Topic area and perimeter 4th grade: Discover the exciting world of area and perimeter with our comprehensive guide tailored for 4th graders. Engaging activities, practical examples, and interactive tools make mastering these concepts both fun and educational.
Table of Content
- How can I teach my fourth-grade students about area and perimeter?
- Understanding the Basics of Area and Perimeter
- Differentiating Between Area and Perimeter
- Simple Formulas for Calculating Area and Perimeter
- YOUTUBE: Skill Builder: Area and Perimeter for 4th Grade
- Practical Examples and Activities for 4th Graders
- Using Visual Aids and Tools to Teach Area and Perimeter
- Interactive Games and Apps for Area and Perimeter Learning
- Common Mistakes and Misconceptions to Address
- Tips for Parents to Support Learning at Home
- Aligning Area and Perimeter Lessons with Common Core Standards
- Preparing for Classroom Assessments on Area and Perimeter
How can I teach my fourth-grade students about area and perimeter?
Teaching area and perimeter to fourth-grade students can be done in a step-by-step manner to ensure understanding and engagement. Here\'s a suggested approach:
- Introduce the concepts of area and perimeter using clear and simple definitions. Explain that area is the measure of the surface inside a shape, while perimeter is the measure of the distance around the shape.
- Show examples of different shapes (rectangles, squares, and triangles) and ask students to identify the length and width of each shape.
- Explain that to find the area of a rectangle or square, you need to multiply the length by the width. Encourage students to practice this formula with various examples.
- For triangles, explain that the area can be found by multiplying the base length by the height and dividing the product by 2. Provide examples and guide students through the calculations.
- Next, focus on perimeter. Explain that to find the perimeter of a shape, you need to add up the lengths of all the sides. Make sure to emphasize that all sides must be added, even if they are not explicitly given.
- Provide practice exercises involving both area and perimeter separately. Have students measure the sides of different shapes using rulers or grids, and then calculate the area and perimeter using the appropriate formulas.
- Once students are comfortable with finding area and perimeter individually, introduce word problems that require them to find both quantities simultaneously. This will help them apply their knowledge in real-life scenarios.
- Relate the concept of area and perimeter to everyday situations, such as measuring the size of a room or fencing a garden. This will reinforce the practicality and relevance of these mathematical concepts.
- Encourage students to explain their reasoning and share their calculations with their peers, fostering discussion and collaboration.
- Continue providing ample opportunities for practice and reinforcement, gradually increasing the level of complexity as students progress.
Remember to create a positive and inclusive learning environment, where students feel comfortable asking questions and making mistakes, as this will enhance their understanding and engagement with the topic.
READ MORE:
Understanding the Basics of Area and Perimeter
Area and perimeter are fundamental concepts in geometry, essential for 4th graders to grasp. The area is the space within a shape, measured in square units, while the perimeter is the total distance around a shape, measured in linear units. Understanding these concepts is crucial for solving real-world problems and advancing in mathematics.
- Area: Calculated by multiplying the length and width of a shape, commonly used for rectangles and squares. For instance, the area of a rectangle is found by multiplying its length by its width.
- Perimeter: Determined by adding up all the sides of a shape. For rectangles and squares, this involves adding the lengths of all four sides.
These concepts are not only vital for mathematical reasoning but also for practical applications in daily life, such as determining the amount of paint needed for a wall or the fencing required for a garden. By mastering area and perimeter, students develop a strong foundation for more complex geometric concepts.
- Begin with simple shapes like rectangles and squares to introduce these concepts.
- Use visual aids and physical objects to make the learning process interactive and engaging.
- Practice with real-life examples to help students understand the practical applications of area and perimeter.
By incorporating a variety of teaching methods and practical examples, educators can effectively convey the basics of area and perimeter to 4th graders, setting a solid foundation for their future mathematical journey.

Differentiating Between Area and Perimeter
Understanding the difference between area and perimeter is crucial for 4th graders. While both are measurements in geometry, they serve distinct purposes and are calculated differently.
- Area: Refers to the space inside a shape. It is measured in square units (such as square inches, square feet, or square meters). The formula for calculating the area varies depending on the shape. For a rectangle, the area is calculated by multiplying its length by its width.
- Perimeter: Represents the distance around the outside of a shape. It is measured in linear units (like inches, feet, or meters). To find the perimeter of a rectangle, you add the lengths of all four sides.
These concepts are distinct yet interconnected. For example, two shapes can have the same perimeter but different areas, or vice versa. Understanding these differences helps students solve a variety of real-world problems, from fencing a yard to tiling a floor.
- Start by exploring simple shapes, such as squares and rectangles, to illustrate the differences between area and perimeter.
- Use diagrams and hands-on activities to make these concepts tangible and easier to grasp.
- Introduce more complex shapes as students become comfortable with the basics.
By differentiating between area and perimeter, students develop a deeper understanding of geometry and are better prepared for more advanced mathematical concepts.

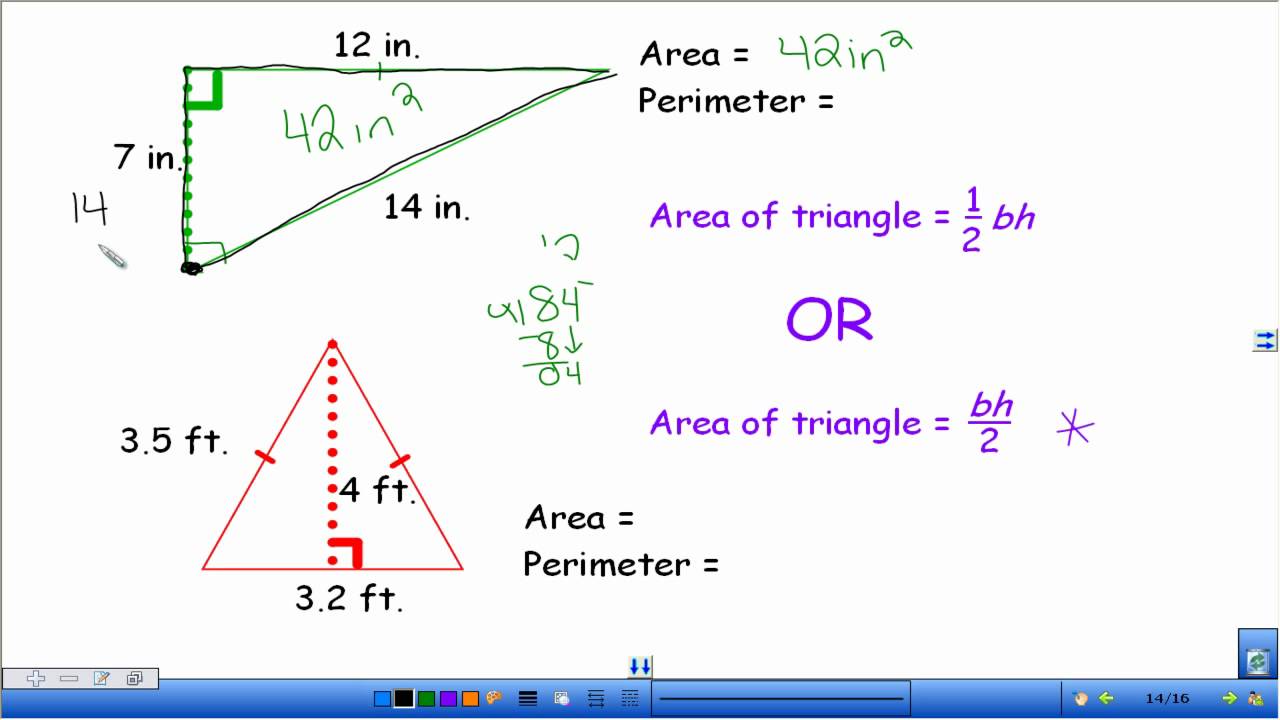
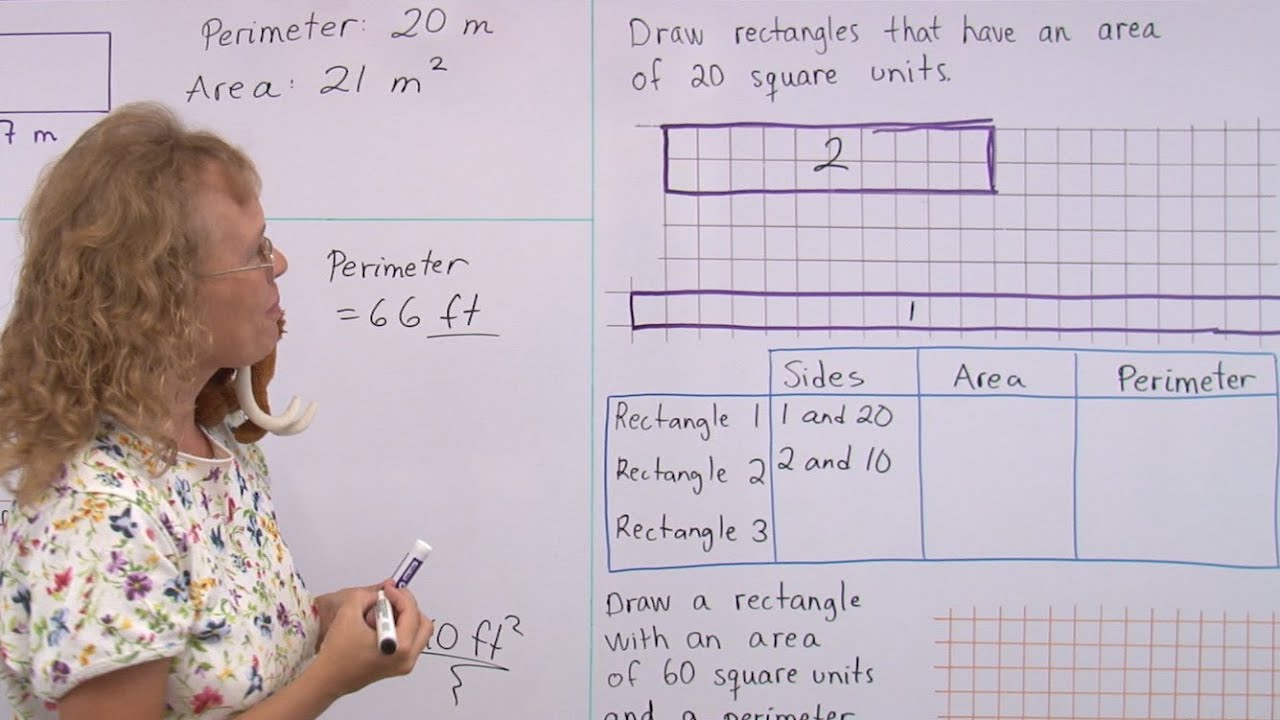
Simple Formulas for Calculating Area and Perimeter
Learning to calculate the area and perimeter of basic shapes is an essential skill for 4th graders. This section will cover the formulas and methods used to calculate the area and perimeter of rectangles, squares, and triangles, which are the most common shapes studied at this grade level.
Rectangles and Squares
For rectangles and squares, the formulas are straightforward:
- Area of a Rectangle: Length × Width
- Perimeter of a Rectangle: 2 × (Length + Width)
- Area of a Square: Side × Side (or Side2)
- Perimeter of a Square: 4 × Side
These formulas are fundamental as they not only help in geometry but also in understanding concepts in real-life contexts like calculating the space in a room or the fence needed for a garden.
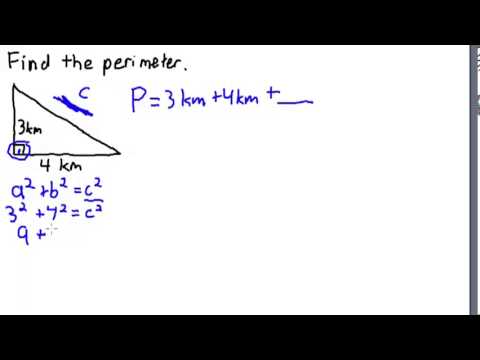
Triangles
Calculating the area and perimeter of triangles involves different formulas depending on the type of triangle:
- Area of a Triangle: (Base × Height) / 2
- Perimeter of a Triangle: Sum of all three sides
For the area of a triangle, the base and height must be perpendicular to each other. Understanding these concepts is crucial for developing spatial awareness and problem-solving skills.
Practice Problems
It\"s important for students to apply these formulas in practical scenarios. The following types of questions can be helpful:
- Calculating the area and perimeter of a room to determine how much paint or flooring is needed.
- Finding the perimeter of a triangular garden to know the length of the fence required.
- Using the area formula to calculate the land area of different shapes on a map.
These practical applications make the learning process engaging and relevant to real-world scenarios.
Visual Aids
Using visual aids like grid paper can be extremely helpful in understanding these concepts. Drawing the shapes and labeling the sides helps in visualizing and better understanding how area and perimeter are calculated.
Conclusion
Mastering the formulas for area and perimeter sets a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. Regular practice with a variety of problems is the key to proficiency in these calculations.

Skill Builder: Area and Perimeter for 4th Grade
Skill Builder: Are you ready to level up your skills? This incredible video is the ultimate skill builder, packed with expert tips, tricks, and techniques to help you master your craft and reach new heights of proficiency. Get ready to unlock your full potential!
How to Find Area and Perimeter
Find: Are you lost in a sea of endless possibilities? Look no further! This captivating video is your ultimate guide to finding what you\'re looking for, whether it\'s inspiration, answers, or that hidden gem you\'ve been searching for. Get ready to embark on an exhilarating journey of discovery!
Practical Examples and Activities for 4th Graders
Engaging 4th graders in learning area and perimeter can be fun and educational with practical examples and activities. These hands-on experiences reinforce their understanding and application of mathematical concepts in real-world contexts.
Crafting with Geometric Shapes
Encourage students to create various shapes using graph paper or large poster boards. They can draw and cut out shapes like rectangles, squares, triangles, and more complex figures like parallelograms or rhombuses. This activity aids in visualizing and understanding the properties of these shapes.
Food-Based Learning
Using food items like cheese crackers or marshmallows, students can form different geometric shapes. This engaging activity helps them to learn about area and perimeter in a fun and interactive way. It\"s important to consider allergies and inclusivity in snack selection.
Math Scavenger Hunt
Create a scavenger hunt throughout the school with various geometric shapes marked out. Students can measure and calculate the area and perimeter of these shapes, making math an adventurous and exciting subject.
Using Grid Worksheets
Worksheets with grid lines help students visualize and calculate the area and perimeter of irregular shapes. These can be a mix of both guided practice and creative exploration where students design their own shapes and then analyze them.
Comparative Analysis
Discuss the similarities and differences between area and perimeter. This can include comparing the two concepts to enhance understanding and clear any confusion, emphasizing how both use measurements but in different ways.
Digital Learning Tools
Incorporate digital resources and online platforms that offer interactive activities and challenges related to area and perimeter. These tools can make learning more dynamic and align with the digital skills of today\"s students.
Conclusion
These activities not only make learning about area and perimeter more engaging for 4th graders but also help them to apply mathematical concepts in practical situations, enhancing their problem-solving and critical-thinking skills.

_HOOK_
Using Visual Aids and Tools to Teach Area and Perimeter
Visual aids and tools are incredibly effective in teaching the concepts of area and perimeter to 4th graders. These resources make abstract ideas more concrete and understandable, enhancing the learning experience.
1. Interactive Worksheets and Practice Problems
Worksheets are a classic tool for teaching area and perimeter. They can be designed to be visually appealing, helping students to grasp the concepts at their own pace. Worksheets may include a variety of shapes like squares, rectangles, and triangles, as well as more complex figures like parallelograms and rhombuses.
2. Exploring Area and Perimeter with Food
Food can be a fun and effective way to teach area and perimeter. Students can use snacks like cheese crackers or marshmallows to create shapes and then calculate their area and perimeter. This hands-on activity is engaging and helps in understanding the concepts in a tangible way.
3. Crafting with Geometric Shapes
Using graph paper or poster boards, students can create various geometric shapes. This activity aids in visualizing and understanding the properties of these shapes, and students can calculate the area and perimeter of their creations.
4. Digital Learning Tools
Online platforms like Khan Academy and eSpark offer interactive activities and challenges related to area and perimeter. These digital resources make learning dynamic and are in line with the digital skills of today\"s students.
5. Classroom Activities
Engaging classroom activities, such as creating unique shapes with blue painter’s tape in the school hallway and organizing scavenger hunts, can make learning area and perimeter exciting. These activities encourage students to apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios.
6. Teaching Similarities and Differences
Discussing the similarities and differences between area and perimeter helps clarify these concepts. While both are forms of measurement, perimeter measures the outside of a shape and area measures the inside.
Conclusion
Using these visual aids and tools, educators can provide a more engaging and comprehensive learning experience for 4th graders studying area and perimeter. The key is to make the lessons interactive, relatable, and fun.

Interactive Games and Apps for Area and Perimeter Learning
Interactive games and apps provide an engaging way for 4th graders to understand and practice area and perimeter concepts. Here are some recommended resources:
- PhET Interactive Simulations - Area Builder: This platform allows students to create shapes using colorful blocks to explore the relationship between perimeter and area. It includes a game mode to build shapes and find the area of various figures, enhancing understanding through interactive challenges.
- SplashLearn - Area Games: SplashLearn offers a variety of games such as \"Find the Area of Shapes Using Unit Shapes,\" \"Multiply to Find the Area,\" and \"Understand Area as Additive.\" These games focus on different aspects of area calculation, helping students to grasp the concept in a fun and interactive manner.
- Math Mammoth - Area and Perimeter Builder: An activity and game combo that allows students to create their own shapes and explore the concepts of area and perimeter. This tool is especially useful for visual and hands-on learning.
- eSpark Learning - Area Adventure: In this game, 4th graders practice finding the area and perimeter of rectangles through an engaging adventure narrative, making learning more relatable and enjoyable.
- Turtle Diary - Area and Perimeter Game: This game teaches students to define and calculate the perimeter and area of squares, rectangles, and other simple polygons. It\"s designed to provide extra practice and reinforce these fundamental geometry concepts.
- Math Playground - Area Blocks: A game where students create shapes with correct area and perimeter, playing either against the computer or a friend. It focuses on problem-solving and spatial reasoning, aligning with Common Core standards for grades 3 and 4.
These interactive tools are designed to make learning about area and perimeter both fun and educational, helping students to develop a solid foundation in these key mathematical concepts.

Common Mistakes and Misconceptions to Address
Understanding area and perimeter can be challenging for 4th graders, and certain misconceptions and mistakes are common. Addressing these effectively can enhance their mathematical understanding:
- Misunderstanding Definitions: Students often confuse the concepts of area and perimeter. It\"s crucial to emphasize that area refers to the space within a shape, measured in square units, while perimeter is the length of the boundary of a shape, measured in linear units.
- Calculation Errors: A common mistake is miscalculating either area or perimeter due to incorrect addition or multiplication of sides. Reinforcing the correct formulas and providing practice in calculating both separately can help.
- Labeling Sides Incorrectly: Some students might label all sides of a shape with the total perimeter value, rather than individual side lengths. Using visual aids and hands-on activities can clarify this concept.
- Confusing Area with Volume: Students may mistakenly think of area in terms of volume. Illustrating the difference between 2D (area) and 3D (volume) figures can rectify this confusion.
- Assuming Multiplication Always Increases the Value: In the context of area, students might believe that multiplication always leads to a larger number, which is not the case when dealing with fractions or decimals in area calculations.
- Inadequate Prior Knowledge: Students\" misconceptions are often rooted in inadequate prior knowledge. Ensuring a strong foundation in basic geometry and measurement can prevent these misunderstandings.
- Lack of Conceptual Understanding: Some students struggle to grasp the relationship between area and perimeter. Activities that allow them to physically manipulate shapes and see the differences in area and perimeter can be beneficial.
Addressing these common mistakes and misconceptions through targeted activities and discussions can significantly improve students\" understanding of area and perimeter.
Tips for Parents to Support Learning at Home
Supporting your child in learning area and perimeter at home can be both fun and effective. Here are some tips and activities to help reinforce these concepts:
- Slow Down the Teaching Process: Don’t rush into formulas. Allow your child to explore and understand the concepts of area and perimeter through practical activities, like building arrays or calculating the area and perimeter of everyday objects.
- Use Everyday Objects: Engage your child in measuring the area and perimeter of items around the house, such as tables, rugs, or garden beds. This brings a practical aspect to their learning and shows real-world applications.
- Creative Projects: Encourage your child to undertake projects that involve area and perimeter. For example, creating a math mosaic using sticky notes, building shapes with LEGO bricks, or designing a tiny house model using cardstock can make learning more interactive and enjoyable.
- Fun with Food: Use food items like cheese crackers or marshmallows to create shapes and calculate their area and perimeter. This can be a fun and delicious way to understand these concepts.
- Games and Songs: Incorporate games like \"Island Conquer\", where students create shapes on a grid, or use catchy songs to remember area and perimeter formulas.
- Real-World Application Activities: Projects like designing a room as an interior designer or building a city on paper can help children understand the practical use of area and perimeter in everyday life.
- Digital Resources: Utilize online platforms like Khan Academy and eSpark for interactive and engaging lessons that make learning area and perimeter more appealing to children.
Remember, the key is to make learning these concepts as engaging and relevant as possible. By incorporating these activities, you can help your child understand area and perimeter in a fun and meaningful way.

Aligning Area and Perimeter Lessons with Common Core Standards
Aligning area and perimeter lessons with Common Core Standards in 4th grade involves a focus on practical application and understanding of these concepts. Here’s how you can align your teaching strategy:
- Apply Formulas in Real-World Problems: Encourage students to apply area and perimeter formulas to real-world scenarios. For example, they could calculate the width of a room given its area and length, treating the area formula as a multiplication equation with an unknown factor (CCSS.Math.Content.4.MD.A.3).
- Representation and Interpretation of Data: Teach students to create and interpret line plots displaying data sets of measurements in fractions of a unit, solving problems involving addition and subtraction of fractions (CCSS.Math.Content.4.MD.B.4).
- Understanding Concepts of Angle and Measurement: Introduce the concept of angles as geometric shapes formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint and how to measure them (CCSS.Math.Content.4.MD.C.5 to CCSS.Math.Content.4.MD.C.7).
- Focus on Geometric Measurement: Emphasize on understanding and measuring angles in whole numbers using tools like protractors and sketching angles of specified measure.
- Integration with Other Mathematical Concepts: Combine lessons on area and perimeter with other 4th grade standards such as place value, operations with whole numbers, and understanding fractions to provide a comprehensive learning experience.
By integrating these Common Core Standards, you can create a holistic teaching approach that not only covers area and perimeter but also connects these concepts with other key mathematical skills.

_HOOK_
READ MORE:
Preparing for Classroom Assessments on Area and Perimeter
Preparing students for assessments in area and perimeter involves engaging, creative, and practical approaches. Here are some effective strategies:
- Engaging Activities: Use interactive activities like creating a math mosaic with square sticky notes, exploring area and perimeter with LEGO bricks, or making shapes and calculating their dimensions. These activities not only reinforce the concepts but also make learning enjoyable.
- Practical Application: Encourage students to apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios. Activities like using floor tiles to calculate area and perimeter or building a city model where they calculate the dimensions of buildings help students see the practical application of these concepts.
- Incorporate Technology: Utilize digital resources like Khan Academy, which offers a comprehensive unit on area and perimeter. This includes quizzes and word problems that can help students practice and master these concepts in a structured manner.
- Worksheets and Assessments: Provide worksheets that cover various levels of difficulty in area and perimeter problems. This can range from basic calculations to more complex problem-solving scenarios, as offered by resources like K5 Learning.
- Food-Based Learning: Bringing food into the classroom for practical exercises, like forming shapes with jelly beans or cheese puffs, can be an engaging way for students to learn about area and perimeter.
- Exploratory Learning: Organize school scavenger hunts or other exploratory activities where students can apply their knowledge of area and perimeter in a fun and interactive setting.
These strategies aim to create a dynamic learning environment where students can grasp area and perimeter concepts effectively while preparing for assessments in a fun and engaging manner.
Embark on an exciting journey through the world of area and perimeter, perfectly tailored for 4th graders. This guide offers a blend of interactive, practical, and fun learning experiences, ensuring a solid foundation in these essential math concepts.