Topic square root of 2500: The square root of 2500 is a fundamental concept in mathematics with numerous applications. In this article, we will explore the calculation, properties, and practical uses of the square root of 2500, providing a clear and insightful guide for students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding this mathematical principle.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 2500
- Introduction to Square Roots
- What is the Square Root of 2500?
- Calculating the Square Root of 2500
- Properties of Square Roots
- Applications of Square Roots
- Methods to Find Square Roots
- Square Roots in Mathematics
- Common Square Roots and Their Values
- Practical Examples Using Square Root of 2500
- Square Root and Its Importance in Real Life
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Xem video về cách tính căn bậc hai của 2500 bằng phương pháp phân tích thừa số nguyên tố. Học cách áp dụng phương pháp này vào các ví dụ thực tế.
Square Root of 2500
The square root of 2500 is calculated as follows:
$$\sqrt{2500} = 50$$

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
Square roots are a fundamental concept in mathematics, representing a value that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. For example, the square root of 2500 is the number which, when squared, equals 2500.
Mathematically, this is expressed as:
\(\sqrt{2500} = 50\)
Key properties of square roots include:
- Square roots of perfect squares are always integers.
- The square root function is the inverse of squaring a number.
- Every positive number has two square roots: a positive and a negative root.
Steps to calculate the square root of a number:
- Identify if the number is a perfect square.
- Use prime factorization to simplify the square root.
- Apply the square root property: \(\sqrt{a \cdot b} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b}\).
- For non-perfect squares, use approximation methods or a calculator.
Understanding square roots is crucial in solving quadratic equations, geometry problems, and various real-world applications such as physics and engineering.
| Number | Square Root |
| 2500 | 50 |
| 144 | 12 |
| 81 | 9 |
By mastering square roots, you gain a deeper understanding of the relationships between numbers and enhance your problem-solving skills in mathematics.
What is the Square Root of 2500?
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For 2500, we can find its square root as follows:
Mathematically, we express this as:
\(\sqrt{2500}\)
To find the square root of 2500, we can follow these steps:
- Recognize that 2500 is a perfect square. A perfect square is a number that has an integer as its square root.
- Use prime factorization to break down 2500 into its prime factors:
- 2500 = 22 × 54
- Apply the square root property:
- \(\sqrt{2500} = \sqrt{(2^2 \times 5^4)}\)
- \(\sqrt{(2^2)} \times \sqrt{(5^4)}\)
- 2 × 52 = 2 × 25 = 50
Thus, the square root of 2500 is:
\(\sqrt{2500} = 50\)
This means that 50 × 50 equals 2500, confirming that 50 is indeed the square root of 2500.
Here is a summary in a table format:
| Number | Square Root |
| 2500 | 50 |
Knowing the square root of 2500 helps in various mathematical calculations and real-world applications, such as in geometry and engineering, where understanding the properties of numbers is essential.
Calculating the Square Root of 2500
Calculating the square root of a number involves finding a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals the original number. Here, we will calculate the square root of 2500 using different methods.
Method 1: Using Prime Factorization
- First, express 2500 as a product of its prime factors:
- 2500 = 22 × 54
- Apply the square root to each factor:
- \(\sqrt{2500} = \sqrt{(2^2 \times 5^4)}\)
- \(\sqrt{(2^2)} \times \sqrt{(5^4)}\)
- 2 × 52 = 2 × 25 = 50
Thus, the square root of 2500 is 50.
Method 2: Estimation and Approximation
- Identify two perfect squares between which 2500 lies (e.g., 2401 (492) and 2601 (512)).
- Since 2500 is exactly in the middle of 2401 and 2601, we can infer that its square root is close to 50.
Method 3: Using a Calculator
Using a scientific calculator, simply input \(\sqrt{2500}\) to get the result:
\(\sqrt{2500} = 50\)
Verification
To verify, multiply the result by itself:
50 × 50 = 2500
This confirms that the square root of 2500 is indeed 50.
| Number | Square Root |
| 2500 | 50 |
Understanding how to calculate the square root of 2500 using different methods enhances mathematical problem-solving skills and provides a solid foundation for more complex calculations.
Properties of Square Roots
Square roots have several important properties that are fundamental in various mathematical concepts. Understanding these properties helps in simplifying expressions and solving equations effectively.
1. Non-Negative Output
The square root of a non-negative number is always non-negative. For any non-negative number \(x\), \(\sqrt{x} \geq 0\).
2. Product Property
The square root of a product is equal to the product of the square roots of the factors. For any non-negative numbers \(a\) and \(b\):
\(\sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}\)
3. Quotient Property
The square root of a quotient is equal to the quotient of the square roots of the numerator and the denominator. For any non-negative numbers \(a\) and \(b\) (with \(b \neq 0\)):
\(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\)
4. Square of a Square Root
The square of the square root of a number returns the original number. For any non-negative number \(x\):
\((\sqrt{x})^2 = x\)
5. Rational and Irrational Square Roots
If a number is a perfect square (e.g., 2500), its square root is a rational number. If a number is not a perfect square, its square root is an irrational number (cannot be expressed as a simple fraction).
6. Additive Property (Non-Applicable)
Note that \(\sqrt{a + b} \neq \sqrt{a} + \sqrt{b}\). This property does not hold for addition under the square root.
7. Square Root of Zero
The square root of zero is zero:
\(\sqrt{0} = 0\)
8. Symmetry
For any positive number \(x\), both \(\sqrt{x}\) and \(-\sqrt{x}\) are roots of the equation \(y^2 = x\). However, \(\sqrt{x}\) usually denotes the principal (non-negative) square root.
| Property | Example |
| Non-Negative Output | \(\sqrt{2500} = 50 \geq 0\) |
| Product Property | \(\sqrt{4 \times 9} = \sqrt{36} = 6\) and \(\sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{9} = 2 \times 3 = 6\) |
| Quotient Property | \(\sqrt{\frac{16}{4}} = \sqrt{4} = 2\) and \(\frac{\sqrt{16}}{\sqrt{4}} = \frac{4}{2} = 2\) |
| Square of a Square Root | \((\sqrt{2500})^2 = 2500\) |
| Rational Square Root | \(\sqrt{2500} = 50\) (rational) |
| Irrational Square Root | \(\sqrt{2} \approx 1.414\) (irrational) |
| Square Root of Zero | \(\sqrt{0} = 0\) |
By understanding these properties, you can simplify complex mathematical problems and enhance your comprehension of algebra and calculus.

Applications of Square Roots
Square roots have a wide range of applications in various fields, making them an essential mathematical concept. Here are some of the key applications:
-
Geometry and Architecture:
Square roots are crucial in calculating areas and dimensions. For example, if the area of a square is known, the length of one side can be found using the square root. This is essential in planning and construction projects to determine the size of components and spaces accurately.
-
Statistics:
In statistics, square roots are used to calculate standard deviation, which measures the dispersion or variability of a set of data points. The standard deviation is the square root of the variance and is vital for interpreting data and making informed decisions based on statistical analysis.
-
Physics:
Square roots appear in various physical formulas, such as those calculating force, energy, and velocity. For instance, the speed of an object can be determined using the square root of the product of acceleration and distance.
-
Finance:
In finance, square roots are used to calculate the volatility of stock prices, a measure of risk. The volatility is derived by taking the square root of the variance of stock returns, helping investors make better investment decisions.
-
Computer Science:
Algorithms that involve geometric and spatial calculations often utilize square roots. Applications include computer graphics, where the distance between points in 2D or 3D space is calculated using the Pythagorean theorem, which involves square roots.
-
Engineering:
Engineers use square roots in designing and analyzing systems and structures. For example, the natural frequency of a structure, such as a bridge, is determined using square roots to ensure it can withstand various stresses and forces.
These applications demonstrate the importance of square roots across different domains, highlighting their role in solving real-world problems and advancing technological and scientific understanding.
Methods to Find Square Roots
Finding the square root of a number can be achieved through several methods, each with its own approach and level of complexity. Below are some common methods used to calculate square roots:
-
Prime Factorization Method
This method involves breaking down the number into its prime factors and then pairing them to find the square root. For example, to find the square root of 2500:
- Factorize 2500 into prime factors: \(2500 = 2^2 \times 5^4\).
- Take the square root of each pair of prime factors: \(\sqrt{2500} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 5^4} = 2 \times 5^2 = 2 \times 25 = 50\).
-
Long Division Method
This is a manual method used to find square roots without a calculator. It involves dividing the number into pairs of digits, starting from the decimal point, and performing a series of division and averaging steps. Here's a brief outline of the steps:
- Start by grouping the digits of the number in pairs from right to left.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first group. Subtract this square from the first group.
- Bring down the next pair of digits. Double the current quotient and find a digit to append that makes the product less than or equal to the current dividend.
- Repeat the steps until the desired precision is reached.
-
Newton-Raphson Method
This iterative method is based on calculus and involves making an initial guess and then refining it using the formula:
\[
x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2} \left( x_n + \frac{S}{x_n} \right)
\]For example, to find \(\sqrt{2500}\):
- Start with an initial guess, \(x_0 = 50\).
- Apply the formula: \(x_1 = \frac{1}{2} \left( 50 + \frac{2500}{50} \right) = 50\).
- Since the guess does not change, \(50\) is the square root of \(2500\).
-
Using a Calculator
The simplest method for finding square roots is to use a scientific calculator, which has a dedicated square root function. Simply enter the number and press the square root button to get the result. For example, inputting \(2500\) and pressing the square root button will give \(50\).
These methods illustrate different ways to approach the problem of finding square roots, from manual calculations to using technology for quick results.
Square Roots in Mathematics
The concept of square roots is a fundamental aspect of mathematics, playing a crucial role in various mathematical operations and applications. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. It is denoted by the radical sign √ or expressed as a fractional exponent.
In mathematical notation, the square root of a number \( x \) is represented as \( \sqrt{x} \) or \( x^{1/2} \). For example, the square root of 2500 is 50, since \( 50 \times 50 = 2500 \).
Properties of Square Roots
- Perfect Squares: A number is a perfect square if its square root is an integer. For instance, 2500 is a perfect square because \( \sqrt{2500} = 50 \).
- Rational and Irrational Numbers: The square root of a perfect square is rational, while the square root of a non-perfect square is irrational. For example, \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \) is rational, but \( \sqrt{2} \) is irrational.
- Positive and Negative Roots: Every positive number has two square roots, one positive and one negative. For instance, the square roots of 2500 are 50 and -50.
- Imaginary Numbers: The square root of a negative number is an imaginary number. For example, \( \sqrt{-2500} = 50i \), where \( i \) is the imaginary unit.
Applications of Square Roots
Square roots are widely used in various fields of mathematics and science:
- Geometry: Square roots are essential in calculating distances, areas, and volumes. For instance, the side length of a square with an area of 2500 square units is \( \sqrt{2500} = 50 \) units.
- Quadratic Equations: Solving quadratic equations often involves finding square roots. For example, solving \( x^2 - 2500 = 0 \) gives \( x = \pm 50 \).
- Trigonometry: Square roots appear in trigonometric functions and identities, such as in the Pythagorean theorem.
- Physics: In physics, square roots are used to calculate quantities like standard deviation in statistics and root mean square values in signal processing.
Practical Examples
Here are some practical examples involving the square root of 2500:
| Example | Calculation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Solving \( x^2 - 2500 = 0 \) | \( x = \pm \sqrt{2500} \) | \( x = \pm 50 \) |
| Area of a square | \( \sqrt{2500} \times \sqrt{2500} \) | 2500 square units |
| Distance calculation | \( \sqrt{(50)^2 + (50)^2} \) | Approximately 70.71 units |
Understanding square roots and their properties is essential for mastering various mathematical concepts and solving complex problems efficiently.
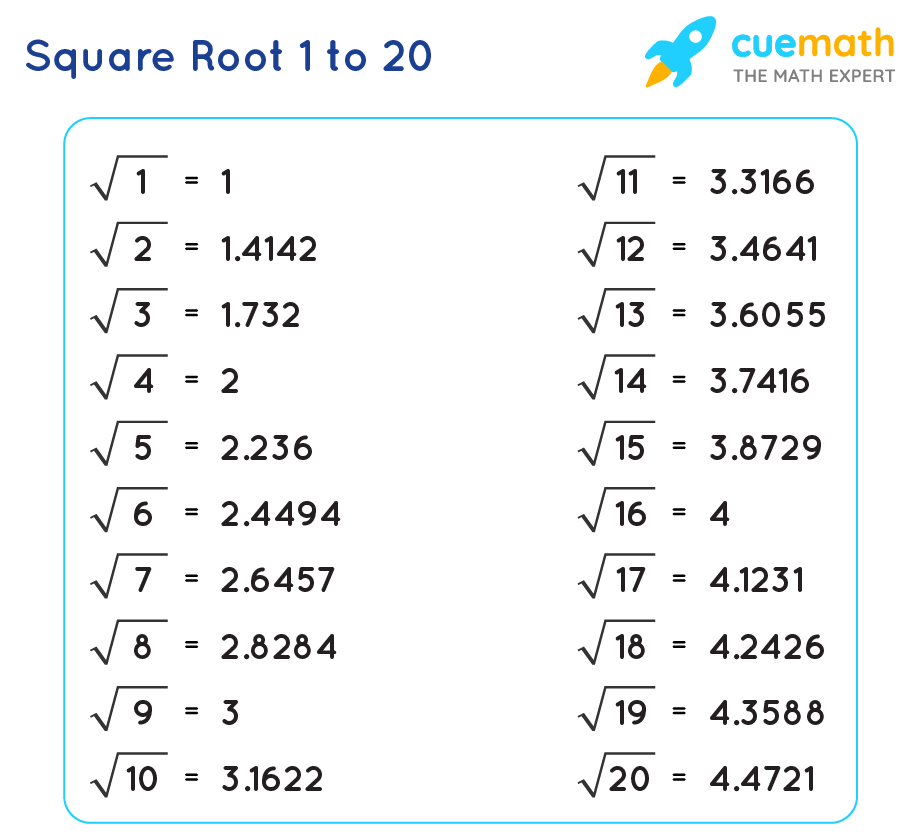
Common Square Roots and Their Values
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Below is a list of common square roots and their approximate values:
| Number | Square | Square Root |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1.000 |
| 2 | 4 | 1.414 |
| 3 | 9 | 1.732 |
| 4 | 16 | 2.000 |
| 5 | 25 | 2.236 |
| 6 | 36 | 2.449 |
| 7 | 49 | 2.646 |
| 8 | 64 | 2.828 |
| 9 | 81 | 3.000 |
| 10 | 100 | 3.162 |
| 11 | 121 | 3.317 |
| 12 | 144 | 3.464 |
| 13 | 169 | 3.606 |
| 14 | 196 | 3.742 |
| 15 | 225 | 3.873 |
| 16 | 256 | 4.000 |
| 17 | 289 | 4.123 |
| 18 | 324 | 4.243 |
| 19 | 361 | 4.359 |
| 20 | 400 | 4.472 |
| 25 | 625 | 5.000 |
| 30 | 900 | 5.477 |
| 40 | 1600 | 6.325 |
| 50 | 2500 | 7.071 |
Knowing these common square roots can be helpful in various mathematical calculations and applications. For instance, they are frequently used in geometry, algebra, and in solving real-world problems that involve area and distance.

Practical Examples Using Square Root of 2500
The square root of 2500 is 50.
Here are some practical examples where the square root of 2500 is used:
- Calculating the side length of a square: If a square has an area of 2500 square units, each side length is the square root of 2500, which is 50 units.
- Distance in a coordinate plane: The distance between points (0, 0) and (50, 50) in a Cartesian plane is 50 units, which corresponds to the square root of the sum of squares of the coordinates (50² + 50² = 5000).
- Time calculations: If an object travels 2500 meters in a straight line, it would take 50 seconds at a constant speed of 50 meters per second, as time equals distance divided by speed.
- Financial calculations: Suppose a principal amount of $2500 grows to $5000. The number of compounding periods required to achieve this growth is 50, calculated using the square root of the growth factor (5000 / 2500 = 2).
Understanding the square root of 2500 helps in various practical scenarios across mathematics, physics, finance, and everyday calculations.
Square Root and Its Importance in Real Life
The square root plays a crucial role in various practical applications:
- Engineering: Engineers use square roots to calculate dimensions, such as determining the size of a room or the strength of materials.
- Finance: Financial analysts use square roots to calculate risk and return, such as in portfolio management and pricing financial instruments.
- Physics: Physicists use square roots in formulas related to motion, energy, and forces, such as calculating velocities or determining gravitational forces.
- Medicine: Medical professionals use square roots in areas like dosage calculations and medical imaging, ensuring accurate treatment and diagnosis.
- Technology: Square roots are fundamental in technology fields like computer graphics, cryptography, and signal processing, enabling advancements in digital imaging and data security.
Understanding the square root of 2500 and its broader applications helps in solving real-world problems efficiently and accurately.
Conclusion
The square root of 2500 is an essential mathematical concept with practical applications across various disciplines. It represents the value which, when multiplied by itself, yields 2500. Understanding square roots, including the specific case of 2500, is crucial in fields such as engineering, finance, physics, medicine, and technology.
Throughout this exploration, we've learned how the square root of 2500 impacts everyday calculations, from determining dimensions in construction to assessing risk in financial investments. Moreover, its significance extends to scientific research, where precise measurements and calculations are paramount.
By grasping the concept of square roots, including specific examples like 2500, individuals can enhance their problem-solving skills and better appreciate the role mathematics plays in our daily lives and technological advancements.
Xem video về cách tính căn bậc hai của 2500 bằng phương pháp phân tích thừa số nguyên tố. Học cách áp dụng phương pháp này vào các ví dụ thực tế.
Video về phương pháp phân tích thừa số nguyên tố của căn bậc hai của 2500
READ MORE:
Xem video về giá trị căn bậc hai của số 2500. Tìm hiểu cách tính toán và ứng dụng của căn bậc hai trong các bài toán thực tế.
GIÁ TRỊ CĂN BẬC HAI CỦA 2500