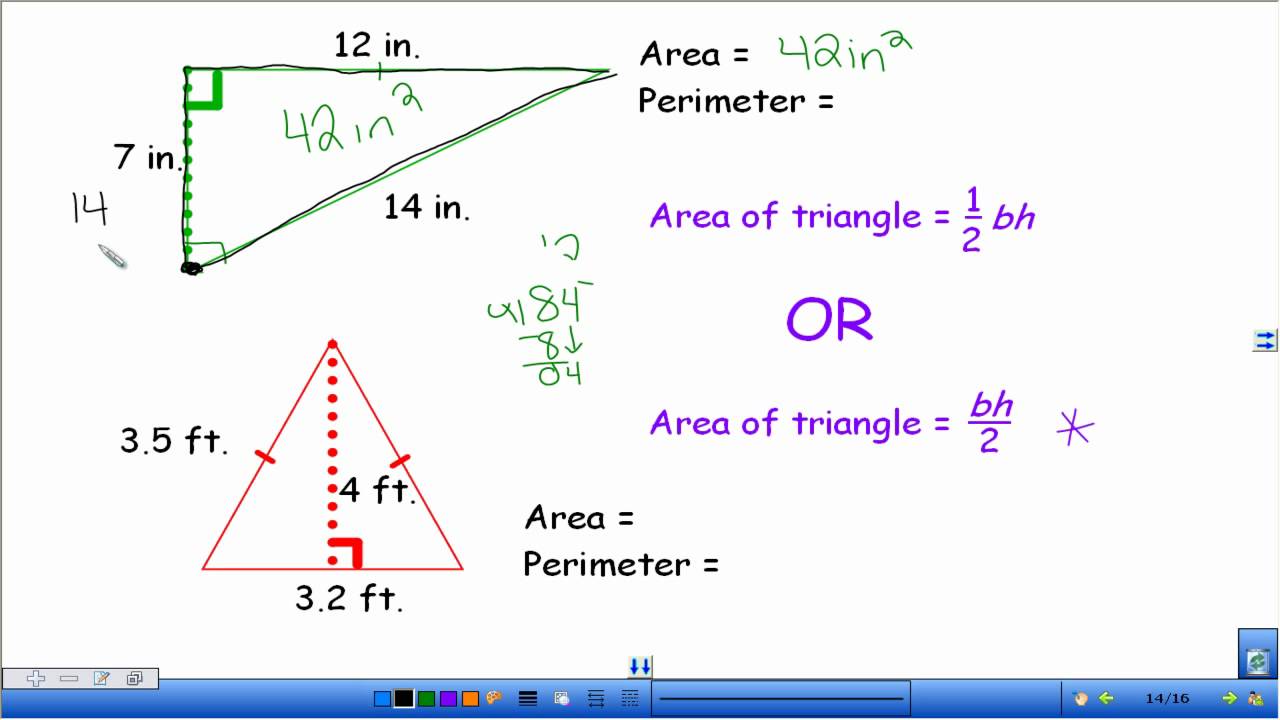
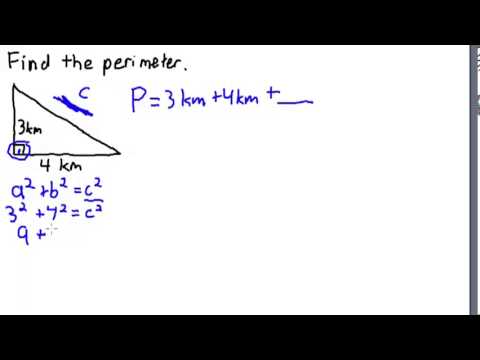
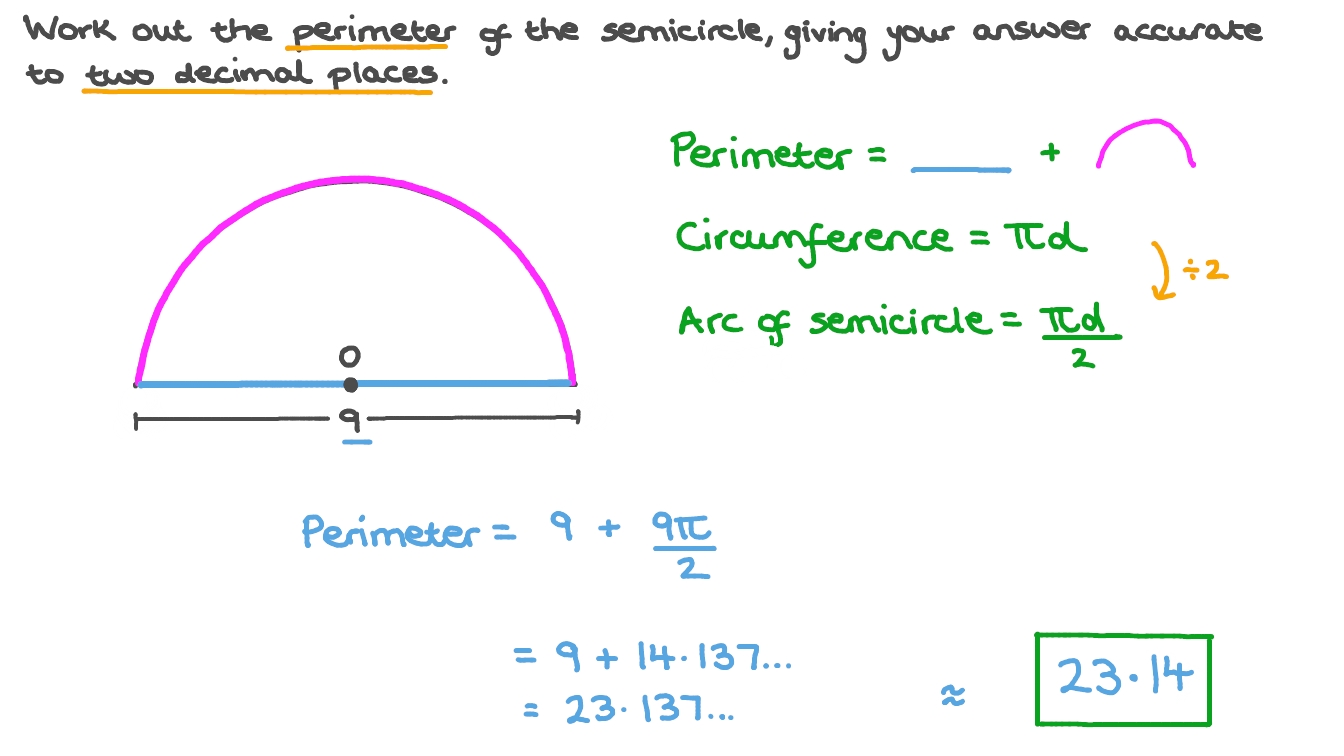
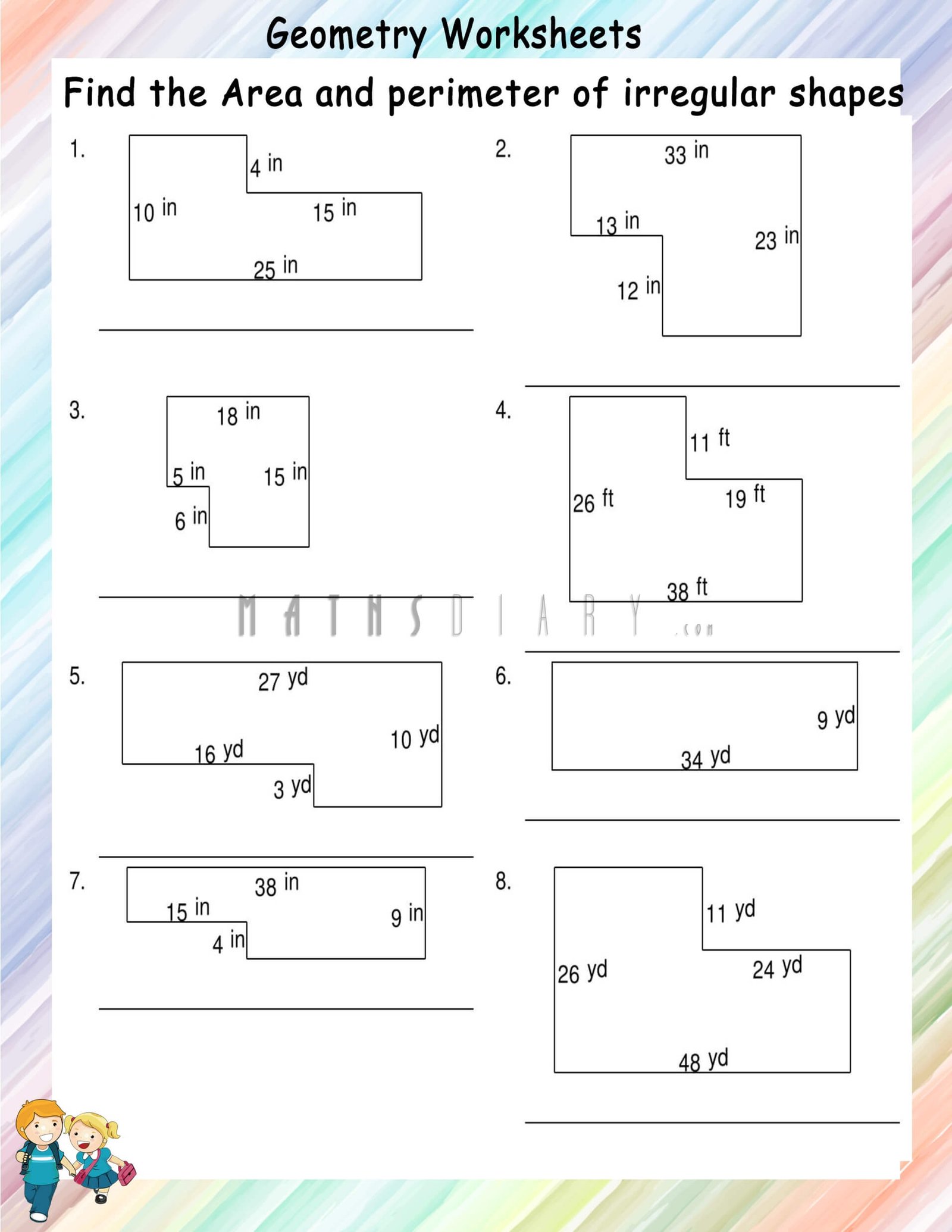
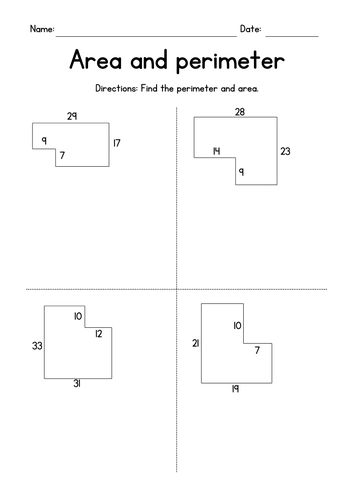
Topic area and perimeter of irregular shapes worksheet: Explore the fascinating world of geometry with our "Area and Perimeter of Irregular Shapes Worksheet," designed to enhance your skills through engaging and comprehensive exercises.
Table of Content
- How to find the area and perimeter of irregular shapes on a worksheet?
- Understanding the Basics of Irregular Shapes
- Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Area
- Techniques for Measuring Perimeter Accurately
- Interactive Worksheets for Practical Learning
- Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- YOUTUBE: Finding the Perimeter and Area of a Composite Shape - L-Shaped Example - Geometry - Math with Mr. J
- Real-World Applications of Area and Perimeter Knowledge
- Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
- Resources and Tools for Enhanced Learning
- Test Your Knowledge: Quiz and Practice Problems
- Feedback and Improvement: Analyzing Common Errors
How to find the area and perimeter of irregular shapes on a worksheet?
To find the area and perimeter of irregular shapes on a worksheet, you can follow these steps:
- Identify the shape: Look at the irregular shape and identify its basic shape or combination of shapes, such as rectangles, triangles, circles, etc.
- Break it down: Break down the irregular shape into smaller, more manageable shapes. For example, if the irregular shape has a combination of rectangles and triangles, break it down into individual rectangles and triangles.
- Measure the sides: Measure the lengths of the sides of each individual shape in the irregular shape.
- Calculate the area: Use the appropriate formulas for each shape to calculate the area of each individual shape. For example:
- Area of a rectangle: Length x Width
- Area of a triangle: 1/2 x Base x Height
- Area of a circle: π x Radius^2
- Add up the areas: Sum up the areas of all the individual shapes to find the total area of the irregular shape.
- Calculate the perimeter: Measure the lengths of all the sides of the irregular shape and add them together to find the perimeter.
By following these steps, you will be able to find the area and perimeter of irregular shapes on a worksheet. Remember to use the appropriate formulas for each shape and double-check your calculations for accuracy.
READ MORE:
Understanding the Basics of Irregular Shapes
Irregular shapes in geometry are intriguing due to their asymmetrical forms, often composed of sides of varying lengths, resulting in unique geometric figures. Unlike regular shapes, irregular shapes don\"t have equal sides or angles, making their area and perimeter calculation more complex but interesting.
To begin understanding these shapes, it\"s essential to recognize that they can often be decomposed into smaller, regular geometric shapes such as triangles, squares, and quadrilaterals. This decomposition is a critical step in calculating their area and perimeter.
- Identify the different regular shapes that can be combined to form the irregular shape. This could involve visualizing the shape as a combination of rectangles, triangles, and other polygons.
- Calculate the area of each of these regular shapes separately. For rectangles, the area is the product of length and width; for triangles, it is half the product of base and height.
- Once you have the areas of all constituent shapes, add them together to get the total area of the irregular shape.
- For perimeter, add the lengths of all the outer sides of the irregular shape. It may require adding the lengths of different shapes that make up the perimeter.
Understanding these basics provides a strong foundation for tackling more complex problems involving irregular shapes. It\"s a skill that finds application in various real-world scenarios, from architecture to landscaping.
As you progress through worksheets and exercises on this topic, remember that practice and visual representation are key to mastering the calculation of area and perimeter of irregular shapes.

Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Area
Calculating the area of irregular shapes can be a fascinating and insightful experience. The key is to break down the complex shape into simpler, regular shapes like rectangles, triangles, or circles. Here\"s a step-by-step guide to help you master this process:
- Identify Regular Shapes: Look at the irregular shape and identify the regular shapes (rectangles, triangles, etc.) that can be formed within it.
- Measure Dimensions: Carefully measure the dimensions (length, width, height, radius) of these regular shapes. Accuracy in measurement is crucial for correct area calculation.
- Calculate Area of Each Shape: Calculate the area of each regular shape using the appropriate formula. For example, area of a rectangle is length × width, and area of a triangle is ½ × base × height.
- Add/Subtract Areas: Add the areas of all these shapes together to get the total area of the irregular shape. In some cases, you might need to subtract the area of any part that does not belong to the main shape.
- Consider Composite Shapes: For complex irregular shapes, consider them as composite shapes made of multiple simple shapes and calculate accordingly.
- Practice with Worksheets: Utilize various worksheets available online for practicing the calculation of area for different irregular shapes. This will enhance your understanding and precision.
Remember, practice is key to mastering the calculation of the area of irregular shapes. Engaging with diverse shapes and problems will sharpen your skills and make you more proficient in geometry.
Techniques for Measuring Perimeter Accurately
Measuring the perimeter of irregular shapes requires a careful approach to ensure accuracy. Here are some techniques that can be effectively used:
- Breaking Down the Shape: Divide the irregular shape into simpler shapes such as rectangles, triangles, or circles. Measure the perimeter of these simpler shapes and then add them together to get the total perimeter of the irregular shape.
- Using a Coordinate Grid: Place the shape on a coordinate grid. Identify the coordinates of the corners (vertices) of the shape. Use the grid to calculate the lengths of the sides by counting the grid units.
- Applying the Distance Formula: For shapes placed on a coordinate grid, use the distance formula to find the lengths of sides between two points. The distance formula is (sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}), where ((x_1, y_1)) and ((x_2, y_2)) are the coordinates of two points.
- Tracing and Measuring: If the shape is on paper, trace it onto graph paper. Measure the lengths of the sides using the graph paper\"s scale. This method is particularly useful for complex or large shapes.
- String and Ruler Method: For physical objects, use a string to trace the perimeter, then measure the length of the string with a ruler. This method is effective for shapes that are not easily divisible into simpler shapes.
- Estimation Techniques: If exact measurement is not possible, estimate the length of curved or uneven sides by comparing them to a known length, such as the width of a ruler or a standard sheet of paper.
These techniques, combined with practice and careful observation, will enhance your ability to measure perimeters of irregular shapes with precision.

Interactive Worksheets for Practical Learning
Interactive worksheets are an essential tool for understanding and mastering the concepts of area and perimeter of irregular shapes. These worksheets offer a range of activities suitable for various grades and difficulty levels.
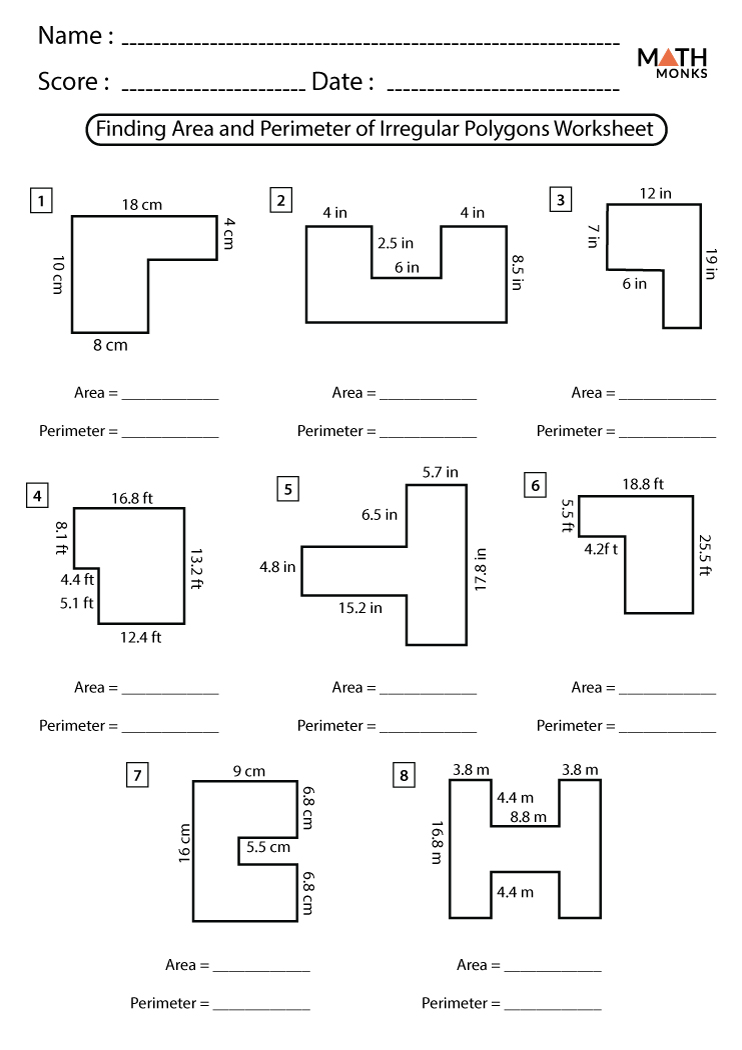
- Rectilinear Figures: Worksheets focusing on rectilinear figures (irregular shapes made up of two or more rectangles) guide students through finding the area of each rectangle and adding them together to find the total area of the irregular shape.
- Grade-Specific Activities: There are worksheets tailored for different grades, ensuring the level of complexity is appropriate for the student\"s age and educational stage. Activities vary from basic shapes in lower grades to more complex shapes in higher grades.
- Compound Shapes: For more advanced learners, worksheets include practice with compound shapes, where students break down complex figures into simpler components, calculate individual areas, and then sum them for the total area.
- Interactive Exercises: Some worksheets use interactive elements, like grid-based calculations, where students can directly engage with the shapes, enhancing their understanding of spatial dimensions and measurements.
- Measurement and Estimation: Worksheets also focus on measuring and estimating the perimeters of irregular shapes, using both standard units and non-standard units like string lengths.
- Visual and Practical Applications: Many worksheets include visual aids such as diagrams and grids, which are particularly helpful in visualizing and solving problems related to area and perimeter of irregular shapes.
These worksheets provide a comprehensive and engaging approach to learning, allowing students to practice and reinforce their understanding of geometric concepts in a structured and interactive manner.

_HOOK_
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Understanding and calculating the area and perimeter of irregular shapes can present several challenges. Below are common obstacles learners face, along with strategies to overcome them:
- Identifying Base Shapes: Irregular shapes can often be broken down into simpler shapes like rectangles, triangles, or circles. The challenge lies in recognizing these shapes. Practice by working on varied examples that require breaking down complex shapes into simpler ones.
- Complex Measurements: Irregular shapes may have sides with different lengths, making measurement difficult. Using a ruler or a grid can help in accurately measuring each side. For digital worksheets, tools like zoom and grid overlays can assist in precise measurements.
- Application of Formulas: Remembering and correctly applying area and perimeter formulas for different shapes is crucial. Create a cheat sheet with formulas for quick reference and regularly practice problems that use these formulas in various combinations.
- Estimation Skills: Sometimes, exact measurements are not possible, especially for curved or irregular sides. Develop estimation skills by comparing with known measures or using estimation strategies like rounding off.
- Calculation Errors: Calculation mistakes are common. Double-check work, use calculators for complex calculations, and practice mental math to enhance accuracy.
- Understanding Composite Shapes: Irregular shapes often involve composite shapes. Practice by identifying individual shapes within a composite figure, calculating their area or perimeter separately, and then combining these to find the total.
Overcoming these challenges requires practice, patience, and a methodical approach to problem-solving. Utilizing a variety of resources and worksheets can provide the necessary practice to master these concepts.
Finding the Perimeter and Area of a Composite Shape - L-Shaped Example - Geometry - Math with Mr. J
Are you fascinated by shapes? Discover the intriguing world of composite shapes in this captivating video! Learn how different shapes can come together to create complex and beautiful designs.
Finding the Area of a Composite Figure - Area of Composite Rectangles
Dive into the world of art and geometry with this enlightening video on composite figures! Explore how various figures can be combined to form unique and visually appealing compositions. Get ready to be inspired!
Real-World Applications of Area and Perimeter Knowledge
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is not only crucial for academic purposes but also has numerous practical applications in real life. Here, we explore several scenarios where this knowledge is invaluable.
Architecture and Interior Design
In architecture and interior design, calculating the area and perimeter of irregular spaces is essential for effective planning and utilization of space. This includes determining the amount of flooring or carpet needed, or evaluating the space for furniture placement and movement.
Landscaping and Gardening
For landscaping and gardening, area and perimeter calculations help in planning garden layouts, installing fencing, or setting up irrigation systems. It ensures optimal use of space and resources.
Art and Craft
In the world of art and craft, these concepts aid in designing layouts and patterns, especially in projects like quilting, where precise measurement is key for aesthetically pleasing designs.
Geography and Mapping
Geographers and cartographers use area and perimeter measurements to create accurate maps and models of terrains, which are vital for urban planning, environmental conservation, and resource management.
Sports Field Design
Designing sports fields and courts also requires knowledge of area and perimeter to ensure standard dimensions are met, impacting the fairness and safety of the sport being played.
Manufacturing and Construction
In manufacturing and construction, these calculations are crucial for material estimation, cost calculation, and efficient layout planning, directly impacting the feasibility and profitability of projects.
Education and Problem-Solving
Educationally, mastering these concepts enhances problem-solving skills. It encourages students to approach complex problems methodically, breaking them down into simpler, manageable parts.
Environmental Planning
For environmental planning, understanding the area and perimeter is important for habitat mapping, resource allocation, and managing natural reserves effectively.
These real-world applications highlight the importance of understanding area and perimeter, not just in mathematical theory, but in practical, everyday scenarios.

Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
Advancing in the study of area and perimeter of irregular shapes opens up a world of complex and intriguing mathematical concepts. Here are some areas for further exploration:
Compound Shapes
Delve into the complexities of compound shapes. Learn to divide these shapes into simpler parts to calculate their area and perimeter. This approach is particularly useful in real-world applications such as construction and design.
Coordinate Planes and Geometry
Use coordinate planes to enhance understanding of shapes in a two-dimensional space. This can lead to better comprehension of how geometric principles apply in practical scenarios, such as in architecture and engineering.
Decimals and Fractions in Measurements
Explore how decimals and fractions are used in the measurements of area and perimeter. This precision is crucial in fields like science and engineering, where exact measurements are necessary.
Practical Applications in Everyday Life
Investigate how the concepts of area and perimeter are used in everyday life. From planning a garden layout to designing a sports field, the practical applications are endless.
Mathematical Puzzles and Challenges
Engage with mathematical puzzles and challenges that involve irregular shapes. These activities not only enhance problem-solving skills but also make learning fun and interactive.
Integration with Other Mathematical Concepts
Discover the integration of area and perimeter with other mathematical concepts such as algebra, trigonometry, and calculus. This interdisciplinary approach provides a deeper understanding of mathematics as a whole.
These advanced concepts and exploration paths will not only deepen your understanding of area and perimeter but also open up new avenues of learning and application in various fields.
Resources and Tools for Enhanced Learning
To master the concepts of area and perimeter of irregular shapes, a variety of resources and tools can be utilized. These resources cater to different levels of learners, from basic to advanced, and provide a comprehensive understanding of the subject.
Worksheets for Practice
- Basic to advanced worksheets: These include exercises for calculating area and perimeter of rectilinear figures, compound shapes, and more complex geometric forms.
- Interactive worksheets: They offer a dynamic learning experience, allowing students to engage with the material in a more hands-on manner.
- Homework and quiz sheets: These are designed to test understanding and help in reinforcing concepts learned in class.
Educational Websites
Websites such as K5 Learning, Super Teacher Worksheets, Cuemath, and Easy Teacher Worksheets offer a range of educational materials. These include:
- Downloadable PDFs for offline practice.
- Structured lessons ranging from basic to advanced levels.
- Interactive learning sessions and video tutorials for enhanced understanding.
Teaching Tools and Aids
- Task cards and flashcards: Useful for quick revisions and practicing problem-solving skills.
- Instructional videos: These can provide visual explanations of complex concepts, making them easier to understand.
- Worksheet generators: Teachers and parents can create customized worksheets to cater to the specific needs of their students or children.
Math Games and Puzzles
Engaging in math games and puzzles is a fun way to learn and apply concepts of area and perimeter in a less formal setting.
Utilizing these resources and tools can greatly enhance the learning experience and provide students with the necessary skills to master the concepts of area and perimeter of irregular shapes.

Test Your Knowledge: Quiz and Practice Problems
Testing your knowledge of the area and perimeter of irregular shapes is an essential part of the learning process. Here are various quizzes and practice problems to help you assess and improve your understanding.
Interactive Quizzes
Participate in interactive quizzes designed to test your understanding of calculating the area and perimeter of irregular shapes. These quizzes typically include multiple-choice questions and instant feedback to help you learn from your mistakes.
Practice Problems
- Beginner Level: Start with basic problems focusing on rectilinear figures and simple compound shapes.
- Intermediate Level: Progress to more challenging problems that involve calculating areas and perimeters of compound shapes using grid references.
- Advanced Level: Tackle complex problems that require breaking down irregular shapes into regular ones, using decimals in measurements, and more in-depth problem-solving.
Worksheet Exercises
Worksheets are a great way to practice. They often include a range of problems from basic to advanced levels and sometimes come with answer keys for self-assessment.
Lesson Reviews and Warm-Ups
Use lesson review sheets and warm-up exercises to refresh your understanding before diving into more complex problems. These resources are particularly useful for reinforcing learning and ensuring a strong grasp of the basics.
Through these quizzes and practice problems, you can effectively test and enhance your understanding of the area and perimeter of irregular shapes, preparing you for more advanced mathematical concepts.
_HOOK_
READ MORE:
Feedback and Improvement: Analyzing Common Errors
When mastering the concepts of area and perimeter of irregular shapes, it\"s crucial to understand and learn from common errors. This section provides insights into typical mistakes and offers strategies for improvement.
Common Mistakes in Calculating Area and Perimeter
- Misinterpreting Dimensions: A frequent error is misunderstanding the dimensions given for a shape. It\"s vital to carefully read and interpret the lengths and widths provided.
- Incorrect Addition or Multiplication: Simple arithmetic errors in adding or multiplying lengths can lead to incorrect area or perimeter calculations. Double-checking calculations is key.
- Overlooking Compound Shapes: Not recognizing that an irregular shape can be broken down into simpler shapes (like rectangles and triangles) often leads to miscalculations.
Strategies for Improvement
- Practice with a Variety of Shapes: Regular practice with different types of irregular shapes enhances familiarity and skill.
- Use of Visual Aids: Diagrams and grid references can be extremely helpful in visualizing and solving problems involving irregular shapes.
- Step-by-Step Approach: Breaking down the process into clear steps can prevent mistakes and ensure a thorough understanding of the concepts.
Resources for Enhanced Learning
Utilizing worksheets and interactive tools, like those found on K5 Learning, Super Teacher Worksheets, Cuemath, and Easy Teacher Worksheets, can provide invaluable practice and reinforce learning. These resources offer a range of problems from basic to advanced levels, often with solutions and explanations to help students learn from their mistakes.
By addressing common errors and employing these strategies, students can significantly improve their ability to calculate the area and perimeter of irregular shapes, laying a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Unlock the secrets of geometry with our comprehensive guide on area and perimeter of irregular shapes. Explore interactive worksheets, master common challenges, and elevate your mathematical skills to new heights. Dive into this fascinating world today!