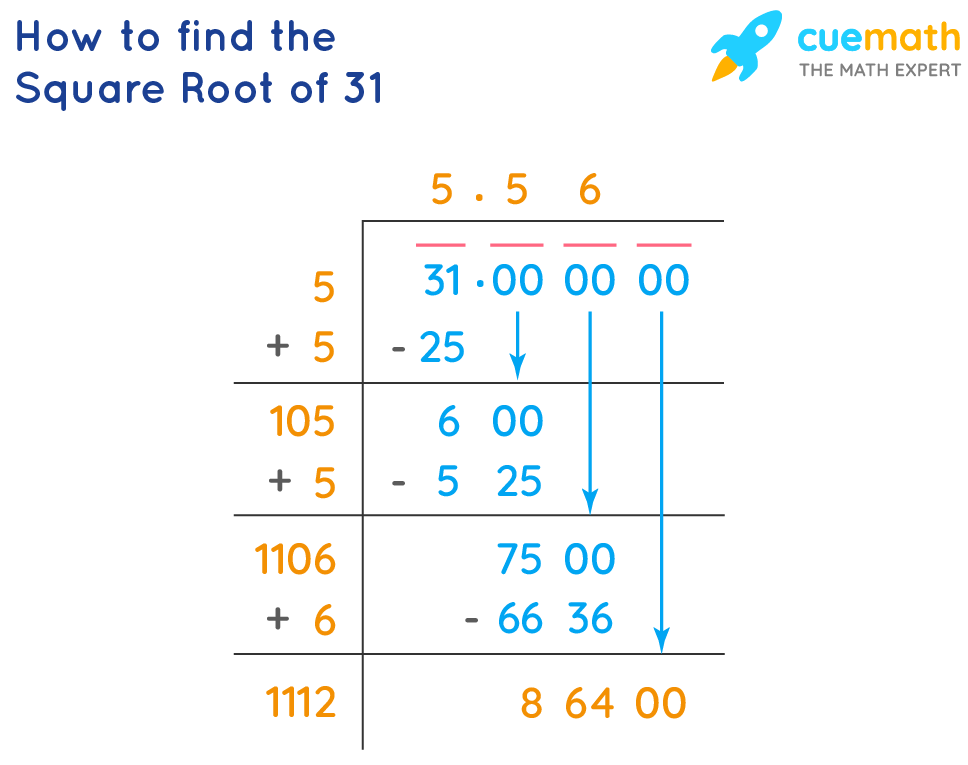
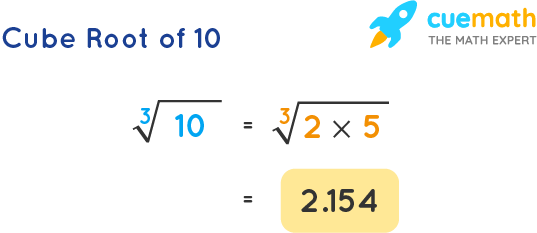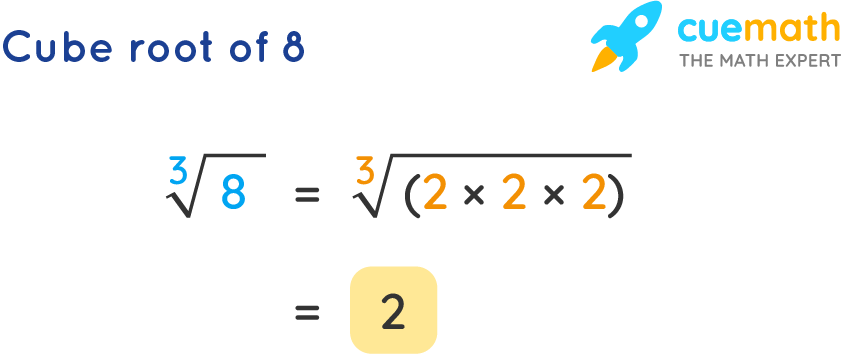Topic 3rd square root calculator: Discover the power of the 3rd Square Root Calculator, your ultimate tool for simplifying cube root calculations. Whether for academic purposes or everyday use, this calculator provides accurate results in seconds. Learn how to effortlessly find cube roots and enhance your mathematical skills with our easy-to-use and efficient calculator.
Table of Content
- 3rd Square Root Calculator
- Introduction to 3rd Square Root Calculator
- Understanding Cube Roots
- How to Calculate Cube Roots
- Manual Calculation vs. Calculator Use
- Features of a Good 3rd Square Root Calculator
- Step-by-Step Guide to Using a 3rd Square Root Calculator
- Common Applications of Cube Roots
- Examples and Practice Problems
- FAQs about Cube Roots and Calculators
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Advanced Topics in Cube Root Calculations
- Online vs. Offline Cube Root Calculators
- Benefits of Using a 3rd Square Root Calculator
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Khám phá mẹo toán học tìm căn bậc ba trong video này. Học cách tính nhanh chóng và chính xác với các bước đơn giản.
3rd Square Root Calculator
A 3rd square root calculator allows you to find the cube root of any given number. The cube root of a number \( x \) is a value \( y \) such that \( y^3 = x \).
How to Use the 3rd Square Root Calculator
- Enter the number for which you want to find the cube root.
- Click on the "Calculate" button.
- The calculator will display the cube root of the entered number.
Examples
- Cube root of 8 is \( \sqrt[3]{8} = 2 \) because \( 2^3 = 8 \).
- Cube root of 27 is \( \sqrt[3]{27} = 3 \) because \( 3^3 = 27 \).
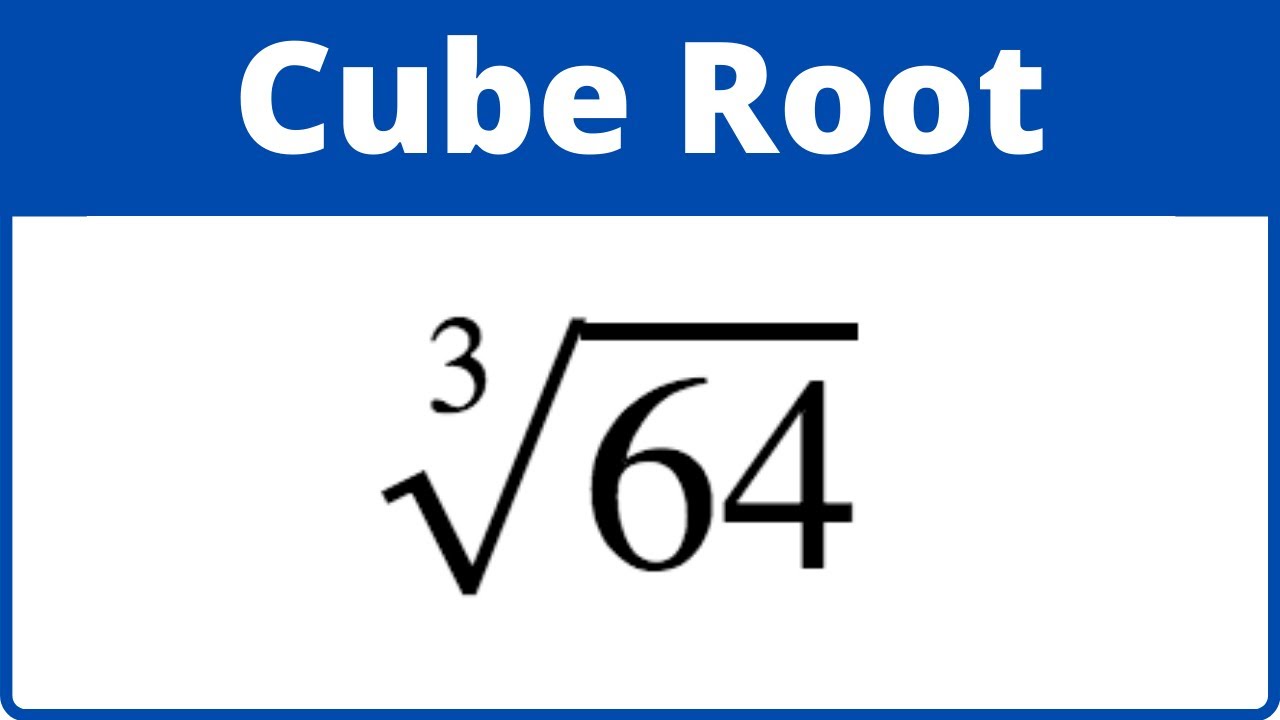
- Cube root of 64 is \( \sqrt[3]{64} = 4 \) because \( 4^3 = 64 \).
Calculator
Use the form below to calculate the cube root of any number:
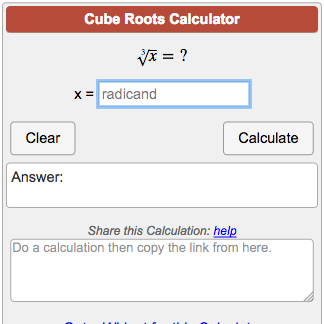
READ MORE:
Introduction to 3rd Square Root Calculator
A 3rd Square Root Calculator, also known as a cube root calculator, is an essential tool for anyone needing to find the cube root of a number quickly and accurately. The cube root of a number \( x \) is the value \( y \) such that \( y^3 = x \). This calculator simplifies the process by providing instant results.
Here are some key features and benefits of using a 3rd Square Root Calculator:
- Accuracy: Provides precise cube root calculations, eliminating errors common in manual calculations.
- Speed: Delivers instant results, saving time and effort.
- Ease of Use: User-friendly interface suitable for all skill levels, from students to professionals.
- Versatility: Useful in various fields, including mathematics, engineering, and finance.
The 3rd Square Root Calculator is particularly helpful in solving problems where finding the cube root is necessary. This can include calculating volumes, solving equations, and working with geometric shapes.
Here is how you can use the 3rd Square Root Calculator:
- Enter the number for which you need to find the cube root into the calculator.
- Press the "Calculate" button.
- View the result, which will be the cube root of the entered number.
For example, to find the cube root of 27, you would enter 27 into the calculator and press "Calculate." The result would be 3, since \( 3^3 = 27 \).
Whether you are a student tackling math homework, an engineer dealing with complex calculations, or someone who simply needs to find cube roots regularly, the 3rd Square Root Calculator is an invaluable tool that makes the process straightforward and efficient.
Understanding Cube Roots
The cube root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself three times, gives the original number. Mathematically, the cube root of \( x \) is represented as \( \sqrt[3]{x} \) or \( x^{1/3} \). For example, the cube root of 27 is 3 because \( 3 \times 3 \times 3 = 27 \).
Cube roots are fundamental in various mathematical and practical applications. They are essential in solving equations involving cubic terms, determining volumes, and understanding geometric properties of shapes.
Here is a step-by-step process to understand cube roots:
- Identify the Number: Determine the number for which you want to find the cube root.
- Prime Factorization (Optional): Break down the number into its prime factors. This can help in manually finding the cube root of perfect cubes.
- Use the Cube Root Formula: Apply the cube root formula \( \sqrt[3]{x} \) to find the cube root of the number.
- Verify the Result: Multiply the result by itself three times to ensure it equals the original number.
Understanding the properties of cube roots can be made easier by exploring some examples:
- The cube root of 8 is \( \sqrt[3]{8} = 2 \), since \( 2 \times 2 \times 2 = 8 \).
- The cube root of 64 is \( \sqrt[3]{64} = 4 \), since \( 4 \times 4 \times 4 = 64 \).
- The cube root of 125 is \( \sqrt[3]{125} = 5 \), since \( 5 \times 5 \times 5 = 125 \).
For non-perfect cubes, calculating cube roots might involve more complex methods or the use of a calculator. Using a 3rd square root calculator simplifies this process by providing accurate results instantly, especially for larger or more complicated numbers.
By understanding cube roots, you can solve a wide range of mathematical problems more effectively and apply this knowledge in real-world scenarios, such as engineering and physics.
How to Calculate Cube Roots
Calculating the cube root of a number can be done using several methods, including manual calculations and using a cube root calculator. Here, we will explore both approaches step-by-step to help you understand and apply them effectively.
Manual Calculation Method
To manually calculate the cube root of a number, follow these steps:
- Estimate the Cube Root: Start with a rough estimate. For example, to find the cube root of 27, you might guess 3 because \( 3^3 = 27 \).
- Refine the Estimate: If the number is not a perfect cube, refine your estimate. For instance, for \( \sqrt[3]{30} \), start with 3, since \( 3^3 = 27 \), and adjust slightly higher.
- Use Long Division Method: Similar to finding square roots, this method involves a more complex algorithm where you divide and average iteratively. This is rarely used due to its complexity.
- Verify the Result: Multiply your result by itself three times to ensure it equals the original number.
Using a Cube Root Calculator
A cube root calculator simplifies the process and provides accurate results instantly. Here is how to use one:
- Enter the Number: Input the number you want to find the cube root for into the calculator.
- Press Calculate: Click the "Calculate" button.
- View the Result: The calculator will display the cube root of the entered number.
For example, using a cube root calculator to find the cube root of 125 involves entering 125 and pressing "Calculate." The result will be 5, since \( 5^3 = 125 \).
Examples of Cube Root Calculations
Here are some examples to illustrate the process:
- The cube root of 8 is \( \sqrt[3]{8} = 2 \), because \( 2 \times 2 \times 2 = 8 \).
- The cube root of 27 is \( \sqrt[3]{27} = 3 \), because \( 3 \times 3 \times 3 = 27 \).
- The cube root of 64 is \( \sqrt[3]{64} = 4 \), because \( 4 \times 4 \times 4 = 64 \).
For non-perfect cubes, using a calculator is especially useful. For instance, the cube root of 30 is approximately 3.107, which can be quickly found using a cube root calculator.
By understanding and applying these methods, you can efficiently calculate cube roots for any given number, enhancing your mathematical problem-solving skills.
Manual Calculation vs. Calculator Use
Calculating cube roots manually and using a calculator both have their own advantages and applications. Below, we explore the methods of manual calculation, the convenience of using calculators, and when each method might be preferable.
Manual Calculation of Cube Roots
Manual calculation of cube roots can be done using various methods, such as estimation and refinement, prime factorization, or using the Newton-Raphson method. Here, we outline a basic step-by-step process for manually estimating a cube root:
- Initial Estimate: Begin with an initial guess. For example, to find the cube root of 27, you might start with a guess of 3 since \(3^3 = 27\).
- Divide and Average: Divide the number by your guess squared, then average the result with twice your guess. For example, if you guessed 3 for \(\sqrt[3]{27}\):
- Divide: \(\frac{27}{3^2} = 3\)
- Average: \(\frac{3 + 3}{3} = 3\)
- Refine: Continue refining your guess by repeating the divide and average step until the result stabilizes. This method works well for perfect cubes.
Using manual methods provides a deeper understanding of the mathematical principles and improves problem-solving skills. However, it can be time-consuming and complex for larger numbers or non-perfect cubes.
Using a Calculator for Cube Roots
Cube root calculators, whether online or as physical devices, offer a quick and accurate way to find cube roots. Here are the steps for using a typical cube root calculator:
- Input the Number: Enter the number for which you want to find the cube root. Most calculators have a dedicated cube root function, often denoted as \(\sqrt[3]{x}\) or a similar symbol.
- Press the Cube Root Button: Activate the cube root function by pressing the corresponding button. For example, to find \(\sqrt[3]{27}\), you would input 27 and press the cube root button.
- Read the Result: The calculator will display the cube root of the number. For \(\sqrt[3]{27}\), the result will be 3.
Calculators are especially useful for large numbers or when high precision is required. They save time and reduce the risk of errors that can occur with manual calculations.
Comparison
| Manual Calculation | Calculator Use |
|---|---|
|
|
In conclusion, both manual calculation and using a calculator have their places in mathematics. Manual calculations foster a deeper understanding, while calculators offer speed and accuracy, making them ideal for practical applications.
Features of a Good 3rd Square Root Calculator
When selecting a 3rd square root (cube root) calculator, it's important to look for certain features that ensure accuracy, efficiency, and ease of use. Here are some key features to consider:
- Accuracy and Precision: The calculator should provide exact results, especially for complex numbers and those requiring high precision. It should also allow users to set the number of decimal places for the result.
- User-Friendly Interface: A simple and intuitive design makes it easy to navigate and use, regardless of the user’s experience level.
- Speed: Fast computation is crucial, especially when working with multiple calculations or under time constraints.
- Step-by-Step Solutions: For educational purposes, a calculator that offers detailed steps of the calculation process can be invaluable for understanding and learning.
- Graphical Representations: Visualizing cube roots and their functions through graphs can enhance comprehension, especially for visual learners.
- Versatility: The ability to handle different types of numbers, including fractions, decimals, and negative numbers, broadens the calculator's applicability.
- Mobile Compatibility: A calculator that works well on both desktop and mobile devices ensures you can perform calculations on the go.
- Additional Mathematical Functions: Features like the ability to solve for variables or perform other related mathematical operations add value and versatility.
Choosing a calculator with these features will not only help you perform cube root calculations more effectively but also enhance your overall mathematical understanding and skills.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a 3rd Square Root Calculator
Calculating the cube root (3rd square root) of a number can be done easily with the help of a 3rd square root calculator. Here is a detailed step-by-step guide to using one effectively:
- Open the Calculator:
Access a reliable 3rd square root calculator. This can be done through various online platforms that offer mathematical calculation tools, such as CalculatorSoup or Symbolab.
- Input the Number:
Enter the number for which you want to find the cube root. Ensure the number is correctly inputted in the designated field.
- Select the Calculation Type:
Some calculators may require you to select the type of calculation you want to perform. Ensure that you have selected the 'cube root' or '3rd root' option.
- Initiate the Calculation:
Click the calculate button to initiate the cube root calculation. The calculator will process the input and provide the result.
- Review the Result:
Once the calculation is complete, the result will be displayed. This is the cube root of the number you entered. For example, if you entered 27, the result will be 3 because \(3^3 = 27\).
- Check for Accuracy:
Verify the result by manually checking or using another calculator if necessary. For manual verification, remember that the cube root of a number \(x\) is \(x^{\frac{1}{3}}\).
Here is an example to illustrate the process:
- Example: To find the cube root of 64:
- Enter 64 in the input field.
- Ensure the calculation type is set to 'cube root'.
- Click on 'calculate' to get the result.
- The result displayed will be 4, since \(4^3 = 64\).
Using a 3rd square root calculator simplifies the process of finding cube roots, especially for large numbers or numbers that are not perfect cubes.
Common Applications of Cube Roots
Cube roots, also known as the 3rd square roots, are used in various fields due to their ability to simplify complex calculations involving volumes and other three-dimensional measurements. Here are some common applications:
-
Geometry and Volume Calculations:
Cube roots are essential in determining the side length of a cube when the volume is known. For instance, if a cube has a volume of \( V \), the side length \( a \) can be found using the cube root: \( a = \sqrt[3]{V} \).
-
Engineering and Architecture:
Engineers and architects often use cube roots to design and analyze structures. Calculating the material needed for cubic components and determining load distributions in three-dimensional space often require the use of cube roots.
-
Physics:
In physics, cube roots are used in various formulas, such as calculating the radius of a sphere from its volume. If the volume \( V \) of a sphere is known, the radius \( r \) can be calculated using the formula: \( r = \left( \frac{3V}{4\pi} \right)^{1/3} \).
-
Economics and Finance:
Cube roots can be used in financial models to determine the compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) over multiple periods. If the initial value \( PV \) and final value \( FV \) are known over \( n \) periods, the CAGR can be calculated as \( CAGR = \left( \frac{FV}{PV} \right)^{1/n} - 1 \).
-
Computer Graphics:
In computer graphics, cube roots are used to normalize vectors and in algorithms for rendering three-dimensional objects. They help in managing the scaling and transformation of 3D models.
Examples and Practice Problems
Understanding and mastering cube roots can be enhanced through practical examples and practice problems. Here are some examples and problems that you can work on to improve your skills:
Example 1: Basic Cube Root Calculation
Find the cube root of 27.
Solution:
\[
\sqrt[3]{27} = 3
\]
This is because \(3 \times 3 \times 3 = 27\).
Example 2: Cube Root of a Larger Number
Find the cube root of 729.
Solution:
\[
\sqrt[3]{729} = 9
\]
This is because \(9 \times 9 \times 9 = 729\).
Example 3: Cube Root of a Negative Number
Find the cube root of -64.
Solution:
\[
\sqrt[3]{-64} = -4
\]
This is because \(-4 \times -4 \times -4 = -64\).
Practice Problems
- Find the cube root of 125.
- Find the cube root of 1000.
- Find the cube root of 216.
- Find the cube root of -27.
- Find the cube root of -343.
Solutions to Practice Problems
1. \[
\sqrt[3]{125} = 5 \quad \text{(since } 5 \times 5 \times 5 = 125\text{)}
\]
2. \[
\sqrt[3]{1000} = 10 \quad \text{(since } 10 \times 10 \times 10 = 1000\text{)}
\]
3. \[
\sqrt[3]{216} = 6 \quad \text{(since } 6 \times 6 \times 6 = 216\text{)}
\]
4. \[
\sqrt[3]{-27} = -3 \quad \text{(since } -3 \times -3 \times -3 = -27\text{)}
\]
5. \[
\sqrt[3]{-343} = -7 \quad \text{(since } -7 \times -7 \times -7 = -343\text{)}
\]
Advanced Practice Problems
For those looking to challenge themselves further, here are some more complex problems involving cube roots:
- Simplify \(\sqrt[3]{64x^6}\).
- Find the cube root of 0.008.
- Simplify \(\sqrt[3]{-125y^3}\).
Solutions to Advanced Practice Problems
1. \[
\sqrt[3]{64x^6} = 4x^2 \quad \text{(since } 4 \times 4 \times 4 = 64 \text{ and } x^2 \times x^2 \times x^2 = x^6\text{)}
\]
2. \[
\sqrt[3]{0.008} = 0.2 \quad \text{(since } 0.2 \times 0.2 \times 0.2 = 0.008\text{)}
\]
3. \[
\sqrt[3]{-125y^3} = -5y \quad \text{(since } -5 \times -5 \times -5 = -125 \text{ and } y \times y \times y = y^3\text{)}
\]

FAQs about Cube Roots and Calculators
Below are some frequently asked questions about cube roots and how to use cube root calculators effectively.
- Q: What is a cube root?
A: A cube root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself three times, gives the original number. For example, the cube root of 8 is 2 because 2×2×2=8.
- Q: Can cube roots be negative?
A: Yes, the cube root of a negative number is also negative. For example, the cube root of -27 is -3 because -3×-3×-3=-27.
- Q: How is the cube root different from a square root?
A: The cube root involves three multiplications of the number (cubing), whereas the square root involves two (squaring). For instance, the square root of 9 is 3, and the cube root of 27 is also 3.
- Q: Is there a standard calculator function for cube roots?
A: Yes, most scientific calculators have a function to calculate cube roots, often denoted as ∛ or x1/3.
- Q: Can I calculate cube roots manually?
A: Yes, it is possible to calculate cube roots manually, but it can be time-consuming and complex, especially for large numbers. It's more efficient to use a calculator for this purpose.
- Q: What is the cube root of zero?
A: The cube root of zero is zero because 0×0×0=0.
- Q: Are there numbers that have more than one cube root?
A: Yes, every non-zero real number has three cube roots: one real root and two complex roots. For instance, the cube root of 8 is 2, but there are also two complex roots.
- Q: How can I calculate the cube root in my head for perfect cubes?
A: For perfect cubes, you can use a mental method. Memorize the cubes of numbers from 1 to 10 along with their last digits. Then, for a given number, estimate the cube root by identifying the closest known cubes.
- Q: Are there any resources to learn more about cube roots?
A: Yes, there are many educational resources available online that provide detailed explanations and practice problems for cube roots. Websites like MathWorld and educational calculators like those found on Calculator.dev and Symbolab are great places to start.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When using a 3rd square root calculator, you might encounter various issues. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
-
Inputting Negative Numbers:
If you're inputting a negative number, ensure the calculator you're using can handle cube roots of negative numbers. For example, the cube root of -27 should be -3 since (-3) × (-3) × (-3) = -27.
-
Decimals and Precision:
For numbers that aren't perfect cubes, the result might be a long decimal. Check the precision settings on your calculator and adjust if necessary. If your result is unexpectedly rounded, try increasing the number of decimal places.
-
Calculator Limitations:
Some online calculators may have limitations on the size of numbers they can handle. Ensure your input values are within the allowable range of the calculator. If your number is very large, consider using a scientific calculator or a more advanced tool.
-
Incorrect Syntax:
Make sure to input the expression correctly. For example, to find the cube root of 64, you should enter it as \( \sqrt[3]{64} \) or 64^(1/3). Incorrect syntax can lead to errors or incorrect results.
-
JavaScript Errors:
If using an online calculator, ensure that JavaScript is enabled in your browser, as many calculators rely on it to function properly.
If you continue to experience issues, refer to the help or FAQ section of the calculator's website for more detailed troubleshooting steps. Additionally, consulting mathematical forums or resources can provide further assistance.
Advanced Topics in Cube Root Calculations
Cube root calculations go beyond the basics and delve into more complex and fascinating areas. Below are some advanced topics that highlight the depth and application of cube roots:
Complex Cube Roots
In mathematics, the cube root of a complex number is also a complex number. For a given complex number \( z = a + bi \), where \( i \) is the imaginary unit, its cube roots can be found using De Moivre's Theorem:
- Express \( z \) in polar form: \( z = r (\cos \theta + i \sin \theta) \)
- Calculate the magnitude: \( r = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \)
- Find the argument: \( \theta = \tan^{-1}(b/a) \)
- Apply De Moivre's Theorem: \( \sqrt[3]{z} = \sqrt[3]{r} \left( \cos \frac{\theta + 2k\pi}{3} + i \sin \frac{\theta + 2k\pi}{3} \right) \) for \( k = 0, 1, 2 \)
Graphical Representations
Visualizing cube root functions helps in understanding their behavior. The graph of the cube root function \( y = \sqrt[3]{x} \) is an S-shaped curve that crosses the origin. Key characteristics include:
- Symmetry: The graph is symmetric with respect to the origin (odd function).
- Intercepts: The only intercept is at (0, 0).
- End Behavior: As \( x \to \infty \), \( y \to \infty \); as \( x \to -\infty \), \( y \to -\infty \).
Higher-Degree Roots
Cube roots are a specific case of nth roots. Calculating higher-degree roots, such as the fourth root or fifth root, involves similar principles but with more complex calculations. The general formula for the nth root of \( a \) is:
\[
\sqrt[n]{a} = a^{1/n}
\]
For example, to find the fourth root of a number, you would use:
\[
\sqrt[4]{a} = a^{1/4}
\]
Applications in Science and Engineering
Cube roots are used in various scientific and engineering fields:
- Physics: Calculating the density of materials when given mass and volume.
- Engineering: Determining dimensions for cubic storage containers.
- Environmental Science: Modeling ecological patterns and population dynamics.
Equation Solving
Advanced calculators can solve equations involving cube roots. For an equation of the form \( x^3 = y \), the solution is:
\[
x = \sqrt[3]{y}
\]
Some advanced calculators provide step-by-step solutions for such equations, enhancing understanding and accuracy.
Using Iterative Methods
Numerical methods, such as the Newton-Raphson method, are used to approximate cube roots when exact methods are not feasible. The iterative formula for finding the cube root of \( a \) is:
\[
x_{n+1} = \frac{2x_n + \frac{a}{x_n^2}}{3}
\]
This method converges quickly to the cube root of \( a \) with an appropriate initial guess.
Exploring Nth Roots
Understanding nth roots broadens the scope of mathematical exploration. The nth root of a number \( a \) is found using:
\[
\sqrt[n]{a} = a^{1/n}
\]
This concept is crucial in various mathematical, scientific, and engineering problems.
Online vs. Offline Cube Root Calculators
Cube root calculators are valuable tools for solving cube roots of numbers. They come in two main forms: online and offline. Each has its advantages and disadvantages. Here, we will explore these in detail to help you decide which option is best for you.
Advantages of Online Cube Root Calculators
- Accessibility: Online calculators can be accessed from any device with an internet connection, making them highly convenient for on-the-go calculations.
- Always Updated: They are often updated automatically with new features and bug fixes.
- No Installation Required: You can use them without the need to download or install any software.
- Variety: Many different calculators are available online, each with unique features and interfaces.
Disadvantages of Online Cube Root Calculators
- Internet Dependency: They require an internet connection, which may not always be available.
- Privacy Concerns: Online tools may collect data, leading to potential privacy issues.
- Ads and Pop-ups: Some free online calculators might display advertisements, which can be distracting.
Advantages of Offline Cube Root Calculators
- Accessibility: Once installed, offline calculators can be used without an internet connection.
- No Distractions: They typically do not have ads or pop-ups, providing a focused user experience.
- Privacy: Offline tools do not track user data, ensuring privacy.
- Stability: They often run more smoothly since they are not dependent on internet speed or connectivity.
Disadvantages of Offline Cube Root Calculators
- Installation Needed: You need to download and install the software, which can be time-consuming.
- Updates: Manual updates might be required to keep the software up-to-date.
- Device Limitation: They can only be used on the device they are installed on, limiting accessibility.
Choosing the Right Calculator for You
When choosing between an online and offline cube root calculator, consider the following factors:
- Internet Access: If you frequently have internet access, an online calculator may be more convenient. If not, an offline calculator would be more reliable.
- Privacy Needs: If you are concerned about data privacy, an offline calculator is a safer option.
- Usage Frequency: For regular, quick calculations, an online calculator is ideal. For intensive use, an offline tool might be better.
Conclusion
Both online and offline cube root calculators have their own sets of advantages and drawbacks. Your choice should depend on your specific needs, such as accessibility, privacy, and how often you require the calculator. By weighing these factors, you can select the calculator that best suits your requirements.

Benefits of Using a 3rd Square Root Calculator
The 3rd square root calculator, also known as a cube root calculator, offers several benefits that make it a valuable tool for both educational and professional purposes. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Accuracy and Precision: Calculating cube roots manually can be error-prone and time-consuming. A 3rd square root calculator ensures precise results, which is crucial for complex mathematical problems and applications in various fields.
- Efficiency: Using a calculator significantly speeds up the process of finding cube roots, allowing users to focus on solving larger problems without getting bogged down in lengthy calculations.
- User-Friendly Interface: Most online cube root calculators are designed to be intuitive and easy to use, even for those with limited mathematical background. This accessibility makes it an excellent tool for students and professionals alike.
- Versatility: These calculators can handle various types of numbers, including integers, decimals, fractions, and even negative numbers. This versatility broadens their applicability in different scenarios, from academic exercises to real-world problems.
- Educational Value: Cube root calculators can serve as learning aids. By providing step-by-step solutions, they help users understand the process of finding cube roots, enhancing their mathematical skills and comprehension.
- Advanced Features: Many 3rd square root calculators come with additional functionalities such as solving equations involving cube roots, graphical representations, and memory functions. These features add value by offering more than just basic calculations.
- Mobile Compatibility: With mobile-friendly designs, these calculators are accessible on smartphones and tablets, making it easy to perform calculations on the go, whether you're in a classroom, office, or fieldwork setting.
- Cost-Effective: Most online cube root calculators are free to use, providing a cost-effective solution for individuals and organizations that need reliable mathematical tools without investing in expensive software.
- Support for Complex Numbers: Some advanced calculators can compute the cube roots of complex numbers, which is particularly useful in higher mathematics, engineering, and physics.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving: By automating the calculation process, these calculators allow users to solve more complex problems efficiently, facilitating better decision-making in fields such as finance, engineering, and science.
In conclusion, the 3rd square root calculator is an essential tool that enhances accuracy, efficiency, and understanding in mathematical calculations. Its versatility and advanced features make it suitable for a wide range of applications, providing substantial benefits to both students and professionals.
Conclusion
The 3rd Square Root Calculator, or cube root calculator, is an essential tool for both students and professionals dealing with mathematical calculations. This tool simplifies the process of finding the cube root of any given number, whether positive or negative, by automating complex calculations and providing accurate results instantly.
One of the key benefits of using a 3rd square root calculator is its efficiency. Manual calculation of cube roots involves several steps and can be prone to errors, especially with large or negative numbers. This calculator eliminates the risk of human error and saves significant time.
Moreover, the calculator is highly versatile. It can handle a variety of inputs, including integers, fractions, and decimals, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in fields such as engineering, physics, and computer science. The ability to quickly compute cube roots facilitates problem-solving and analytical tasks, enhancing productivity and precision.
The 3rd square root calculator also supports educational purposes. Students learning about cube roots can use the calculator to verify their manual calculations and better understand the concept through practical application. It provides immediate feedback, which is crucial for effective learning and mastering mathematical concepts.
In addition, online cube root calculators are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, offering convenience and flexibility. This means users can perform calculations on-the-go without the need for physical tools or extensive mathematical knowledge.
Overall, the 3rd square root calculator is a valuable tool that combines accuracy, efficiency, and convenience. It not only simplifies complex calculations but also supports learning and professional tasks, making it an indispensable resource in various domains.
Khám phá mẹo toán học tìm căn bậc ba trong video này. Học cách tính nhanh chóng và chính xác với các bước đơn giản.
Mẹo Toán Học Tìm Căn Bậc Ba
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn cách tìm lập phương và căn bậc ba của một số bằng máy tính khoa học. Video này giúp bạn sử dụng máy tính một cách hiệu quả và chính xác.
Cách Tìm Lập Phương và Căn Bậc Ba của Một Số Bằng Máy Tính Khoa Học