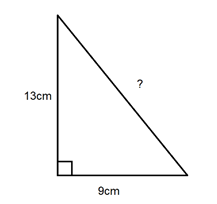
Topic what is the perimeter of this right triangle: Explore the intriguing world of geometry as we unravel the secrets of calculating the perimeter of a right triangle. This engaging journey will not only enhance your mathematical skills but also broaden your understanding of geometric principles.
Table of Content
- What is the perimeter of this right triangle?
- Definition and Formula for the Perimeter of a Right Triangle
- Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Perimeter
- Examples of Perimeter Calculations in Different Right Triangles
- Common Mistakes to Avoid in Perimeter Calculations
- Practical Applications of Right Triangle Perimeter in Real Life
- YOUTUBE: Area and Perimeter of a Right Triangle | Math with Mr. J
- Tools and Resources for Perimeter Calculation
- Tips for Remembering the Perimeter Formula
- FAQs on Right Triangle Perimeter
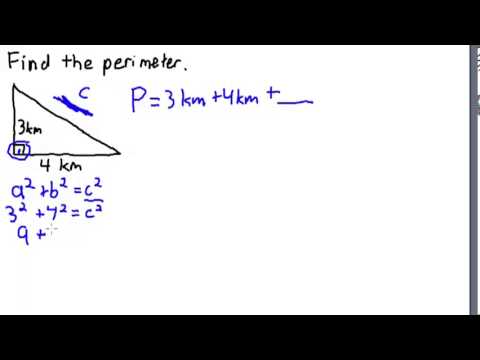
What is the perimeter of this right triangle?
To find the perimeter of a right triangle, we need to know the lengths of its three sides. Let\'s assume the lengths of the two legs are a and b, and the length of the hypotenuse (the longest side) is c.
Using the Pythagorean theorem, we can relate the lengths of the sides:
- a2 + b2 = c2
To find the perimeter, we need to add up the lengths of all three sides. So, the perimeter (P) is given by:
- P = a + b + c
Therefore, to find the perimeter of the right triangle, you would need to know the lengths of all three sides.
READ MORE:
Definition and Formula for the Perimeter of a Right Triangle
The perimeter of a right triangle is defined as the total distance around the triangle. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all three sides: the base, the height (or altitude), and the hypotenuse. This can be represented as P = a + b + c, where \"a\", \"b\", and \"c\" are the sides of the triangle.
One of the key concepts for calculating the perimeter is the Pythagorean theorem, which states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. This theorem is written as c² = a² + b², where \"a\" and \"b\" are the sides forming the right angle and \"c\" is the hypotenuse.
- Example 1: If a right triangle has a base of 5 units and a hypotenuse of 13 units, we can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the height. Assuming the height is \"a\", the formula becomes (13)² = (5)² + a², leading to a = 12 units. Therefore, the perimeter of this triangle is 5 + 13 + 12 = 30 units.
- Example 2: In the case of special right triangles like a 30°-60°-90° triangle, the sides are in a ratio of 1:√3:2. Knowing one side length allows for the calculation of the others and subsequently the perimeter.
It\"s important to include the correct units in the final answer, matching the units used for the side lengths. This ensures accuracy and clarity in representing the perimeter of the triangle.
Understanding these principles and applying the Pythagorean theorem where necessary, you can calculate the perimeter of any right triangle.

Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a right triangle involves a straightforward process that can be done in a few simple steps. Here\"s how you can calculate it effectively:
- Identify the sides: Label the sides of the right triangle as base (b), height (p), and hypotenuse (h).
- Use Pythagoras Theorem if necessary: If the length of one side is unknown, use the Pythagorean theorem, which states that h² = b² + p². Solve for the unknown side.
- Calculate the perimeter: Add the lengths of all three sides. The formula for the perimeter of a right triangle is Perimeter = b + p + h.
Example Calculations:
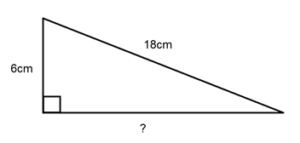
- If you have a right triangle with base = 6 units and height = 8 units, first calculate the hypotenuse using Pythagoras theorem: hypotenuse = √(6² + 8²) = √(36 + 64) = √100 = 10 units. The perimeter is then 6 + 8 + 10 = 24 units.
- For a right triangle with known sides, simply add them up. For example, if the sides are 3 inches, 4 inches, and 5 inches, the perimeter is 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 inches.
- In cases of right triangles with special ratios like a 30°-60°-90° triangle or a 45°-45°-90° triangle, use the known ratios to find the missing sides before calculating the perimeter.
Remember, always include the correct units in your final answer, and use the Pythagorean theorem for right triangles when one side length is unknown.

Examples of Perimeter Calculations in Different Right Triangles
Different types of right triangles can have varying methods for perimeter calculation. Here are some examples illustrating this:
- Standard Right Triangle: For a right triangle with a base of 5 units and a hypotenuse of 13 units, first find the height using the Pythagorean theorem. This gives a height of 12 units, resulting in a perimeter of 5 + 13 + 12 = 30 units.
- Pythagorean Triple: A right triangle with sides that are integers, like 3, 4, 5 or 5, 12, 13, is known as a Pythagorean triangle. For instance, a triangle with sides 3, 4, and 5 units has a perimeter of 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 units.
- Special Right Triangles: For a 30°-60°-90° right triangle with one side length known, the other sides follow a ratio of 1:√3:2. For instance, if one side is 5 units, the other sides can be determined as 5√3 and 10 units, and the perimeter calculated accordingly. Similarly, a 45°-45°-90° right triangle has sides in a 1:1:√2 ratio.
- Triangles with an Unknown Side: In cases where one side length is missing, use the given perimeter and known sides to find the unknown length. For example, if a right triangle has two sides of 17 inches each and a perimeter of 48 inches, the third side can be found as 48 - (17 + 17) = 14 inches.
- Isosceles Right Triangle: For a right isosceles triangle with equal legs of 6 inches, use the Pythagorean theorem to find the hypotenuse, which in this case is 6√2 inches. The perimeter then becomes 6 + 6 + 6√2 inches.
These examples showcase how the perimeter of a right triangle can be calculated in various scenarios using basic geometric principles and the Pythagorean theorem.
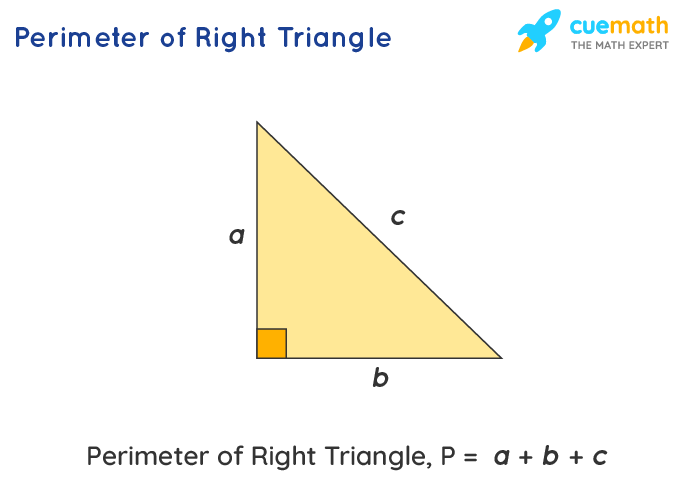
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Perimeter Calculations
Calculating the perimeter of a right triangle requires precision and attention to detail. Avoiding common mistakes ensures accuracy in your calculations. Here are some typical errors and how to avoid them:
- Not Using the Pythagorean Theorem Correctly: Remember, for a right triangle with sides \"a\" and \"b\", and hypotenuse \"c\", the theorem states (a^2 + b^2 = c^2). Ensure you\"re solving for the correct side when one is unknown.
- Ignoring Units of Measurement: Consistency in units is crucial. If the sides are measured in different units, convert them to the same unit before adding.
- Miscalculating Side Lengths: Accurate measurement of sides is key. Even a small error can lead to a significant miscalculation in the perimeter.
- Forgetting to Add All Sides: The perimeter is the sum of all three sides. Ensure all sides, including the hypotenuse, are accounted for in your calculation.
- Round-off Errors: Be cautious with rounding off numbers. Do it only after you have calculated the final perimeter.
By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can improve the accuracy of your perimeter calculations for right triangles.

_HOOK_
Practical Applications of Right Triangle Perimeter in Real Life
Understanding the perimeter of right triangles is not just a mathematical exercise; it has numerous practical applications in real life. Here are some of the ways this knowledge is applied:
- Architecture and Construction: Architects and engineers often use right triangles to design buildings and structures. Calculating the perimeter helps in determining the total length of materials needed for construction.
- Land Surveying: Surveyors use right triangles to calculate distances across land. By measuring two sides of a triangle, they can calculate the third side, helping in mapping and property boundary determinations.
- Navigation and Mapping: Navigators and cartographers use the principles of right triangles to plot courses and create maps, especially in marine and aerial navigation.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers often employ right triangles in their work to create visually appealing and structurally sound designs.
- Science and Technology: In fields like physics and engineering, right triangles are used to solve problems involving forces, vectors, and motion.
- Crafts and DIY Projects: Right triangles are frequently used in woodworking, quilting, and other crafts, where precise measurements and angles are important.
- Educational Tools: Teaching concepts of geometry often involves using right triangles to explain basic principles of trigonometry and mathematics.
These examples highlight the importance of understanding right triangle perimeter calculations in various professional and everyday contexts.
Area and Perimeter of a Right Triangle | Math with Mr. J
Discover the secrets of calculating perimeter in a fun and engaging way! Join us as we explore the world of shapes and learn how to calculate their perimeters effortlessly. You\'ll be amazed at how quickly you\'ll become a geometry whiz!
Elegant way to find the Perimeter of a Right Triangle | step-by-step explanation | math maths
Get ready to be captivated by the sheer elegance of this fashion show! From delicate lace to shimmering sequins, experience the blend of sophistication and glamour as models graciously walk the runway in the most elegant outfits. Join us to indulge in a night of pure style and sophistication.
Tools and Resources for Perimeter Calculation
Various tools and resources can assist in accurately calculating the perimeter of a right triangle. Here are some valuable tools and resources:
- Online Calculators: Websites like Calculator.net offer right triangle calculators where you input two values (sides or angles), and the calculator computes the other dimensions, including the perimeter (www.calculator.net).
- Perimeter Calculator Apps: Platforms such as A.Tools provide perimeter calculators for different shapes, including triangles, where you input side lengths to calculate the perimeter (www.a.tools).
- Step-by-Step Solutions: Websites like Symbolab offer calculators for calculating the area and perimeter of right-angled triangles, guiding you through each step of the calculation process (www.symbolab.com).
- Educational Websites: Sites like Mathematical Way provide detailed explanations and formulas for calculating the perimeter of right triangles using methods like the Pythagorean theorem and the Leg Rule (www.mathematicalway.com).
- Comprehensive Triangle Calculators: Calculator.io provides a right triangle calculator that not only calculates perimeter but also displays calculation steps and scaled views of the triangle (www.calculator.io).
These tools not only simplify the calculation process but also provide educational insights into the geometry of right triangles.

Tips for Remembering the Perimeter Formula
Calculating the perimeter of a right triangle can be a straightforward process with the right approach. Here are some tips to help you remember and apply the formula effectively:
- Know the Basics: The perimeter of a right triangle is the sum of its three sides. Remember, P = a + b + c, where \"a\", \"b\", and \"c\" are the sides of the triangle.
- Pythagoras Theorem: For cases where one side length is unknown, use the Pythagoras theorem (c² = a² + b²). Remember, in a right triangle, \"c\" is the hypotenuse.
- Special Triangles: In an isosceles right triangle, the two legs are equal. Use the formula P = 2l + h, where \"l\" is the length of the equal legs and \"h\" is the hypotenuse. The hypotenuse can be found as h = √2 × l.
- Unit Consistency: Ensure all the side measurements are in the same unit before adding them together.
- Visual Representation: Drawing the triangle and labeling its sides can often help in visualizing and solving the problem more effectively.
- Mnemonic Devices: Create a simple phrase or rhyme to remember the formula, such as “Add all sides, don’t hide, to find the right triangle\"s stride”.
- Practice: Regularly practicing with different sets of measurements can help reinforce your understanding and recall of the formula.
With these tips in mind, calculating the perimeter of a right triangle can become an easier and more intuitive process. Remember, practice and understanding the underlying principles are key to mastering this concept.
READ MORE:
FAQs on Right Triangle Perimeter
- What is the Perimeter of a Right Angled Triangle in Math?
- The perimeter of a right-angled triangle is the sum of the lengths of all three sides. This includes the hypotenuse, the height (altitude), and the base. If the sides are x, y, and z, then the perimeter is calculated as P = x + y + z.
- What is the Pythagoras Theorem for a Right Angled Triangle?
- The Pythagoras theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (c) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides (a and b). It is represented as c² = a² + b².
- How is the Perimeter of a Right Triangle Calculated When One Side is Unknown?
- When one side of the right triangle is unknown, you can use the Pythagoras theorem to find it. For instance, if the hypotenuse (c) is unknown, it can be calculated as c = √(a² + b²). Once all sides are known, add them together to get the perimeter: P = a + b + c.
- What is the Difference Between Area and Perimeter of a Right Angled Triangle?
- The area of a right-angled triangle is the amount of space it occupies, calculated using the formula: Area = ½ × base × height. The perimeter is the total length of the triangle\"s boundary, calculated as the sum of all three sides.
- Can a Triangle Have the Same Area and Perimeter?
- A triangle can have the same area and perimeter in some special cases. These shapes, having an equal perimeter and area, are known as equable shapes.
- How to Find the Perimeter of an Isosceles Right Triangle?
- In an isosceles right triangle, where two legs are equal, the perimeter is calculated using P = 2l + h, where \"l\" is the length of the equal legs and \"h\" is the hypotenuse. The hypotenuse can be found using h = √(l² + l²).
- How to Calculate the Perimeter of a Triangle With Coordinates?
- If the coordinates of a triangle\"s vertices are given, the lengths of its sides can be calculated using the distance formula. The perimeter is then the sum of these side lengths.
Mastering the concept of a right triangle\"s perimeter opens doors to a deeper understanding of geometry and its practical applications. With this knowledge, you\"re now equipped to solve real-life problems and appreciate the elegance of mathematical principles.