine the perimeter, you can accurately measure and solve problems related to various irregular shapes.
To calculate the perimeter of an irregular shape, follow these steps:
- Identify and Measure: Identify each side of the irregular shape and measure their lengths accurately. Use appropriate units such as centimeters, meters, or inches.
- List the Side Lengths: Write down the length of each side. This helps in ensuring no side is left out during the calculation.
- Add the Lengths: Sum all the measured lengths to get the total perimeter. This can be expressed as \( P = \text{side}_1 + \text{side}_2 + \text{side}_3 + \ldots \)
Let's consider an example:
For an irregular pentagon with sides of 7 units, 8 units, 3 units, 5 units, and 6 units, the perimeter calculation would be:
\[ P = 7 + 8 + 3 + 5 + 6 = 29 \text{ units} \]
Understanding these basics allows you to handle more complex shapes and ensures accuracy in your calculations. Whether you are working on school assignments, construction projects, or any task requiring geometric measurements, knowing how to find the perimeter of irregular shapes is an invaluable skill.
Definition of Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is defined as the total distance around the boundary of a two-dimensional figure. It is a linear measure, which means it is measured in units of length such as centimeters, meters, inches, or feet. The concept of perimeter is applicable to both regular and irregular shapes.
To calculate the perimeter, you simply add up the lengths of all the sides of the shape. Here is a step-by-step explanation:
- Identify the Shape: Determine if the shape is regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles are not equal).
- Measure Each Side: Use a ruler or measuring tape to measure the length of each side of the shape.
- Sum the Lengths: Add the lengths of all the sides together to find the perimeter. This can be expressed as: \[ \text{Perimeter} = \sum_{i=1}^{n} \text{side}_i \] where \( n \) is the number of sides.
Examples
- Regular Shape: For a square with each side measuring 4 cm, the perimeter is calculated as: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 = 16 \text{ cm} \]
- Irregular Shape: For an irregular pentagon with sides measuring 5 cm, 7 cm, 4 cm, 6 cm, and 3 cm, the perimeter is calculated as: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 5 + 7 + 4 + 6 + 3 = 25 \text{ cm} \]
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter is essential for various real-world applications, such as determining the amount of material needed to fence a garden or the length of trim required for a picture frame.
Steps to Calculate Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of an irregular shape involves a few straightforward steps. Follow these steps to determine the perimeter accurately:
- Identify the Shape: Examine the shape to understand its sides and structure. Ensure you can see all the sides clearly.
- Measure Each Side: Use a ruler or measuring tape to measure the length of each side. Write down each measurement. For example, if you have an irregular pentagon, measure all five sides.
- List the Side Lengths: Create a list of all the measured lengths. This helps in keeping track of all sides and ensures no side is missed.
- Add the Lengths: Sum all the measured lengths to find the total perimeter. The general formula for the perimeter of an irregular shape is: \[ P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} \text{side}_i \] where \( n \) is the number of sides.
For better understanding, let's consider an example:
Example: Suppose you have an irregular hexagon with sides measuring 5 cm, 7 cm, 4 cm, 6 cm, 3 cm, and 8 cm. The perimeter is calculated as follows:
\[
P = 5 + 7 + 4 + 6 + 3 + 8 = 33 \text{ cm}
\]
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any irregular shape, ensuring precision in measurements and calculations.
Formulas for Different Shapes
Calculating the perimeter of different shapes involves using specific formulas based on the type of shape. Here are the formulas for some common shapes:
- Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of its three sides. \[ P = a + b + c \]
- Square: Since all four sides of a square are equal, the perimeter is four times the length of one side. \[ P = 4 \times a \]
- Rectangle: The perimeter of a rectangle is twice the sum of its length and width. \[ P = 2 \times (l + w) \]
- Circle (Circumference): The perimeter of a circle, known as the circumference, is calculated using the radius. \[ C = 2 \pi r \]
- Parallelogram: The perimeter of a parallelogram is the sum of twice the base and twice the side. \[ P = 2a + 2b \]
- Irregular Polygon: The perimeter of an irregular polygon is the sum of all its sides. \[ P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} \text{side}_i \]
These formulas allow you to calculate the perimeter of various shapes accurately. For example:
Example 1: Calculate the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 5 cm and a width of 3 cm.
\[
P = 2 \times (5 + 3) = 2 \times 8 = 16 \text{ cm}
\]
Example 2: Calculate the perimeter of an irregular pentagon with side lengths 4 cm, 5 cm, 7 cm, 6 cm, and 8 cm.
\[
P = 4 + 5 + 7 + 6 + 8 = 30 \text{ cm}
\]
Using these formulas, you can find the perimeter of any regular or irregular shape, making it easier to solve geometric problems and apply these calculations in real-life scenarios.

Examples
Let's explore some examples to better understand how to calculate the perimeter of irregular shapes. These examples will help illustrate the process step-by-step.
Example 1: Irregular Pentagon
Consider an irregular pentagon with the following side lengths: 5 cm, 7 cm, 3 cm, 6 cm, and 4 cm. To find the perimeter, we add all the side lengths together:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 5 \, \text{cm} + 7 \, \text{cm} + 3 \, \text{cm} + 6 \, \text{cm} + 4 \, \text{cm} = 25 \, \text{cm}
\]
Example 2: Irregular Hexagon
Next, consider an irregular hexagon with side lengths of 8 m, 6 m, 5 m, 7 m, 4 m, and 9 m. The perimeter is calculated by summing these lengths:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 8 \, \text{m} + 6 \, \text{m} + 5 \, \text{m} + 7 \, \text{m} + 4 \, \text{m} + 9 \, \text{m} = 39 \, \text{m}
\]
Example 3: Irregular Quadrilateral
Consider an irregular quadrilateral with sides of 12 ft, 15 ft, 10 ft, and 9 ft. To find the perimeter, we add all four sides:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 12 \, \text{ft} + 15 \, \text{ft} + 10 \, \text{ft} + 9 \, \text{ft} = 46 \, \text{ft}
\]
Example 4: Irregular Shape with Mixed Units
In some cases, you may need to convert units before calculating the perimeter. For instance, if you have an irregular shape with sides of 2 m, 150 cm, 1.5 m, and 200 cm, you need to convert all lengths to the same unit (e.g., meters) before summing them:
\[
150 \, \text{cm} = 1.5 \, \text{m} \quad \text{and} \quad 200 \, \text{cm} = 2 \, \text{m}
\]
So, the perimeter is:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2 \, \text{m} + 1.5 \, \text{m} + 1.5 \, \text{m} + 2 \, \text{m} = 7 \, \text{m}
\]
Example 5: Complex Irregular Shape
For a more complex irregular shape, such as one composed of a rectangle and a triangle, calculate the perimeter by summing all individual side lengths. For example, if a shape consists of a rectangle (length 8 m, width 4 m) attached to a triangle (base 4 m, height 3 m), find the perimeter as follows:
First, calculate the perimeter of each section, then sum them:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 8 \, \text{m} + 4 \, \text{m} + 4 \, \text{m} + 3 \, \text{m} + 5 \, \text{m} = 24 \, \text{m}
\]
These examples illustrate the process of calculating the perimeter for various irregular shapes, highlighting the importance of accurately measuring and summing all side lengths.
Common Mistakes and Tips
Calculating the perimeter of irregular shapes can sometimes lead to mistakes. Here are common errors and tips to avoid them:
Common Mistakes
- Missing a Side: One common mistake is forgetting to include a side in your calculation. This can be avoided by systematically adding the lengths and marking each side as you go.
- Double Counting: Another frequent error is counting a side more than once. To prevent this, start at one point and move around the shape in one direction, crossing off each side after including it in the total.
- Incorrect Units: Using different units for side lengths without converting them to a common unit can lead to incorrect results. Always convert all measurements to the same unit before summing them.
- Confusing Perimeter with Area: Perimeter is the total length around the shape, whereas area is the measure of the surface within the shape. Ensure you are calculating the correct measure.
Tips for Accurate Calculation
- Start at One Corner: Begin at one corner of the shape and move around the perimeter in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. This helps ensure all sides are included once.
- Use a Checklist: Write down each side length as you measure it and check it off once added to the total. This method helps keep track of all measurements.
- Convert Units: Before starting the calculation, convert all side lengths to the same unit (e.g., all to meters or all to centimeters) to avoid errors.
- Break Down Complex Shapes: For complex shapes, divide them into simpler shapes (rectangles, triangles) whose perimeters are easier to calculate, and then sum the perimeters of these simpler shapes.
- Double-Check Calculations: After calculating the perimeter, recheck your measurements and addition to ensure accuracy.
By following these tips and being aware of common mistakes, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any irregular shape.
Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
The concept of perimeter is widely used in various real-life scenarios. Here are some common applications:
-
Landscaping and Gardening:
When planning the layout of a garden, knowing the perimeter helps in determining the length of the fencing required. It also helps in estimating the amount of materials needed for creating borders or pathways around the garden.
-
Construction and Architecture:
In construction, the perimeter is used to calculate the amount of materials needed for the foundation, walls, and roofing. It is also essential for determining the dimensions of different sections of a building and ensuring that the design adheres to the planned layout.
-
Sports Fields and Courts:
Sports fields and courts, such as football fields, tennis courts, and running tracks, require precise measurement of the perimeter to ensure they meet official standards. This ensures fair play and consistency across different venues.
-
Interior Design:
When designing interiors, the perimeter of a room is crucial for determining the lengths of baseboards, crown moldings, and other decorative elements. It also helps in planning the layout of furniture and other fixtures.
-
Manufacturing:
In manufacturing, the perimeter of parts and components must be calculated to ensure they fit together correctly. This is especially important in industries like automotive and aerospace, where precision is key.
-
Fencing and Security:
For securing a property, the perimeter measurement is necessary to determine the length of the fencing required. It helps in planning the installation of gates and other security features to ensure complete coverage.
-
Art and Design:
Artists and designers often use the concept of perimeter when creating frames for paintings, sculptures, and other artworks. Knowing the perimeter helps in ensuring that the artwork fits within the designated space.
-
Urban Planning:
Urban planners use perimeter measurements to design and organize city layouts, including roads, parks, and residential areas. This helps in efficient space utilization and better infrastructure development.
Practice Problems
Practicing how to find the perimeter of irregular shapes is a great way to master this concept. Below are some practice problems with step-by-step solutions:
-
Problem 1: Find the perimeter of an irregular shape with the following side lengths: 5 cm, 7 cm, 3 cm, 6 cm, 4 cm.
- Add all the side lengths together: \( 5 \, \text{cm} + 7 \, \text{cm} + 3 \, \text{cm} + 6 \, \text{cm} + 4 \, \text{cm} \).
- \( 5 + 7 + 3 + 6 + 4 = 25 \, \text{cm} \).
- The perimeter of the shape is \( 25 \, \text{cm} \).
-
Problem 2: An irregular pentagon has side lengths of 8 m, 5 m, 7 m, 10 m, and 6 m. Calculate its perimeter.
- Add all the side lengths together: \( 8 \, \text{m} + 5 \, \text{m} + 7 \, \text{m} + 10 \, \text{m} + 6 \, \text{m} \).
- \( 8 + 5 + 7 + 10 + 6 = 36 \, \text{m} \).
- The perimeter of the pentagon is \( 36 \, \text{m} \).
-
Problem 3: Find the perimeter of an L-shaped figure with the following sides: 12 ft, 15 ft, 9 ft, 6 ft, 3 ft, 8 ft.
- Add all the side lengths together: \( 12 \, \text{ft} + 15 \, \text{ft} + 9 \, \text{ft} + 6 \, \text{ft} + 3 \, \text{ft} + 8 \, \text{ft} \).
- \( 12 + 15 + 9 + 6 + 3 + 8 = 53 \, \text{ft} \).
- The perimeter of the L-shaped figure is \( 53 \, \text{ft} \).
-
Problem 4: A garden has an irregular boundary with side lengths of 14 m, 18 m, 11 m, and 20 m. What is the perimeter?
- Add all the side lengths together: \( 14 \, \text{m} + 18 \, \text{m} + 11 \, \text{m} + 20 \, \text{m} \).
- \( 14 + 18 + 11 + 20 = 63 \, \text{m} \).
- The perimeter of the garden is \( 63 \, \text{m} \).
-
Problem 5: An irregular shape has side lengths of 4.5 cm, 3.2 cm, 7.8 cm, and 6.1 cm. Find its perimeter.
- Add all the side lengths together: \( 4.5 \, \text{cm} + 3.2 \, \text{cm} + 7.8 \, \text{cm} + 6.1 \, \text{cm} \).
- \( 4.5 + 3.2 + 7.8 + 6.1 = 21.6 \, \text{cm} \).
- The perimeter of the shape is \( 21.6 \, \text{cm} \).

Frequently Asked Questions
-
Q: What is the perimeter of an irregular shape?
A: The perimeter of an irregular shape is the total distance around the shape. It is found by adding the lengths of all the sides of the shape.
-
Q: How do you find the perimeter of an irregular shape?
A: To find the perimeter of an irregular shape, follow these steps:
- Measure the length of each side of the shape.
- Write down each length.
- Add all the lengths together to get the total perimeter.
-
Q: Can you use a formula to find the perimeter of an irregular shape?
A: There is no single formula for finding the perimeter of all irregular shapes since their sides can vary greatly. However, the general approach is to sum the lengths of all sides of the shape.
-
Q: What tools can help measure the sides of an irregular shape?
A: Tools like rulers, measuring tapes, and laser distance measurers can be used to measure the sides of an irregular shape accurately.
-
Q: How can I ensure accurate measurements for an irregular shape?
A: To ensure accurate measurements:
- Use a reliable and calibrated measuring tool.
- Measure each side more than once and take the average if necessary.
- Make sure the shape is flat and stable while measuring.
-
Q: Are there any real-life examples where finding the perimeter of an irregular shape is necessary?
A: Yes, some real-life examples include:
- Determining the length of fencing needed for an irregularly shaped garden.
- Measuring the boundary of a plot of land for construction purposes.
- Calculating the trim needed to go around an irregularly shaped floor or ceiling.
-
Q: What if the irregular shape has curved sides?
A: For shapes with curved sides, you may need to use a flexible measuring tape to follow the contours of the curves. Alternatively, you can break the shape into smaller, more manageable segments, measure each segment, and then sum the lengths.
Khám phá cách tính diện tích và chu vi của các hình dạng bất quy tắc với video này. Hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu giúp bạn nắm bắt khái niệm một cách nhanh chóng.
Diện Tích và Chu Vi của Các Hình Dạng Bất Quy Tắc
READ MORE:
Khám phá cách tính chu vi và diện tích của các hình hợp, bao gồm ví dụ hình chữ L, với hướng dẫn dễ hiểu từ Mr. J.
Tìm Chu Vi và Diện Tích của Hình Hợp | Ví Dụ Hình Chữ L | Hình Học | Toán với Mr. J