Topic what is the perimeter of abcd: Discover the intriguing world of geometry as we explore "What is the Perimeter of ABCD?" Unveil the secrets of calculating perimeters for various shapes, enhancing your understanding of this fundamental geometric concept.
Table of Content
- What is the perimeter of ABCD?
- Introduction to Perimeter Calculation
- Types of Shapes and Their Perimeters
- Formulas for Calculating Perimeter
- Specifics of Calculating Perimeter for Quadrilaterals
- YOUTUBE: Find the Perimeter of the Rectangle ABCD | Minute Math
- Perimeter in Different Geometric Contexts
- Practical Applications of Perimeter Calculation
- Advanced Concepts: Perimeter on Coordinate Planes
- Using Technology and Tools for Perimeter Calculation
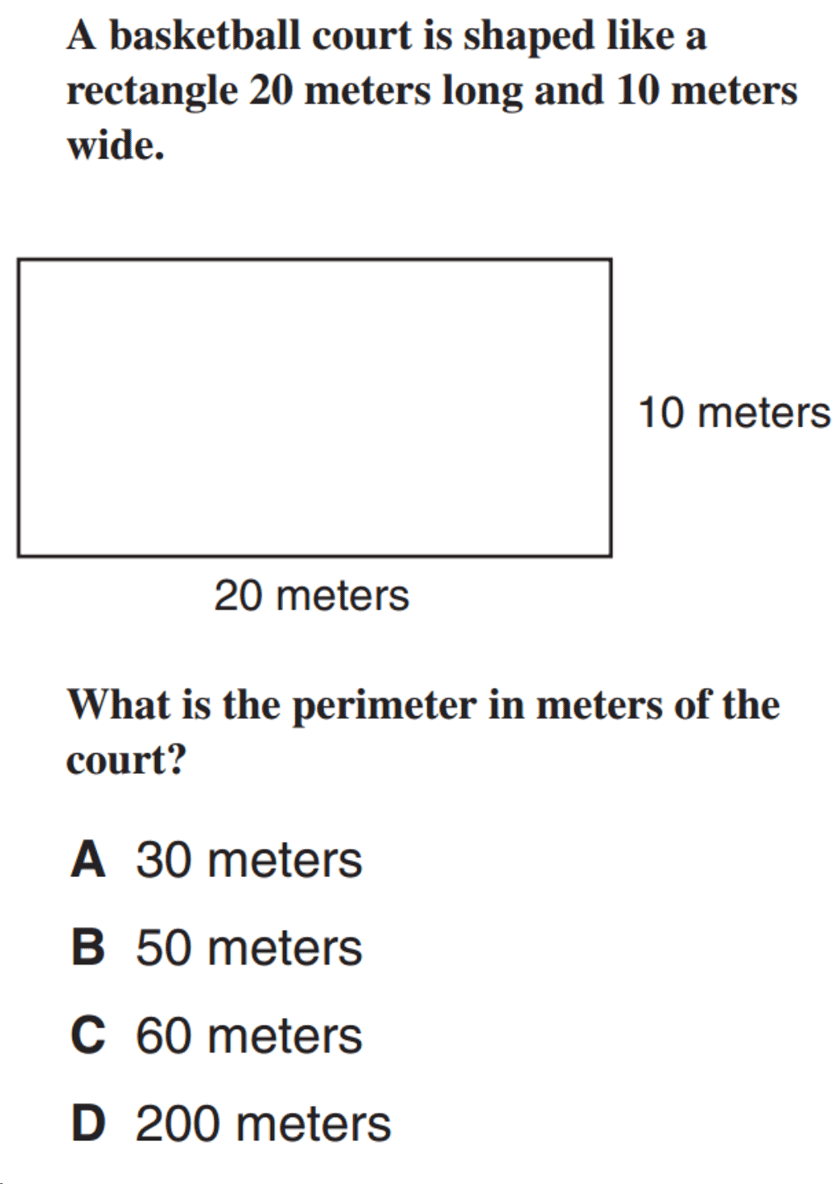
What is the perimeter of ABCD?
The perimeter of ABCD can be determined by adding the lengths of all four sides of the quadrilateral.
To find the perimeter, you need to know the lengths of the sides of ABCD. Once you have the lengths, you can add them together to get the total perimeter.
Here are the steps to calculate the perimeter of ABCD:
- Identify the lengths of the sides of ABCD. Let\'s say the lengths of the sides are a, b, c, and d.
- Add the lengths of all four sides together. This can be done using the formula: perimeter = a + b + c + d.
- Calculate the sum of the lengths to find the perimeter value.
For example, let\'s say the lengths of the sides of ABCD are: a = 5 units, b = 7 units, c = 6 units, and d = 4 units.
Using the formula, the perimeter of ABCD is:
| perimeter = a + b + c + d | = 5 + 7 + 6 + 4 | = 22 units |
So, the perimeter of ABCD is 22 units.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter Calculation
Understanding the concept of perimeter is essential in geometry. Perimeter refers to the total length of the edges around a two-dimensional shape. For a quadrilateral like ABCD, it involves summing the lengths of all four sides.
- Perimeter is a linear measure, representing the boundary of a shape.
- It\"s crucial in various real-life applications, such as fencing a garden or framing a picture.
- The formula for perimeter varies based on the shape. For rectangles, it\"s twice the sum of length and width; for irregular shapes, it\"s the sum of all sides.
Calculating the perimeter provides a foundational understanding of geometry, essential for further exploration of more complex geometric concepts.

Types of Shapes and Their Perimeters
Understanding the concept of perimeter is essential in geometry. Perimeter refers to the total length of the edges around a two-dimensional shape. For a quadrilateral like ABCD, it involves summing the lengths of all four sides.
- Perimeter is a linear measure, representing the boundary of a shape.
- It\"s crucial in various real-life applications, such as fencing a garden or framing a picture.
- The formula for perimeter varies based on the shape. For rectangles, it\"s twice the sum of length and width; for irregular shapes, it\"s the sum of all sides.
Calculating the perimeter provides a foundational understanding of geometry, essential for further exploration of more complex geometric concepts.

Formulas for Calculating Perimeter
Understanding the concept of perimeter is essential in geometry. Perimeter refers to the total length of the edges around a two-dimensional shape. For a quadrilateral like ABCD, it involves summing the lengths of all four sides.
- Perimeter is a linear measure, representing the boundary of a shape.
- It\"s crucial in various real-life applications, such as fencing a garden or framing a picture.
- The formula for perimeter varies based on the shape. For rectangles, it\"s twice the sum of length and width; for irregular shapes, it\"s the sum of all sides.
Calculating the perimeter provides a foundational understanding of geometry, essential for further exploration of more complex geometric concepts.

Specifics of Calculating Perimeter for Quadrilaterals
A quadrilateral, a four-sided polygon, can be regular or irregular. Regular quadrilaterals have equal sides and angles, while irregular ones do not. The perimeter of a quadrilateral is the total length of its four sides.
General Formula for Quadrilateral Perimeter
The basic formula for calculating the perimeter (P) of a quadrilateral is:
P = a + b + c + d
- a, b, c, d: Lengths of the four sides of the quadrilateral.
Types of Quadrilaterals and Their Perimeter Formulas
- Square: All sides equal (a). Perimeter = 4a.
- Rectangle: Opposite sides equal (length = l, width = w). Perimeter = 2(l + w).
- Rhombus: All sides equal (a). Perimeter = 4a. Similar to a square but with different angles.
- Parallelogram: Opposite sides equal (base = b, side = s). Perimeter = 2(b + s).
- Trapezoid: No general formula due to varied side lengths. Perimeter is the sum of all sides.
- Kite: Two pairs of adjacent equal sides (a and b). Perimeter = 2(a + b).
Calculating Perimeter with Different Units
It\"s crucial to use consistent units (like cm, m) for all side lengths when calculating the perimeter. If sides are given in different units, convert them to the same unit before adding.
Practical Tips for Accurate Measurement
- Use a ruler or measuring tape for straight sides.
- For irregular shapes, a string can be laid along the boundary and then measured.
- Ensure precision in measurement to avoid errors in perimeter calculation.
Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
Understanding the perimeter of quadrilaterals is useful in fields like architecture, interior design, and landscaping, where precise measurements are crucial for planning and building.

_HOOK_
Find the Perimeter of the Rectangle ABCD | Minute Math
\"Discover the fascinating world of perimeters and how they play a crucial role in geometry. Join us in this captivating video where we unlock the secrets of perimeter and its importance in various shapes and designs!\"
Find the Perimeter of the Rectangle ABCD | Fast & Easy Explanation
\"Uncover the hidden beauty of rectangles and their endless possibilities. Immerse yourself in this visually stunning video that showcases the versatility and elegance of the timeless rectangle shape. Prepare to be amazed!\"
Perimeter in Different Geometric Contexts
The concept of perimeter is applicable to various geometric shapes, each with unique characteristics. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter in different contexts is crucial in geometry.
Regular Polygons
For regular polygons (like a square or an equilateral triangle), the perimeter is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by the number of sides.
Perimeter (P) = Side length (a) × Number of sides (n)
Circles
In a circle, the perimeter is known as the circumference and is calculated using the radius (r) or diameter (d).
- Circumference (C) = 2πr or πd
Irregular Polygons
Irregular polygons do not have equal sides. To find the perimeter, sum the lengths of all sides.
Perimeter (P) = Sum of all side lengths
Complex Shapes
For complex shapes, divide them into known shapes, calculate each perimeter, and sum them up.
Perimeter on Coordinate Plane
When dealing with shapes on a coordinate plane, use distance formula to find the lengths of sides and then sum these lengths for the perimeter.
Perimeter in Real-Life Scenarios
- Fencing a garden (rectangular or circular).
- Creating borders in interior design.
- Planning athletic tracks (oval or circular).
Tools for Measuring Perimeter
Use rulers, measuring tapes, or digital tools for accurate measurements. For circular objects, use string and measure its length.

Practical Applications of Perimeter Calculation
Understanding the concept of perimeter, particularly in the context of various shapes such as quadrilaterals, is crucial in numerous practical fields. The perimeter, which is the total length of the outline of a shape, finds extensive applications in everyday life and professional domains.
- Architecture and Construction: In architecture and construction, the perimeter calculation is essential for determining the boundary lengths of buildings, gardens, or any land area. This assists in planning the layout, fencing, and landscaping effectively.
- Manufacturing: In the manufacturing industry, knowing the perimeter of objects is vital for material estimation, cutting, and assembly processes, especially in industries like garment manufacturing, metal fabrication, and carpentry.
- Geography and Surveying: Perimeter calculations are used in geography and land surveying to estimate the boundaries of plots, fields, and geographical areas for legal, construction, or agricultural purposes.
- Educational Tools: In education, perimeter problems enhance students\" understanding of geometry, measurement, and mathematical applications in real-life situations.
- Interior Design: Interior designers use perimeter measurements to plan room layouts, determine the amount of materials needed like paint or baseboard materials, and optimize space utilization.
- Sports Fields: Accurate perimeter measurements are crucial for designing and marking out sports fields and courts, ensuring standard dimensions for fair play.
- Gardening and Landscaping: Perimeter knowledge is essential in gardening and landscaping for designing garden beds, lawns, and determining the length of fences or paths.
- Fashion and Textile Design: In fashion, the concept of perimeter aids in pattern making and designing clothing, ensuring proper fit and material usage.
- Technology and Software Development: Perimeter calculations are employed in software development, particularly in graphics and design software, to create accurate models and visual representations.
- Science and Research: In various scientific research fields, perimeter measurements are used in experiments and practical applications, like in ecology for habitat mapping.
The practical applications of perimeter calculation are diverse and impact many aspects of daily life and professional sectors. An understanding of how to calculate and apply perimeter measurements is therefore beneficial in a wide range of scenarios.
Advanced Concepts: Perimeter on Coordinate Planes
Calculating the perimeter of shapes on coordinate planes introduces an advanced level of understanding in geometry. This method is particularly useful in scenarios where the sides of a shape are not readily measurable and must be determined through their coordinates.
- Identifying Coordinates: Begin by identifying the coordinates of each vertex of the shape on the coordinate plane. For a quadrilateral ABCD, these would be A(x1, y1), B(x2, y2), C(x3, y3), and D(x4, y4).
- Calculating Side Lengths: Use the distance formula, ( d = sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} ), to calculate the lengths of each side of the shape. Apply this formula to each pair of adjacent vertices.
- Summation of Side Lengths: Add up the lengths of all sides to get the perimeter of the shape. For a quadrilateral, this would be the sum of the lengths of AB, BC, CD, and DA.
Additionally, special attention should be given to shapes with sides parallel to the axes, as their lengths can be directly determined by the differences in their respective coordinates.
- If a side is parallel to the x-axis, its length is the absolute difference between the x-coordinates of its end points.
- If a side is parallel to the y-axis, its length is the absolute difference between the y-coordinates of its end points.
Understanding perimeter calculation on coordinate planes is essential for advanced geometry applications, including computer graphics, architectural design, and in various fields of engineering and science.

READ MORE:
Using Technology and Tools for Perimeter Calculation
Modern technology offers a variety of tools and methods to simplify and enhance the accuracy of perimeter calculations. These tools range from basic digital tools to advanced software, making perimeter calculations more efficient and precise in various fields.
- Graphing Calculators: Advanced calculators can compute perimeter for standard shapes, and some models allow for inputting the coordinates of vertices, making it easier to calculate the perimeter of irregular shapes.
- Computer Software: Software programs like AutoCAD and SketchUp are used in engineering and architecture for precise measurements, including perimeters of complex shapes in design plans.
- Online Calculators: Websites offer perimeter calculators where users can input dimensions of shapes to quickly obtain perimeter values. These are useful for quick estimates and educational purposes.
- Mobile Apps: Numerous mobile apps are available that can measure perimeters using augmented reality (AR) technology, allowing users to measure real-world objects easily.
- Educational Software: Interactive learning platforms, like Khan Academy and Desmos, provide virtual tools for students to explore and understand perimeter concepts interactively.
- Measurement Tools: Digital rulers and laser measures offer precise and easy ways to measure lengths, which can then be used to calculate perimeters manually.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): In fields like geography and urban planning, GIS software is used to calculate perimeters of large areas, like plots of land and water bodies, based on satellite data.
These technological tools not only simplify the process of perimeter calculation but also enhance the learning experience in educational settings and increase efficiency in professional applications.
Modern technology offers a variety of tools and methods to simplify and enhance the accuracy of perimeter calculations. These tools range from basic digital tools to advanced software, making perimeter calculations more efficient and precise in various fields.
These technological tools not only simplify the process of perimeter calculation but also enhance the learning experience in educational settings and increase efficiency in professional applications.