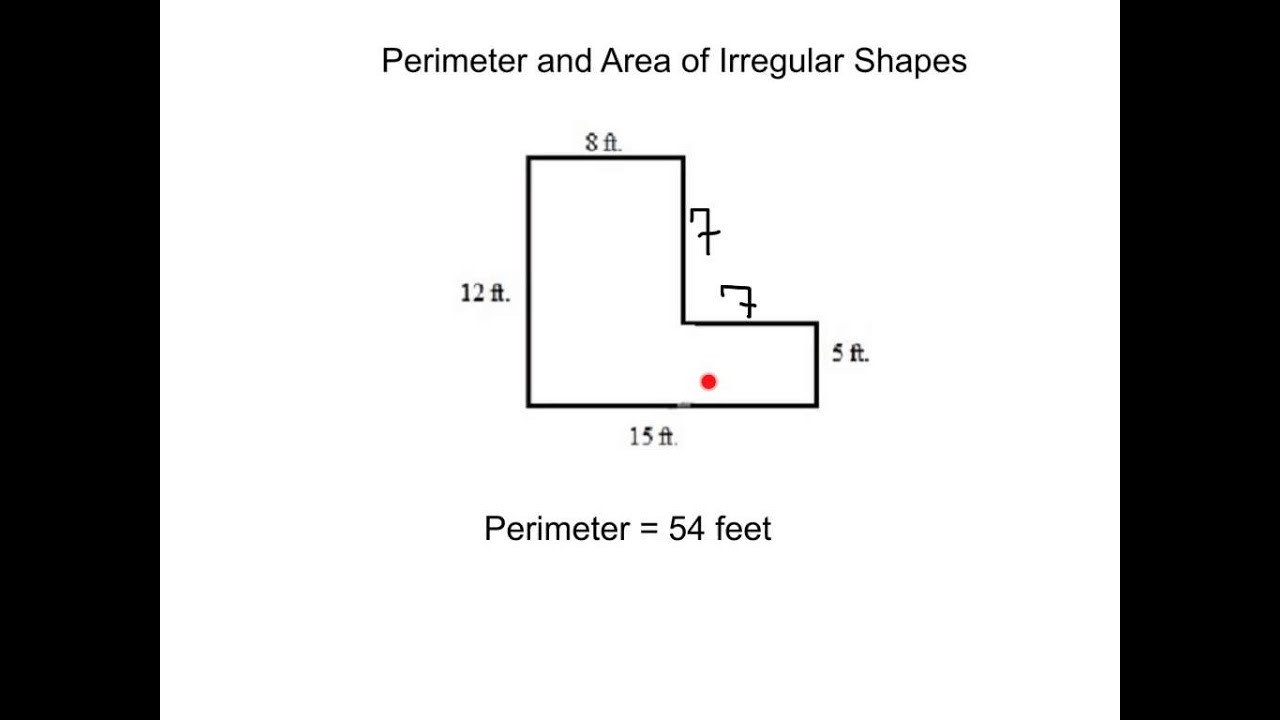
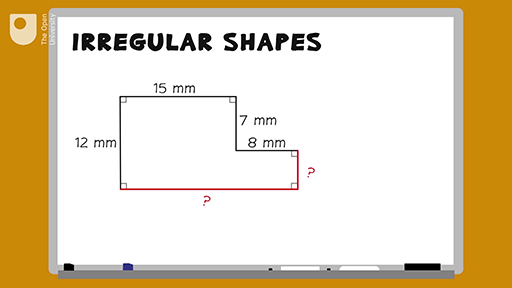
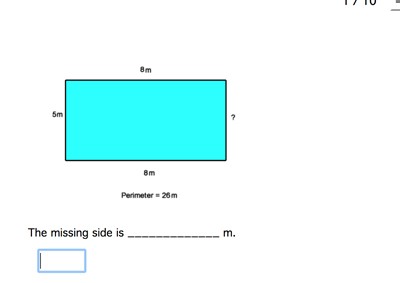
Topic how do you find perimeter of a quadrilateral: Discover the simplest and most effective methods to find the perimeter of a quadrilateral. This guide covers essential formulas, step-by-step instructions, and practical examples to help you master the concept. Whether you're a student or a geometry enthusiast, learn how to accurately calculate the perimeter of any quadrilateral with confidence.
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of a Quadrilateral
- Introduction to Perimeter of a Quadrilateral
- Basic Definition and Concept
- Types of Quadrilaterals
- Formula for Perimeter of a Quadrilateral
- Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Perimeter
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Special Cases and Formulas
- Rectangle Perimeter Calculation
- Square Perimeter Calculation
- Parallelogram Perimeter Calculation
- Trapezoid Perimeter Calculation
- Tips for Accurate Measurement
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Video này giới thiệu cách tính chu vi của các hình bình hành và cách áp dụng công thức tính chu vi trong các bài toán thực tế.
How to Find the Perimeter of a Quadrilateral
The perimeter of a quadrilateral is the total distance around the outside of the shape. To find the perimeter, you simply add the lengths of all four sides. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to do this:
Step-by-Step Guide
- Identify the lengths of all four sides of the quadrilateral.
- Sum the lengths of all four sides.
Formula
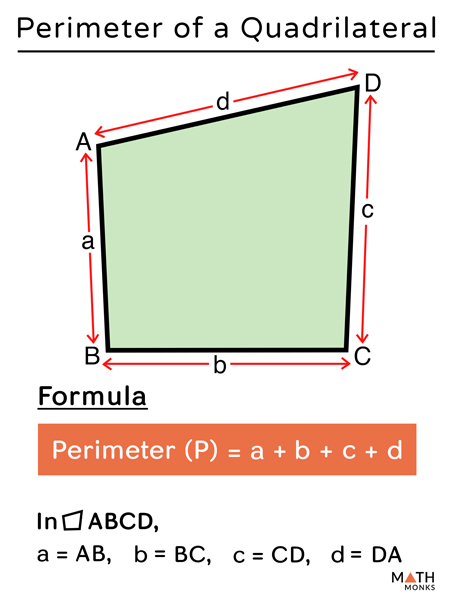
Let the lengths of the sides of the quadrilateral be \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \). The formula for the perimeter \( P \) is:
\( P = a + b + c + d \)
Example Calculation
Consider a quadrilateral with the following side lengths:
- Side \( a = 5 \, \text{cm} \)
- Side \( b = 7 \, \text{cm} \)
- Side \( c = 6 \, \text{cm} \)
- Side \( d = 4 \, \text{cm} \)
The perimeter \( P \) can be calculated as follows:
\( P = 5 \, \text{cm} + 7 \, \text{cm} + 6 \, \text{cm} + 4 \, \text{cm} = 22 \, \text{cm} \)
Special Cases
For specific types of quadrilaterals, you can use additional properties to find the perimeter:
- Rectangle: If a quadrilateral is a rectangle, with opposite sides equal, the perimeter can be found using \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) and \( w \) are the lengths of the rectangle's sides.
- Square: If a quadrilateral is a square, with all sides equal, the perimeter can be found using \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the length of one side.
Tips
- Ensure all side lengths are in the same unit before adding.
- Double-check measurements for accuracy.
By following these steps and using the formula provided, you can easily find the perimeter of any quadrilateral.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter of a Quadrilateral
The perimeter of a quadrilateral is the total distance around the four sides of the shape. It is an essential concept in geometry, often used in various practical applications. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter is fundamental for solving more complex geometric problems.
Here is a detailed step-by-step guide to understanding and calculating the perimeter of a quadrilateral:
- Identify the Type of Quadrilateral:
- Square: All four sides are equal.
- Rectangle: Opposite sides are equal and parallel.
- Parallelogram: Opposite sides are equal and parallel.
- Trapezoid: At least one pair of parallel sides.
- Irregular Quadrilateral: No sides are necessarily equal or parallel.
- Measure the Length of Each Side:
Use a ruler or a measuring tape to measure each side of the quadrilateral accurately. Note down the lengths in the same unit (e.g., centimeters, meters).
- Apply the Perimeter Formula:
The general formula for the perimeter \( P \) of a quadrilateral with sides \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \) is:
\( P = a + b + c + d \)
- Special Cases:
- Square: If each side \( s \) is equal, the perimeter is \( P = 4s \).
- Rectangle: With length \( l \) and width \( w \), the perimeter is \( P = 2(l + w) \).
- Parallelogram: With equal opposite sides \( a \) and \( b \), the perimeter is \( P = 2(a + b) \).
- Trapezoid: With sides \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \), the perimeter is \( P = a + b + c + d \).
By following these steps and using the appropriate formulas, you can easily determine the perimeter of any quadrilateral. This knowledge is not only useful in academic settings but also in various real-world applications such as construction, land surveying, and design.
Basic Definition and Concept
A quadrilateral is a polygon with four sides, four vertices, and four angles. The perimeter of a quadrilateral is the total length of its boundaries, which is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. Calculating the perimeter is straightforward, but it is essential to understand the basic concepts involved.
Here are the fundamental concepts to grasp when working with quadrilaterals:
- Understanding Sides and Vertices:
Each quadrilateral has four sides, labeled as \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \). The points where the sides meet are called vertices.
- Sum of Side Lengths:
The perimeter \( P \) of a quadrilateral is found by adding the lengths of all four sides. The formula is given by:
\( P = a + b + c + d \)
- Types of Quadrilaterals:
- Square: All sides are equal, and all angles are 90 degrees.
- Rectangle: Opposite sides are equal, and all angles are 90 degrees.
- Parallelogram: Opposite sides are equal and parallel, but angles are not necessarily 90 degrees.
- Trapezoid (or Trapezium): At least one pair of opposite sides is parallel.
- Rhombus: All sides are equal, and opposite angles are equal.
- Irregular Quadrilateral: Sides and angles can be of different lengths and measures.
- Measurement Units:
Ensure all side lengths are measured in the same unit (e.g., centimeters, meters, inches). Consistent units are crucial for accurate calculations.
Understanding these basic definitions and concepts is essential for accurately calculating the perimeter of any quadrilateral. Whether dealing with regular or irregular quadrilaterals, the same principles apply, ensuring you can determine the perimeter with confidence.
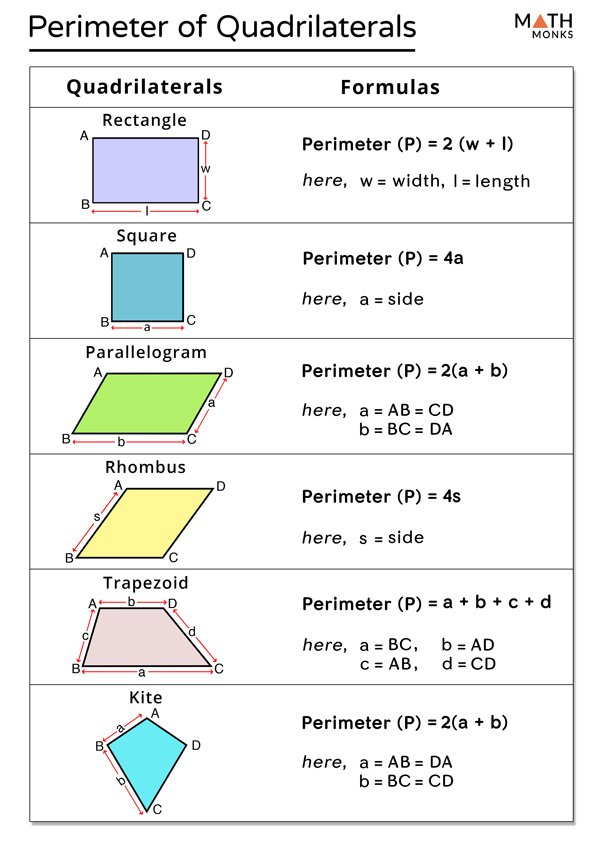
Types of Quadrilaterals
Quadrilaterals are polygons with four sides, and they come in various types based on the lengths of their sides and the measures of their angles. Understanding the different types of quadrilaterals is crucial for accurately calculating their perimeter and solving geometric problems. Here are the main types of quadrilaterals:
- Square:
- All four sides are equal in length.
- All four angles are right angles (90 degrees).
- The formula for the perimeter \( P \) is \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the length of one side.
- Rectangle:
- Opposite sides are equal in length.
- All four angles are right angles (90 degrees).
- The formula for the perimeter \( P \) is \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Parallelogram:
- Opposite sides are equal and parallel.
- Opposite angles are equal, but angles are not necessarily 90 degrees.
- The formula for the perimeter \( P \) is \( P = 2(a + b) \), where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Rhombus:
- All four sides are equal in length.
- Opposite angles are equal.
- The formula for the perimeter \( P \) is \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the length of one side.
- Trapezoid (or Trapezium):
- At least one pair of opposite sides is parallel.
- Non-parallel sides can be of different lengths.
- The formula for the perimeter \( P \) is \( P = a + b + c + d \), where \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Kite:
- Two pairs of adjacent sides are equal in length.
- One pair of opposite angles are equal.
- The formula for the perimeter \( P \) is \( P = 2(a + b) \), where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the pairs of equal sides.
- Irregular Quadrilateral:
- No sides are necessarily equal in length.
- Angles can vary and do not conform to any specific criteria.
- The formula for the perimeter \( P \) is \( P = a + b + c + d \), where \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \) are the lengths of the sides.
Each type of quadrilateral has its unique properties and formulas for calculating the perimeter. Understanding these types and their characteristics helps in solving geometric problems effectively and accurately.
Formula for Perimeter of a Quadrilateral
The perimeter of a quadrilateral is the total distance around its four sides. To calculate the perimeter, you need to know the lengths of all four sides. Here is a detailed explanation of the formula and how to use it:
- Identify the Side Lengths:
Label the four sides of the quadrilateral as \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \). These represent the lengths of each side.
- Use the General Formula:
The general formula to find the perimeter \( P \) of a quadrilateral is:
\( P = a + b + c + d \)
- Special Formulas for Specific Quadrilaterals:
- Square: All sides are equal, so if \( s \) is the length of one side, the perimeter \( P \) is:
\( P = 4s \)
- Rectangle: Opposite sides are equal, so if \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width, the perimeter \( P \) is:
\( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Parallelogram: Opposite sides are equal, so if \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the sides, the perimeter \( P \) is:
\( P = 2(a + b) \)
- Rhombus: All sides are equal, so if \( s \) is the length of one side, the perimeter \( P \) is:
\( P = 4s \)
- Trapezoid: No special properties for equal sides, so use the general formula where \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \) are the side lengths:
\( P = a + b + c + d \)
- Kite: Two pairs of adjacent sides are equal, so if \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of these pairs, the perimeter \( P \) is:
\( P = 2(a + b) \)
- Square: All sides are equal, so if \( s \) is the length of one side, the perimeter \( P \) is:
- Example Calculation:
Consider a quadrilateral with sides \( a = 5 \, \text{cm} \), \( b = 7 \, \text{cm} \), \( c = 6 \, \text{cm} \), and \( d = 4 \, \text{cm} \). The perimeter \( P \) is calculated as follows:
\( P = 5 \, \text{cm} + 7 \, \text{cm} + 6 \, \text{cm} + 4 \, \text{cm} = 22 \, \text{cm} \)
By using these formulas, you can easily find the perimeter of any quadrilateral, whether it is a regular shape like a square or an irregular shape with no equal sides.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a quadrilateral involves summing the lengths of all its sides. Here is a detailed step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
- Identify the Type of Quadrilateral:
Before calculating the perimeter, determine the type of quadrilateral you are working with (square, rectangle, parallelogram, rhombus, trapezoid, or an irregular quadrilateral). This helps in applying the appropriate formula if necessary.
- Measure the Lengths of All Sides:
Use a ruler or measuring tape to measure the length of each side accurately. Label the sides as \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \). Ensure all measurements are in the same unit (e.g., centimeters, meters).
- Apply the General Formula:
The general formula for finding the perimeter \( P \) of a quadrilateral is:
\( P = a + b + c + d \)
- Calculate the Perimeter for Special Quadrilaterals:
- Square: If all sides \( s \) are equal, use the formula:
\( P = 4s \)
- Rectangle: If the length is \( l \) and the width is \( w \), use the formula:
\( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Parallelogram: If the lengths of the sides are \( a \) and \( b \), use the formula:
\( P = 2(a + b) \)
- Rhombus: If all sides \( s \) are equal, use the formula:
\( P = 4s \)
- Kite: If the lengths of the pairs of equal sides are \( a \) and \( b \), use the formula:
\( P = 2(a + b) \)
- Square: If all sides \( s \) are equal, use the formula:
- Example Calculation:
Consider an irregular quadrilateral with side lengths \( a = 8 \, \text{cm} \), \( b = 5 \, \text{cm} \), \( c = 7 \, \text{cm} \), and \( d = 6 \, \text{cm} \). To find the perimeter \( P \), apply the general formula:
\( P = 8 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm} + 7 \, \text{cm} + 6 \, \text{cm} = 26 \, \text{cm} \)
- Verify Your Calculation:
Double-check your measurements and calculations to ensure accuracy. This step is crucial to avoid any errors in the final result.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can confidently calculate the perimeter of any quadrilateral, ensuring precision and accuracy in your geometric calculations.
Examples and Practice Problems
To better understand how to calculate the perimeter of a quadrilateral, let's go through some examples and practice problems. These will help solidify the concepts and ensure you can apply the formulas correctly.
Example 1: Calculating the Perimeter of a Rectangle
Consider a rectangle with a length of 10 cm and a width of 5 cm. To find the perimeter \( P \), use the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle:
\( P = 2(l + w) \)
Substitute the given values:
\( P = 2(10 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm}) = 2(15 \, \text{cm}) = 30 \, \text{cm} \)
Example 2: Calculating the Perimeter of a Square
Consider a square with a side length of 4 cm. To find the perimeter \( P \), use the formula for the perimeter of a square:
\( P = 4s \)
Substitute the given value:
\( P = 4(4 \, \text{cm}) = 16 \, \text{cm} \)
Example 3: Calculating the Perimeter of a Parallelogram
Consider a parallelogram with sides of 6 cm and 8 cm. To find the perimeter \( P \), use the formula for the perimeter of a parallelogram:
\( P = 2(a + b) \)
Substitute the given values:
\( P = 2(6 \, \text{cm} + 8 \, \text{cm}) = 2(14 \, \text{cm}) = 28 \, \text{cm} \)
Practice Problems
Try solving these practice problems to reinforce your understanding:
- Find the perimeter of a trapezoid with sides measuring 7 cm, 5 cm, 9 cm, and 6 cm.
- Calculate the perimeter of a rhombus with each side measuring 10 cm.
- Determine the perimeter of a kite with pairs of adjacent sides measuring 8 cm and 12 cm.
- Find the perimeter of an irregular quadrilateral with sides measuring 4 cm, 8 cm, 5 cm, and 7 cm.
Solutions:
- The perimeter of the trapezoid is \( P = 7 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm} + 9 \, \text{cm} + 6 \, \text{cm} = 27 \, \text{cm} \).
- The perimeter of the rhombus is \( P = 4(10 \, \text{cm}) = 40 \, \text{cm} \).
- The perimeter of the kite is \( P = 2(8 \, \text{cm} + 12 \, \text{cm}) = 2(20 \, \text{cm}) = 40 \, \text{cm} \).
- The perimeter of the irregular quadrilateral is \( P = 4 \, \text{cm} + 8 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm} + 7 \, \text{cm} = 24 \, \text{cm} \).
By working through these examples and practice problems, you will gain a better understanding of how to calculate the perimeter of various quadrilaterals, ensuring you can tackle any related geometric problems with confidence.
Special Cases and Formulas
In addition to the general formula for the perimeter of a quadrilateral, there are special cases where specific formulas can be applied to simplify the calculation. Understanding these special cases and their corresponding formulas is essential for efficiently solving perimeter-related problems. Below are some of these special cases and their formulas:
Square
A square has all four sides equal. Therefore, the perimeter \( P \) can be calculated using the formula:
\( P = 4s \)
where \( s \) is the length of one side.
Rectangle
In a rectangle, opposite sides are equal and all angles are right angles. The perimeter \( P \) is calculated using the formula:
\( P = 2(l + w) \)
where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
Parallelogram
A parallelogram has opposite sides that are equal and parallel. The formula for the perimeter \( P \) is:
\( P = 2(a + b) \)
where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the sides.
Rhombus
All sides of a rhombus are equal in length. The perimeter \( P \) is given by:
\( P = 4s \)
where \( s \) is the length of one side.
Trapezoid (or Trapezium)
A trapezoid has at least one pair of parallel sides. The perimeter \( P \) is calculated by summing the lengths of all four sides:
\( P = a + b + c + d \)
where \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \) are the lengths of the sides.
Kite
A kite has two pairs of adjacent sides that are equal. The perimeter \( P \) is calculated using the formula:
\( P = 2(a + b) \)
where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the pairs of equal sides.
Irregular Quadrilateral
An irregular quadrilateral does not have any special properties in terms of side lengths or angles. The perimeter \( P \) is simply the sum of the lengths of all sides:
\( P = a + b + c + d \)
where \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \) are the lengths of the sides.
Example Calculations
Let's go through a few example calculations to illustrate these special cases:
- Square: If each side of the square is 5 cm, the perimeter is:
\( P = 4(5 \, \text{cm}) = 20 \, \text{cm} \)
- Rectangle: If the length is 10 cm and the width is 4 cm, the perimeter is:
\( P = 2(10 \, \text{cm} + 4 \, \text{cm}) = 2(14 \, \text{cm}) = 28 \, \text{cm} \)
- Parallelogram: If the sides are 8 cm and 6 cm, the perimeter is:
\( P = 2(8 \, \text{cm} + 6 \, \text{cm}) = 2(14 \, \text{cm}) = 28 \, \text{cm} \)
- Rhombus: If each side is 7 cm, the perimeter is:
\( P = 4(7 \, \text{cm}) = 28 \, \text{cm} \)
- Trapezoid: If the sides are 3 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, and 6 cm, the perimeter is:
\( P = 3 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm} + 4 \, \text{cm} + 6 \, \text{cm} = 18 \, \text{cm} \)
- Kite: If the pairs of equal sides are 6 cm and 9 cm, the perimeter is:
\( P = 2(6 \, \text{cm} + 9 \, \text{cm}) = 2(15 \, \text{cm}) = 30 \, \text{cm} \)
- Irregular Quadrilateral: If the sides are 2 cm, 5 cm, 3 cm, and 4 cm, the perimeter is:
\( P = 2 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm} + 3 \, \text{cm} + 4 \, \text{cm} = 14 \, \text{cm} \)
These special cases and formulas provide a streamlined approach to calculating the perimeter of various types of quadrilaterals, making it easier to solve related geometric problems.
Rectangle Perimeter Calculation
To find the perimeter of a rectangle, you can use the following formula:
Perimeter = 2 \times (length + width)
Where:
- Length is the measurement of the longer side of the rectangle.
- Width is the measurement of the shorter side of the rectangle.
Here's a step-by-step guide to calculating the perimeter of a rectangle:
- Measure the length of the longer side of the rectangle.
- Measure the width of the shorter side of the rectangle.
- Use the formula Perimeter = 2 \times (length + width) to calculate the perimeter.
- Substitute the measured values into the formula.
- Multiply the sum of the length and width by 2 to get the perimeter.
For example, if the length of the rectangle is 5 units and the width is 3 units, the perimeter would be:
Perimeter = 2 \times (5 + 3) = 2 \times 8 = 16 units
So, the perimeter of the rectangle is 16 units.

Square Perimeter Calculation
To find the perimeter of a square, you can use the following formula:
Perimeter = 4 \times side
Where:
- Side is the measurement of any one side of the square. Since all sides of a square are equal, you can choose any side.
Here's a step-by-step guide to calculating the perimeter of a square:
- Measure the length of any one side of the square.
- Use the formula Perimeter = 4 \times side to calculate the perimeter.
- Substitute the measured value into the formula.
- Multiply the side length by 4 to get the perimeter.
For example, if the length of one side of the square is 6 units, the perimeter would be:
Perimeter = 4 \times 6 = 24 units
So, the perimeter of the square is 24 units.
Parallelogram Perimeter Calculation
To find the perimeter of a parallelogram, you need to follow these steps:
- Identify the length of adjacent sides. In a parallelogram, opposite sides are equal in length.
- Add the lengths of all sides together. Since opposite sides are equal, you can choose any two adjacent sides to represent the length and multiply by 2.
- Use the formula Perimeter = 2 \times (side1 + side2) to calculate the perimeter.
- Substitute the measured values into the formula.
- Multiply the sum of the two adjacent sides by 2 to get the perimeter.
For example, if two adjacent sides of the parallelogram measure 5 units and 8 units respectively, the perimeter would be:
Perimeter = 2 \times (5 + 8) = 2 \times 13 = 26 units
So, the perimeter of the parallelogram is 26 units.
Trapezoid Perimeter Calculation
To find the perimeter of a trapezoid, you can follow these steps:
- Identify the length of the two parallel sides (the bases).
- Measure the lengths of the non-parallel sides (the legs).
- Add the lengths of all sides together.
- Use the formula Perimeter = base1 + base2 + leg1 + leg2 to calculate the perimeter.
- Substitute the measured values into the formula.
For example, if the lengths of the bases of the trapezoid are 6 units and 10 units respectively, and the lengths of the legs are 4 units and 7 units respectively, the perimeter would be:
Perimeter = 6 + 10 + 4 + 7 = 27 units
So, the perimeter of the trapezoid is 27 units.
Tips for Accurate Measurement
- Use a high-quality measuring tool, such as a ruler or a tape measure, to ensure precision.
- Ensure that the measuring tool is aligned properly with the edges of the quadrilateral to avoid errors.
- Measure each side multiple times to verify the accuracy of your measurements.
- Double-check your measurements to catch any mistakes before calculating the perimeter.
- Take measurements in the same units to avoid conversion errors.
- For irregular quadrilaterals, break down the shape into simpler forms (such as triangles or rectangles) and calculate the perimeter of each part separately before summing them up.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Confusing the perimeter with other geometric measurements, such as area or diagonal length.
- Incorrectly measuring the sides of the quadrilateral, leading to inaccurate calculations.
- Overlooking the need to account for units of measurement, which can result in calculation errors.
- Not considering the distinction between different types of quadrilaterals and applying the wrong formulas.
- Forgetting to include all sides of the quadrilateral when calculating the perimeter.
- Relying solely on estimation rather than precise measurement, which can lead to significant errors.
- Ignoring the importance of verifying measurements and calculations for accuracy.
Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
The concept of perimeter finds various applications in real-life scenarios:
- Fencing: When determining the amount of fencing needed for a property, perimeter calculations are essential to ensure accurate estimation and purchase of materials.
- Construction: Perimeter measurements are crucial in construction projects for determining the amount of material required for enclosing structures or laying foundations.
- Landscaping: Planning outdoor spaces often involves calculating perimeters to design pathways, gardens, or retaining walls.
- Property Development: Real estate developers use perimeter calculations to assess the size and boundaries of land parcels for planning subdivisions or building layouts.
- Home Improvement: Perimeter measurements are useful for homeowners when installing features like decking, patios, or swimming pools.
- Geometry: Understanding perimeter concepts is fundamental in geometry education and is applied in various mathematical problems and real-world scenarios.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is perimeter?
Perimeter is the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
-
How do you find the perimeter of a quadrilateral?
To find the perimeter of a quadrilateral, add the lengths of all its four sides together.
-
What are the formulas for finding the perimeter of different types of quadrilaterals?
For a rectangle, the perimeter formula is Perimeter = 2 \times (length + width). For a square, it's Perimeter = 4 \times side. For a parallelogram, it's Perimeter = 2 \times (side1 + side2). For a trapezoid, it's Perimeter = base1 + base2 + leg1 + leg2.
-
Why is it important to accurately measure the sides of a quadrilateral?
Accurate measurements ensure precise calculations of the perimeter, which is crucial in various fields such as construction, engineering, and design.
-
Can perimeter be negative?
No, perimeter cannot be negative. It is always a non-negative quantity representing the total length of the boundary.
Conclusion
Understanding how to find the perimeter of a quadrilateral is essential in various practical situations. Whether you're working on a construction project, planning a landscaping design, or simply solving mathematical problems, knowing how to calculate perimeter accurately is valuable.
By following the appropriate formulas and measurement techniques outlined in this guide, you can confidently determine the perimeter of different types of quadrilaterals. Remember to double-check your measurements and calculations to ensure accuracy.
Perimeter not only has practical applications in real-life scenarios but also forms the foundation of geometric concepts. Mastering perimeter calculations equips you with valuable skills applicable in both academic and professional settings.
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of perimeter calculations for quadrilaterals, you're ready to tackle various challenges with confidence and precision.
Video này giới thiệu cách tính chu vi của các hình bình hành và cách áp dụng công thức tính chu vi trong các bài toán thực tế.
Tính Chu Vi Các Hình Bình Hành
READ MORE:
Cách xác định chu vi của tứ giác bằng công thức khoảng cách của bốn điểm