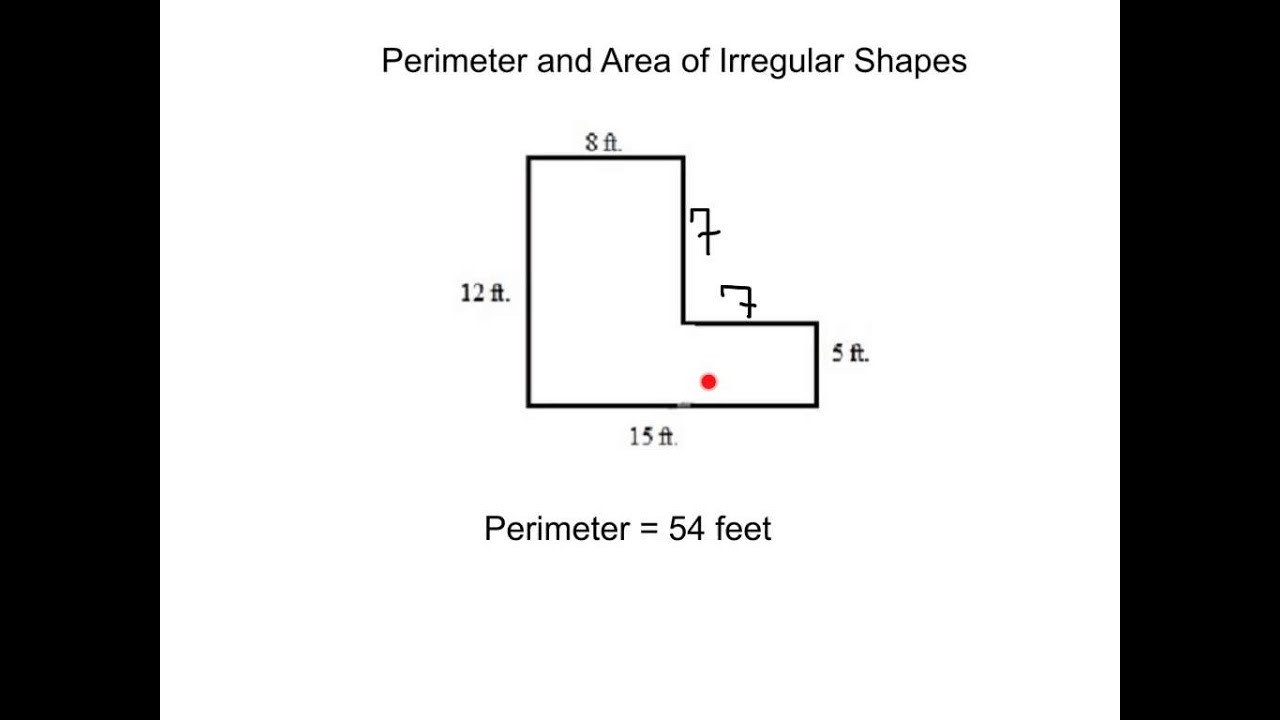
Topic find the perimeter and area of the figure pictured below: Understanding how to find the perimeter and area of a figure is a fundamental skill in geometry. In this guide, we'll break down the steps and methods for calculating these measurements for various shapes. Whether you're dealing with polygons or complex figures, our easy-to-follow instructions will help you solve these problems accurately.
Table of Content
- Finding the Perimeter and Area of a Figure
- Introduction
- Basic Concepts
- Formulas and Definitions
- Examples of Different Geometric Shapes
- Step-by-Step Solutions
- Practice Problems
- Advanced Topics
- Conclusion
- Resources
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn tính chu vi và diện tích của hình đa giác chữ L sử dụng số thập phân. Video này giải thích cách tiếp cận từng bước một cách rõ ràng và dễ hiểu.
Finding the Perimeter and Area of a Figure
To calculate the perimeter and area of a given figure, follow these steps:
Perimeter Calculation
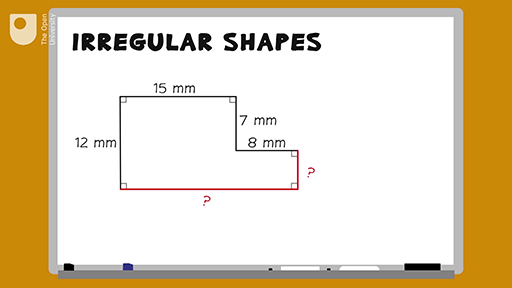
- Identify all the side lengths of the figure.
- Add up all the side lengths to find the total perimeter.
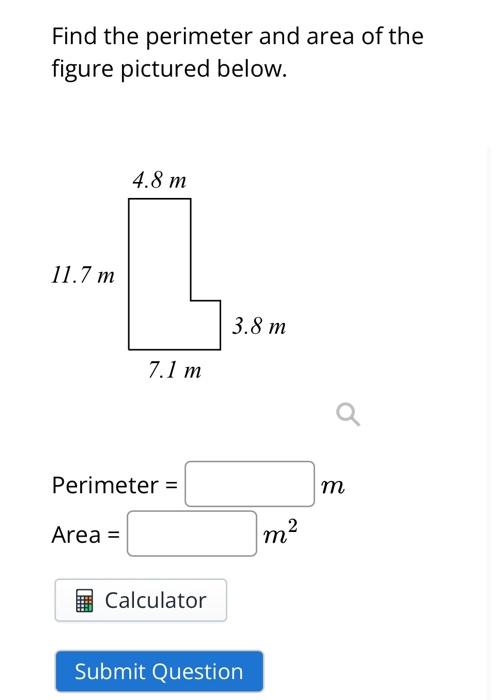
For example, if the side lengths are \(7.4\, \text{m}\), \(2.3\, \text{m}\), \(4.1\, \text{m}\), \(9.1\, \text{m}\), \(3.3\, \text{m}\), and \(11.4\, \text{m}\), the perimeter \(P\) is:
\[
P = 7.4 + 2.3 + 4.1 + 9.1 + 3.3 + 11.4 = 37.6\, \text{m}
\]
Area Calculation
To find the area, you can divide the figure into simpler shapes such as rectangles. Then, calculate the area of each shape and sum them up.
- For the given figure, divide it into two rectangles:
| Left Rectangle: | Area = \(7.4 \times 2.3 = 17.02\, \text{m}^2\) |
| Right Rectangle: | Area = \(9.1 \times 3.3 = 30.03\, \text{m}^2\) |
| Total Area: | Area = \(17.02 + 30.03 = 47.05\, \text{m}^2\) |
Alternatively, calculate the area by subtracting the area of a smaller rectangle from a larger enclosing rectangle:
\[
\text{Area} = (7.4 \times 11.4) - (4.1 \times 9.1) = 84.36 - 37.31 = 47.05\, \text{m}^2
\]
Summary
- Perimeter: \(37.6\, \text{m}\)
- Area: \(47.05\, \text{m}^2\)
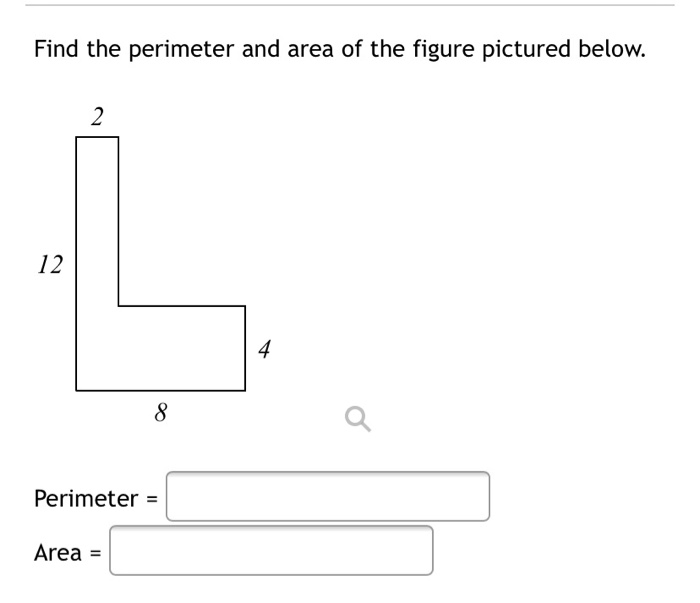
READ MORE:
Introduction
Finding the perimeter and area of a given geometric figure involves a few key steps depending on the shape of the figure. For a composite figure, we often break it down into simpler shapes like rectangles, triangles, or trapezoids, calculate each part separately, and then sum the results. This method helps in accurately determining the overall perimeter and area. In this guide, we will walk through these steps with examples to provide a clear understanding.
Basic Concepts
Understanding how to find the perimeter and area of a figure is crucial in geometry. These concepts apply to various shapes, each with specific formulas. Below are the basic concepts you need to grasp:
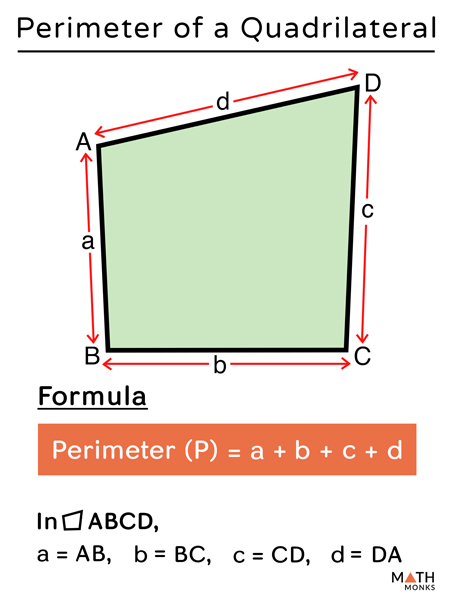
- Perimeter: The perimeter of a shape is the total length of its outer edges. For polygons, this is the sum of the lengths of all sides. For curved shapes, such as circles, the perimeter is called the circumference.
- Area: The area is the measure of the space inside a two-dimensional shape. It is expressed in square units, such as square meters or square feet.
Step-by-Step Guide to Finding Perimeter and Area
- Identify the Shape: Determine the type of shape you are working with (e.g., rectangle, triangle, circle).
- Measure Dimensions: Measure all the necessary dimensions (e.g., lengths of sides for polygons, radius for circles).
- Apply the Perimeter Formula:
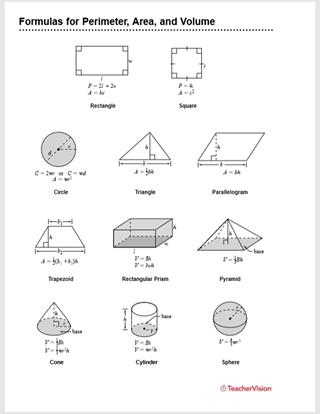
- Rectangle: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
- Square: \( P = 4a \)
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Circle (Circumference): \( C = 2\pi r \)
- Apply the Area Formula:
- Rectangle: \( A = l \times w \)
- Square: \( A = a^2 \)
- Triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} b \times h \)
- Circle: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
By following these steps, you can accurately determine the perimeter and area of any given figure.
Formulas and Definitions
To find the perimeter and area of various geometric figures, it's essential to understand and apply the correct formulas. Here are the key formulas and definitions you need to know:
- Perimeter: The total distance around a figure. For polygons, sum the lengths of all sides. For circles, the perimeter is known as the circumference.
- Area: The amount of space enclosed within a figure, measured in square units.
Common Formulas
| Shape | Perimeter Formula | Area Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangle | \(P = 2l + 2w\) | \(A = l \times w\) |
| Square | \(P = 4a\) | \(A = a^2\) |
| Triangle | \(P = a + b + c\) | \(A = \frac{1}{2} b \times h\) |
| Circle | \(C = 2\pi r\) | \(A = \pi r^2\) |
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Identify the Shape: Determine the type of figure you are dealing with.
- Measure Necessary Dimensions: For polygons, measure the side lengths; for circles, measure the radius or diameter.
- Apply the Perimeter Formula: Use the appropriate formula from the table above to calculate the perimeter.
- Apply the Area Formula: Use the relevant formula to calculate the area.
By following these steps and using the provided formulas, you can accurately find the perimeter and area of various geometric figures.
Examples of Different Geometric Shapes
Understanding how to find the perimeter and area of various geometric shapes is fundamental in geometry. Here are some examples with step-by-step methods to calculate their perimeter and area:
- Square
- Perimeter Formula: \( P = 4a \)
where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- Area Formula: \( A = a^2 \)
where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- Perimeter Formula: \( P = 4a \)
- Rectangle
- Perimeter Formula: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Area Formula: \( A = lw \)
where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Perimeter Formula: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
- Triangle
- Perimeter Formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Area Formula: \( A = \frac{1}{2}bh \)
where \( b \) is the base and \( h \) is the height.
- Perimeter Formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Circle
- Circumference Formula: \( C = 2\pi r \)
where \( r \) is the radius.
- Area Formula: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
where \( r \) is the radius.
- Circumference Formula: \( C = 2\pi r \)
- Trapezoid
- Perimeter Formula: \( P = a + b + c + d \)
where \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Area Formula: \( A = \frac{1}{2}(a + b)h \)
where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the parallel sides, and \( h \) is the height.
- Perimeter Formula: \( P = a + b + c + d \)
- Parallelogram
- Perimeter Formula: \( P = 2a + 2b \)
where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Area Formula: \( A = bh \)
where \( b \) is the base and \( h \) is the height.
- Perimeter Formula: \( P = 2a + 2b \)
By understanding these formulas, you can solve various geometric problems, helping to develop a strong foundation in geometry.

Step-by-Step Solutions
Solving for the perimeter and area of a figure requires understanding the specific shape and applying the appropriate formulas. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you through the process.
-
Identify the Shape
Determine the type of geometric shape you are working with. Common shapes include rectangles, squares, triangles, circles, and more complex polygons.
-
Measure Dimensions
Measure all necessary dimensions of the shape. For polygons, this typically includes the lengths of all sides. For circles, measure the radius or diameter.
-
Apply Perimeter Formulas
- Rectangle: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
- Square: \( P = 4a \)
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Circle (Circumference): \( C = 2\pi r \)
Use the appropriate formula to calculate the perimeter based on the dimensions measured.
-
Apply Area Formulas
- Rectangle: \( A = l \times w \)
- Square: \( A = a^2 \)
- Triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \)
- Circle: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
Use the appropriate formula to calculate the area based on the dimensions measured.
-
Check Units and Convert if Necessary
Ensure all measurements are in the same units. Convert units if needed to maintain consistency.
-
Verify Your Results
Double-check all calculations to ensure accuracy. Verify that the formulas were applied correctly and that all measurements were accurate.
By following these steps, you can accurately determine the perimeter and area of various geometric shapes.
Practice Problems
Practice problems are essential for mastering the concepts of finding the perimeter and area of various geometric shapes. Below are several problems designed to help you apply the formulas and methods discussed in previous sections.
-
Problem 1: Find the perimeter and area of a rectangle with a length of 8 meters and a width of 5 meters.
Solution:
- Perimeter: \(P = 2(l + w) = 2(8 + 5) = 26 \text{ meters}\)
- Area: \(A = l \times w = 8 \times 5 = 40 \text{ square meters}\)
-
Problem 2: Calculate the area and perimeter of a triangle with sides of 7 meters, 8 meters, and 5 meters.
Solution:
- Perimeter: \(P = a + b + c = 7 + 8 + 5 = 20 \text{ meters}\)
- Area: Using Heron's formula: \[s = \frac{a + b + c}{2} = \frac{7 + 8 + 5}{2} = 10 \text{ meters}\] \[A = \sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} = \sqrt{10(10-7)(10-8)(10-5)} = \sqrt{10 \times 3 \times 2 \times 5} = \sqrt{300} = 17.32 \text{ square meters}\]
-
Problem 3: A composite shape is formed by a rectangle and a semicircle on one of its shorter sides. The rectangle has a length of 10 meters and a width of 4 meters. Calculate the perimeter and area of this shape.
Solution:
- Perimeter: \[P = 2l + 2r + \pi r = 2 \times 10 + 2 \times 4 + \pi \times 2 = 20 + 8 + 6.28 = 34.28 \text{ meters}\]
- Area: \[A = l \times w + \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 = 10 \times 4 + \frac{1}{2} \pi \times 2^2 = 40 + 6.28 = 46.28 \text{ square meters}\]
Practicing these problems will help you understand and apply the concepts of perimeter and area in various contexts. Try to solve them step by step and refer to the formulas and definitions as needed.
Advanced Topics
In this section, we delve into more complex aspects of finding perimeters and areas, focusing on applications in real-world scenarios and advanced geometric shapes. We will cover:
Applications in Real-World Problems
Understanding the concepts of perimeter and area is crucial for solving real-world problems. Below are some common applications:
- Landscaping and Architecture: Calculating the perimeter and area of various plots and structures for design and layout.
- Construction: Determining the amount of materials needed for building projects based on surface area measurements.
- Urban Planning: Designing parks, roads, and other infrastructure by calculating areas and perimeters of land parcels.
- Fabrication: Cutting materials like fabric, metal, or wood accurately to required shapes and sizes.
Advanced Geometric Shapes
Beyond basic shapes like rectangles, triangles, and circles, we encounter more complex figures. Let's explore some advanced shapes and how to find their perimeters and areas:
- Ellipses:
- Parabolas:
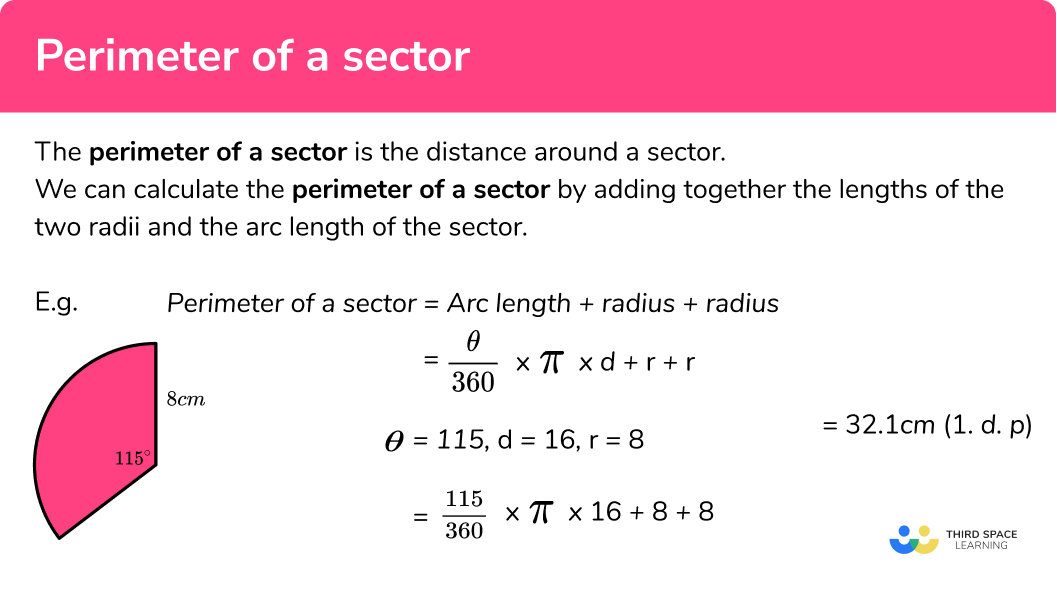
- Sector of a Circle:
- Regular Polygons:
The perimeter \( P \) of an ellipse is approximated by:
\[ P \approx \pi \left( 3(a + b) - \sqrt{(3a + b)(a + 3b)} \right) \]
where \( a \) is the semi-major axis and \( b \) is the semi-minor axis.
The area \( A \) of an ellipse is given by:
\[ A = \pi a b \]
The area under a parabolic segment can be found using integral calculus, but for specific cases like a parabolic arch, simpler formulas may apply.
The area \( A \) of a sector with radius \( r \) and angle \( \theta \) (in radians) is:
\[ A = \frac{1}{2} r^2 \theta \]
The perimeter \( P \) includes the arc length and the two radii:
\[ P = 2r + r\theta \]
The perimeter \( P \) of a regular polygon with \( n \) sides each of length \( s \) is:
\[ P = n s \]
The area \( A \) is given by:
\[ A = \frac{1}{4} n s^2 \cot \left( \frac{\pi}{n} \right) \]
Composite Shapes
For complex shapes composed of multiple basic shapes, the total area and perimeter can be found by dividing the shape into simpler parts:
- Divide the shape: Break the complex shape into basic geometric shapes (e.g., rectangles, triangles, circles).
- Calculate individual areas and perimeters: Use the respective formulas for each basic shape.
- Sum the areas: Add up the areas of all individual shapes to get the total area.
- Sum the perimeters: Add the perimeters of all outer edges of the basic shapes to get the total perimeter, ensuring not to double count shared edges.
Using Technology for Advanced Calculations
Modern tools and software can greatly assist in calculating the perimeter and area of complex shapes. Consider using:
- Geometric Software: Programs like AutoCAD or GeoGebra for precise calculations and visualizations.
- Online Calculators: Various websites provide calculators for specific shapes and compound figures.
- Spreadsheets: Tools like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets can automate calculations with built-in functions and custom formulas.
Conclusion
Understanding how to find the perimeter and area of various geometric figures is a fundamental skill in geometry that has practical applications in everyday life, from architecture and construction to land measurement and design.
Here are the key takeaways from our exploration:
- Perimeter: This is the total distance around a figure. For polygons, add the lengths of all sides. For circles, the perimeter is called the circumference, calculated using \( C = 2\pi r \).
- Area: This is the space contained within a figure. Different shapes have specific formulas:
- Rectangle: \( A = l \times w \)
- Triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} b \times h \)
- Circle: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
- Composite Shapes: Break them into simpler shapes, calculate individual areas, and sum them up. For perimeter, ensure shared edges are not double-counted.
Advanced topics covered include applications in real-world problems, such as using geometry in construction and urban planning, and understanding complex shapes like ellipses and sectors. Utilizing technology, such as geometric software and online calculators, can simplify these calculations.
By mastering these concepts, you can approach both academic problems and practical projects with confidence and precision.
Resources
To further explore the concepts of perimeter and area, and to enhance your understanding, the following resources are highly recommended:
- Further Reading:
- - Comprehensive tutorials and practice problems.
- - Easy-to-understand explanations and examples.
- Online Calculators:
- - Calculate the perimeter of various shapes effortlessly.
- - Find the area of different geometric shapes.
- Interactive Tools:
- - Visualize and manipulate geometric shapes to understand perimeter and area better.
- - Engaging games and activities for practicing these concepts.
Hướng dẫn tính chu vi và diện tích của hình đa giác chữ L sử dụng số thập phân. Video này giải thích cách tiếp cận từng bước một cách rõ ràng và dễ hiểu.
Tìm Chu Vi và Diện Tích của Hình Đa Giác Chữ L Sử Dụng Số Thập Phân
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của hình chữ nhật hợp thành khi các cạnh bị thiếu. Video giải thích từng bước giúp bạn dễ dàng hiểu và áp dụng.
Tìm Chu Vi của Hình Chữ Nhật Hợp Thành với Các Cạnh Thiếu