Topic area and perimeter activities: Discover the excitement of learning with our "Area and Perimeter Activities", designed to creatively enhance your understanding of geometry in a fun and interactive way.
Table of Content
- What are some creative area and perimeter activities for the classroom?
- Understanding the Basics of Area and Perimeter
- Interactive Area and Perimeter Learning Games
- Hands-On Activities for Teaching Area and Perimeter
- Using Real-Life Examples to Teach Area and Perimeter
- Area and Perimeter Worksheets and Printables
- Techniques for Differentiating Area and Perimeter Lessons
- YOUTUBE: Area and Perimeter Song For Kids 3rd 4th Grade
- Assessment Strategies for Area and Perimeter Understanding
- Technology Integration in Area and Perimeter Education
- Parental Involvement in Area and Perimeter Learning
- Advanced Concepts in Area and Perimeter for Higher Grades
What are some creative area and perimeter activities for the classroom?
Here are some creative area and perimeter activities for the classroom:
- Create an anchor chart to introduce the concepts of area and perimeter. This chart can include definitions, formulas, and examples.
- Decorate your classroom with posters or pictures that showcase real-life examples of area and perimeter, such as buildings, landscapes, or famous landmarks.
- Use four square grids and colored tiles to practice finding the area and perimeter of different shapes. Students can arrange the tiles on the grid to create shapes and then calculate their area and perimeter.
- Engage students in hands-on activities like creating their own shapes using paper or manipulatives and measuring their area and perimeter using rulers or measuring tapes.
- Create a scavenger hunt where students search for objects in the classroom or school that represent different shapes. They can then measure and calculate the area and perimeter of these objects.
- Introduce songs or chants that teach the formulas or concepts of area and perimeter to make learning more fun and memorable.
- Organize an outdoor game where students have to measure and calculate the area and perimeter of specific areas or objects in the schoolyard or playground.
- Encourage exploratory learning by providing materials like Cheez-It crackers or Rice Chex cereal for students to arrange in different shapes and explore the relationship between area and perimeter.
- Utilize geoboards, which are square boards with pegs, to help students visualize and manipulate shapes while calculating their area and perimeter.
READ MORE:
Understanding the Basics of Area and Perimeter
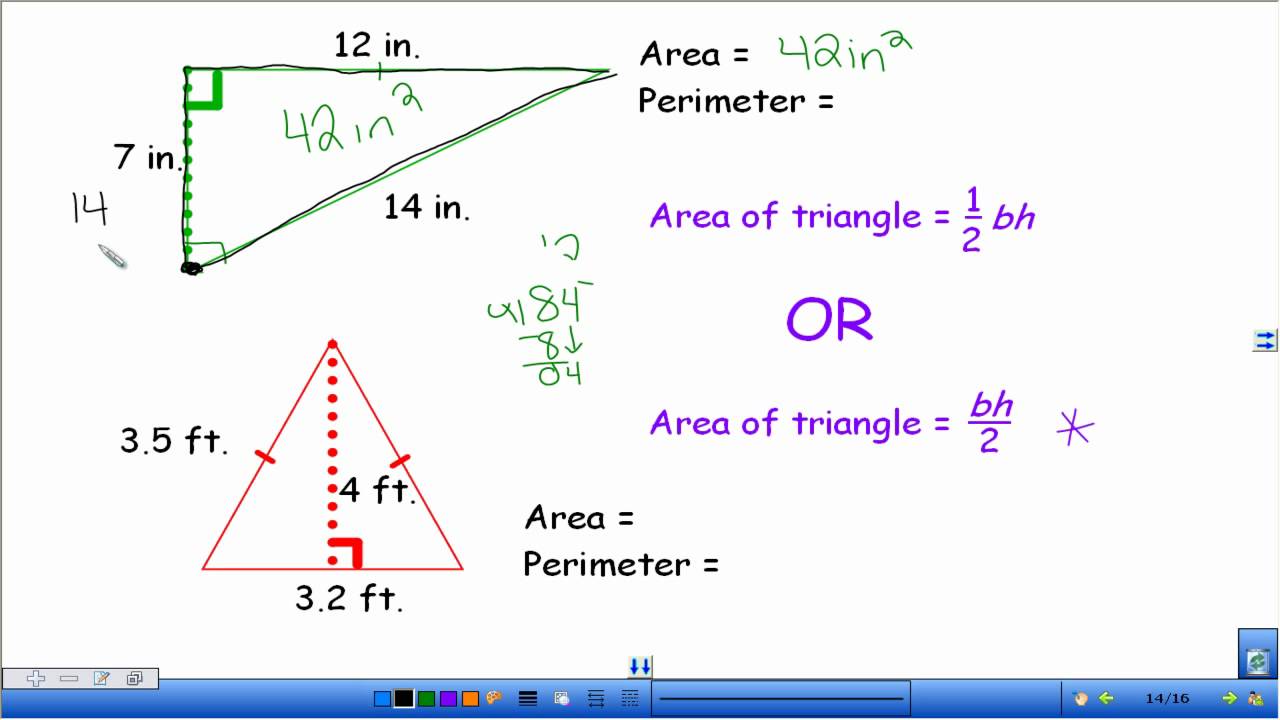
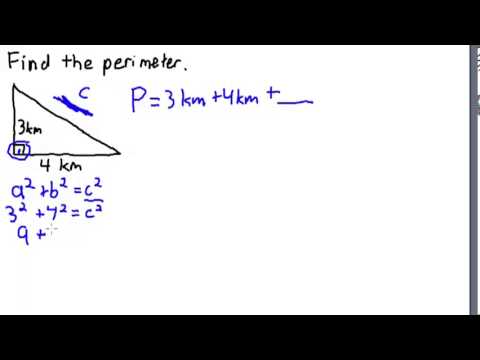
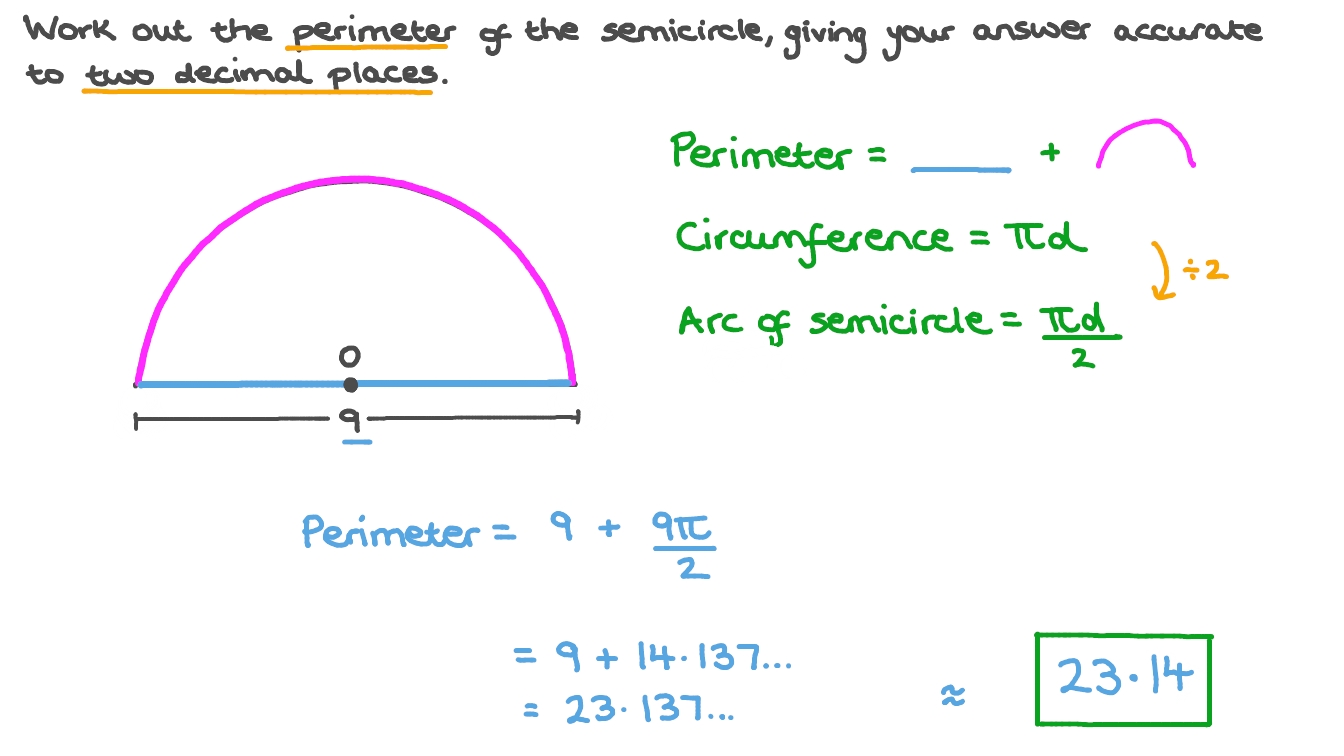
Area and perimeter are fundamental concepts in geometry, vital for understanding the measurement of two-dimensional spaces. Area refers to the space within a shape, typically measured in square units, while perimeter is the total distance around a shape. Grasping these concepts is crucial for practical applications in everyday life and advanced mathematical calculations.
- Defining Area: The area of a shape is calculated by determining the amount of space inside the boundary of the shape. For regular shapes like squares and rectangles, the area is found by multiplying the length by the width.
- Understanding Perimeter: Perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a shape. It is calculated by adding up the lengths of all the sides. For regular polygons, this is often a simple process of multiplying the length of one side by the total number of sides.
- Formulas for Common Shapes: Key formulas for area and perimeter include:
- Area of a rectangle: length × width
- Perimeter of a rectangle: 2 × (length + width)
- Area of a square: side × side
- Perimeter of a square: 4 × side
- Visualizing Concepts: Visual aids, like graph paper and geometric shapes, help in understanding how area and perimeter are calculated and why these measurements are important.
- Real-World Applications: These concepts have practical applications in everyday life, such as determining the amount of paint needed for a wall (area) or the length of fencing required for a garden (perimeter).
Grasping the basics of area and perimeter paves the way for exploring more complex geometrical concepts and their applications in various fields.

Interactive Area and Perimeter Learning Games
Interactive games are a fantastic way to engage students in learning the concepts of area and perimeter. Here are some activities and games that can make learning these mathematical concepts fun and engaging:
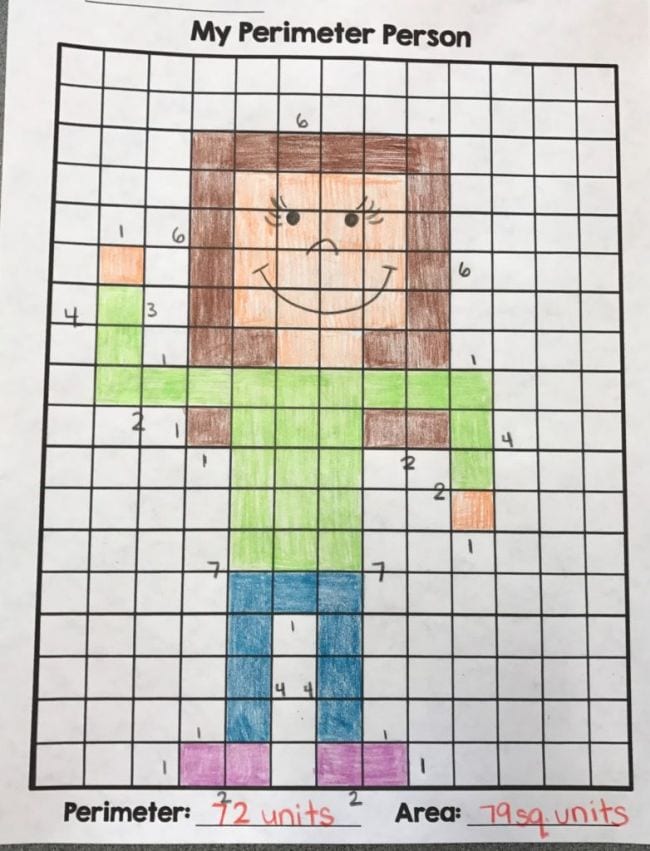
- Math Mosaics: Students can use square sticky notes to create a mosaic, such as a self-portrait or other themes. They then calculate the area and perimeter of their creations.
- LEGO Brick Challenges: Utilizing LEGO bricks, students can explore area and perimeter by constructing various shapes and calculating their dimensions.
- Area and Perimeter Songs: Incorporating music, students can learn catchy tunes that help them remember the formulas and applications of area and perimeter.
- Graph Paper Drawings: Students can create drawings on graph paper using complete squares, and then calculate the area and perimeter of different elements in their artwork.
- Scavenger Hunts: A fun way to learn is through scavenger hunts where students find objects or figures and calculate their area and perimeter.
- Conquer the Area Game: A partner game using dice and grid sheets, where students roll the dice to determine the dimensions of a shape they must draw and calculate its area.
- Perimeter, Area, and Volume with Picture Books: Integrating picture books that focus on these concepts can help students visualize and understand area and perimeter in real-world contexts.
- Area and Perimeter Bingo: A classroom game where students solve area and perimeter problems to complete their bingo cards.
- Building Projects: Students can engage in projects like designing a tiny house or a city, where they calculate the area and perimeter for different components of their designs.
- Interactive Task Cards: Task cards can be used in various interactive ways, such as in board games or classroom activities, to practice area and perimeter calculations.
These activities not only help students understand the concepts of area and perimeter but also allow them to apply these concepts in creative and practical ways, enhancing their learning experience.
Hands-On Activities for Teaching Area and Perimeter
Engaging students in hands-on activities is a great way to teach the concepts of area and perimeter. Here are some creative ideas:
- Floor Tile Shapes: Using square floor tiles and blue painter’s tape, students can create various shapes to calculate their areas and perimeters. This activity allows for both solving given shapes and creativity in designing new ones.
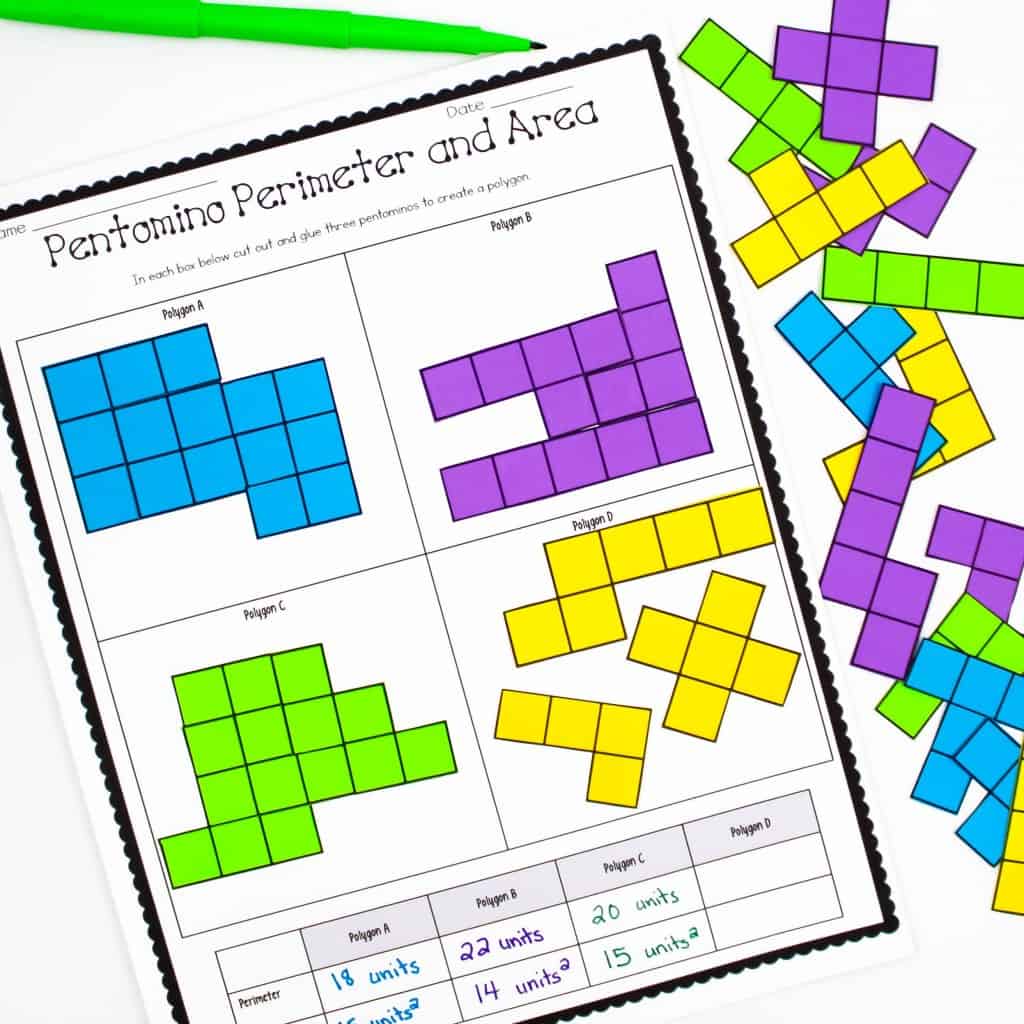
- Pentominoes: Similar to Tetris blocks, pentominoes can be used to trace shapes on graph paper, allowing students to calculate the area and perimeter of these shapes.
- Kite Building: Students can construct kites using given materials and then measure their area and perimeter. This activity combines crafting skills with geometry and ends with an exciting outdoor flying session.
- Interior Design Project: A real-life application of area and perimeter where students arrange furniture in a room, ensuring everything fits perfectly.
- City Building: An activity where students design a city and calculate the area and perimeter of each building, integrating volume for a more comprehensive learning experience.
- Island Conquer Game: In this game, students plot rectangles or “islands” on a grid, calculating the area and perimeter. The player with the most island area wins.
- Geoboards: Using geoboards and elastic bands, students can create shapes and calculate their area and perimeter, offering a tactile learning experience.
- Area and Perimeter Robots: A craft project where students use graph paper to build a robot with specific area and perimeter measurements, allowing for creativity and mathematical precision.
- Wrapping Paper Scoot: An activity where students measure the area and/or perimeter of different pieces of wrapping paper placed around the room, adding a festive touch to geometry practice.
- Interactive Notebooks and Centers: Integrating area and perimeter activities into interactive notebooks and math centers can provide differentiated, engaging practice for students.
These activities not only make learning area and perimeter fun but also help students see their practical applications in everyday life.

Using Real-Life Examples to Teach Area and Perimeter
Teaching area and perimeter through real-life examples makes the concepts more tangible and engaging for students. Here are some practical and fun activities:
- Floor Tile Shapes: Utilizing square floor tiles and blue painter’s tape, students can create shapes on the floor, measuring their areas and perimeters, and even design their own shapes for their classmates to solve.
- Pentominoes: Inspired by Tetris, pentomino blocks can be used to form shapes on grid paper, challenging students to calculate their area and perimeter.
- Kite Building: Students construct kites and then calculate their area and perimeter, followed by a discussion on how these measurements might affect kite flying.
- Interior Design Project: A real-life application where students arrange furniture in a given space, using area and perimeter calculations to ensure everything fits.
- City Building: Students collaborate to design a city, calculating area and perimeter for each structure, integrating volume for a comprehensive approach.
- Geoboards: A hands-on tool where students create shapes and calculate their area and perimeter.
- Area and Perimeter Robot: A craft-based activity where students build a robot using specific area and perimeter measurements on graph paper.
- Measuring with Wrapping Paper: A festive activity where students measure the area and perimeter of different pieces of wrapping paper, making learning feel like a celebration.
- Interactive Notebooks: Utilizing interactive notebooks for differentiated activities, helping students engage with area and perimeter in a personalized manner.
- Construction Decisions: Stepping into complex problem-solving, students apply their understanding of area and perimeter to construction-related decisions.
These activities not only make learning area and perimeter more enjoyable but also help students understand their practical applications in everyday life.
_HOOK_
Area and Perimeter Worksheets and Printables
Worksheets and printables are essential tools in teaching area and perimeter concepts effectively. They offer structured and engaging ways for students to practice and reinforce their understanding. Here are some creative ideas for area and perimeter worksheets and printables:
- Ordering Rectangles Activity: Using grid paper, students can draw rectangles with a given perimeter, find the area of each rectangle, and then arrange them from smallest to largest area. This activity helps in understanding the relationship between area and perimeter.
- Fixed Area and Perimeter Worksheets: Challenge students to draw and label all possible rectangles with a specific perimeter or area, such as 24 units. This helps develop abstract thinking and problem-solving skills related to geometry.
- Construction Decisions: Engage students in more complex problem-solving where they apply their knowledge of area and perimeter to construction-related scenarios. This approach bridges the gap between theoretical understanding and practical application.
- Problem-Solving Activities: Worksheets that focus on problem-solving can teach students that area is additive - they can add or subtract sections to find the total area. These activities enhance students\" analytical skills.
- Integrating Art: Encourage creativity by having students partition their names written in block letters into rectangles on grid paper, and then calculate the area for each section. This artistic integration makes learning fun and memorable.
- Interactive Notebook Inserts: Provide students with interactive notebook activities that are differentiated to meet various learning needs. These can include various tasks and challenges related to area and perimeter.
- Geoboard Challenges: Incorporate geoboard activities where students create shapes and calculate their area and perimeter. This hands-on approach is engaging and helps in solidifying concepts.
These worksheets and printables not only enhance the learning experience but also cater to different learning styles, ensuring that all students can grasp these fundamental mathematical concepts.

Techniques for Differentiating Area and Perimeter Lessons
To effectively teach area and perimeter, it\"s essential to differentiate the lessons to cater to diverse learning styles and abilities. Here are some techniques that can be applied:
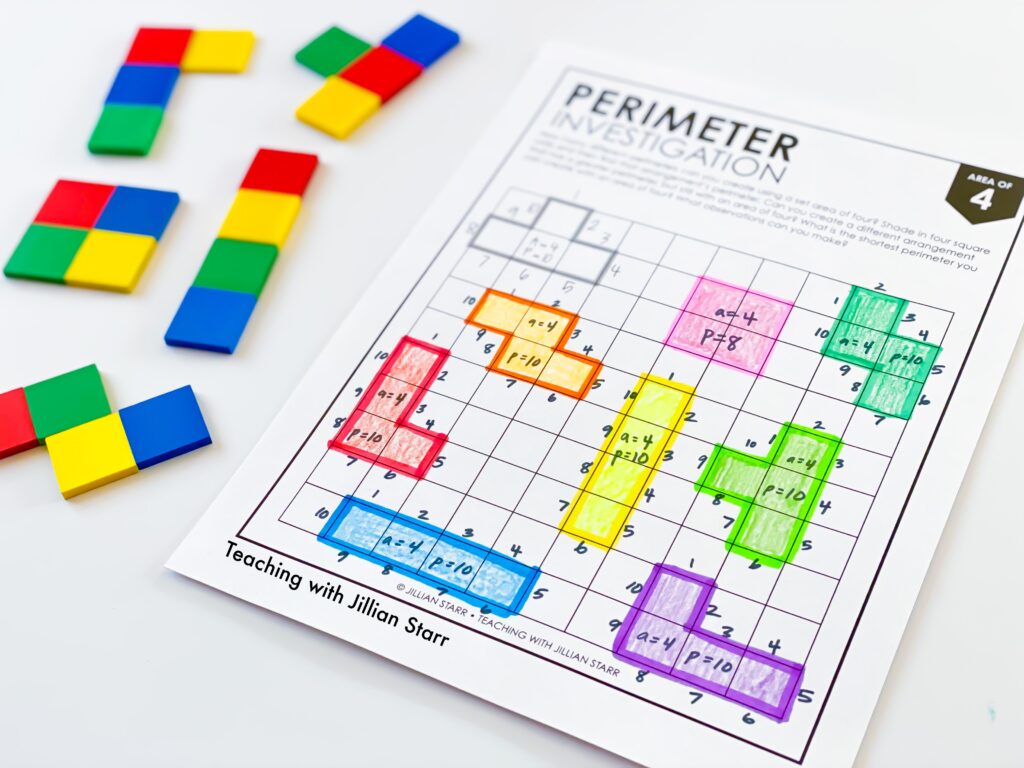
- Manipulatives and Hands-On Activities: Using physical objects like square tiles or geoboards allows students to create shapes and directly measure their area and perimeter. This tactile approach is particularly effective for kinesthetic learners.
- Real-World Applications: Incorporating real-life examples, such as designing a room or building a city, helps students understand the practical application of area and perimeter. Activities like measuring objects in the classroom can also enhance learning.
- Visual and Interactive Elements: Using visual aids like graph paper for drawing shapes or interactive notebooks can help visual learners better grasp these concepts. Coloring and labeling different shapes can make learning more engaging.
- Game-Based Learning: Educational games, such as \"Conquer the Area\" where students roll dice to create shapes and calculate their area, can make learning more fun and interactive.
- Use of Technology: Incorporating technology, such as digital task cards or online resources, can provide an interactive platform for students to practice and apply their knowledge in area and perimeter.
- Problem-Solving Challenges: Offering problem-solving activities where students must apply their understanding of area and perimeter in complex scenarios can help develop critical thinking skills.
- Art Integration: Integrating art projects, like creating a robot or an object and finding its area and perimeter, can be an effective way to engage creative learners.
- Varied Assessments: Using different forms of assessments, such as performance-based tasks, can help evaluate understanding in a way that suits each student\"s learning style.
These differentiation techniques can enhance the learning experience, ensuring that each student has the opportunity to understand and apply the concepts of area and perimeter effectively.
Area and Perimeter Song For Kids 3rd 4th Grade
Song: \"Discover a captivating melody that will touch your heart and uplift your spirit. Immerse yourself in the enchanting lyrics and soulful rhythm of this extraordinary song. Watch the video now to experience pure musical bliss.\"
Interactive Way of Teaching Area Perimeter Math Concepts
Interactive: \"Dive into an exhilarating world where you become an active participant. Engage with this interactive video that will challenge your mind and captivate your senses. Step into a new dimension of entertainment and embark on a thrilling journey like never before.\"
Assessment Strategies for Area and Perimeter Understanding
Effective assessment of area and perimeter understanding involves a variety of strategies to cater to different learning styles. Here are some approaches:
- Hands-On Manipulatives: Use tools like geoboards or square tiles for students to create shapes and calculate area and perimeter. This approach helps assess their practical understanding of the concepts.
- Real-Life Application Tasks: Engage students in activities that involve measuring real objects or designing layouts, such as room planning or city building. These tasks assess their ability to apply concepts in real-world situations.
- Project-Based Assessments: Projects like constructing a kite or creating a robot with specific area and perimeter can be used for performance-based assessment, focusing on creativity and practical application of knowledge.
- Interactive and Visual-Based Activities: Incorporating activities that use block paper, graph paper, or interactive notebooks helps in assessing students\" visual and spatial understanding of area and perimeter.
- Math Games and Challenges: Implementing games like \"Island Conquer\" or \"Conquer the Area\" where students engage in competitive tasks involving area and perimeter calculations can be an enjoyable way to assess understanding.
- Worksheet Activities: Providing worksheets with a range of problems, from simple calculations to complex shapes and real-life objects, can be an effective way to assess individual understanding and problem-solving skills.
Combining these diverse assessment methods ensures a comprehensive understanding of students\" abilities in area and perimeter, catering to their unique learning styles and preferences.

Technology Integration in Area and Perimeter Education
Integrating technology in teaching area and perimeter offers a dynamic and interactive approach to learning these concepts. Here are some effective strategies:
- Interactive Software and Apps: Utilize educational software and apps that allow students to explore area and perimeter in an engaging way. These tools often include interactive elements that visually demonstrate how area and perimeter are calculated, making the concepts more accessible and understandable.
- Online Games and Simulations: Implement online games and simulations that focus on area and perimeter. These can range from simple games for basic understanding to more complex simulations for advanced learners, offering a fun and competitive environment for learning.
- Digital Worksheets and Activities: Use digital worksheets and activities for practice and assessment. These can be tailored to individual student needs and offer instant feedback, enhancing the learning experience.
- Project-Based Learning with Technology: Encourage students to undertake project-based learning activities where they can apply their knowledge of area and perimeter in real-world contexts, using technology as a tool for research, design, and presentation.
- Virtual Manipulatives: Incorporate virtual manipulatives such as online geoboards or digital blocks, allowing students to create and manipulate shapes to understand area and perimeter concepts better.
- Interactive Whiteboards: Make use of interactive whiteboards in the classroom for teaching area and perimeter. They provide a visual and hands-on way for students to interact with the concepts being taught.
- Educational Videos and Tutorials: Integrate educational videos and tutorials that explain area and perimeter concepts. These can be used as supplementary materials to reinforce learning.
- Collaborative Learning Platforms: Use collaborative platforms where students can work together on area and perimeter problems, share their solutions, and receive feedback from peers and teachers.
By integrating technology into area and perimeter education, teachers can provide a more enriched, engaging, and effective learning experience for their students.
Parental Involvement in Area and Perimeter Learning
Encouraging parental involvement in teaching area and perimeter can significantly enhance a child\"s learning experience. Here are some strategies to involve parents effectively:
- Practical Home Activities: Parents can engage children in everyday activities that involve area and perimeter, such as measuring rooms for new furniture, calculating the area for a new garden bed, or even using floor tiles to create shapes and measure their dimensions.
- Interactive Games: Families can play educational games that focus on area and perimeter. For example, a game like \"Island Conquer\" involves plotting rectangles or \"islands\" on a grid and calculating their area and perimeter, making for an engaging and competitive learning experience.
- Educational Projects: Encourage parents to work on projects with their children, like building a kite or designing a dream house using graph paper. Such activities allow the application of area and perimeter in a fun and creative context.
- Use of Technology: Guide parents to educational apps and online resources that offer interactive learning experiences in area and perimeter. These tools often include games, simulations, and digital worksheets that can be both informative and entertaining.
- Help with Homework: Parents can assist children with homework or worksheets related to area and perimeter, helping them understand the concepts and solve problems.
- Reading Together: Sharing educational books that incorporate area and perimeter concepts, like \"Spaghetti and Meatballs for All: A Mathematical Story\" by Marilyn Burns, can be a delightful way to combine learning with reading time.
Parental involvement in area and perimeter learning not only reinforces classroom teachings but also shows practical applications of these concepts, making math more enjoyable and relatable for students.

_HOOK_
READ MORE:
Advanced Concepts in Area and Perimeter for Higher Grades
Exploring advanced concepts in area and perimeter offers students a deeper understanding of geometry and its real-world applications. Here are some engaging activities designed to challenge and inspire higher grade students:
1. Complex Shapes and Their Properties
- Explore area and perimeter calculations for a variety of shapes like triangles, trapezoids, and circles. This includes understanding the formulas for each shape and practicing calculations.
- Use graph paper for visual representation and better understanding.
2. Real-World Application Projects
- Engage in projects like designing a city layout, where students calculate the area and perimeter of different buildings and parks.
- Interior design activities, where students arrange furniture in a given space considering the area and perimeter constraints.
- Creating kites or other craft projects, measuring their dimensions, and discussing how area and perimeter affect their design and functionality.
3. Hands-On Manipulatives and Games
- Utilize manipulatives such as pattern blocks, square tiles, and sticky notes to explore area and perimeter in a tactile way. This can include creating various shapes and calculating their dimensions.
- Introduce educational games that incorporate area and perimeter calculations, such as \"Island Conquer\" where students plot rectangles on grids and calculate their dimensions.
4. Advanced Problem-Solving Exercises
- Challenge students with problems that require them to find missing lengths or dimensions in given shapes or to compare areas and perimeters of different shapes.
- Introduce puzzles and word problems that focus on area and perimeter, encouraging critical thinking and application of concepts.
5. Integrating Art and Geometry
- Incorporate art projects where students use grid paper to create designs or letters, partitioning them into geometrical shapes and calculating the area of each section.
6. Technology Integration
Use digital tools and software for creating and solving area and perimeter problems. This can include interactive worksheets, online quizzes, and geometry software programs.
7. Collaborative Learning and Discussions
Encourage group discussions and collaborative problem-solving to deepen understanding and allow for the sharing of different strategies and perspectives.
Discover the world of area and perimeter through engaging activities that blend learning with fun, fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation for geometry in real-world contexts. Join us on this exciting mathematical journey!