Topic find the area and perimeter of each shape: Understanding how to find the area and perimeter of various shapes is essential for solving many real-world problems. This article will guide you through the formulas and methods for calculating these measurements for different geometric shapes, helping you master these important mathematical concepts.
Table of Content
- Find the Area and Perimeter of Each Shape
- Introduction to Area and Perimeter
- Basic Concepts
- Formulas for Common Shapes
- Calculation Methods
- Applications in Real Life
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi và diện tích của hình hợp với ví dụ hình chữ L. Phù hợp cho học sinh học hình học và toán học.
Find the Area and Perimeter of Each Shape
This guide provides the formulas and methods to find the area and perimeter of various geometric shapes.
Area and Perimeter Definitions
- Area: The space enclosed within the boundary of a two-dimensional shape, measured in square units (e.g., cm2, m2).
- Perimeter: The total length of the boundary of a shape, measured in linear units (e.g., cm, m).
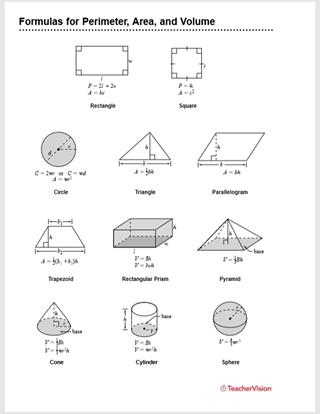
Common Shapes and Their Formulas
| Shape | Area Formula | Perimeter Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangle | \( \text{Area} = l \times w \) | \( \text{Perimeter} = 2(l + w) \) |
| Square | \( \text{Area} = a^2 \) | \( \text{Perimeter} = 4a \) |
| Triangle | \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} b \times h \) | \( \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \) |
| Circle | \( \text{Area} = \pi r^2 \) | \( \text{Circumference} = 2 \pi r \) |
| Parallelogram | \( \text{Area} = b \times h \) | \( \text{Perimeter} = 2(a + b) \) |
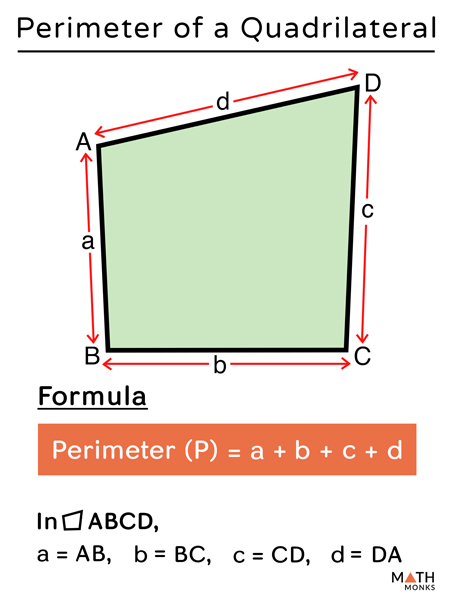
| Trapezoid | \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} (a + b) \times h \) | \( \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d \) |
Examples
Rectangle
For a rectangle with length \( l = 6 \, \text{cm} \) and width \( w = 4 \, \text{cm} \):
- Area: \( 6 \times 4 = 24 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Perimeter: \( 2(6 + 4) = 20 \, \text{cm} \)
Circle
For a circle with radius \( r = 3 \, \text{cm} \):
- Area: \( \pi \times 3^2 \approx 28.27 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Circumference: \( 2 \pi \times 3 \approx 18.85 \, \text{cm} \)
Triangle
For a triangle with base \( b = 5 \, \text{cm} \) and height \( h = 12 \, \text{cm} \):
- Area: \( \frac{1}{2} \times 5 \times 12 = 30 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Perimeter: If the sides are \( 5 \, \text{cm}, 12 \, \text{cm}, \) and \( 13 \, \text{cm} \), then \( 5 + 12 + 13 = 30 \, \text{cm} \)
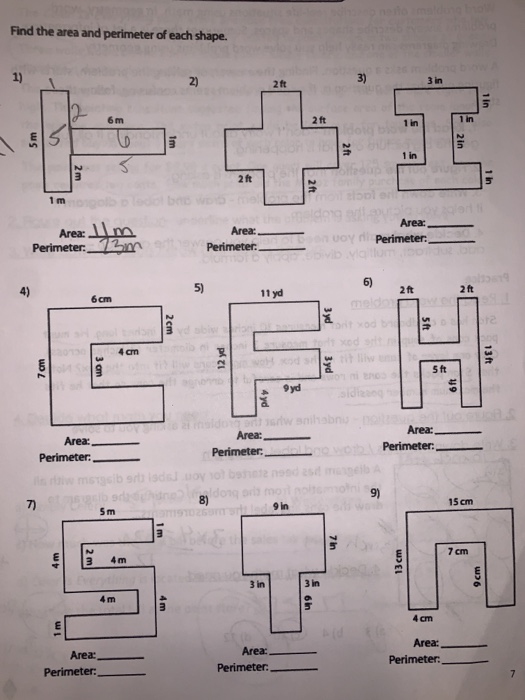
READ MORE:
Introduction to Area and Perimeter
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is essential in geometry. The area of a shape refers to the amount of space enclosed within its boundaries, while the perimeter is the total distance around the shape. Both concepts are fundamental for solving problems related to various geometric figures, whether they are regular or irregular shapes.
To calculate the area and perimeter of different shapes, specific formulas are used. These formulas vary depending on the type of shape and its dimensions. Below, we explore the definitions, significance, and basic formulas for calculating the area and perimeter of common geometric shapes.
Area
The area of a shape is the total space enclosed within its boundaries. It is measured in square units (e.g., square meters, square centimeters). The formula for the area depends on the shape:
- Rectangle: \( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
- Square: \( \text{Area} = \text{side}^2 \)
- Triangle: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Circle: \( \text{Area} = \pi r^2 \), where \( r \) is the radius
Perimeter
The perimeter is the total length of the boundary of a shape. It is measured in linear units (e.g., meters, centimeters). The formula for the perimeter also depends on the shape:
- Rectangle: \( \text{Perimeter} = 2(\text{length} + \text{width}) \)
- Square: \( \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{side} \)
- Triangle: \( \text{Perimeter} = \text{side}_1 + \text{side}_2 + \text{side}_3 \)
- Circle: \( \text{Circumference} = 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius
Learning these concepts and formulas is crucial for solving various practical problems, such as determining the amount of material needed for construction, calculating the space required for installations, and more.
Basic Concepts
Understanding the basic concepts of area and perimeter is fundamental in geometry. The area is the measure of space within a two-dimensional shape, while the perimeter is the distance around the shape. Each geometric shape has its specific formulas for calculating these properties.
Area
The area of a shape is the amount of space enclosed within its boundaries. It is measured in square units, such as square meters (m²), square centimeters (cm²), or square inches (in²). Here are the formulas for some common shapes:
- Square: Area = \( a^2 \) (where \( a \) is the length of a side)
- Rectangle: Area = \( l \times w \) (where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width)
- Triangle: Area = \( \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \) (where \( b \) is the base and \( h \) is the height)
- Circle: Area = \( \pi r^2 \) (where \( r \) is the radius)
Perimeter
The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a shape. It is measured in linear units, such as meters (m), centimeters (cm), or inches (in). Here are the formulas for some common shapes:
- Square: Perimeter = \( 4a \) (where \( a \) is the length of a side)
- Rectangle: Perimeter = \( 2(l + w) \) (where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width)
- Triangle: Perimeter = \( a + b + c \) (where \( a, b, \) and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides)
- Circle: Circumference = \( 2\pi r \) (where \( r \) is the radius)
Application Examples
Calculating area and perimeter is essential in various real-life applications, such as determining the amount of paint needed to cover a wall (area) or the length of fencing required to enclose a garden (perimeter). These concepts also play a crucial role in advanced fields such as architecture, engineering, and land surveying.
Formulas for Common Shapes
Understanding the formulas for the area and perimeter of common shapes is essential in geometry. These formulas help in calculating the size of surfaces and the length of boundaries. Below are detailed formulas for various shapes:
Rectangle
- Perimeter: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Area: \( A = l \times w \)
Square
- Perimeter: \( P = 4a \)
- Area: \( A = a^2 \)
Triangle
- Perimeter: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Area: \( A = \frac{1}{2} b \times h \)
Circle
- Circumference: \( C = 2\pi r \)
- Area: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
Parallelogram
- Perimeter: \( P = 2(a + b) \)
- Area: \( A = b \times h \)
Trapezoid
- Perimeter: \( P = a + b + c + d \)
- Area: \( A = \frac{1}{2}(a + b) \times h \)
Ellipse
- Area: \( A = \pi a b \)
Sector
- Area: \( A = \frac{1}{2} r^2 \theta \)
Each shape has specific formulas that are used to determine their area and perimeter based on their dimensions. These fundamental formulas are crucial for solving various geometric problems.
Calculation Methods
Calculating the area and perimeter of various shapes is fundamental in geometry. Understanding these concepts allows us to solve real-world problems efficiently. Below, we outline the step-by-step methods for calculating the area and perimeter of common shapes.
Square
- Area: \( A = a^2 \), where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- Perimeter: \( P = 4a \).
Rectangle
- Area: \( A = l \times w \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Perimeter: \( P = 2l + 2w \).
Triangle
- Area: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \), where \( b \) is the base and \( h \) is the height.
- Perimeter: \( P = a + b + c \), where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
Circle
- Area: \( A = \pi r^2 \), where \( r \) is the radius.
- Perimeter (Circumference): \( C = 2\pi r \).
Parallelogram
- Area: \( A = b \times h \), where \( b \) is the base and \( h \) is the height.
- Perimeter: \( P = 2a + 2b \), where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the sides.
Trapezoid
- Area: \( A = \frac{1}{2} (a + b) \times h \), where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the parallel sides, and \( h \) is the height.
- Perimeter: \( P = a + b + c + d \), where \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \) are the lengths of the sides.
These formulas form the basis for calculating the area and perimeter of the most common geometric shapes. Practicing these methods will help in mastering the calculations and applying them to various mathematical problems.
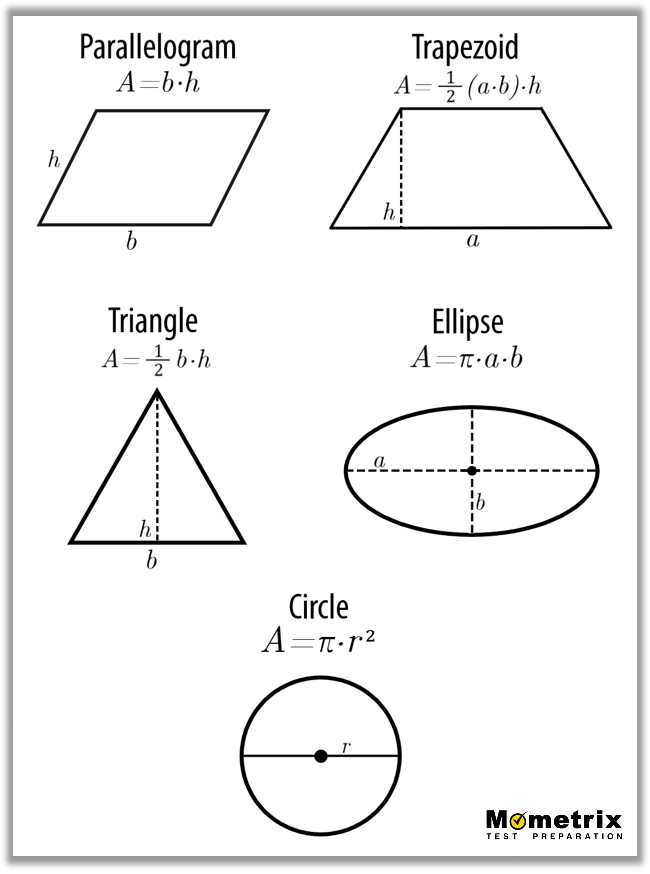
Applications in Real Life
Understanding the area and perimeter of various shapes has numerous practical applications in everyday life. Here are some common examples:
-
Home Improvement and Construction
When planning to build or renovate structures, knowing the area and perimeter is crucial. For instance, if you're constructing a garden shed, you'll need to calculate the perimeter to determine the amount of fencing required and the area to know the amount of ground to be leveled. Similarly, when installing tiles, you need the area to estimate how many tiles to purchase.
-
Example: Building a shed with a length of 10 feet and a width of 12 feet:
Perimeter = 2 × (Length + Width) = 2 × (10 + 12) = 44 feet
Area = Length × Width = 10 × 12 = 120 square feet
-
-
Gardening and Landscaping
When designing a garden, calculating the perimeter is necessary for setting up fences to protect plants from animals. The area helps in planning the layout and deciding how many plants can be accommodated.
-
Example: For a garden of 20 feet by 30 feet:
Perimeter = 2 × (Length + Width) = 2 × (20 + 30) = 100 feet
Area = Length × Width = 20 × 30 = 600 square feet
-
-
Interior Design
In interior design, knowing the area of walls and floors is important for purchasing the correct amount of paint, wallpaper, or flooring materials. Calculating the perimeter helps in installing baseboards or crown molding.
-
Example: Painting a room that is 15 feet long and 14 feet wide:
Perimeter = 2 × (Length + Width) = 2 × (15 + 14) = 58 feet
Area = Length × Width = 15 × 14 = 210 square feet
-
-
Real Estate
In real estate, determining the area of land parcels is essential for buying, selling, and legal purposes. The perimeter can be used for installing fences or other boundary markers.
-
Example: Surveying a piece of land with sides of 60, 72, 90, 108, and 120 feet:
Perimeter = 60 + 72 + 90 + 108 + 120 = 450 feet
-
-
Sports Fields
Calculating the area of sports fields is necessary for maintenance, marking boundaries, and ensuring the field meets regulatory standards. The perimeter helps in setting up fences or tracks around the field.
-
Example: For a soccer field that is 100 meters long and 64 meters wide:
Perimeter = 2 × (Length + Width) = 2 × (100 + 64) = 328 meters
Area = Length × Width = 100 × 64 = 6400 square meters
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
1. Why are area and perimeter important?
Area and perimeter are fundamental concepts in geometry, essential for understanding other mathematical topics such as volume, algebra, and trigonometry. They are also used in everyday life for tasks like measuring land, constructing buildings, and crafting objects.
-
2. How do you calculate the area of a square park with a perimeter of 320 meters?
Given the perimeter of the square is 320 meters, each side of the square is \( \frac{320}{4} = 80 \) meters. The area of the square is \( 80 \times 80 = 6400 \) square meters.
-
3. How do you find the area of a rhombus using its diagonals?
The area of a rhombus can be calculated using its diagonals with the formula \( \frac{1}{2} \times d_1 \times d_2 \), where \( d_1 \) and \( d_2 \) are the lengths of the diagonals.
-
4. How do you calculate the perimeter of any closed shape?
The perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of all the sides of the shape. For example, the perimeter of a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \) is \( 2 \times (l + w) \).
-
5. What is the relationship between perimeter and area?
The perimeter is the total distance around the boundary of a shape, while the area is the amount of space enclosed within that boundary. They are related but distinct properties of geometric figures.
-
6. What are the formulas for the area and perimeter of common shapes?
- Square: Area = \( s^2 \), Perimeter = \( 4s \)
- Rectangle: Area = \( l \times w \), Perimeter = \( 2(l + w) \)
- Triangle: Area = \( \frac{1}{2} \times base \times height \), Perimeter = \( a + b + c \)
- Circle: Area = \( \pi r^2 \), Circumference = \( 2\pi r \)
-
7. How can area and perimeter be applied in real life?
These concepts are used in various fields including architecture, engineering, and agriculture. For instance, they help in determining the amount of materials needed for construction, planning the layout of land, and designing objects.
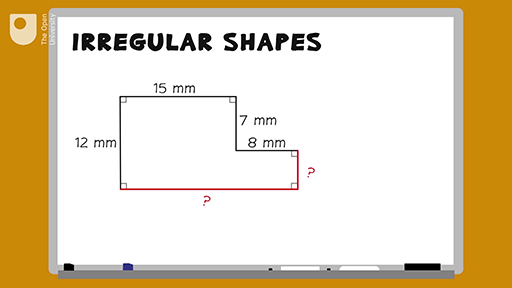
Video hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi và diện tích của hình hợp với ví dụ hình chữ L. Phù hợp cho học sinh học hình học và toán học.
Tìm Chu Vi và Diện Tích của Hình Hợp | Ví Dụ Hình Chữ L | Hình Học | Toán với Thầy J
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách tìm diện tích và chu vi của hình chữ nhật. Phù hợp cho học sinh học hình học và toán học.
Cách Tìm Diện Tích và Chu Vi của Hình Chữ Nhật