Topic search perimeter for escaped prisoner: Exploring the critical tactics in establishing a search perimeter for an escaped prisoner, this article delves into the dynamic strategies and multidisciplinary approaches vital for ensuring public safety and successful apprehension.
Table of Content
- How far has the search perimeter been expanded for the escaped prisoner?
- Understanding the Nature of Prison Escapes
- Establishing Initial Search Parameters and Perimeters
- Utilizing Technology and Surveillance in Manhunts
- Challenges Posed by Geography and Environment
- Coordination Among Law Enforcement Agencies
- Community Involvement and Public Safety Measures
- YOUTUBE: Police: Escaped prisoner in PA slipped through search perimeter
- Learning from Past Escapes: Case Studies and Analyses
- Legal and Ethical Considerations in Prisoner Hunts
- Psychological Aspects of Escaped Prisoner Behavior
- Future Innovations in Search and Capture Tactics
How far has the search perimeter been expanded for the escaped prisoner?
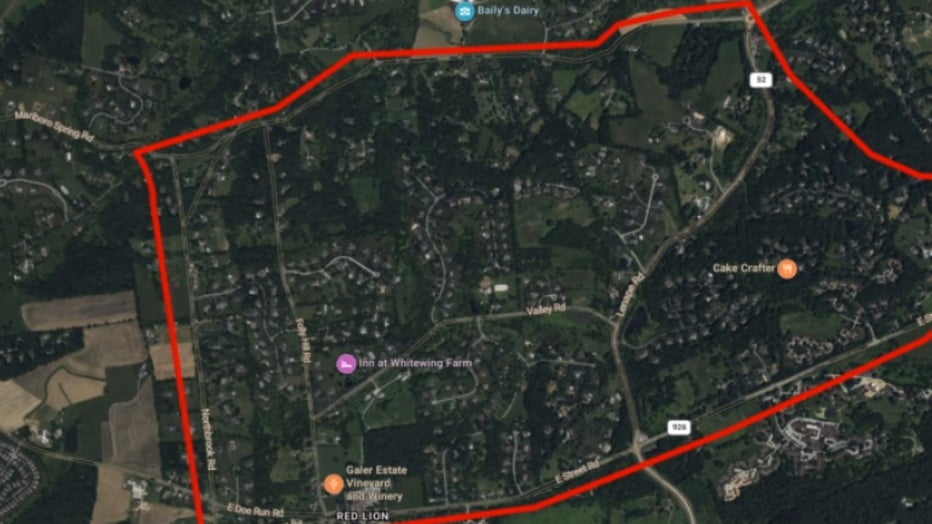
The search perimeter for the escaped prisoner Danelo Cavalcante has been expanded, as per the Google search results.
The exact distance or area covered by the expanded search perimeter is not provided in the search results.
Law enforcement officials have widened the search perimeter in response to the prison escape.
The search perimeter expansion may involve multiple steps and measures to ensure a thorough search and capture of the escaped prisoner.
As additional information about the search perimeter\'s size or specific measures taken is not available, it is best to refer to official news sources or local authorities for the most accurate and up-to-date information on the search efforts.
READ MORE:
Understanding the Nature of Prison Escapes
Prison escapes, though rare, are complex events that require understanding various factors. These include inmate profiles, security lapses, and environmental aspects.
- Inmate Profiles: Understanding the characteristics of inmates who attempt escapes, such as their criminal history, behavior in prison, and motivations.
- Security Lapses: Analyzing common security breaches in prisons, ranging from physical barriers to staff vigilance and technological failures.
- Environmental Aspects: The role of geographical location, terrain, and local community in shaping the nature of prison escapes.
- Methods of Escape: Identifying common methods used by prisoners to escape, including physical breach, deception, or external assistance.
- Psychological Factors: The mindset of escapees and how it influences their decision to escape and subsequent actions.
- Impact of Technology: How modern technology, both in terms of prison security and tracking technology, affects the nature of escapes.
Understanding these factors is crucial for law enforcement and correctional facilities to develop effective strategies to prevent and respond to prison escapes.

Establishing Initial Search Parameters and Perimeters
Creating an effective search perimeter for an escaped prisoner involves several critical steps to ensure a swift and safe resolution.
- Immediate Response: Mobilize a rapid response team as soon as an escape is confirmed.
- Initial Perimeter Setup: Establish an immediate containment area around the prison, factoring in the time elapsed since the escape.
- Gathering Intelligence: Collect information about the escapee, including physical description, known associates, and potential destinations.
- Expanding the Search Area: Based on escape time and possible modes of transportation, determine the expanded search radius.
- Coordinating with Local Authorities: Engage local law enforcement for broader search efforts and public safety alerts.
- Utilizing Technology: Deploy drones, helicopters, and other surveillance technology to monitor large areas.
- Public Awareness: Issue public alerts with descriptions and advisories, while soliciting tips and sightings.
- Continuous Assessment: Regularly reassess and adjust the perimeter based on the latest intelligence and sightings.
- Specialized Teams: Deploy K-9 units, SWAT teams, and other specialized units for targeted search operations.
- Engaging Community Support: Work with local communities to heighten awareness and gather information.
Each of these steps plays a crucial role in ensuring a thorough and methodical approach to locating and apprehending an escaped prisoner.

Utilizing Technology and Surveillance in Manhunts
The use of advanced technology and surveillance methods has become indispensable in the search for escaped prisoners, enhancing both efficiency and safety.
- Drone Surveillance: Deploying drones for aerial views, especially in difficult terrain or dense areas, providing real-time imagery to command centers.
- Heat-Sensing Technology: Utilizing thermal imaging cameras to detect body heat in night searches or in areas with limited visibility.
- GPS Tracking: If the escapee was wearing a GPS monitoring device, leveraging this technology to track movements.
- Facial Recognition Software: Using facial recognition tools to identify the escapee in surveillance footage from public places or traffic cameras.
- Social Media Monitoring: Scanning social media platforms for potential leads or sightings reported by the public.
- Electronic Data Analysis: Gathering and analyzing data from electronic devices and communication networks to predict possible locations.
- Mobile Phone Tracing: Tracing the escapee’s mobile phone usage to pinpoint location, if the device is active.
- Inter-agency Data Sharing: Sharing information and resources across different law enforcement agencies for a coordinated approach.
- Public Alert Systems: Using mass communication tools like Amber Alerts to inform and engage the public in the search.
Integrating these technological tools requires specialized training and coordination, ensuring law enforcement can respond rapidly and effectively to prison escapes.

Challenges Posed by Geography and Environment
The geography and environment present unique challenges in the search for escaped prisoners, influencing search strategies and resource allocation.
- Diverse Terrains: Escaped prisoners can hide in various terrains - urban areas, dense forests, or rugged mountains - each requiring different search tactics.
- Weather Conditions: Weather can significantly impact the search. For instance, heavy rain can erase tracks, while extreme heat or cold can affect both the escapee and the search teams.
- Access and Mobility: Certain areas may be difficult to access, hindering search efforts. This includes regions with limited road networks or hostile terrains.
- Resource Allocation: Extensive and challenging terrains require more resources, including manpower and technology, for effective coverage.
- Local Knowledge: Escapees familiar with the local geography may have an advantage, necessitating the involvement of local authorities with area-specific knowledge.
- Environmental Hazards: Search teams must be prepared for potential hazards like wildlife, hazardous materials, or difficult weather conditions.
- Public Safety: In urban areas, ensuring public safety while conducting a search is crucial, requiring clear communication and coordination.
Understanding these challenges is essential for formulating effective search strategies that adapt to the specific environmental and geographical context of each case.

_HOOK_
Coordination Among Law Enforcement Agencies
Effective coordination among various law enforcement agencies is pivotal in the search for escaped prisoners, ensuring a unified and efficient response.
- Establishing a Command Center: Setting up a central command center for coordination and communication among different agencies.
- Role Allocation: Defining specific roles and responsibilities for each agency to prevent overlap and ensure efficient use of resources.
- Information Sharing: Implementing systems for rapid and secure exchange of information, including escape details, sightings, and intelligence reports.
- Joint Operations: Organizing joint operations with local, state, and federal agencies, including SWAT, K-9 units, and air support.
- Community Policing: Involving local police in the search efforts, leveraging their knowledge of the area and community relations.
- Interagency Training: Conducting regular joint training exercises to prepare for coordinated responses to prison escapes.
- Legal and Jurisdictional Considerations: Understanding and respecting the legal boundaries and jurisdictional limits of each agency.
- Public Communication: Designating a spokesperson or a unified communication team for public updates and alerts.
- Resource Sharing: Pooling resources such as manpower, vehicles, and technology for a more comprehensive search operation.
- After-Action Review: Conducting joint reviews post-operation to learn from the experience and improve future coordination.
This interagency collaboration is essential to create a cohesive strategy that maximizes the likelihood of quickly locating and apprehending the escaped prisoner.
Community Involvement and Public Safety Measures
Engaging the community and implementing public safety measures are crucial aspects of managing the search for an escaped prisoner.
- Public Alerts and Communication: Providing timely and accurate information to the public, using various channels like local media, social media, and community alert systems.
- Community Vigilance: Encouraging residents to report any suspicious activity or sightings and to stay alert, while avoiding direct confrontations with the escapee.
- Safety Guidelines: Issuing guidelines for personal safety, such as locking doors, monitoring surroundings, and staying indoors if necessary.
- Collaboration with Community Leaders: Working with community leaders and organizations to disseminate information and gather local intelligence.
- Use of Local Surveillance: Leveraging local surveillance systems, such as home security cameras, to gather potential leads or sightings.
- School and Public Area Safety: Implementing precautionary measures in schools and public areas, and coordinating with institutions for lockdowns if required.
- Volunteer Support: Organizing volunteer groups for support activities, under the supervision of law enforcement.
- Addressing Public Concerns: Holding community meetings or providing hotlines for inquiries and concerns to maintain public confidence and cooperation.
- Respect for Privacy and Legal Boundaries: Ensuring community involvement respects legal boundaries and individual privacy.
- Post-Incident Support: Providing resources and support to the community post-capture, addressing any psychological impacts or continued safety concerns.
Through these measures, law enforcement agencies can effectively harness community support while ensuring public safety during the search for an escaped prisoner.

Police: Escaped prisoner in PA slipped through search perimeter
\"Discover the thrilling story of a daring escape as we delve into the incredible true account of an escaped convict\'s journey to freedom. Join us as we unravel the twists and turns that led to this heart-pounding escape.\"
Escaped PA inmate still believed within specific perimeter, police confirm
\"Uncover the shocking truth behind the life of an inmate as we explore the challenges, triumphs, and hardships they face within the prison walls. Dive into this gripping video and gain a deeper understanding of the inmate experience.\"
Learning from Past Escapes: Case Studies and Analyses
Analyzing past prison escapes provides valuable insights into improving current security measures and search strategies.
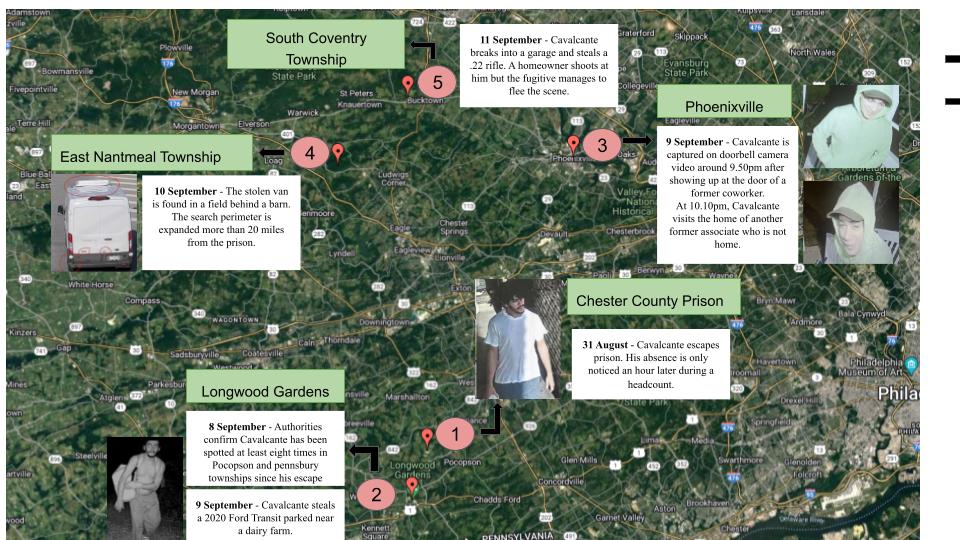
- Case Study of Danelo Cavalcante: Cavalcante, a convicted murderer, escaped by scaling a wall and navigating through razor wire. His escape highlighted the importance of monitoring and quickly responding to unusual activities within prison grounds.
- Challenges in Manhunt: The search for Cavalcante involved multiple sightings and extensive manhunt operations, emphasizing the need for coordinated efforts across various law enforcement agencies.
- Use of Technology: The case demonstrated the use of surveillance cameras and public alerts in tracking the escapee\"s movements.
- Escape of Noah Roush and Jatonia Bryant: Their escape from the Dub Brassell Adult Detention Center underlines the need for vigilant security measures even for non-violent offenders.
- Community Involvement: Both cases show the importance of public alerts and community involvement in reporting sightings and suspicious activities.
- Importance of Rapid Response: The quick mobilization of law enforcement and clear communication channels were crucial in these manhunts.
- Learning from Mistakes: Each escape offers lessons on potential security lapses and areas for improvement in prison management and perimeter security.
These case studies underline the need for continuous improvement in security protocols, technology use, and inter-agency cooperation to prevent future escapes and ensure public safety.

Legal and Ethical Considerations in Prisoner Hunts
Conducting prisoner hunts involves navigating complex legal and ethical considerations to ensure the rights of all involved are respected.
- Adherence to Legal Standards: Ensuring all search operations comply with local, state, and federal laws, including respecting constitutional rights.
- Use of Force: Establishing clear guidelines for the use of force, balancing the need for public safety with the rights of the escapee.
- Privacy Concerns: Addressing privacy issues, especially when using surveillance technology and accessing personal data.
- Community Impact: Considering the impact of search operations on local communities, including potential disruptions and safety concerns.
- Media Relations: Managing information released to the media to avoid prejudicing potential legal proceedings and maintaining public trust.
- Interagency Collaboration: Ensuring cooperative efforts among agencies adhere to jurisdictional boundaries and legal frameworks.
- Accountability: Maintaining transparency and accountability in all actions taken during the search operation.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Being aware of and sensitive to the cultural dynamics of the area where the search is conducted.
- Human Rights Considerations: Upholding human rights standards, especially in handling the escapee upon capture.
- Post-Capture Procedures: Adhering to legal procedures and rights of the escapee, including access to legal representation and fair treatment.
Recognizing and addressing these legal and ethical considerations is crucial to conducting responsible and effective prisoner hunts.

Psychological Aspects of Escaped Prisoner Behavior
Understanding the psychological mindset of escaped prisoners is critical in predicting their actions and effectively planning the search.
- Desperation and Survival Instinct: Escaped prisoners often operate under a heightened sense of desperation, making them potentially more dangerous and unpredictable.
- Stress and Panic Responses: The stress of escape and evasion can lead to panic, influencing their decision-making and potentially leading to mistakes.
- Patterns of Behavior: Analyzing past behavior and criminal history can provide insights into possible actions post-escape, such as seeking shelter, contacting acquaintances, or attempting to flee the area.
- Psychological Profiling: Utilizing psychological profiling to anticipate the escapee\"s next moves, based on known personality traits and criminal history.
- Impact of Incarceration: The effects of long-term incarceration, such as institutionalization, may influence their ability to adapt and survive outside prison.
- Mental Health Considerations: Addressing any known mental health issues that may impact the escapee\"s behavior and risk assessment.
- Influence of Substance Abuse: If substance abuse is a factor, it may increase unpredictability and risk in their behavior.
- Social Connections: Escapees may attempt to contact family or former associates, which can provide leads in the search.
- Resourcefulness and Adaptation: Some escapees may demonstrate high levels of resourcefulness and adaptation, utilizing skills learned inside or outside of prison to evade capture.
- Coping Mechanisms: Understanding any coping mechanisms the escapee might use, such as blending into communities or living off the grid.
These psychological insights are essential for law enforcement to stay one step ahead in the search for an escaped prisoner.
_HOOK_
READ MORE:
Future Innovations in Search and Capture Tactics
In light of recent prison escapes, future innovations in search and capture tactics are crucial. These innovations aim to address the challenges posed by advanced escape methods and environmental conditions.
Advanced Surveillance Technologies
- Drone Technology: Enhanced with thermal imaging and night vision for tracking in diverse terrains and low visibility conditions.
- AI-Powered Surveillance: Artificial Intelligence systems to analyze security footage, predict escape routes, and alert authorities in real-time.
Improved Perimeter Security
- Smart Fencing: Electrified fences with sensors to detect climbing or tampering.
- Biometric Scanning: Advanced biometric systems at key exit points to prevent unauthorized access.
Enhanced Communication and Coordination
- Integrated Communication Networks: Ensuring seamless coordination among various law enforcement agencies.
- Community Alert Systems: Public notification systems to inform and involve the community in a safe manner.
Robotic Assistance and Autonomous Vehicles
- Robotic Ground Units: Robots equipped with cameras and sensors to search difficult terrains.
- Autonomous Patrol Vehicles: Self-driving vehicles for continuous perimeter surveillance.
Training and Preparedness
- Virtual Reality Training: Simulating escape scenarios to train personnel in effective response strategies.
- Continuous Learning: Regular workshops on latest technologies and tactics for law enforcement.
Exploring cutting-edge strategies for establishing search perimeters for escaped prisoners, this article offers insightful, innovative solutions for enhancing security and ensuring public safety in our ever-evolving world.