Topic how to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle: Calculating the perimeter of a semicircle involves understanding both its curved and straight components. This comprehensive guide will help you learn the formula and steps required to find the perimeter of a semicircle efficiently. Dive into practical examples and clear explanations to master this essential mathematical skill.
Table of Content
- How to Calculate the Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Introduction
- Understanding the Semicircle
- Perimeter of a Semicircle Formula
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Examples
- Common Mistakes
- Applications in Real Life
- Practice Problems
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách tính chu vi nửa hình tròn, bao gồm công thức và ví dụ minh họa.
How to Calculate the Perimeter of a Semicircle
The perimeter of a semicircle includes the straight edge along the diameter and the curved edge which is half the circumference of the circle.
Formulas
- If the radius (r) is known:
\[ P = r(\pi + 2) \] - If the diameter (d) is known:
\[ P = \frac{\pi d}{2} + d \]
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Determine whether you have the radius or the diameter of the semicircle.
- If you have the diameter, you can convert it to radius by dividing by 2.
- Use the appropriate formula to calculate the perimeter.
- Plug in the value of π (typically 3.14 or \(\frac{22}{7}\)) and the radius or diameter into the formula.
Example Calculation
Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 7 cm.
| Step | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Formula | \[ P = r(\pi + 2) \] |
| Substitute Values | \[ P = 7(3.14 + 2) \] |
| Calculate | \[ P = 7 \times 5.14 = 35.98 \text{ cm} \] |
Thus, the perimeter of the semicircle is 35.98 cm.
Additional Information
- The perimeter of a semicircle can also be referred to as its circumference.
- The perimeter calculation combines linear and curved components: the straight diameter and the half-circumference.

READ MORE:
Introduction
The perimeter of a semicircle combines the linear distance around the curved part of the semicircle and the diameter. Understanding how to calculate this perimeter is crucial for various applications in geometry and practical problems. In this section, we will explore the step-by-step process to determine the perimeter of a semicircle, including the necessary formulas and example calculations to illustrate the method clearly.
Understanding the Semicircle
A semicircle is a geometric shape that represents half of a circle, divided along its diameter. Understanding its properties is crucial for various applications in mathematics, architecture, and engineering. Below, we will explore the fundamental aspects of a semicircle.
First, let's define some basic terms:
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of the semicircle to any point on its curved edge.
- Diameter (d): The straight line passing through the center of the semicircle, touching both ends of the semicircle. It is twice the radius (d = 2r).
- π (Pi): A mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.142, used in calculations involving circles.
The perimeter of a semicircle is the total length of its boundary, which consists of the curved edge (half of the circle's circumference) and the straight edge (the diameter).
To calculate the perimeter (P) of a semicircle:
- Determine the radius (r) of the semicircle.
- Use the formula: \( P = \pi r + d \) or \( P = \pi r + 2r \).
For example, if the radius of a semicircle is 7 units, the perimeter would be calculated as follows:
- Calculate the curved edge (half the circumference): \( \pi r = 3.142 \times 7 = 21.994 \) units.
- Add the diameter: \( 2r = 2 \times 7 = 14 \) units.
- Thus, the perimeter \( P = 21.994 + 14 = 35.994 \) units.
Understanding these basic properties and calculations of a semicircle is essential for solving various practical and theoretical problems.
Perimeter of a Semicircle Formula
The perimeter of a semicircle is a combination of the curved part of the semicircle and the diameter. To find the perimeter, you need to know either the radius or the diameter of the semicircle. The formula to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle is derived as follows:
- The circumference of a full circle is given by \(C = 2\pi r\), where \(r\) is the radius.
- Since a semicircle is half of a circle, the curved part of the perimeter is half of the circumference: \(\frac{1}{2} \times 2\pi r = \pi r\).
- To this, we add the diameter, which is twice the radius: \(d = 2r\).
Therefore, the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle becomes:
\[\text{Perimeter} = \pi r + 2r = r(\pi + 2)\]
Let's break this down step by step:
- Measure the radius (\(r\)) of the semicircle.
- Multiply the radius by \(\pi\) (approximately 3.14159).
- Add the diameter (which is \(2r\)) to the result from step 2.
- The final formula can be written as \(P = r(\pi + 2)\).
Here's an example to illustrate:
| Radius (r) | Perimeter Calculation | Result |
| 5 units | \(5(\pi + 2)\) | Approximately 21.42 units |
| 10 units | \(10(\pi + 2)\) | Approximately 44.28 units |
This formula is universal and can be used for any semicircle as long as the radius is known. The step-by-step process ensures accuracy and ease in calculating the perimeter.
Step-by-Step Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of a semicircle involves understanding its components: the curved part, which is half the circumference of a full circle, and the straight part, which is the diameter. Below are the detailed steps to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle:
- Identify the radius (r):
The radius is the distance from the center of the semicircle to any point on its curved edge. If the diameter (d) is given instead, remember that the radius is half of the diameter:
- r = d / 2
- Calculate the curved part:
The curved part of the semicircle is half the circumference of the full circle. The circumference of a full circle is given by 2πr, so half of that is:
- Curved part = πr
- Add the diameter:
The perimeter of the semicircle includes the straight part, which is the diameter. So, the total perimeter P is:
- P = πr + d
- Since d = 2r, the formula can also be written as:
- P = πr + 2r
- Combine the terms:
Factor out the common term r from the formula to simplify it:
- P = r(π + 2)
- Example Calculation:
Let's say the radius of the semicircle is 7 cm. Using the formula, we can find the perimeter:
- P = r(π + 2)
- P = 7(3.14 + 2)
- P = 7(5.14)
- P = 36.98 cm
By following these steps, you can accurately determine the perimeter of any semicircle. Whether you have the radius or the diameter, the process remains straightforward and ensures you obtain the correct measurement for the perimeter.

Examples
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle can be enhanced by working through specific examples. Here are a few illustrative problems:
-
Example 1: Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a diameter of 10 units.
- First, calculate the radius: \( r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \) units.
- Use the perimeter formula: \( P = r(\pi + 2) \).
- Substitute the radius into the formula: \( P = 5(\pi + 2) \).
- Calculate the result: \( P \approx 5(3.14 + 2) = 25.7 \) units.
-
Example 2: Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 8 units.
- Use the perimeter formula: \( P = r(\pi + 2) \).
- Substitute the radius into the formula: \( P = 8(\pi + 2) \).
- Calculate the result: \( P \approx 8(3.14 + 2) = 41.12 \) units.
-
Example 3: A semicircle has a perimeter of 27 units. What is the radius?
- Start with the perimeter formula: \( P = r(\pi + 2) \).
- Set the given perimeter into the equation: \( 27 = r(\pi + 2) \).
- Solve for the radius: \( r = \frac{27}{\pi + 2} \).
- Calculate the result: \( r \approx \frac{27}{3.14 + 2} = 5.25 \) units.
These examples demonstrate the practical application of the perimeter formula for semicircles. By following these steps, you can accurately determine the perimeter of any semicircle given either the diameter or the radius.
Common Mistakes
Calculating the perimeter of a semicircle can sometimes lead to errors. Here are some common mistakes to watch out for:
- Confusing Radius and Diameter: The radius is half the diameter. Using the diameter where the radius is needed (or vice versa) results in incorrect calculations.
- Incorrect Value of Pi: Using an overly simplified value of π (pi) can lead to inaccuracies. It is recommended to use at least 3.14 or the π button on your calculator for precision.
- Forgetting the Straight Edge: The perimeter of a semicircle includes both the curved edge (half the circumference of a circle) and the straight edge (diameter). Neglecting to add the diameter results in underestimating the perimeter.
- Mathematical Errors: Simple arithmetic mistakes, such as incorrect addition or multiplication, can skew the result. Always double-check your calculations.
- Overlooking Units: Ensure all measurements are in the same unit before starting the calculation to avoid inconsistencies.
- Mixing Up Perimeter with Area: Remember that perimeter measures the boundary length, whereas area measures the space enclosed. These are different calculations requiring different formulas.
By being aware of these common pitfalls, you can improve the accuracy of your perimeter calculations and deepen your understanding of geometric principles.
Applications in Real Life
Understanding the perimeter of a semicircle is not only crucial for academic purposes but also has several practical applications in everyday life. Here are some examples:
-
Architectural Design
In architectural design, semicircles are often used in the construction of arches, bridges, and curved walkways. Calculating the perimeter helps in determining the amount of materials needed for construction, such as the length of the railing required for a curved balcony.
-
Landscaping
Landscapers often use semicircular designs for gardens, ponds, and flower beds. Knowing the perimeter is essential for laying out borders, installing edging, and planning the length of fencing or pathways.
-
Gardening
When creating a semicircular garden bed or hedge, the perimeter calculation helps in estimating the length of plants or fencing needed to encircle the area. This ensures an even distribution of plants and materials.
-
Furniture Design
Designing furniture with semicircular elements, such as tables or seating arrangements, requires precise perimeter measurements to ensure proper fit and aesthetic appeal. This is particularly useful in custom furniture design where specific dimensions are required.
-
Urban Planning
In urban planning, semicircular roadways and roundabouts are common. Calculating the perimeter of these structures helps in planning the pavement, curbs, and landscaping around these areas, ensuring smooth traffic flow and efficient space utilization.
-
Event Planning
For events held in open spaces, semicircular stages or seating arrangements are often used. Knowing the perimeter helps in setting up barriers, arranging seats, and planning entry and exit points for efficient crowd management.
-
Construction
When constructing curved elements like domes or arches, understanding the perimeter of the semicircle is essential. This calculation aids in the accurate cutting of materials and ensures structural stability.
-
Art and Sculptures
Artists and sculptors often incorporate semicircular shapes in their works. Calculating the perimeter helps in planning the dimensions and ensuring that the piece fits well within the designated space.
These examples illustrate the importance of understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle in various real-life scenarios. Accurate measurements ensure the efficient use of materials and successful implementation of designs.
Practice Problems
Practice problems help reinforce the concept of calculating the perimeter of a semicircle. Below are several problems to practice, along with detailed steps to solve them.
-
Problem 1: Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a diameter of 12 cm.
- Calculate the radius: \( r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{12}{2} = 6 \) cm
- Use the perimeter formula: \( P = r(\pi + 2) \)
- Substitute the values: \( P = 6(\pi + 2) \)
- Assuming \( \pi \approx 3.14 \): \( P = 6(3.14 + 2) = 6 \times 5.14 = 30.84 \) cm
-
Problem 2: Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 7 inches.
- Use the perimeter formula: \( P = r(\pi + 2) \)
- Substitute the values: \( P = 7(\pi + 2) \)
- Assuming \( \pi \approx 3.14 \): \( P = 7(3.14 + 2) = 7 \times 5.14 = 35.98 \) inches
-
Problem 3: A semicircle has a perimeter of 100 cm. Find its radius.
- Use the perimeter formula: \( P = r(\pi + 2) \)
- Rearrange to solve for \( r \): \( r = \frac{P}{\pi + 2} \)
- Substitute \( P = 100 \) and \( \pi \approx 3.14 \): \( r = \frac{100}{3.14 + 2} = \frac{100}{5.14} \approx 19.46 \) cm
-
Problem 4: Calculate the perimeter of a semicircle with a diameter of 20 meters.
- Calculate the radius: \( r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{20}{2} = 10 \) meters
- Use the perimeter formula: \( P = r(\pi + 2) \)
- Substitute the values: \( P = 10(\pi + 2) \)
- Assuming \( \pi \approx 3.14 \): \( P = 10(3.14 + 2) = 10 \times 5.14 = 51.4 \) meters
These practice problems should help you get comfortable with calculating the perimeter of a semicircle. Make sure to double-check your calculations and understand each step thoroughly. Happy learning!
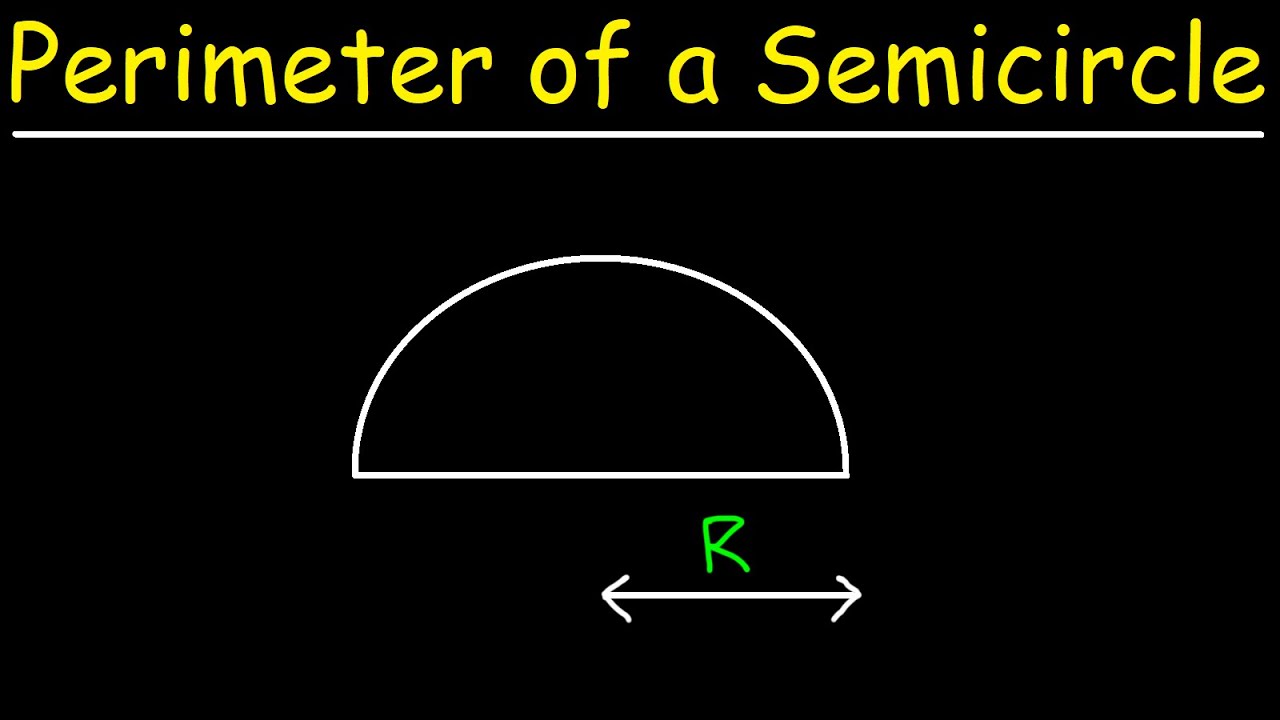
Conclusion
The calculation of the perimeter of a semicircle is a fundamental concept in geometry, combining the knowledge of both circles and straight lines. By understanding the formula \( P = r(\pi + 2) \), where \( r \) is the radius of the semicircle, we can easily determine the perimeter by adding the semicircle's curved edge and its diameter.
Practicing this calculation can enhance your problem-solving skills in various applications, ranging from simple geometric problems to complex engineering and architectural designs. The ability to accurately calculate the perimeter of a semicircle is not only crucial in academic settings but also in real-world situations where precision is paramount.
By mastering this concept, students and professionals alike can confidently approach related mathematical challenges. Whether you are determining the materials needed for a construction project or solving a geometry problem, understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle provides a strong foundation in mathematical principles.
In summary, the formula \( P = r(\pi + 2) \) is essential for calculating the perimeter of a semicircle. It encapsulates the combined length of the semicircular arc and the diameter, offering a clear and efficient method for obtaining this measurement. As you continue to apply this knowledge, you will find its relevance and importance in a wide range of practical and theoretical contexts.
Hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách tính chu vi nửa hình tròn, bao gồm công thức và ví dụ minh họa.
Cách Tính Chu Vi Nửa Hình Tròn
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn chi tiết từ Corbettmaths về cách tính chu vi nửa hình tròn, bao gồm công thức và ví dụ minh họa.
Chu Vi Nửa Hình Tròn - Corbettmaths