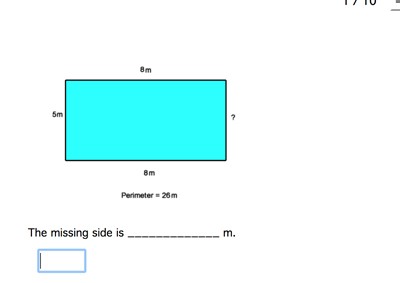
Topic how do you find the perimeter of an odd shape: Discover the steps to accurately find the perimeter of any odd shape. This guide simplifies the process, providing clear instructions and practical examples. Whether you are dealing with complex polygons or irregular figures, you'll learn how to measure their boundaries effectively. Perfect for students, teachers, and anyone interested in geometry.
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of an Odd Shape
- Introduction to Perimeter
- Understanding the Perimeter of Regular Shapes
- Formulas for Regular Polygons
- Steps to Calculate Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
- Perimeter of Common Irregular Shapes
- Examples of Finding Perimeters
- Practical Applications of Perimeter Calculations
- Frequently Asked Questions
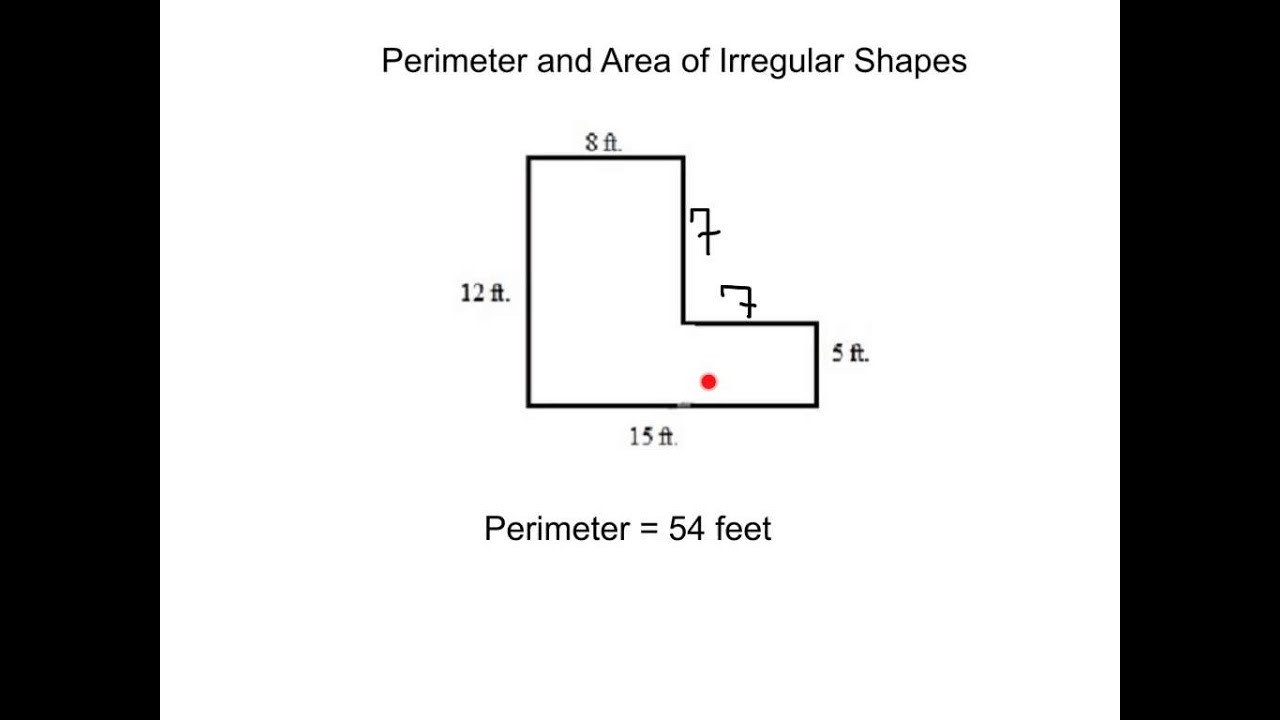
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi và diện tích của hình hợp, bao gồm ví dụ về hình chữ L. Học hình học cùng Mr. J để nắm vững kiến thức toán học.
How to Find the Perimeter of an Odd Shape
Finding the perimeter of an odd or irregular shape can be approached in several ways, depending on the specific characteristics of the shape. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
Step-by-Step Guide
- Identify and Measure All Sides
- Begin by measuring the lengths of all the sides of the irregular shape. Make sure to note each measurement accurately.
- Add the Side Lengths
- Once you have all the side lengths, add them together to get the total perimeter. The formula for the perimeter (P) of an irregular shape with sides a, b, c, etc., is:
- Once you have all the side lengths, add them together to get the total perimeter. The formula for the perimeter (P) of an irregular shape with sides a, b, c, etc., is:
- Consider Missing Lengths
- If some side lengths are missing, try to find them using the properties of the shape or by measuring additional distances.
- Sum of All Sides
- Add all the side lengths together to obtain the perimeter of the shape. For example, if you have an irregular pentagon with side lengths of 4, 2, 3, 3, and 2 units:
- Add all the side lengths together to obtain the perimeter of the shape. For example, if you have an irregular pentagon with side lengths of 4, 2, 3, 3, and 2 units:
Example Calculation
Let's say you have an irregular shape with the following sides: 10 cm, 5 cm, 7 cm, and 8 cm. To find the perimeter, you would add these side lengths together:
Applications
Understanding how to find the perimeter of irregular shapes is crucial in various fields such as:
- Engineering and Architecture: For designing and estimating materials for structures with non-standard shapes.
- Geography and Land Surveying: For measuring and managing land areas with irregular boundaries.
- Manufacturing: For planning resources and estimating costs for odd-shaped materials.
Conclusion
Finding the perimeter of an irregular shape involves measuring and summing all its sides. This method is simple yet effective and can be applied in various practical scenarios from everyday tasks to professional fields.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter
Perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a two-dimensional shape. It is an essential concept in geometry, used to measure the boundaries of various shapes, whether they are regular or irregular.
For regular shapes, calculating the perimeter is straightforward using specific formulas. However, finding the perimeter of an odd or irregular shape can be more challenging. Here are the steps to help you determine the perimeter of such shapes:
- Identify the shape and break it down into simpler, regular shapes if possible.
- Measure the length of each side of the shape. Use appropriate tools like rulers or measuring tapes for accuracy.
- Sum the lengths of all the sides to find the total perimeter.
For instance, consider a shape with five sides of varying lengths. Measure each side and add them together:
| Side | Length |
|---|---|
| Side 1 | 5 cm |
| Side 2 | 7 cm |
| Side 3 | 4 cm |
| Side 4 | 6 cm |
| Side 5 | 3 cm |
| Total Perimeter | 25 cm |
By following these steps, you can accurately determine the perimeter of any irregular shape, ensuring precise measurements for practical applications.
Understanding the Perimeter of Regular Shapes
Regular shapes have sides of equal length and angles of equal measure. Calculating the perimeter of these shapes involves using simple, well-defined formulas. Here is a step-by-step guide to understanding the perimeter of common regular shapes:
- Square: A square has four equal sides. To find its perimeter, multiply the length of one side by four.
Formula: \( P = 4a \)
Example: If the side length \( a \) is 5 cm, the perimeter \( P \) is \( 4 \times 5 = 20 \) cm. - Rectangle: A rectangle has opposite sides of equal length. The perimeter is the sum of twice the length and twice the width.
Formula: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
Example: If the length \( l \) is 6 cm and the width \( w \) is 3 cm, the perimeter \( P \) is \( 2 \times 6 + 2 \times 3 = 12 + 6 = 18 \) cm. - Equilateral Triangle: An equilateral triangle has three equal sides. To find its perimeter, multiply the length of one side by three.
Formula: \( P = 3a \)
Example: If the side length \( a \) is 4 cm, the perimeter \( P \) is \( 3 \times 4 = 12 \) cm. - Regular Pentagon: A regular pentagon has five equal sides. To find its perimeter, multiply the length of one side by five.
Formula: \( P = 5a \)
Example: If the side length \( a \) is 2 cm, the perimeter \( P \) is \( 5 \times 2 = 10 \) cm.
Understanding these basic formulas helps in calculating the perimeter of regular shapes efficiently. Here’s a summary table for quick reference:
| Shape | Formula |
|---|---|
| Square | \( P = 4a \) |
| Rectangle | \( P = 2l + 2w \) |
| Equilateral Triangle | \( P = 3a \) |
| Regular Pentagon | \( P = 5a \) |
With these formulas, you can easily find the perimeter of any regular shape, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in your calculations.
Formulas for Regular Polygons
Regular polygons are shapes with all sides and angles equal. Calculating their perimeter involves simple multiplication. Here are the formulas for some common regular polygons:
- Equilateral Triangle: A triangle with three equal sides.
Formula: \( P = 3a \)
Example: If each side \( a \) is 4 cm, the perimeter \( P \) is \( 3 \times 4 = 12 \) cm. - Square: A polygon with four equal sides.
Formula: \( P = 4a \)
Example: If each side \( a \) is 5 cm, the perimeter \( P \) is \( 4 \times 5 = 20 \) cm. - Regular Pentagon: A polygon with five equal sides.
Formula: \( P = 5a \)
Example: If each side \( a \) is 3 cm, the perimeter \( P \) is \( 5 \times 3 = 15 \) cm. - Regular Hexagon: A polygon with six equal sides.
Formula: \( P = 6a \)
Example: If each side \( a \) is 2 cm, the perimeter \( P \) is \( 6 \times 2 = 12 \) cm. - Regular Octagon: A polygon with eight equal sides.
Formula: \( P = 8a \)
Example: If each side \( a \) is 1.5 cm, the perimeter \( P \) is \( 8 \times 1.5 = 12 \) cm.
These formulas can be applied to any regular polygon, making perimeter calculation straightforward. Below is a summary table of the formulas for quick reference:
| Shape | Number of Sides | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Equilateral Triangle | 3 | \( P = 3a \) |
| Square | 4 | \( P = 4a \) |
| Regular Pentagon | 5 | \( P = 5a \) |
| Regular Hexagon | 6 | \( P = 6a \) |
| Regular Octagon | 8 | \( P = 8a \) |
By knowing these formulas, you can quickly and accurately determine the perimeter of any regular polygon.
Steps to Calculate Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
Calculating the perimeter of irregular shapes can be more complex than regular polygons, but with a systematic approach, it becomes manageable. Here are the detailed steps to help you find the perimeter of any irregular shape:
- Identify the Shape: Examine the shape and identify all its sides. Note that irregular shapes may not have uniform sides or angles.
- Measure Each Side: Use a ruler, measuring tape, or any suitable tool to measure the length of each side. For curved edges, use a string to trace the edge and then measure the string.
- Record Measurements: Write down the measurements of all sides. It's crucial to be as accurate as possible to ensure the correct perimeter calculation.
- Sum the Lengths: Add the lengths of all the measured sides to get the total perimeter.
Formula: \( P = a + b + c + \ldots + n \)
Example: If an irregular shape has sides of lengths 3 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, and 6 cm, the perimeter \( P \) is \( 3 + 5 + 4 + 6 = 18 \) cm.
Here’s a sample calculation for better understanding:
| Side | Length (cm) |
|---|---|
| Side 1 | 3 |
| Side 2 | 5 |
| Side 3 | 4 |
| Side 4 | 6 |
| Total Perimeter | 18 |
For irregular shapes with curves, such as circles or arcs, additional steps include:
- Curved Edges: Measure curved edges using flexible tools like string, then straighten and measure the string.
- Arcs: Calculate the length of an arc using the formula \( L = r\theta \), where \( r \) is the radius and \( \theta \) is the angle in radians.
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any irregular shape, ensuring precise measurements for various applications.
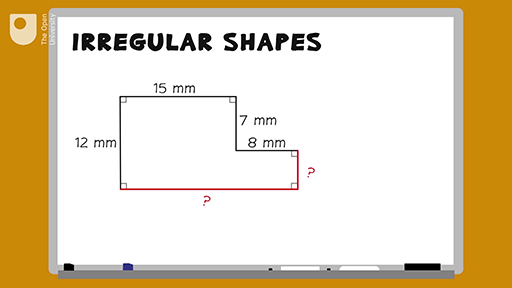
Perimeter of Common Irregular Shapes
Irregular shapes often pose a challenge in calculating the perimeter due to their non-uniform sides and angles. Here are detailed steps and examples for finding the perimeter of some common irregular shapes:
- Irregular Polygon: An irregular polygon has sides of different lengths.
- Measure each side of the polygon.
- Sum the lengths of all sides.
Example: For an irregular polygon with sides of 4 cm, 7 cm, 5 cm, and 6 cm:
Perimeter: \( P = 4 + 7 + 5 + 6 = 22 \) cm
- Irregular Quadrilateral: A quadrilateral with sides of different lengths and angles.
- Measure each of the four sides.
- Sum the lengths of all sides.
Example: For an irregular quadrilateral with sides of 3 cm, 8 cm, 5 cm, and 7 cm:
Perimeter: \( P = 3 + 8 + 5 + 7 = 23 \) cm
- Irregular Shape with Curved Edges: Shapes that include curves, such as semi-circles or composite shapes.
- Measure the straight sides using a ruler or tape measure.
- Measure the curved edges using a flexible tool like a string, then straighten and measure the string.
- Sum the lengths of all sides and curves.
Example: For a shape with straight sides of 4 cm, 6 cm, and a curved edge (semi-circle) with a radius of 3 cm:
Straight sides: \( 4 + 6 = 10 \) cm
Curved edge: \( \pi r \) (half of the circle’s circumference)
\( \pi \times 3 \approx 9.42 \) cm (since \( \pi \approx 3.14 \))
Perimeter: \( 10 + 9.42 = 19.42 \) cm
To summarize, the key to finding the perimeter of irregular shapes is to accurately measure each segment and then sum them up. This approach can be applied to various irregular shapes, ensuring precise perimeter calculations.
Examples of Finding Perimeters
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of various shapes is crucial. Here are some detailed examples to illustrate the process:
Example 1: Irregular Quadrilateral
Consider an irregular quadrilateral with the following side lengths:
- Side 1: 5 cm
- Side 2: 7 cm
- Side 3: 4 cm
- Side 4: 6 cm
Steps:
- Measure each side.
- Sum the lengths of all sides:
Perimeter: \( P = 5 + 7 + 4 + 6 = 22 \) cm
Example 2: Irregular Polygon
Consider an irregular polygon with the following side lengths:
- Side 1: 3 cm
- Side 2: 5 cm
- Side 3: 6 cm
- Side 4: 2 cm
- Side 5: 4 cm
Steps:
- Measure each side.
- Sum the lengths of all sides:
Perimeter: \( P = 3 + 5 + 6 + 2 + 4 = 20 \) cm
Example 3: Shape with a Curved Edge
Consider a shape with straight sides and a curved edge (semi-circle) with the following dimensions:
- Straight side 1: 8 cm
- Straight side 2: 5 cm
- Curved edge (semi-circle) with radius: 2 cm
Steps:
- Measure the straight sides:
Straight sides: \( 8 + 5 = 13 \) cm - Calculate the length of the curved edge:
Curved edge: \( \pi r \) (half of the circle’s circumference)
\( \pi \times 2 \approx 6.28 \) cm (since \( \pi \approx 3.14 \)) - Sum the lengths of all sides:
Perimeter: \( 13 + 6.28 = 19.28 \) cm
These examples demonstrate how to approach finding the perimeter of various irregular shapes. By accurately measuring each side and using appropriate formulas, you can determine the perimeter for any shape.
Practical Applications of Perimeter Calculations
Perimeter calculations are essential in various real-world applications, ranging from construction to design and daily tasks. Here are some practical examples of how perimeter calculations are used:
Construction and Landscaping
In construction and landscaping, accurate perimeter measurements ensure proper planning and resource allocation.
- Fencing: Calculating the perimeter of a property determines the amount of fencing material required. For example, a rectangular yard with sides of 30 m and 50 m has a perimeter of \(2 \times (30 + 50) = 160 \) m.
- Pathways: Knowing the perimeter of garden beds or pathways helps in purchasing the correct amount of materials like bricks or stones.
Interior Design
In interior design, perimeter calculations assist in space planning and decoration.
- Flooring: When installing baseboards or moldings, measuring the perimeter of a room ensures accurate material estimates. For a room of 4 m by 5 m, the perimeter is \(2 \times (4 + 5) = 18 \) m.
- Wallpaper and Paint: Knowing the perimeter helps in calculating the amount of wallpaper or paint needed to cover the walls of a room.
Sports and Recreation
Perimeter calculations are crucial in designing and maintaining sports facilities.
- Tracks: The perimeter of running tracks or swimming pools must be measured for accurate distance markers. For an oval track with semi-major axis of 50 m and semi-minor axis of 30 m, the approximate perimeter (ellipse) can be calculated using \( \pi \times \left( 50 + 30 \right) = 251.2 \) m.
- Playing Fields: Ensuring that playing fields have correct dimensions for games like soccer or tennis involves calculating and marking their perimeters accurately.
Daily Life
Even in daily tasks, perimeter calculations come in handy.
- Gardening: When planning garden layouts or installing garden beds, calculating the perimeter helps in determining the length of materials needed for borders.
- Home Improvement: Tasks like adding new trim to windows or doors require precise perimeter measurements to ensure proper fitting and aesthetics.
Understanding and applying perimeter calculations in these contexts not only ensures efficiency and accuracy but also helps in resource management and cost-saving.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions and answers about finding the perimeter of odd shapes:
- Q1: What is the perimeter?
- Q2: How do you find the perimeter of an irregular shape?
- Identify and measure all the sides of the shape.
- Write down the length of each side.
- Add all the side lengths together to get the total perimeter.
- Q3: What are some tips for calculating the perimeter of irregular shapes?
- Label each side to avoid counting a side more than once or missing a side.
- Cross off each side after adding its length to keep track.
- Start from one corner and move around the shape in one direction to ensure all sides are included.
- For complex shapes, look for sides that add up to easier numbers to simplify the calculation.
- Q4: Can a shape with some equal sides still be irregular?
- Q5: What units are used to measure the perimeter?
- Q6: How do you find the perimeter of a shape with curved sides?
- For a full circle: \( \text{Circumference} = 2\pi r \)
- For an arc: \( \text{Arc Length} = \theta r \), where \( \theta \) is the angle in radians.
- Q7: Are there any online tools to help calculate the perimeter?
A1: The perimeter of a shape is the total length of its boundary. To find the perimeter, you add the lengths of all the sides of the shape. The units of the perimeter will be the same as the units of the side lengths (e.g., cm, m, inches, feet).
A2: To find the perimeter of an irregular shape, follow these steps:
For example, if an irregular shape has sides of 4 cm, 5 cm, 7 cm, and 3 cm, the perimeter is 4 + 5 + 7 + 3 = 19 cm.
A3: Here are some tips:
A4: Yes, a shape can be irregular even if some sides are equal. An irregular shape is defined by having at least one side or angle that is different from the others. For example, a triangle with sides 5 cm, 5 cm, and 7 cm is irregular because not all sides are equal.
A5: The units used to measure the perimeter are the same as those used to measure the sides of the shape. Common units include millimeters (mm), centimeters (cm), meters (m), inches (in), and feet (ft). Make sure to use the same unit for all sides before adding them together.
A6: To find the perimeter of a shape with curved sides, you need to measure the length of the curved parts (often called arcs) and add them to the lengths of the straight sides. If the shape is a circle or includes circular arcs, you can use formulas for the circumference of a circle or the length of an arc:
A7: Yes, there are many online tools and calculators that can help you find the perimeter of both regular and irregular shapes. These tools often allow you to input the lengths of the sides, and they will compute the perimeter for you. Some examples include geometry calculators and educational websites that offer interactive perimeter calculation activities.

Video hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi và diện tích của hình hợp, bao gồm ví dụ về hình chữ L. Học hình học cùng Mr. J để nắm vững kiến thức toán học.
Tìm Chu Vi và Diện Tích của Hình Hợp | Ví Dụ Hình Chữ L | Hình Học | Toán với Mr. J
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách tính diện tích và chu vi của các hình bất quy tắc. Học hình học để hiểu rõ hơn về các hình dạng phức tạp.
Diện Tích và Chu Vi của Các Hình Bất Quy Tắc