Topic square root of 1/25: The square root of 1/25 is a fundamental mathematical concept with various applications in different fields. In this article, we will explore the calculation of the square root of 1/25, its properties, and practical uses. Whether you're a student, educator, or enthusiast, understanding this concept will enhance your mathematical knowledge and skills.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Square Root of 1/25
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Understanding the Square Root of 1/25
- Methods to Calculate Square Roots
- Step-by-Step Calculation of √1/25
- Properties of Square Roots
- Special Cases and Examples
- Examples:
- Applications of Square Roots in Real Life
- Frequently Asked Questions
- YOUTUBE: Xem video về Canh tác tiêu quyên 1/25 để hiểu rõ hơn về chủ đề này và xem liệu nó có phù hợp với bài viết về từ khóa 'square root of 1/25' không.
Understanding the Square Root of 1/25
The square root of a fraction can be simplified by taking the square root of the numerator and the denominator separately. Let's break down the process of finding the square root of
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Rewrite the fraction under the square root as the division of square roots:
\[ \sqrt{\frac{1}{25}} = \frac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{25}} \] - Calculate the square root of the numerator and the denominator separately:
\(\sqrt{1} = 1\) \(\sqrt{25} = 5\)
- Divide the results:
\[ \frac{1}{5} = 0.2 \]
Therefore, the square root of
Additional Examples
Here are some other examples of square roots of fractions:
| Fraction | Square Root |
|---|---|
Conclusion
The method to simplify the square root of a fraction involves taking the square root of the numerator and denominator separately and then dividing the results. This process can be applied to any fraction, as demonstrated above.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
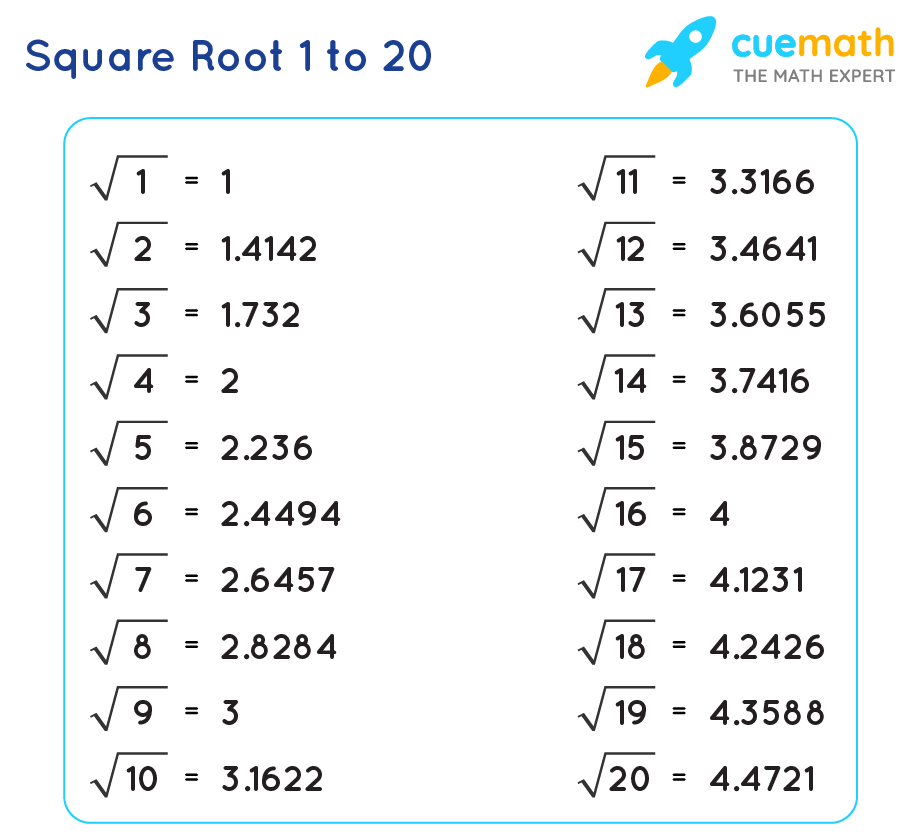
The concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics and essential for understanding various algebraic and geometric principles. A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 25 is 5 because 5 * 5 = 25.
Square roots can be represented using the radical symbol (√). For instance, the square root of 25 is written as √25. There are both positive and negative square roots for any given positive number. However, when referring to the principal square root, we typically mean the positive value.
Properties of Square Roots
- Non-negative Numbers: The square root of a non-negative number is always non-negative.
- Zero: The square root of zero is zero.
- Negative Numbers: The square root of a negative number is not a real number; it is an imaginary number.
Calculating Square Roots
There are various methods to calculate square roots, including:
- Prime Factorization: Breaking down a number into its prime factors can help in finding the square root of perfect squares.
- Long Division Method: A step-by-step method used to find the square roots of both perfect and non-perfect squares.
- Using a Calculator: The most straightforward way to find square roots, especially for non-perfect squares.
For example, to find the square root of 1/25, we can use the property of square roots of fractions:
Applications of Square Roots
Square roots are used in various fields such as physics, engineering, and finance. They help in solving equations, understanding geometric properties, and analyzing data. Mastery of square roots enhances problem-solving skills and mathematical understanding.
Understanding the Square Root of 1/25
The square root of a fraction is determined by taking the square root of both the numerator and the denominator. For the fraction \( \frac{1}{25} \), this process involves the following steps:
- Rewrite the square root of the fraction as the division of square roots: \( \sqrt{\frac{1}{25}} = \frac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{25}} \).
- Find the square root of the numerator and the denominator separately. The square root of 1 is 1, and the square root of 25 is 5.
- Divide the results to get the square root of the fraction: \( \frac{1}{5} = 0.2 \).
Thus, the square root of \( \frac{1}{25} \) is \( \frac{1}{5} \), which equals 0.2. This method can be applied to any fraction to find its square root by following similar steps.
Methods to Calculate Square Roots
Calculating square roots can be approached using various methods, each suitable for different types of numbers and levels of precision required. Here, we outline some of the most common methods for calculating square roots:
-
Prime Factorization
This method is useful for perfect squares. Break down the number into its prime factors and pair the prime factors. The product of these pairs will give the square root.
- Example: To find the square root of 25, factorize it to \(5 \times 5\). The square root of 25 is 5.
-
Long Division Method
This method is used for non-perfect squares. It involves a step-by-step division process to obtain the square root.
- Step 1: Start from the left, pair the digits of the number.
- Step 2: Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair. This is the first digit of the square root.
- Step 3: Subtract the square of the first digit from the first pair, and bring down the next pair of digits. This becomes the new dividend.
- Step 4: Double the number already obtained in the quotient, and find a new digit for the quotient such that the new number formed when multiplied gives a product less than or equal to the dividend.
- Repeat steps 3 and 4 until all pairs are brought down.
-
Estimation and Approximation
For quick approximations, especially useful in mental math:
- Identify the two perfect squares between which the number lies.
- Estimate the decimal value based on how close the number is to the lower or upper perfect square.
- Refine the estimate by averaging and checking the square.
Example: To estimate the square root of 20, note that it lies between 16 (\(4^2\)) and 25 (\(5^2\)). Since 20 is closer to 16, an initial estimate is 4.5. Refining gives approximately 4.47.
-
Using a Calculator
The most straightforward method for finding square roots, especially for non-perfect squares and for high precision, is using a calculator.
- Input the number and press the square root function to get the result.
- Most scientific calculators also provide step-by-step solutions and simplifications.
-
Newton's Method (Heron's Method)
A numerical method to approximate the square root of a number:
- Start with an initial guess \( x_0 \).
- Use the formula \( x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2} \left( x_n + \frac{S}{x_n} \right) \), where \( S \) is the number whose square root you want to find.
- Repeat the process until the desired level of accuracy is achieved.
This method converges quickly and is useful for both manual calculations and programming algorithms.
By understanding and using these methods, one can effectively calculate the square root of any given number, enhancing both mathematical skills and problem-solving abilities.
Step-by-Step Calculation of √1/25
Calculating the square root of a fraction involves a few straightforward steps. Here, we will walk through the process of finding the square root of 1/25 step-by-step.
-
Express the fraction in a form suitable for square rooting:
\(\sqrt{\frac{1}{25}}\)
-
Separate the square root of the numerator and the denominator:
\(\frac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{25}}\)
-
Calculate the square roots of the numerator and the denominator individually:
- Square root of 1: \(\sqrt{1} = 1\)
- Square root of 25: \(\sqrt{25} = 5\)
-
Write the simplified fraction using the results from step 3:
\(\frac{1}{5}\)
-
Thus, the square root of \(\frac{1}{25}\) is:
\(\frac{1}{5} = 0.2\)
This method shows how breaking down the fraction into simpler parts can help in easily calculating its square root. Using this approach, you can find the square root of any fraction efficiently.

Properties of Square Roots
The properties of square roots are fundamental in understanding how they function within mathematics. Here are some key properties explained in detail:
-
Positive and Negative Roots: Every positive number has two square roots: one positive and one negative. For example, the square roots of 25 are +5 and -5.
-
Perfect Squares: A perfect square is an integer that is the square of another integer. For example, 16 is a perfect square because it is 42.
-
Rational and Irrational Roots: The square root of a perfect square is a rational number. However, the square root of a non-perfect square is an irrational number. For instance, √4 = 2 (rational), but √2 is irrational.
-
Square Root of a Product: The square root of a product is the product of the square roots of the factors. Mathematically, √(ab) = √a * √b. For example, √(4*9) = √4 * √9 = 2 * 3 = 6.
-
Square Root of a Quotient: The square root of a quotient is the quotient of the square roots of the numerator and the denominator. This is expressed as √(a/b) = √a / √b. For example, √(1/25) = √1 / √25 = 1 / 5 = 0.2.
-
Square Root of Negative Numbers: The square root of a negative number is an imaginary number. This is because no real number squared results in a negative value. For example, √(-9) is 3i.
-
Even and Odd Perfect Squares: The square root of an even perfect square is even, and the square root of an odd perfect square is odd. For instance, √144 = 12 (even), and √225 = 15 (odd).
-
Zeros in Square Roots: If a number ends with an odd number of zeros, its square root will be irrational. For example, √3000 is irrational.
Understanding these properties helps in simplifying complex mathematical problems and enhances number sense in arithmetic operations.
Special Cases and Examples
The concept of square roots often involves special cases that simplify the calculation process. Understanding these special cases can help in recognizing patterns and applying them effectively. Here are some notable special cases and examples:
-
Perfect Squares:
- When a number is a perfect square, its square root is an integer. For example, the square root of 25 is 5 because 52 = 25.
- Similarly, the square root of 1 is 1 because 12 = 1.
-
Fractions:
- The square root of a fraction can be found by taking the square root of the numerator and the denominator separately. For instance, the square root of 1/25 is 1/5 because √1 = 1 and √25 = 5.
-
Negative Numbers:
- The square root of a negative number involves imaginary numbers. For example, √-1 is represented as i, where i is the imaginary unit.
-
Zero:
- The square root of 0 is 0, since 02 = 0.
Examples:
| Number | Square Root |
| 16 | 4 |
| 9 | 3 |
| 1/4 | 1/2 |
| 1/16 | 1/4 |
By recognizing and understanding these special cases, you can quickly and accurately determine the square roots of various numbers, enhancing your problem-solving skills in mathematics.
Applications of Square Roots in Real Life
Square roots find numerous applications in real-world scenarios, ranging from engineering and physics to finance and everyday measurements. Here are some practical uses:
- Engineering and Construction: Engineers use square roots extensively in calculations involving forces, structures, and materials. For example, when determining the length of the sides of a square for a building foundation or calculating the required strength of materials, square roots are essential.
- Electrical Engineering: Square roots are vital in electrical engineering for calculating voltage, current, and impedance in AC circuits. They help determine power dissipation, signal amplitude, and resonance frequencies in various electronic components and systems.
- Physics: In physics, square roots appear in equations related to motion, energy, and waves. For instance, when calculating the speed of sound in a medium or determining the energy stored in a capacitor, square roots play a crucial role.
- Finance: Square roots are used in finance for risk assessment and portfolio management. Financial analysts use them to calculate standard deviations, volatility measures, and asset pricing models, aiding in decision-making processes.
- Medicine and Biology: Square roots are applied in medical imaging to process data from MRI and CT scans, assisting in diagnostics and treatment planning. In biological sciences, they help analyze growth rates, enzyme kinetics, and population dynamics.
- Navigation and Geography: Square roots are fundamental in navigation for calculating distances between points on maps or globes, determining angular distances, and correcting for distortions in different map projections.

Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about the square root of 1/25:
- What is the square root of 1/25?
The square root of 1/25 is 1/5 or 0.2. This is because the square root of a fraction is the square root of the numerator divided by the square root of the denominator.
- How do you calculate the square root of 1/25?
To calculate the square root of 1/25, you can take the square root of the numerator (1) and divide it by the square root of the denominator (5). Therefore, √(1/25) = √1 / √25 = 1/5.
- Is 1/5 the only square root of 1/25?
No, -1/5 is also a square root of 1/25. In general, every positive number has two square roots: one positive and one negative.
- Why is the square root of 1/25 important?
The square root of 1/25 is important because it represents the principal square root of the fraction, providing a fundamental value in mathematical calculations and real-world applications.
- Can the square root of 1/25 be simplified further?
No, the square root of 1/25 is already in its simplest form as 1/5.
Xem video về Canh tác tiêu quyên 1/25 để hiểu rõ hơn về chủ đề này và xem liệu nó có phù hợp với bài viết về từ khóa 'square root of 1/25' không.
Canh tác tiêu quyên 1/25 - Video chuyên sâu
READ MORE:
Xem video về Đâu là Căn bậc hai? | Toán học cùng thầy J để hiểu rõ hơn về chủ đề này và xem liệu nó có phù hợp với bài viết về từ khóa 'square root of 1/25' không.
Đâu là Căn bậc hai? | Toán học cùng thầy J