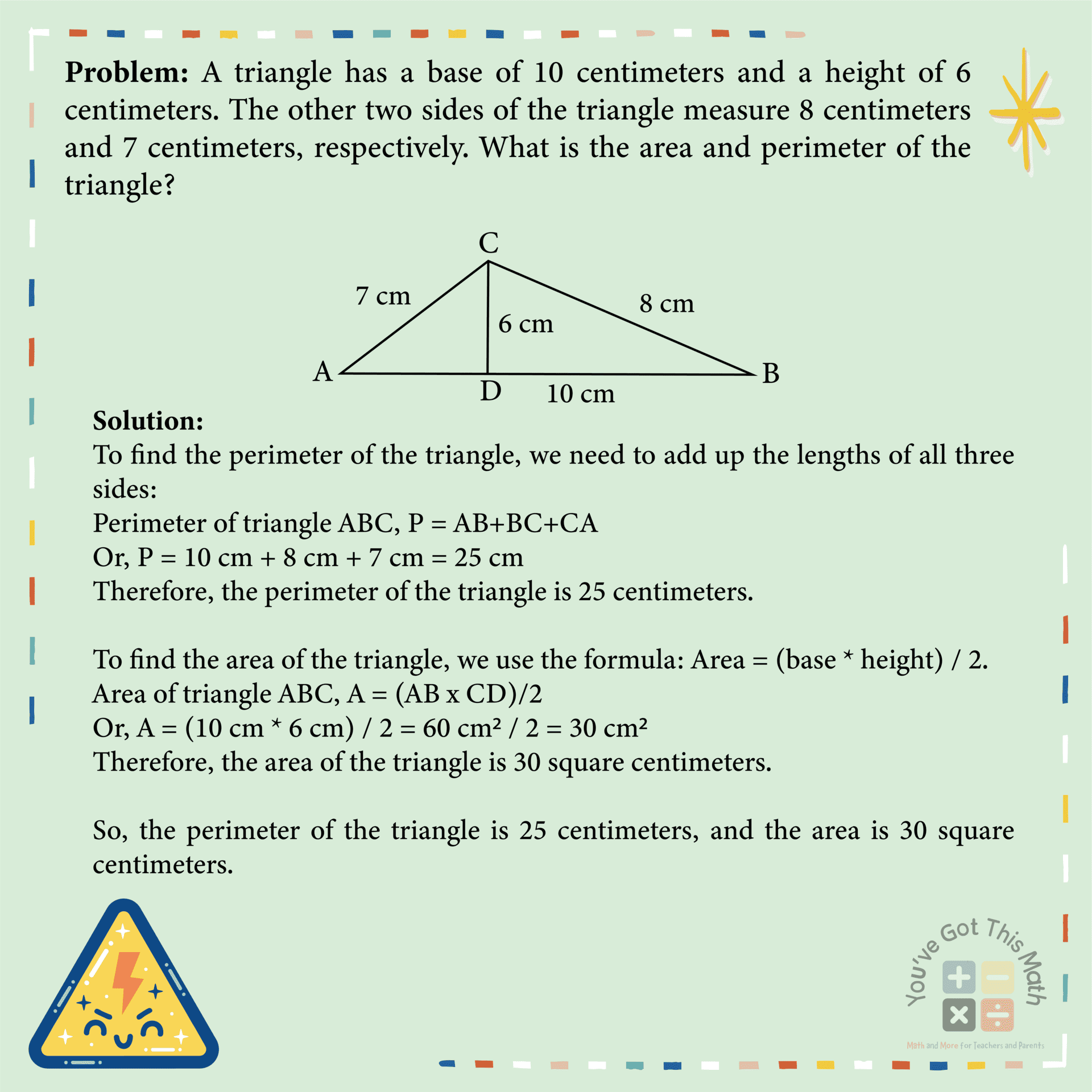
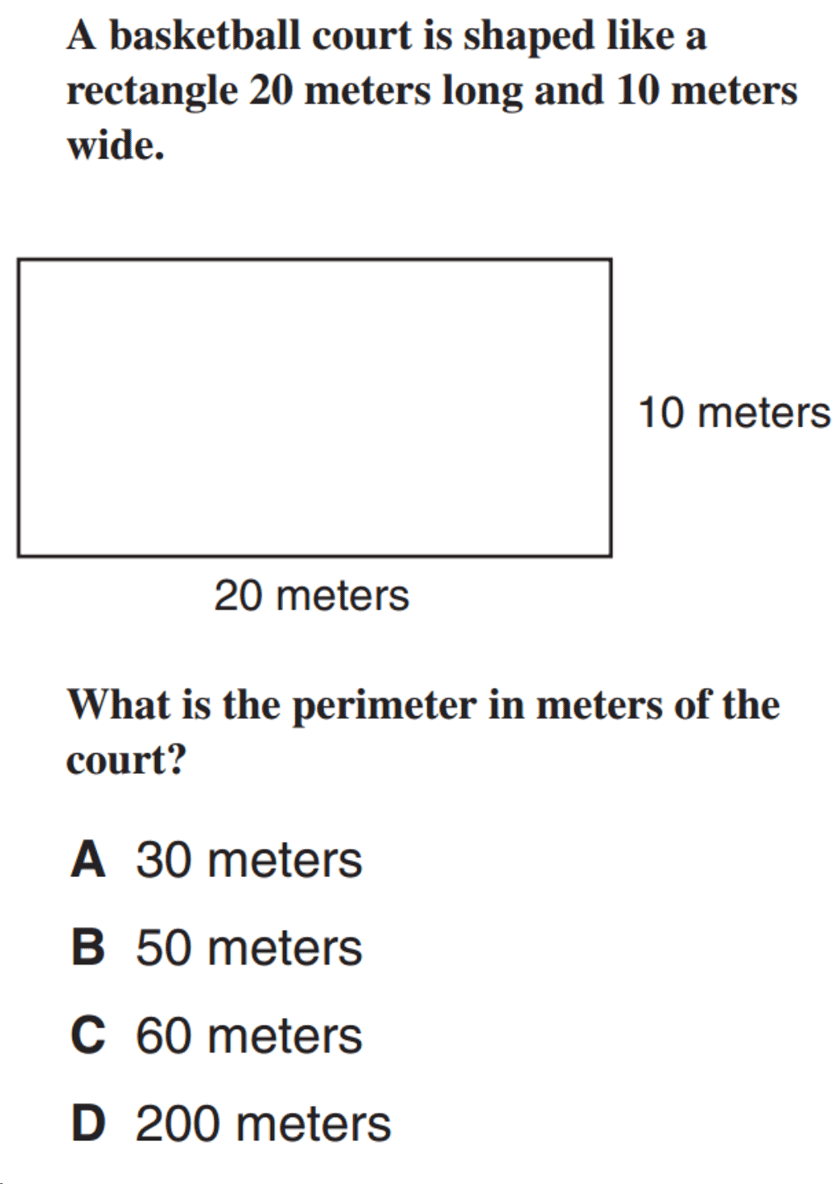
Topic triangle area and perimeter practice problems: Embark on a mathematical journey with our comprehensive guide to "Triangle Area and Perimeter Practice Problems", designed to enhance your geometry skills through engaging and diverse problem-solving activities.
Table of Content
- How to solve triangle area and perimeter practice problems?
- Understanding Triangle Geometry
- Basic Formulas for Area and Perimeter of Triangles
- Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Triangle Area
- Practice Problems on Triangle Perimeter Calculation
- Advanced Problems: Area of Scalene and Right Triangles
- Utilizing Heron\"s Formula in Practice Problems
- YOUTUBE: Area of a Triangle
- Interactive Exercises for Area and Perimeter
- Real-World Applications: Understanding the Importance
- Additional Resources and Worksheets for Practice
- Expert Tips for Solving Complex Triangle Problems
How to solve triangle area and perimeter practice problems?
To solve triangle area and perimeter practice problems, follow these steps:
- Identify the given information about the triangle. This may include the side lengths, angles, or other relevant measurements.
- For finding the area of a triangle:
- If the triangle is a right triangle, you can use the formula: Area = (base * height) / 2. Ensure that the base and height are perpendicular.
- If the triangle is not a right triangle, you can use Heron\'s Formula. Heron\'s Formula states that the area of a triangle with side lengths a, b, and c is given by: Area = sqrt(s * (s - a) * (s - b) * (s - c)), where s is the semi-perimeter of the triangle calculated as: s = (a + b + c) / 2.
- For finding the perimeter of a triangle:
- Add up all the side lengths of the triangle to get the perimeter. If the triangle is equilateral, all sides are equal, so simply multiply the length of one side by 3 to find the perimeter.
Remember to carefully read the given problem to understand which measurements are provided and which values need to be calculated.
Practice solving a variety of triangle area and perimeter problems to improve your understanding and problem-solving skills.
READ MORE:
Understanding Triangle Geometry
The study of triangles in geometry revolves around understanding their properties, types, and formulas for calculating area and perimeter. A triangle is a three-sided polygon, and its characteristics depend on the length of its sides and the angles between them.
- Types of Triangles: Triangles are categorized based on their side lengths (equilateral, isosceles, scalene) and angles (acute, right, obtuse).
- Area Calculation: The area of a triangle can be calculated using the formula: Area = 1/2 × base × height. For right triangles, the base and height are the two perpendicular sides. In the case of scalene triangles, Heron\"s formula or trigonometric methods may be used.
- Perimeter Calculation: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of its three sides. This is straightforward for equilateral triangles but requires precise measurements for scalene and isosceles triangles.
- Practical Problems: Solving practical problems often involves applying these concepts to find missing sides or angles, using additional geometry principles like the Pythagorean theorem in right triangles.
- Worksheets and Practice: Various resources offer practice problems and worksheets, helping to reinforce understanding through problems of varying difficulty, from basic to more advanced levels involving fractions, decimals, and complex problem-solving scenarios.
Mastering the basics of triangle geometry is crucial for advancing in geometry and encountering a wide range of practical and theoretical applications.
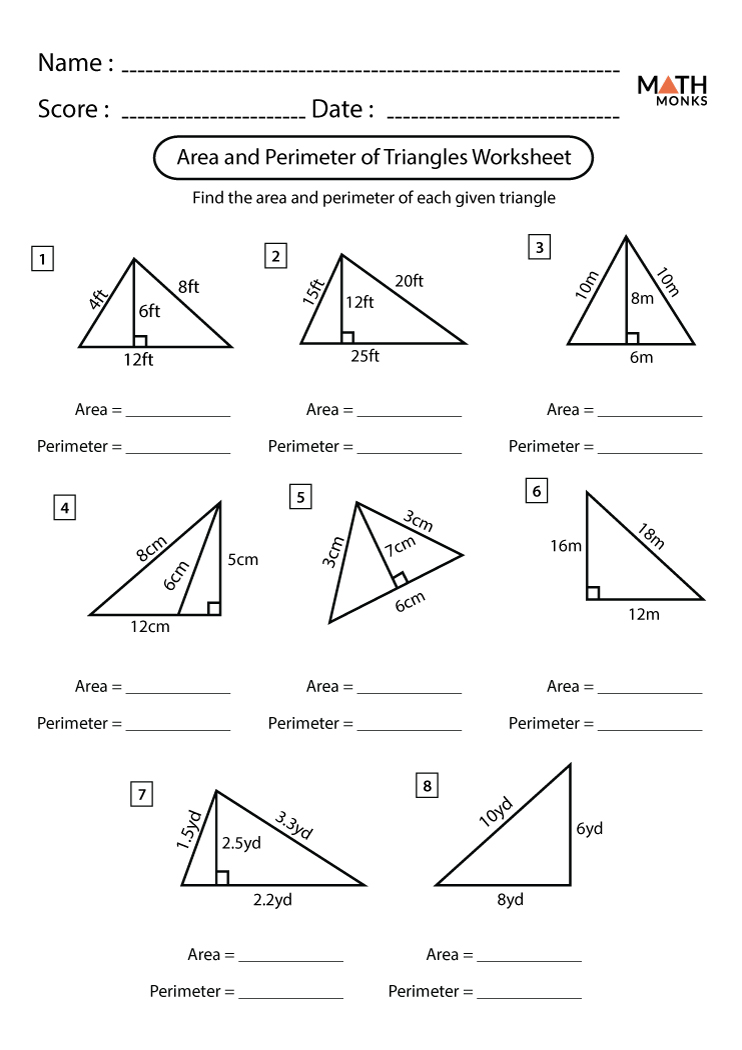
Basic Formulas for Area and Perimeter of Triangles
Understanding the basic formulas for calculating the area and perimeter of triangles is essential in geometry. These formulas vary based on the type of triangle.
- Area of a Triangle: The general formula for the area of a triangle is ( ext{Area} = frac{1}{2} imes ext{base} imes ext{height} ). This formula is applicable to all types of triangles.
- Perimeter of a Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of its three sides, represented as ( ext{Perimeter} = a + b + c ), where ( a ), ( b ), and ( c ) are the lengths of the sides.
- Right Triangle: For right triangles, the area can also be calculated using the two perpendicular sides as the base and height.
- Scalene Triangle: In scalene triangles, where all sides are different, Heron\"s formula can be used. Heron\"s formula states that the area of a triangle with sides of length ( a ), ( b ), and ( c ) and semi-perimeter ( s ) (where ( s = frac{a + b + c}{2} )) is given by ( sqrt{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)} ).
- Equilateral Triangle: For an equilateral triangle with all sides equal to ( a ), the area is ( frac{sqrt{3}}{4} imes a^2 ) and the perimeter is ( 3a ).
These formulas are fundamental in solving various geometry problems and are widely used in different levels of mathematical education, from basic to advanced geometry.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Triangle Area
Calculating the area of a triangle is a fundamental skill in geometry. This step-by-step guide will help you understand how to accurately determine the area of different types of triangles.
- Identify the Type of Triangle: Knowing whether your triangle is equilateral, isosceles, scalene, or right-angled is crucial as it determines the method you will use.
- Measure the Base and Height: For most triangles, you will need to measure or be given the base (the bottom side) and the height (the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite vertex).
- Use the Basic Area Formula: The general formula for the area of a triangle is ( ext{Area} = frac{1}{2} imes ext{base} imes ext{height} ). Apply this formula using your measurements.
- Applying Heron\"s Formula for Scalene Triangles: If you have a scalene triangle, use Heron\"s formula. First, calculate the semi-perimeter (half of the sum of all sides) and then apply ( ext{Area} = sqrt{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)} ), where ( s ) is the semi-perimeter and ( a ), ( b ), ( c ) are the sides of the triangle.
- Special Case - Right Triangle: For right-angled triangles, simply use the two perpendicular sides as the base and height in the basic area formula.
- Equilateral Triangle: If the triangle is equilateral (all sides equal), and each side is of length ( a ), use the formula ( frac{sqrt{3}}{4} imes a^2 ).
- Review and Practice: Regular practice with various triangle types and dimensions is key. Utilize worksheets and practice problems to enhance your understanding and speed.
Remember, accuracy in measurement and application of the correct formula is key to successfully determining the area of triangles.
big.gif)
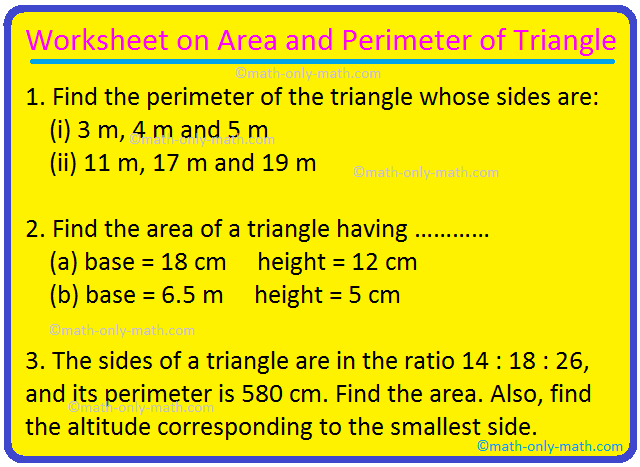
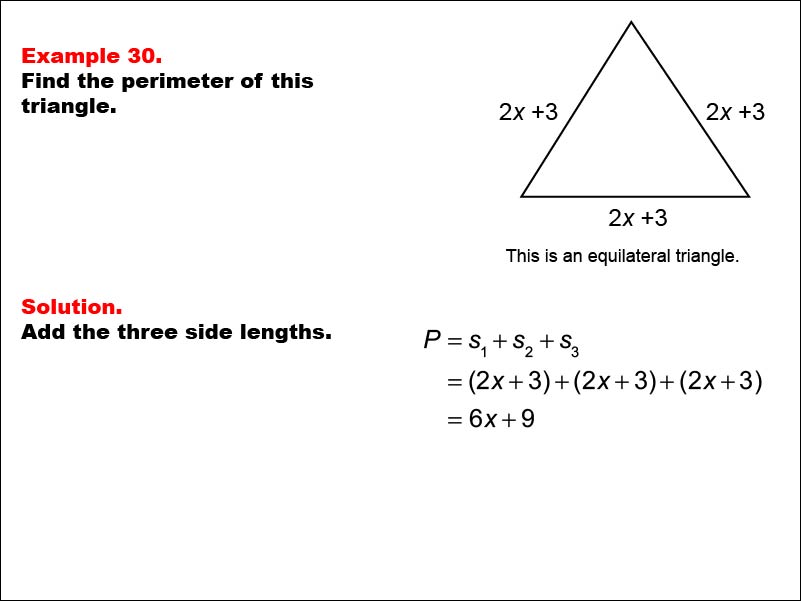
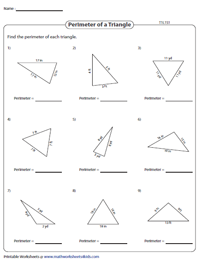
Practice Problems on Triangle Perimeter Calculation
Developing proficiency in calculating the perimeter of triangles involves practicing with a variety of triangle types and dimensions. This section provides practice problems to enhance your skills in perimeter calculation.
- Basic Perimeter Calculation: Start with simple problems where you add up the lengths of the three sides of the triangle. This is the basic formula for calculating the perimeter.
- Diverse Triangle Types: Include problems involving different types of triangles, such as equilateral, isosceles, and scalene, to provide a comprehensive understanding of perimeter calculations.
- Using Triangle Properties: Integrate problems that require using properties of triangles, like the sum of any two sides being greater than the third side, to find missing side lengths before calculating the perimeter.
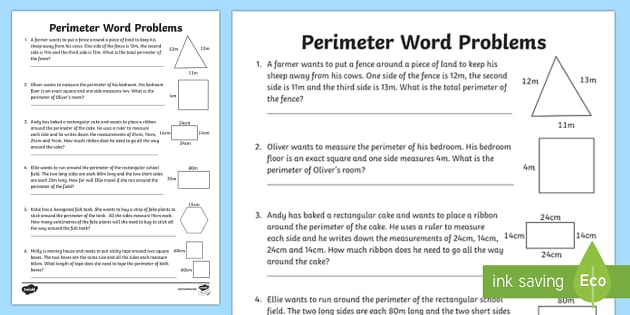
- Word Problems: Incorporate real-life scenarios and word problems that require calculating the perimeter of triangles, enhancing practical understanding and application skills.
- Interactive Problems: Provide interactive and visually engaging problems, like those involving diagrams or real-life objects, to make learning more engaging and effective.
These practice problems aim to build a strong foundational understanding of perimeter calculation in triangles, catering to learners from elementary to high school levels.
_HOOK_
Advanced Problems: Area of Scalene and Right Triangles
Understanding the area calculation for scalene and right triangles is an important step in advancing your geometry skills. This section provides challenging problems to deepen your understanding.
- Scalene Triangle Area Calculation: Practice calculating the area of scalene triangles using Heron\"s formula, which requires knowledge of all three side lengths. Heron\"s formula is particularly useful for triangles where the height is not readily apparent.
- Right Triangle Area Challenges: Right triangles offer a unique case where the area can be calculated using the two sides that form the right angle as the base and height. Incorporate problems that involve finding the area of right triangles with various side lengths.
- Problem-Solving with Real-Life Contexts: Include problems set in real-world contexts where students have to deduce unknown sides or angles of triangles before calculating the area.
- Integration of Algebraic Concepts: For more advanced learners, integrate algebraic expressions in the problems, where students first need to solve for unknowns using algebra before they can calculate the area.
- Exploring Triangles on Grids: Practice problems involving triangles plotted on grids can help students visualize and better understand the concepts of area and perimeter in a more tangible way.
This approach to advanced problems in calculating the area of scalene and right triangles is designed to enhance problem-solving skills and deepen understanding of geometric concepts.

Utilizing Heron\"s Formula in Practice Problems
Mastering Heron\"s Formula is essential for calculating the area of scalene triangles, where traditional methods are not applicable. This section introduces practice problems to enhance your understanding and application of Heron\"s Formula.
- Understanding Heron\"s Formula: Begin with a clear explanation of Heron\"s Formula: Area = √[s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)], where s is the semi-perimeter of the triangle, and a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides. Emphasize the importance of calculating the semi-perimeter accurately.
- Simple Application Problems: Start with basic problems where students calculate the area of scalene triangles given the lengths of all three sides. These problems help in familiarizing students with the formula\"s application.
- Intermediate-Level Challenges: Introduce problems where one or more sides need to be calculated using additional information or geometric properties before applying Heron\"s Formula.
- Real-World Scenarios: Provide context-based problems that mimic real-life situations, such as determining the area of irregular plots of land, requiring students to think critically and apply Heron\"s Formula effectively.
- Integration with Other Concepts: Design problems that combine Heron\"s Formula with other geometric concepts, such as angles or circumferences, to solve more complex problems.
- Problem-Solving Strategies: Encourage students to develop strategies for identifying when to use Heron\"s Formula and how to approach these problems logically and systematically.
This approach aims to build a comprehensive understanding of Heron\"s Formula through a variety of practice problems, enhancing both conceptual knowledge and problem-solving skills.
Area of a Triangle
\"Discover the mesmerizing beauty and symbolic meaning behind the mystical triangle in our captivating video. Explore its geometric wonders and explore the secrets it holds for personal growth and spiritual awakening. Join us on this enlightening journey into the world of triangles!\"
How to Find the Area of a Triangle
\"Embark on a thrilling quest as we help you unlock the power of finding hidden treasures in our exciting video. Learn expert techniques and gain insider knowledge to become a master of finding precious artifacts and uncovering life\'s hidden gems. Get ready for an adventure of a lifetime!\"
Interactive Exercises for Area and Perimeter
Mastering Heron\"s Formula is essential for calculating the area of scalene triangles, where traditional methods are not applicable. This section introduces practice problems to enhance your understanding and application of Heron\"s Formula.
- Understanding Heron\"s Formula: Begin with a clear explanation of Heron\"s Formula: Area = √[s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)], where s is the semi-perimeter of the triangle, and a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides. Emphasize the importance of calculating the semi-perimeter accurately.
- Simple Application Problems: Start with basic problems where students calculate the area of scalene triangles given the lengths of all three sides. These problems help in familiarizing students with the formula\"s application.
- Intermediate-Level Challenges: Introduce problems where one or more sides need to be calculated using additional information or geometric properties before applying Heron\"s Formula.
- Real-World Scenarios: Provide context-based problems that mimic real-life situations, such as determining the area of irregular plots of land, requiring students to think critically and apply Heron\"s Formula effectively.
- Integration with Other Concepts: Design problems that combine Heron\"s Formula with other geometric concepts, such as angles or circumferences, to solve more complex problems.
- Problem-Solving Strategies: Encourage students to develop strategies for identifying when to use Heron\"s Formula and how to approach these problems logically and systematically.
This approach aims to build a comprehensive understanding of Heron\"s Formula through a variety of practice problems, enhancing both conceptual knowledge and problem-solving skills.

Real-World Applications: Understanding the Importance
Mastering Heron\"s Formula is essential for calculating the area of scalene triangles, where traditional methods are not applicable. This section introduces practice problems to enhance your understanding and application of Heron\"s Formula.
- Understanding Heron\"s Formula: Begin with a clear explanation of Heron\"s Formula: Area = √[s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)], where s is the semi-perimeter of the triangle, and a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides. Emphasize the importance of calculating the semi-perimeter accurately.
- Simple Application Problems: Start with basic problems where students calculate the area of scalene triangles given the lengths of all three sides. These problems help in familiarizing students with the formula\"s application.
- Intermediate-Level Challenges: Introduce problems where one or more sides need to be calculated using additional information or geometric properties before applying Heron\"s Formula.
- Real-World Scenarios: Provide context-based problems that mimic real-life situations, such as determining the area of irregular plots of land, requiring students to think critically and apply Heron\"s Formula effectively.
- Integration with Other Concepts: Design problems that combine Heron\"s Formula with other geometric concepts, such as angles or circumferences, to solve more complex problems.
- Problem-Solving Strategies: Encourage students to develop strategies for identifying when to use Heron\"s Formula and how to approach these problems logically and systematically.
This approach aims to build a comprehensive understanding of Heron\"s Formula through a variety of practice problems, enhancing both conceptual knowledge and problem-solving skills.

Additional Resources and Worksheets for Practice
For those seeking to enhance their understanding and skills in calculating the area and perimeter of triangles, a wealth of resources and worksheets are available online. These materials are designed to cater to various levels of difficulty, ensuring a comprehensive learning experience for both beginners and advanced learners.
Online Practice Problems
- Khan Academy\"s Practice Exercises: Khan Academy offers a series of practice problems that focus on calculating the area of triangles. These exercises are interactive and cover different types of triangles, providing a hands-on learning experience.
Printable Worksheets
For those who prefer traditional methods of learning, printable worksheets are a great option. They allow for practice in a structured format and can be a valuable resource for teachers in classroom settings.
- Math Goodies\" Worksheets: This website offers a variety of worksheets focused on the perimeter and area of triangles. Each worksheet comes with detailed instructions and problems that range from basic to advanced levels, making them suitable for a wide range of learners.
Interactive Learning Tools
Interactive learning tools provide a dynamic way to understand the concepts of triangle geometry. They often include visual aids and real-time problem-solving scenarios that can enhance the learning experience.
- Geometry Games: Engaging in geometry-themed games can help reinforce the concepts learned in a fun and interactive way.
- Animated Tutorials: These tutorials use animations to explain the principles of triangle geometry, making complex concepts easier to understand.
Advanced Learning Resources
For those looking to dive deeper into the subject, there are resources that cover advanced topics like Heron\"s Formula and the properties of special triangles.
- Heron\"s Formula Exercises: These exercises focus on the application of Heron\"s Formula in calculating the area of various types of triangles.
- Scalene and Right Triangle Problems: These problems are designed to test and enhance understanding of the more complex triangle types.
Overall, these resources provide a comprehensive platform for learners at all levels to practice and perfect their skills in triangle geometry, particularly in the areas of area and perimeter calculation.
_HOOK_
READ MORE:
Expert Tips for Solving Complex Triangle Problems
Mastering the art of solving complex triangle problems involves understanding various concepts and strategies. Below are expert tips and techniques to enhance your problem-solving skills in the area and perimeter of triangles.
Understanding Different Types of Triangles
Knowledge of different types of triangles - scalene, isosceles, equilateral, and right-angled - is crucial. Each type has unique properties that dictate how you calculate their area and perimeter.
Using Appropriate Formulas
- Area of a Triangle: For right-angled triangles, use the formula ( ext{Area} = frac{1}{2} imes ext{base} imes ext{height} ). For scalene triangles, Heron\"s formula can be effective, which is ( ext{Area} = sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} ), where ( s ) is the semi-perimeter.
- Perimeter of a Triangle: The perimeter is the sum of all sides. For equilateral triangles, it\"s three times the length of one side, and for other types, add the lengths of all sides.
Problem-Solving Strategies
- Break down the problem: Start by identifying the type of triangle and the known elements like sides, angles, or area.
- Visual Representation: Drawing the triangle can provide a clearer understanding of the problem, especially for complex geometrical problems.
- Apply Relevant Theorems: The Pythagorean Theorem is essential for right triangles, while the Triangle Inequality Theorem can be crucial for understanding the relation between the sides of a triangle.
Advanced Techniques
For more advanced problems, understanding the sine and cosine rules can be beneficial. These are especially useful in non-right triangles where traditional methods might not apply.
Practice with Variety
Practicing with a variety of problems is key to mastering triangle geometry. Tackling problems of different complexity levels and types helps build a deeper understanding and hones problem-solving skills.
Remember, patience and practice are essential in mastering complex triangle problems. With time and effort, even the most challenging problems can become manageable.
Embark on a journey to master the fascinating world of triangle geometry. Explore our comprehensive resources for practicing and solving area and perimeter problems, and unlock your potential in understanding these fundamental mathematical concepts.