Topic quarter circle perimeter: Explore the intriguing world of geometry with our comprehensive guide on the "Quarter Circle Perimeter", a fundamental concept that illuminates the beauty of mathematics in everyday life.
Table of Content
- How to calculate the perimeter of a quarter circle?
- Defining the Quarter Circle
- Formula for Calculating the Perimeter
- Step-by-Step Guide to Perimeter Calculation
- Practical Examples and Applications
- Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
- Historical Context of the Quarter Circle Perimeter
- YOUTUBE: Perimeter of a Quarter Circle
- Challenges and Limitations in Perimeter Calculation
- Alternative Methods and Tools for Calculation
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Additional Resources and References
How to calculate the perimeter of a quarter circle?
To calculate the perimeter of a quarter circle, you can follow these steps:
- First, determine the radius of the quarter circle.
- Multiply the radius by 2 to obtain the diameter of the full circle.
- Calculate the circumference of the full circle using the formula:
- Divide the circumference of the full circle by 4 to find the circumference of the quarter circle:
- The result is the perimeter of the quarter circle.
C = 2πr (where C is the circumference and r is the radius)
Quarter Circle Circumference = C / 4
Please note that π represents the mathematical constant pi (approximately 3.14159).
READ MORE:
Defining the Quarter Circle
A quarter circle, also known as a quadrant, is a geometric figure representing one-fourth of a full circle. This intriguing shape is formed by dividing a circle into four equal segments.
- Basic Concept: Imagine cutting a full pie into four equal slices. Each slice represents a quarter circle. It retains the curved edge of the pie, along with two straight lines meeting at a right angle.
- Components: It comprises two key components - the arc (a portion of the circle\"s circumference) and the radius (the line from the center to the perimeter).
- Characteristics: The quarter circle is unique for its 90-degree sector, where the angle at the circle’s center measures exactly one-quarter of the total 360 degrees in a circle.
- Applications: Its practical applications span various fields, including architecture, engineering, and mathematics, particularly in understanding circular shapes and their properties.
Understanding the quarter circle is crucial for delving into more complex geometric concepts, as it embodies both linear and curvilinear properties, offering a fascinating insight into the world of geometry.

Formula for Calculating the Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a quarter circle is a straightforward process once you understand the formula. The perimeter of a quarter circle combines the lengths of the curved arc and the two radii.
- Formula: The formula for the perimeter (P) of a quarter circle with radius (r) is given by P = πr/2 + 2r. This formula combines the arc length (πr/2, which is a quarter of the circle\"s circumference) and the lengths of the two radii (2r).
- Step-by-Step Calculation:
- Identify the radius of the quarter circle.
- Calculate the arc length using πr/2, where π (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
- Add twice the radius (2r) to the arc length.
- The sum gives you the perimeter of the quarter circle.
- Example: For a quarter circle with a radius of 4 units, the perimeter would be calculated as follows:
- Arc length = π(4)/2 = 2π ≈ 6.283
- Adding the radii = 2(4) = 8
- Total Perimeter = 6.283 + 8 ≈ 14.283 units
This formula is essential in fields of geometry, architecture, and design, where precise measurements are crucial.

Step-by-Step Guide to Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of a quarter circle is a straightforward process once you understand the formula. The perimeter of a quarter circle combines the lengths of the curved arc and the two radii.
- Formula: The formula for the perimeter (P) of a quarter circle with radius (r) is given by P = πr/2 + 2r. This formula combines the arc length (πr/2, which is a quarter of the circle\"s circumference) and the lengths of the two radii (2r).
- Step-by-Step Calculation:
- Identify the radius of the quarter circle.
- Calculate the arc length using πr/2, where π (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
- Add twice the radius (2r) to the arc length.
- The sum gives you the perimeter of the quarter circle.
- Example: For a quarter circle with a radius of 4 units, the perimeter would be calculated as follows:
- Arc length = π(4)/2 = 2π ≈ 6.283
- Adding the radii = 2(4) = 8
- Total Perimeter = 6.283 + 8 ≈ 14.283 units
This formula is essential in fields of geometry, architecture, and design, where precise measurements are crucial.
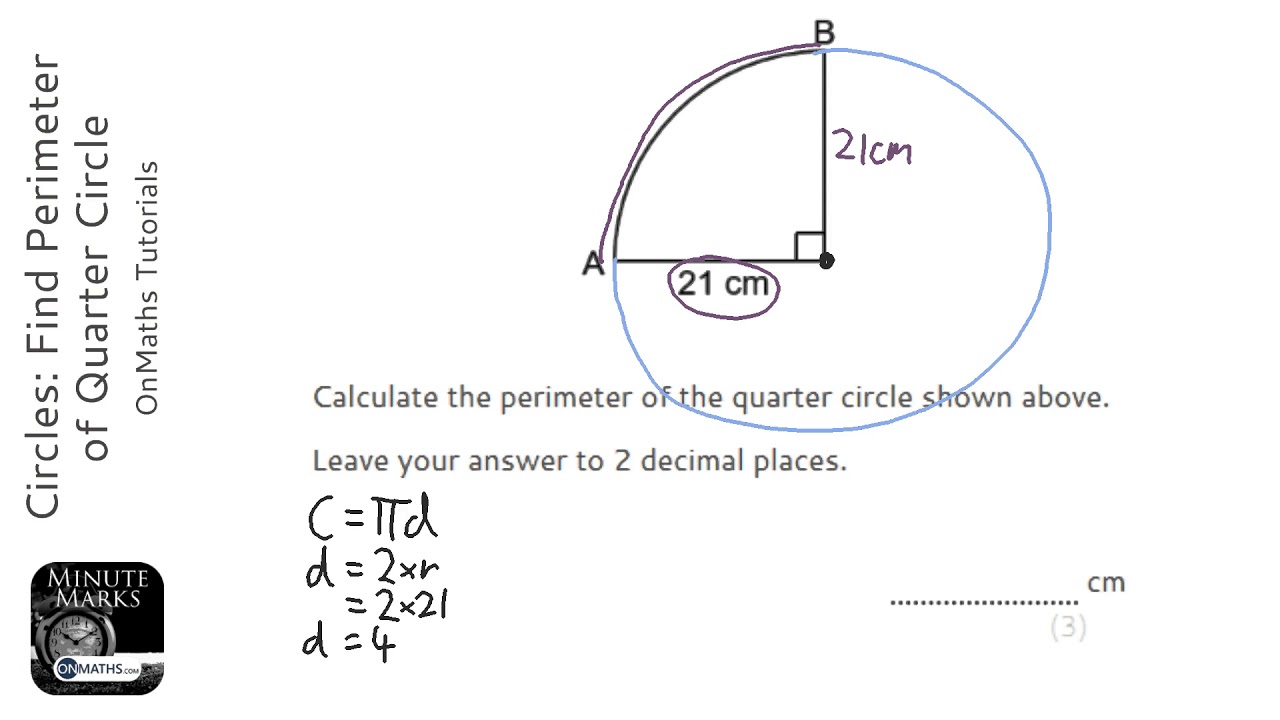
Practical Examples and Applications
Calculating the perimeter of a quarter circle is a straightforward process once you understand the formula. The perimeter of a quarter circle combines the lengths of the curved arc and the two radii.
- Formula: The formula for the perimeter (P) of a quarter circle with radius (r) is given by P = πr/2 + 2r. This formula combines the arc length (πr/2, which is a quarter of the circle\"s circumference) and the lengths of the two radii (2r).
- Step-by-Step Calculation:
- Identify the radius of the quarter circle.
- Calculate the arc length using πr/2, where π (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
- Add twice the radius (2r) to the arc length.
- The sum gives you the perimeter of the quarter circle.
- Example: For a quarter circle with a radius of 4 units, the perimeter would be calculated as follows:
- Arc length = π(4)/2 = 2π ≈ 6.283
- Adding the radii = 2(4) = 8
- Total Perimeter = 6.283 + 8 ≈ 14.283 units
This formula is essential in fields of geometry, architecture, and design, where precise measurements are crucial.

_HOOK_
Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
Understanding the perimeter of a quarter circle often leads to certain misconceptions. This section aims to clarify these common misunderstandings and provide accurate information.
- Misconception: The perimeter of a quarter circle is half the circumference of the circle.
- Clarification: The perimeter of a quarter circle includes one-fourth of the circle\"s circumference plus the lengths of two radii. The correct formula is Perimeter = ( r + r + (frac{2πr}{4}) = 2r + (frac{πr}{2}) ).
- Misconception: The radius of a quarter circle is different from the radius of the original circle.
- Clarification: The radius of a quarter circle is the same as the radius of the original circle from which it is derived.
- Misconception: Calculating the perimeter of a quarter circle is the same as calculating the circumference of the circle.
- Clarification: The perimeter calculation of a quarter circle is unique, as it combines the arc length (one-fourth of the circle\"s circumference) and the length of two radii. Hence, the formula is Perimeter = (0.5 imes π imes r + 2r).
- Misconception: The area of a quarter circle is half the area of the circle.
- Clarification: The area of a quarter circle is one-fourth of the area of the full circle, calculated using the formula Area = (frac{πr^2}{4}).
- Misconception: The central angle of a quarter circle is 45 degrees.
- Clarification: The central angle that generates a quarter circle is 90 degrees, as it represents one-fourth of the circle\"s 360 degrees.
Understanding these clarifications helps in accurate calculations and application of the quarter circle\"s geometric properties in various contexts.

Historical Context of the Quarter Circle Perimeter
The concept of a quarter circle and its perimeter has been a subject of study and application throughout history, particularly in the fields of geometry and architecture. Understanding its historical context provides a deeper appreciation of this geometric figure.
- The quarter circle, often referred to as a quadrant, is an ancient geometric shape. It represents one-fourth of a circle and has been studied since the times of early Greek mathematicians.
- In historical architectural designs, the quarter circle was used for constructing arches and domes. The understanding of its properties was crucial for the stability and aesthetic of these structures.
- The calculation of the perimeter of a quarter circle, which includes one-fourth of the circle\"s circumference plus the lengths of two radii, was essential in planning and constructing various architectural elements in ancient buildings.
- Throughout history, the quarter circle has also been present in various forms of art and design, symbolizing completeness and balance, yet representing a part of a whole.
- The mathematical principles governing the quarter circle and its perimeter have been foundational in the development of geometry as a field of study. They have also been instrumental in teaching mathematical concepts in educational systems over the centuries.
- With the evolution of mathematical understanding, the quarter circle\"s properties have been applied in more advanced fields like engineering, physics, and computer graphics, showcasing its timeless relevance.
The study of the quarter circle\"s perimeter is not just a mathematical exercise, but a journey through the rich history of geometry and its applications in various aspects of human civilization.

Perimeter of a Quarter Circle
Discover the mesmerizing world of quarter circles as we explore the beauty and elegance of this unique geometric shape. Join us in our video to unveil the secrets behind quarter circles and unlock a whole new perspective on geometry!
Calculating Perimeter of Quarter Circle
Learn how to master the art of calculating perimeter in our informative and engaging video. Whether you\'re a math whiz or just seeking to sharpen your skills, our step-by-step guide will have you calculating perimeters like a pro in no time!
Challenges and Limitations in Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of a quarter circle presents unique challenges and limitations. Understanding these can help in more accurate and effective geometric calculations.
- Dependence on Accurate Radius Measurement: The accuracy of the quarter circle\"s perimeter calculation heavily relies on the precise measurement of the radius. Even slight errors in radius measurement can lead to significant inaccuracies in the perimeter.
- Complexity in Manual Calculation: The formula for the perimeter of a quarter circle, which includes a quarter of the circle\"s circumference plus the lengths of two radii, can be complex to calculate manually, especially without a calculator that can process π (pi).
- Limited Applicability in Irregular Shapes: The standard formula for perimeter calculation is applicable only to perfect quarter circles. In real-world scenarios, especially in natural and artistic contexts, quarter circles may not be perfect, rendering the formula less useful.
- Difficulty in Visualizing Geometric Properties: For learners and practitioners, visualizing the geometric properties and understanding the relationship between radius, arc length, and perimeter in a quarter circle can be challenging.
- Challenges in Application to Larger Structures: When applying the concept of quarter circle perimeter in architecture or large-scale designs, the challenges of scale and precision can significantly affect the outcome and effectiveness of the design.
- Limitations in Mathematical Modeling: In mathematical modeling and computer-aided design, accurately representing the perimeter of a quarter circle can be limited by the resolution and capabilities of the software or modeling tools used.
Despite these challenges, with proper understanding and application of mathematical principles, the calculation of the perimeter of a quarter circle can be mastered and effectively utilized in various fields.
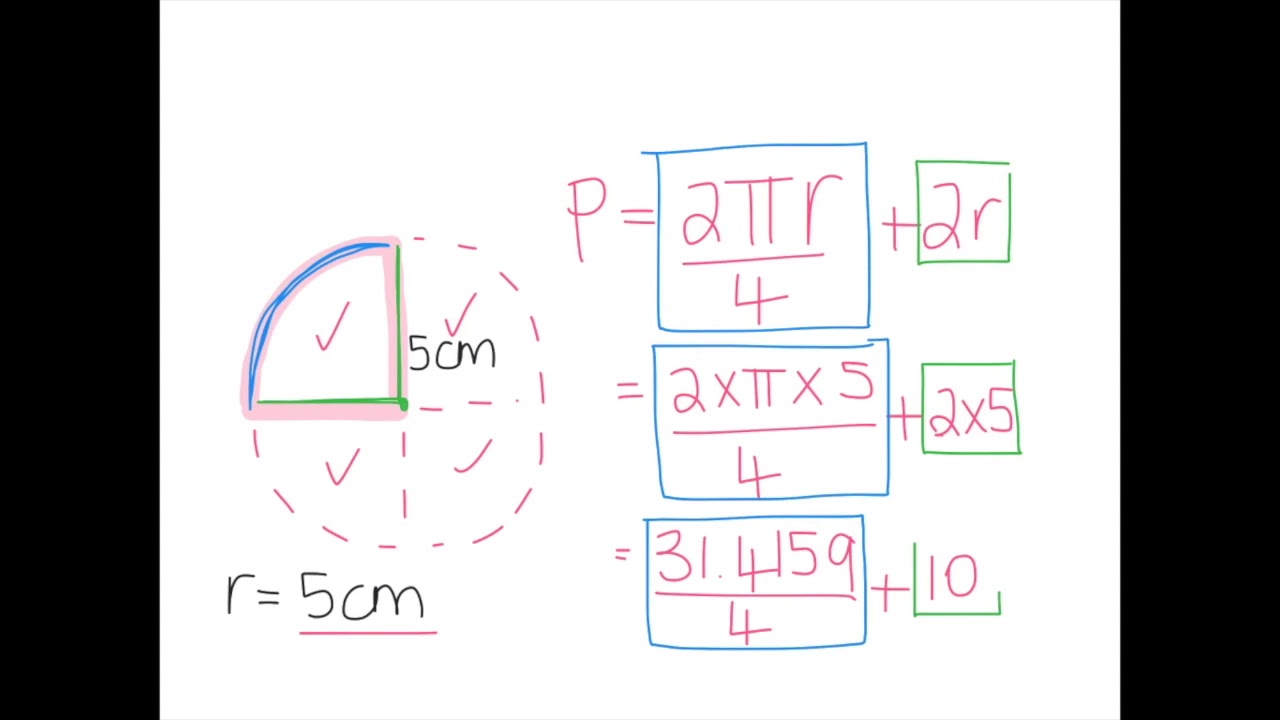
Alternative Methods and Tools for Calculation
While the standard mathematical formula is the most common method for calculating the perimeter of a quarter circle, there are alternative methods and tools that can be utilized, each with their own set of advantages and limitations.
- Using a Measuring Tape: This method involves directly measuring the curved edge and the two radii of the quarter circle. It is simple and doesn\"t require complex calculations. However, it might not be accurate for large circles due to difficulty in measuring the curve precisely.
- Calculator and Mathematical Software: Digital tools like calculators and mathematical software can offer high accuracy in calculations. They are particularly useful for complex calculations involving Pi (π). These tools often have built-in functions to calculate circle perimeters and other related geometric properties.
- Estimation: In situations where exact precision is not required, estimation can be a quick method to approximate the perimeter. However, this method lacks accuracy and should be used cautiously.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software: CAD software can be extremely precise for geometric calculations and is useful in professional fields like architecture and engineering. However, it requires specialized knowledge and access to the software.
- Protractor: For a more visual approach, a protractor can be used to measure the angles and estimate the arc length. This method is less accurate and more suited for educational purposes or rough sketches.
Each of these methods offers a different balance of accuracy, convenience, and applicability. The choice of method largely depends on the context of the calculation, the required precision, and the available resources.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the formula for the perimeter of a quarter circle?
- The formula for the perimeter of a quarter circle is ( P = frac{pi r}{2} + 2r ), where ( r ) is the radius of the circle.
- How do you calculate the perimeter of a quarter circle?
- To calculate the perimeter, add the length of the two radii to the length of the arc (which is a quarter of the circle\"s circumference). This can be done using the formula ( P = frac{pi r}{2} + 2r ).
- Can I calculate the perimeter of a quarter circle without knowing the radius?
- No, the radius is essential for calculating the perimeter of a quarter circle as it is used in the formula.
- Is the perimeter of a quarter circle the same as half the circle\"s circumference?
- No, the perimeter of a quarter circle is not half the circle\"s circumference. It includes one-fourth of the circle\"s circumference plus the lengths of two radii.
- What tools can I use to calculate the perimeter of a quarter circle?
- Tools such as a regular calculator, mathematical software, or online calculators that can calculate Pi can be used for this purpose.
- Are there alternative methods for calculating the perimeter of a quarter circle?
- Yes, alternative methods include using measuring tape for direct measurement or estimation techniques, although they may not provide the same accuracy as the standard formula.

_HOOK_
READ MORE:
Additional Resources and References
For those interested in expanding their knowledge about quarter circles and their perimeters, a variety of resources and references are available. These include educational websites, interactive calculators, and textbooks that offer detailed explanations, examples, and exercises.
- Educational Websites: Websites such as Khan Academy, Coursera, and educational sections of university websites offer tutorials, videos, and articles that explain geometric concepts, including quarter circles.
- Interactive Calculators: Online calculators and software like Desmos, GeoGebra, and Omni Calculator provide tools for visualizing and calculating the properties of quarter circles.
- Mathematics Textbooks: Textbooks at various educational levels cover the topic of quarter circles in their geometry sections, offering detailed explanations and worked examples.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Udemy and edX offer courses in geometry that include modules on circle properties, including quarter circles.
- Mathematical Software: Software such as MATLAB and Mathematica are powerful tools for more advanced calculations and visualizations related to quarter circles.
- YouTube Channels: Educational YouTube channels like Numberphile and 3Blue1Brown offer engaging video content that explains mathematical concepts in an accessible way.
These resources cater to different learning styles and levels, making it easier for anyone to deepen their understanding of quarter circles and their geometric properties.
Embark on an intriguing geometric journey with our comprehensive exploration of the quarter circle perimeter, unveiling its fascinating complexities, practical applications, and timeless relevance in the world of mathematics and beyond.