Topic what is the perimeter of triangle abc: Explore the intriguing world of geometry as we delve into understanding the perimeter of Triangle ABC, a fundamental concept that bridges theory and real-world applications in mathematics.
Table of Content
- What is the perimeter of Triangle ABC?
- Definition and Basic Formula
- Perimeter of Different Types of Triangles
- Calculating Perimeter with Known Side Lengths
- Using the Pythagorean Theorem
- Advanced Methods: Law of Cosines and Sines
- YOUTUBE: Find the perimeter of the triangle ABC
- Perimeter in Coordinate Geometry
- Practical Examples and Applications
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the perimeter of Triangle ABC?
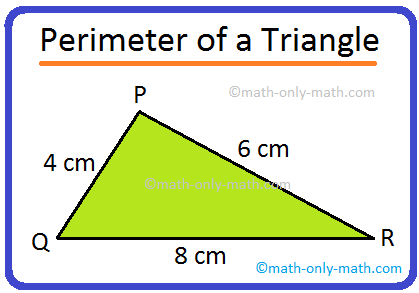
The perimeter of Triangle ABC can be found by adding the lengths of all three sides.
Let\'s say the lengths of the sides are AB, BC, and AC.
Using the given information from the search results:
- AB = 3
- BC = 5
- AC = 4
To find the perimeter, we add the lengths of all three sides:
Perimeter = AB + BC + AC
Substituting the given lengths:
Perimeter = 3 + 5 + 4
Simplifying the expression:
Perimeter = 12
Therefore, the perimeter of Triangle ABC is 12 units.
READ MORE:
Definition and Basic Formula
The perimeter of a triangle, often symbolized as P, is the total distance around the triangle. It is calculated by adding up the lengths of its three sides. This fundamental concept in geometry applies to all types of triangles, whether they are scalene, isosceles, equilateral, or right-angled.
To put it simply, if a triangle has sides of lengths \"a\", \"b\", and \"c\", then the perimeter (P) can be represented by the formula:
- P = a + b + c
This formula is versatile and straightforward, applicable regardless of the type of triangle as long as the lengths of all three sides are known.
- For an equilateral triangle, where all sides are of equal length \"s\", the perimeter is given by P = 3s.
- In the case of an isosceles triangle, which has two sides of equal length \"l\" and a base \"b\", the perimeter is P = 2l + b.
- For a right-angled triangle, one can use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the lengths of the missing sides if necessary, before applying the perimeter formula.
In addition to these specific cases, other geometric principles like the Law of Sines and the Law of Cosines can be used to calculate the perimeter when less information is available, such as certain angles and side lengths.

Perimeter of Different Types of Triangles
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of various types of triangles is key to grasping basic geometric principles. Each type of triangle – equilateral, isosceles, scalene, and right triangle – has its unique characteristics that influence how its perimeter is determined.
- Equilateral Triangle: In an equilateral triangle, all three sides are of equal length. If each side is \"s\", the perimeter is calculated as P = 3s.
- Isosceles Triangle: This type has two sides of equal length. If the equal sides are \"l\" and the base is \"b\", the perimeter is P = 2l + b.
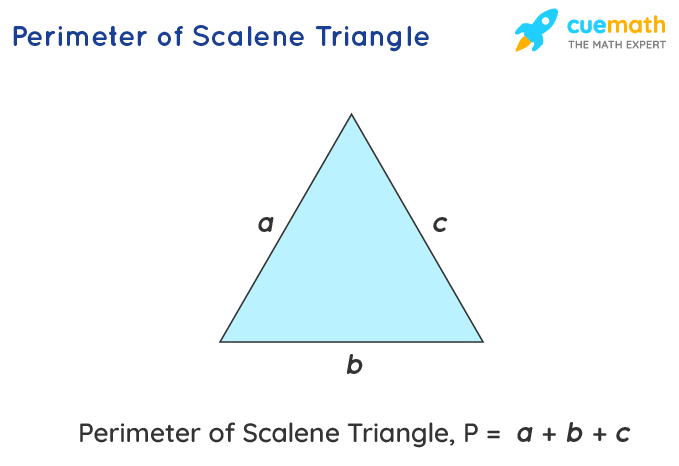
- Scalene Triangle: A scalene triangle has no equal sides. If the sides are \"a\", \"b\", and \"c\", the perimeter is the sum of these sides, P = a + b + c.
- Right Triangle: For right triangles, the perimeter can be found by adding the two legs and the hypotenuse. If the legs are \"a\" and \"b\", and the hypotenuse is \"c\", then P = a + b + c. The Pythagorean theorem can help in finding the length of the hypotenuse if it\"s unknown.
These formulas provide a straightforward method for calculating the perimeter of any triangle, making it an essential aspect of geometric studies and practical applications alike.

Calculating Perimeter with Known Side Lengths
Calculating the perimeter of a triangle with known side lengths is a straightforward process. This section will guide you through the steps for different scenarios, including various types of triangles and situations where you may not have all the side lengths directly provided.
- Standard Triangles: The basic formula for calculating the perimeter of any triangle when all side lengths are known is P = a + b + c. This applies to all triangle types - equilateral, isosceles, and scalene.
- Triangles with Missing Sides: In some cases, you might not have all the side lengths. For example, in right triangles, if you know two sides, you can find the third using the Pythagorean theorem. For an isosceles or equilateral triangle, knowing one side can be enough as the other sides are equal or proportional.
- Using Trigonometry: In situations where you have a side and two angles (ASA) or two sides and an angle (SAS), trigonometric principles such as the Law of Sines or Cosines come in handy. The Law of Cosines, for example, is used to find the third side in a SAS triangle before calculating the perimeter.
- Practical Examples: Consider a triangle with sides 4 inches, 3 inches, and a missing side. First, calculate the missing side (if it\"s a right triangle, use the Pythagorean theorem). Then add up the lengths of all three sides to find the perimeter.
It\"s important to include the correct units in your final answer and use appropriate formulas based on the information you have about the triangle.

Using the Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental principle in geometry, particularly useful in calculating the perimeter of a right triangle. This theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. This can be expressed as (c^2 = a^2 + b^2), where \"c\" is the hypotenuse and \"a\" and \"b\" are the other two sides.
- Identifying the Sides: First, identify the lengths of the two shorter sides of the triangle, often labeled as \"a\" and \"b\".
- Applying the Theorem: Use the theorem (c^2 = a^2 + b^2) to find the length of the hypotenuse \"c\".
- Calculating the Perimeter: Once you have all three side lengths, calculate the perimeter by adding them together. The perimeter (P) of a right triangle is given by (P = a + b + c).
For example, in a right triangle with sides of 3 inches and 4 inches, the length of the hypotenuse can be found using the Pythagorean Theorem: (5^2 = 3^2 + 4^2). Therefore, the hypotenuse is 5 inches, and the perimeter of the triangle is (3 + 4 + 5 = 12) inches.
This theorem is not only limited to academic problems but also finds practical application in various fields, including architecture, construction, and navigation.

_HOOK_
Advanced Methods: Law of Cosines and Sines
The Law of Cosines and Sines are advanced methods used in calculating the perimeter of triangles, especially when certain side lengths or angles are unknown. These laws are particularly useful in solving non-right triangles – that is, triangles without a 90-degree angle.
- Law of Cosines: This law helps find a missing side of a triangle when you know two sides and the angle between them. It is given by the formula (c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab cdot cos(gamma)), where \"c\" is the length of the side opposite the angle (gamma), and \"a\" and \"b\" are the lengths of the other two sides. Once you find the third side, you can calculate the perimeter as the sum of all three sides.
- Law of Sines: This law is used when you know two angles and a side (ASA condition) or two sides and a non-included angle (SSA condition). The law states that the ratio of the length of a side to the sine of its opposite angle is the same for all sides and angles in the triangle. It is expressed as (frac{a}{sin(A)} = frac{b}{sin(B)} = frac{c}{sin(C)}). This can help find the missing sides, which can then be used to calculate the perimeter.
These methods require a good understanding of trigonometry and are vital for complex problems where direct measurement is not possible. They are commonly used in fields such as surveying, astronomy, and engineering.

Find the perimeter of the triangle ABC
Learn about the fascinating concept of perimeter in this video, where you\'ll discover how to calculate the distance around a shape. Mastering perimeter will not only impress your friends but also boost your math skills!
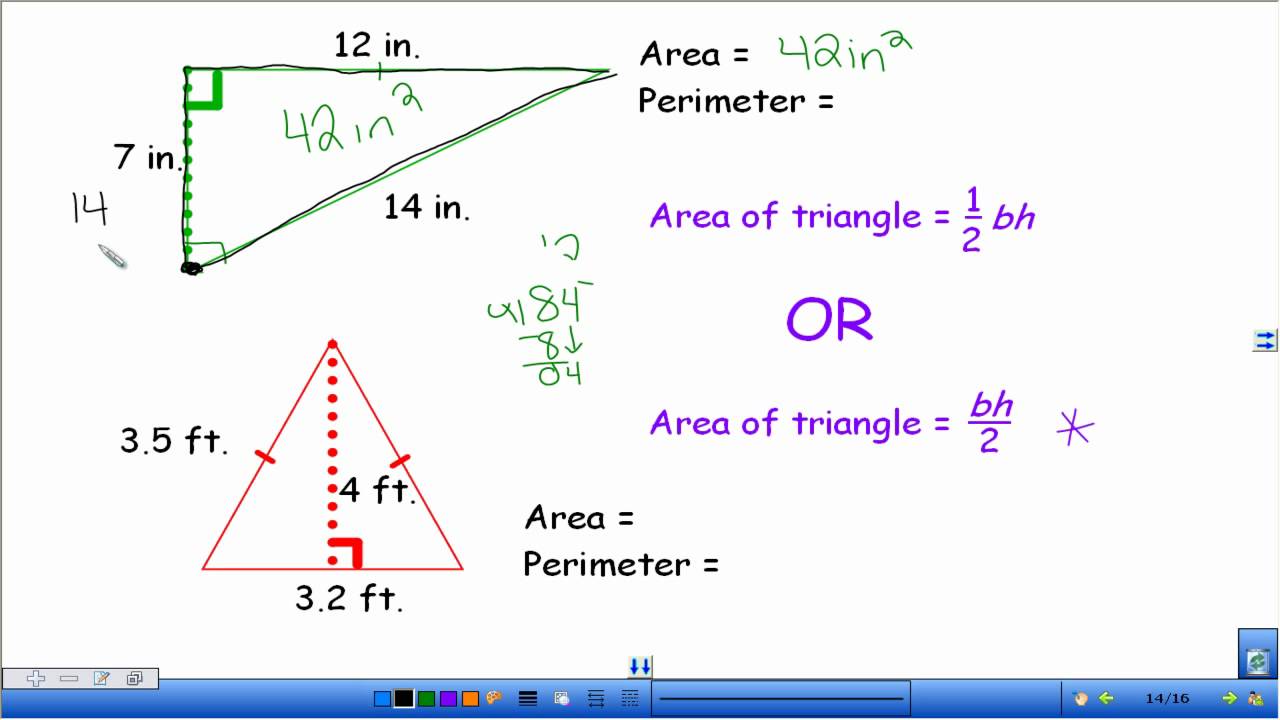
Area & Perimeter of a Triangle
Dive into the world of area with this captivating video that will unlock the secrets of calculating the surface within a shape. Understanding area is essential for real-life applications and will empower you to solve complex problems with confidence.
Perimeter in Coordinate Geometry
In coordinate geometry, the perimeter of a triangle can be calculated using the distance formula. This method is particularly useful when the vertices of the triangle are known, and the triangle is plotted on a coordinate plane.
- Determining the Coordinates: Identify the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle, usually given as A(x₁, y₁), B(x₂, y₂), and C(x₃, y₃).
- Applying the Distance Formula: Use the distance formula, (d = sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}), to calculate the lengths of the sides of the triangle. Calculate the distances between points A and B, B and C, and C and A.
- Calculating the Perimeter: Add up the lengths of the three sides to find the perimeter of the triangle. If the sides are represented as AB, BC, and CA, then the perimeter P is given by P = AB + BC + CA.
This method is widely used in various applications such as land surveying, mapping, and in any field where precise measurements are required. It allows for the calculation of the perimeter of a triangle when direct measurement is not feasible.
Practical Examples and Applications
The concept of calculating the perimeter of a triangle extends beyond theoretical geometry and finds practical applications in various fields. Here are some examples and applications:
- Architecture and Construction: Architects and builders often use the concept of triangle perimeters in designing and constructing roofs, trusses, and bridges. The accurate calculation of perimeters is crucial for structural integrity and material estimation.
- Land Surveying: In land surveying, the perimeter of triangular plots is calculated for boundary determination and area calculation. This is essential for property delineation and legal documentation.
- Navigation and Mapping: Triangulation, a method based on the properties of triangles, is used in navigation and mapping to determine distances and plot locations, with the perimeter playing a crucial role in these calculations.
- Education: In educational settings, teaching the concept of triangle perimeters helps students understand basic geometric principles and improves their problem-solving skills.
- Everyday Problem Solving: Calculating the perimeter of triangular spaces can be useful in everyday scenarios, such as determining the amount of fencing required for a triangular garden or the border length for triangular decorative elements.
These examples illustrate the wide-ranging applications of this fundamental geometric concept, highlighting its importance in both professional and everyday contexts.

READ MORE:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
When learning about the perimeter of triangles, several common questions often arise. Here are some of the most frequently asked questions and their answers to enhance your understanding:
- How do you find the perimeter of a triangle with missing sides? To find the perimeter of a triangle when some sides are missing, you can use various methods such as the Pythagorean Theorem for right triangles, or the Law of Sines and Cosines for non-right triangles. For coordinate geometry problems, the distance formula can be applied.
- Is the perimeter of a triangle always equal to the sum of its three sides? Yes, the perimeter of any triangle is always the sum of its three sides, regardless of the type of triangle.
- Can the perimeter of a triangle be calculated if only angles are known? It\"s not possible to determine the perimeter of a triangle only from its angles. At least one side length is necessary to calculate the perimeter using trigonometric methods.
- What is the perimeter of an equilateral triangle with a side length of \"a\"? The perimeter of an equilateral triangle is simply three times the length of one side, so it would be 3a.
- How is the perimeter of a triangle used in real life? The concept of triangle perimeters is used in various fields such as architecture, construction, land surveying, and in numerous practical applications like gardening or art.
These FAQs cover basic to advanced aspects of calculating the perimeter of a triangle, providing a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental geometric concept.
In conclusion, understanding the perimeter of Triangle ABC reveals the elegance and utility of geometry in both theoretical and practical realms, enhancing our appreciation of this fundamental concept in our daily lives and various professional fields.