Topic area and perimeter worksheets 3rd grade: Discover engaging and educational area and perimeter worksheets tailored for 3rd graders. These worksheets help young learners grasp essential geometry concepts while improving their problem-solving skills. Designed to be both fun and informative, they provide students with the practice needed to excel in understanding area and perimeter.
Table of Content
- Area and Perimeter Worksheets for 3rd Grade
- Introduction
- Understanding Area and Perimeter
- Basic Concepts of Area
- Basic Concepts of Perimeter
- Worksheets and Practice Problems
- Printable PDFs for Area and Perimeter
- Interactive Activities
- Using Visual Aids
- Word Problems Involving Area and Perimeter
- Advanced Problems for 3rd Graders
- Games and Interactive Exercises
- Tips for Teachers and Parents
- Additional Resources and References
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Học cách tính chu vi và diện tích các hình không đều trong video dành cho học sinh lớp 3. Video hữu ích và thú vị, giúp các em nắm vững kiến thức toán học một cách dễ dàng.
Area and Perimeter Worksheets for 3rd Grade
Third-grade students can benefit greatly from practicing area and perimeter worksheets. These worksheets help students understand geometric concepts and improve their problem-solving skills. Below are some resources and examples of worksheets available for download and practice.
Benefits of Area and Perimeter Worksheets
- Visually appealing and engaging for students.
- Allows students to work at their own pace.
- Gradually increases in difficulty to ensure concept mastery.
- Improves logical and reasoning skills.
- Printable PDFs for convenient practice.
Printable Worksheets
These worksheets can be downloaded in PDF format and are available for free. They cover a range of topics within area and perimeter calculations:
- : Practice finding the perimeter of given figures.
- : Calculate the missing side length to complete the perimeter.
- : Count or multiply to find the area of each figure.
- : Draw shapes with given areas on a grid.
- : Find the area of plane figures by counting or multiplying units.
Sample Problems
| Worksheet | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Measure Perimeter | Practice finding the perimeter of given figures. | |
| Find the Missing Side Length | Calculate the missing side length to complete the perimeter. | |
| Finding Area | Count or multiply to find the area of each figure. | |
| Drawing Shapes | Draw shapes with given areas on a grid. | |
| Area of Plane Figures | Find the area of plane figures by counting or multiplying units. |
Additional Resources
For more detailed and varied worksheets, you can explore the following websites:
These resources provide a wide range of printable worksheets that cater to different aspects of learning area and perimeter for third-grade students.

READ MORE:
Introduction
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is crucial for 3rd-grade students as they begin to explore more advanced geometry topics. Area and perimeter worksheets designed for 3rd graders provide a hands-on approach to learning, helping students visualize and calculate the dimensions of various shapes. These worksheets often include engaging activities, such as measuring the sides of rectangles, calculating the area of complex figures, and solving real-world problems.
Through a step-by-step method, students start with basic shapes and gradually move to more intricate figures, ensuring a comprehensive grasp of the subject. Here's what students will typically encounter:
- Calculating the area of rectangles using the formula \( A = l \times w \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Finding the perimeter of various shapes by summing the lengths of their sides.
- Understanding and applying the concepts to irregular shapes and more complex geometric figures.
- Engaging in practical exercises that relate these mathematical concepts to real-world scenarios.
These activities not only solidify their mathematical foundation but also enhance their problem-solving skills, preparing them for future mathematical challenges.
Understanding Area and Perimeter
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is essential for 3rd-grade students as it lays the foundation for more advanced math topics. These concepts help in developing spatial awareness and problem-solving skills. Here's a step-by-step guide to help students grasp these important mathematical ideas:
- Introduction to Area and Perimeter
- Area: The space inside a shape, measured in square units.
- Perimeter: The distance around a shape, measured in linear units.
- Calculating Area
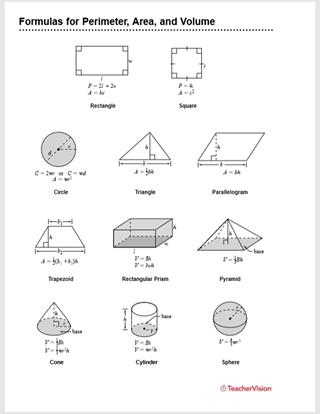
- Rectangles and Squares: Multiply length by width for rectangles. For squares, multiply the length of one side by itself.
Formula: \( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \) for rectangles and \( \text{Area} = \text{side}^2 \) for squares. - Irregular Shapes: Break down into smaller regular shapes, calculate their areas, and sum them up.
- Rectangles and Squares: Multiply length by width for rectangles. For squares, multiply the length of one side by itself.
- Calculating Perimeter
- Rectangles and Squares: Add up all the sides. For rectangles, add length and width, then multiply by 2. For squares, multiply the length of one side by 4.
Formula: \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \) for rectangles and \( \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{side} \) for squares. - Polygons: Sum the lengths of all sides.
- Rectangles and Squares: Add up all the sides. For rectangles, add length and width, then multiply by 2. For squares, multiply the length of one side by 4.
- Using Worksheets
- Practice Problems: Start with simple shapes and gradually move to more complex ones.
- Interactive Activities: Use grid paper or online tools to visualize and calculate area and perimeter.
- Real-life Applications: Apply these concepts to solve real-world problems like finding the amount of paint needed for a wall or fencing for a garden.
By understanding and practicing these steps, students will be able to master the concepts of area and perimeter, boosting their confidence and proficiency in mathematics.
Basic Concepts of Area
Understanding the basic concepts of area is crucial for students in 3rd grade. Area is defined as the amount of space inside the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is measured in square units, such as square centimeters (cm²), square meters (m²), or square inches (in²).
Here are the steps to calculate the area of simple shapes:
-
Rectangles and Squares: The area is calculated by multiplying the length by the width.
-
\text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width}
-
-
Triangles: The area is calculated by multiplying the base by the height and then dividing by 2.
-
\text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height}
-
These worksheets help students to understand and practice these calculations through a variety of problems. They include exercises where students calculate the area of given shapes, compare areas, and solve word problems involving area.
By practicing with these worksheets, students will build a strong foundation in geometry, enhancing their spatial reasoning and problem-solving skills.
Basic Concepts of Perimeter
Understanding the perimeter is essential for young students as it forms the foundation for more advanced geometry. The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around its edges. For simple shapes like rectangles and squares, the perimeter can be calculated by adding the lengths of all sides.
- Rectangle: To find the perimeter of a rectangle, add the lengths of all four sides. Since opposite sides are equal, the formula is: \[ P = 2 \times (length + width) \]
- Square: Since all four sides of a square are equal, the perimeter is: \[ P = 4 \times side \]
- Irregular Shapes: For shapes with unequal sides, simply sum the lengths of all the sides: \[ P = side_1 + side_2 + side_3 + \ldots + side_n \]
Using perimeter worksheets, students can practice these concepts by solving problems involving different shapes. These worksheets help reinforce the understanding and application of perimeter in various scenarios.

Worksheets and Practice Problems
Engaging students with area and perimeter worksheets can solidify their understanding of these fundamental concepts. Below are some practice problems and worksheet activities designed for 3rd graders:
- **Measure Perimeter:** Practice finding the perimeter of various shapes by adding up the lengths of all sides.
- **Perimeter Problems:** Determine the missing side lengths of different figures when given the perimeter.
- **Finding Area:** Calculate the area of shapes by counting units or using multiplication. This helps in understanding square units.
- **Drawing Shapes:** Draw shapes on grids to match a given area, enhancing spatial awareness and understanding of area measurement.
- **Area of Plane Figures:** Practice finding the area of different plane figures using counting and multiplication strategies.
These worksheets are designed to build a solid foundation in geometry, ensuring students can confidently calculate both area and perimeter in various contexts.
Printable PDFs for Area and Perimeter
Printable PDFs for area and perimeter worksheets are a valuable resource for 3rd-grade students to enhance their understanding and practice of these concepts. These worksheets offer a variety of problems that range from basic to advanced levels, ensuring comprehensive learning. Below is a detailed step-by-step guide on how to effectively use these resources.
- Start with Basic Shapes:
- Begin by understanding the formulas for area and perimeter of basic shapes like squares, rectangles, and triangles.
- Use worksheets that focus on these shapes to build a strong foundation.
- Gradually Increase Complexity:
- Progress to more complex shapes such as parallelograms, trapezoids, and polygons.
- Work on problems that involve irregular shapes to challenge the students' understanding.
- Incorporate Real-Life Problems:
- Use worksheets that include word problems related to real-life scenarios to make learning more engaging.
- Encourage students to apply the concepts of area and perimeter to solve these problems.
- Utilize Visual Aids:
- Employ worksheets with grids and visual aids to help students visualize the shapes and their dimensions.
- Drawing shapes on grids can aid in comprehending the calculation of area and perimeter.
- Review and Reinforce:
- Regularly review the concepts using different sets of worksheets to reinforce learning.
- Use printable PDFs for quick and easy access to a variety of problems.
By following these steps and utilizing a range of worksheets available in printable PDF format, students can achieve a thorough understanding of area and perimeter, setting a strong mathematical foundation for future learning.
Interactive Activities
Engage your students with these exciting and interactive activities to reinforce their understanding of area and perimeter:
-
Math Mosaic:
Have students use square sticky notes to create a mosaic. They can design self-portraits or any other theme, and calculate the area and perimeter of their creations.
-
LEGO Bricks:
Use LEGO bricks to build shapes and calculate their area and perimeter. This hands-on activity helps students visualize mathematical concepts in a fun way.
-
Block Letter Names:
Students draw their names using block letters on grid paper, then calculate the area and perimeter of each letter. If names are too long, initials can be used instead.
-
Floor Tiles Activity:
Use blue painter’s tape to create shapes on square floor tiles. Students calculate the area and perimeter of the shapes and then create their own shapes for others to solve.
-
Pentominoes:
Utilize pentomino blocks to trace shapes on grid paper. Students then calculate the area and perimeter of these shapes, integrating the familiar game of Tetris into their learning.
-
Building a Kite:
Provide materials for students to build kites. After construction, they measure and calculate the area and perimeter of their kites. Discuss how these measurements affect the kite's flight.
-
Interior Designer Project:
Students act as interior designers, arranging furniture within a given space. They must ensure everything fits by calculating the area and perimeter of the furniture and the room.
-
City Building:
Students work together to build a city from paper or blocks, calculating the area and perimeter of each building. This activity also introduces volume calculations for a comprehensive learning experience.
-
Island Conquer Game:
In this game, students plot points to create rectangles or "islands" on a grid, then calculate their area and perimeter. The student with the largest total island area wins.
-
Pi Plate Activity:
Introduce students to the concept of π by using pie plates. Have them calculate the area and perimeter of circles, transitioning from polygons to circular shapes.
Using Visual Aids
Visual aids are powerful tools to help students understand the concepts of area and perimeter. Here are several effective visual aids and activities to incorporate into your lessons:
-
Math Mosaics:
Students can create self-portrait mosaics or any other theme using square sticky notes. This activity not only engages creativity but also helps students calculate the area by counting the number of sticky notes used.
-
LEGO Bricks:
Use LEGO bricks to explore area and perimeter. Have students build various shapes with the bricks and then calculate the area and perimeter of each shape. This hands-on activity makes learning fun and interactive.
-
Floor Tiles Activity:
Utilize square floor tiles and blue painter’s tape to create different shapes on the classroom floor. Students can then calculate the area and perimeter of these shapes, promoting a physical and engaging way to understand these concepts.
-
Pentominoes:
Pentomino blocks are excellent for teaching area and perimeter. Students can trace the blocks on grid paper and calculate the area and perimeter of the traced shapes, reinforcing their understanding through visualization and measurement.
-
Building Kites:
Have students construct kites and measure their area and perimeter. This activity not only teaches mathematical concepts but also incorporates a fun outdoor activity when students fly their kites, discussing how the dimensions affect the flight.
-
Interior Design Project:
Engage students in a project where they act as interior designers, filling a room with furniture on grid paper. They must calculate the area and perimeter of the room and each piece of furniture, demonstrating real-life applications of these mathematical concepts.
These activities use visual aids to make the abstract concepts of area and perimeter more concrete and understandable for 3rd-grade students, enhancing their learning experience through creativity and hands-on practice.
Word Problems Involving Area and Perimeter
Word problems are a great way to apply the concepts of area and perimeter to real-life situations. Here are some examples and steps to help 3rd graders solve these types of problems:
-
Understanding the Problem: Read the problem carefully to understand what is being asked. Identify whether you need to find the area or the perimeter.
-
Identify the Measurements: Determine the length and width (or other necessary measurements) provided in the problem.
-
Apply the Formulas: Use the appropriate formula to find the area or perimeter.
- Area of a rectangle: \( A = \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
- Perimeter of a rectangle: \( P = 2(\text{length} + \text{width}) \)
-
Solve the Problem: Perform the calculations and write down the answer with the correct units.
-
Check Your Work: Review the problem and your solution to ensure accuracy.
Here are some example word problems:
-
Example 1: The playground at school is a rectangle that is 20 meters long and 15 meters wide. What is the area of the playground?
Solution: \( A = 20 \times 15 = 300 \) square meters.
-
Example 2: A rectangular garden has a length of 8 meters and a width of 5 meters. How much fencing is needed to go around the garden?
Solution: \( P = 2(8 + 5) = 2 \times 13 = 26 \) meters.
-
Example 3: A classroom has an area of 45 square meters and a width of 5 meters. What is the length of the classroom?
Solution: \( \text{Length} = \frac{45}{5} = 9 \) meters.
Practice these word problems to improve your skills in calculating area and perimeter. Use worksheets and interactive activities to make learning more engaging and fun!
Advanced Problems for 3rd Graders
Advanced area and perimeter problems challenge 3rd graders to apply their understanding of these concepts in more complex situations. These problems often involve multiple steps, requiring students to use critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Here are some advanced problem types:
-
Complex Shapes:
Students may be given composite shapes, which are combinations of rectangles, squares, and other polygons. They need to break these shapes into simpler components, calculate the area and perimeter of each, and then combine the results.
Example:
- Find the area and perimeter of a shape made by combining a rectangle with a triangle.
-
Real-World Applications:
Problems that involve real-world scenarios, such as designing a garden or floor plan, help students understand the practical uses of area and perimeter calculations.
Example:
- A rectangular garden is 8 feet long and 6 feet wide. A triangular flower bed with a base of 4 feet and height of 3 feet is placed inside the garden. Calculate the remaining area of the garden and its perimeter.
-
Irregular Shapes:
These problems involve calculating the perimeter and area of irregular shapes, requiring students to use formulas creatively and understand how different shapes fit together.
Example:
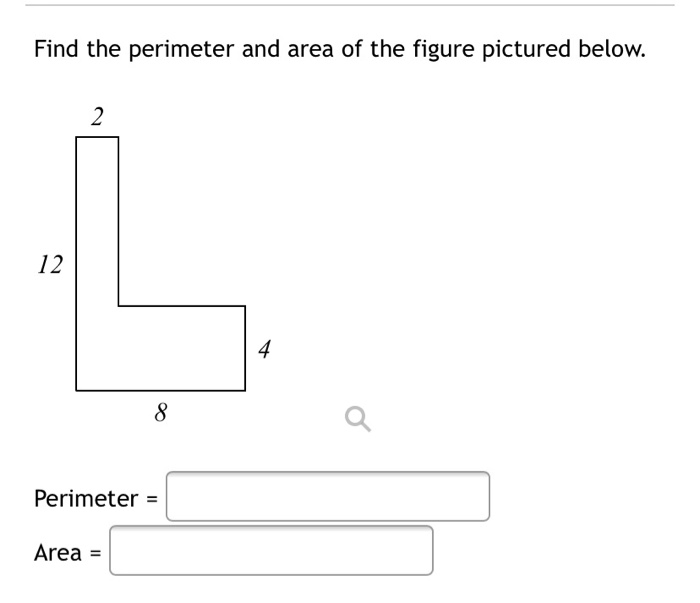
- Determine the perimeter and area of an L-shaped figure formed by two rectangles.
-
Word Problems:
Word problems integrate area and perimeter concepts into engaging stories or practical tasks, enhancing comprehension and application skills.
Example:
- John wants to put a fence around his rectangular yard. The yard is 15 feet long and 10 feet wide, but there is a 2-foot wide gate on one side. Calculate the length of the fence required.
-
Variable Measurements:
Problems where dimensions change dynamically, requiring students to adapt their calculations based on new data provided within the problem.
Example:
- A rectangular field’s length is doubled and its width is tripled. If the original dimensions were 5 feet by 3 feet, what are the new area and perimeter?
These advanced problems not only help solidify students' understanding of area and perimeter but also enhance their ability to tackle complex mathematical challenges.
Games and Interactive Exercises
Engaging students in learning about area and perimeter can be made fun and interactive through various games and exercises. Here are some creative ideas to incorporate into your teaching:
-
Shape Hunt: Organize a scavenger hunt where students search for objects of different shapes around the classroom or at home. Once they find an object, they can measure and calculate its area and perimeter.
-
Interactive Online Games: Utilize online platforms like SplashLearn, which offer a variety of games focusing on perimeter and area. These games help students learn by solving problems in a playful and engaging manner. For example, students might have to calculate the perimeter of a digital garden or determine the area of different shapes to progress through levels.
-
Area and Perimeter Puzzles: Provide students with puzzles where they need to fit shapes together to form a specific area or perimeter. This can be done with physical puzzle pieces or through digital apps that allow for interactive manipulation of shapes.
-
Math Centers: Set up math centers in the classroom with different activities. One center could have grid paper and markers for students to draw shapes and calculate their area and perimeter. Another center might have building blocks for creating three-dimensional shapes and measuring their dimensions.
-
Real-World Problems: Incorporate real-world scenarios where students need to solve problems involving area and perimeter. For instance, ask them to design a small park and calculate the amount of fencing required (perimeter) or the space available for a playground (area).
-
Interactive Whiteboard Activities: Use interactive whiteboards to display shapes and involve the whole class in calculating area and perimeter. Students can take turns coming up to the board to solve problems, fostering a collaborative learning environment.
These activities not only make learning about area and perimeter more engaging but also help students apply mathematical concepts in practical, hands-on ways.
Tips for Teachers and Parents
Helping children understand the concepts of area and perimeter can be engaging and enjoyable with the right strategies. Here are some effective tips for teachers and parents:
Engage with Hands-On Activities
-
Use Everyday Objects:
Incorporate everyday objects like LEGO bricks, tiles, and even paper clips to demonstrate area and perimeter. For instance, have students use LEGO bricks to build shapes and then calculate the area and perimeter of their creations.
-
Create Math Mosaics:
Projects like making mosaics using sticky notes or colored paper can help students visualize and calculate area and perimeter in a creative way.
-
Interactive Floor Activities:
Use painter’s tape on the floor to create large shapes that students can measure. This physical activity helps kinesthetic learners understand the concepts better.
Incorporate Technology and Games
-
Online Resources:
Utilize online platforms that offer interactive worksheets and games. Websites like Khan Academy and Quizizz provide engaging problems and instant feedback.
-
Educational Apps:
There are numerous apps available that make learning area and perimeter fun through interactive challenges and rewards.
Use Real-World Applications
-
Interior Design Projects:
Have students design a room, planning the placement of furniture based on area and perimeter calculations. This helps them see the practical application of their math skills.
-
Outdoor Activities:
Build kites or plant gardens, and measure the area and perimeter as part of the project. These activities make learning tangible and memorable.
Encourage Creative Problem Solving
-
Word Problems:
Introduce word problems that require critical thinking. Challenge students to find solutions to scenarios they might encounter in daily life, such as fencing a garden or tiling a floor.
-
STEM Integration:
Integrate science and engineering projects that require calculations of area and perimeter, fostering a multidisciplinary approach to learning.
Support at Home
-
Practice Together:
Parents can practice with their children by measuring household items or spaces. This reinforces classroom learning in a familiar environment.
-
Use Visual Aids:
Keep visual aids like charts and reference cards handy to help children recall formulas and methods easily.
By incorporating these strategies, teachers and parents can make learning area and perimeter a positive and enriching experience for 3rd graders.

Additional Resources and References
For educators and parents looking to enhance their teaching strategies and provide more engaging learning experiences, here are some valuable resources and references:
-
K5 Learning:
Offers a variety of worksheets focused on calculating the area and perimeter of rectangles, suitable for different grade levels. These worksheets come with measurement units (inches, feet) to help students practice with real-world scenarios.
-
Education.com:
Provides comprehensive third-grade perimeter worksheets that walk students through educator-created word problems and exercises, helping them learn to calculate the perimeter for various shapes.
-
Math Center:
Offers over 4,500 free worksheets for learning and practicing math, including resources for understanding the area and perimeter of rectangles and other shapes. These worksheets are designed by experts to meet the demands of different educational standards.
-
Cuemath:
Features printable PDFs for third-grade area and perimeter worksheets. These resources provide ample practice to help students improve their skills and perform better in exams.
-
Teachers Pay Teachers:
Offers a fun and engaging set of area and perimeter worksheets. These resources include a mix of Google Slides and printable PDFs, making it easy for teachers to integrate into their lessons.
These resources not only provide diverse and engaging materials for students but also offer valuable tools and references for educators and parents to support their teaching efforts effectively.
Conclusion
Learning about area and perimeter is a crucial part of the 3rd-grade math curriculum, providing students with foundational skills that will support their future mathematical learning. Through the variety of worksheets, practice problems, and interactive activities presented in this collection, students can gain a comprehensive understanding of these concepts in an engaging and enjoyable way.
By consistently practicing and applying their knowledge, students will become proficient in calculating area and perimeter, which are essential skills not only for academic success but also for real-life problem-solving. Teachers and parents play a significant role in guiding and supporting students through these learning processes, ensuring they have the tools and confidence needed to excel.
In conclusion, the provided resources, including printable PDFs, word problems, and interactive games, offer diverse and effective methods to reinforce the learning of area and perimeter. By leveraging these resources, educators and parents can create a positive and supportive learning environment that encourages curiosity and mastery of mathematical concepts.
Remember, the journey of learning math is a cumulative process, and every step taken towards understanding area and perimeter builds a stronger foundation for future mathematical endeavors. Encourage students to practice regularly, ask questions, and explore different approaches to problem-solving to enhance their learning experience.
Học cách tính chu vi và diện tích các hình không đều trong video dành cho học sinh lớp 3. Video hữu ích và thú vị, giúp các em nắm vững kiến thức toán học một cách dễ dàng.
Chu vi và Diện tích các Hình không đều Lớp 3
READ MORE:
So sánh diện tích và chu vi trong bài học toán lớp 3 theo tiêu chuẩn Common Core. Video giúp học sinh hiểu rõ sự khác biệt và cách tính toán dễ dàng.
DIỆN TÍCH VS CHU VI // Toán lớp 3 // Toán học theo tiêu chuẩn Common Core