Topic perimeter formula of a pentagon: Explore the intriguing world of geometry with our comprehensive guide on the "Perimeter Formula of a Pentagon," where we simplify this fundamental concept for enthusiasts and learners alike.
Table of Content
- Key Concepts and Definition
- YOUTUBE: Perimeter of Pentagon: Formula, Examples, and Regular vs Irregular
- Regular vs. Irregular Pentagon: Different Formulas
- Step-by-Step Calculation of Regular Pentagon Perimeter
- Calculating Perimeter for an Irregular Pentagon
- Practical Examples of Pentagon Perimeter Calculation
- Common Misconceptions and Corrections
- Importance of Apothem and Area in Pentagon Calculations
- Comparative Analysis with Other Polygons
- Interactive Tools and Calculators for Pentagon Perimeter
- Additional Resources and Learning Materials
Key Concepts and Definition
The concept of a pentagon, a polygon with five sides, is pivotal in geometry. Understanding its perimeter, which is the total distance around its boundary, is essential for various applications in mathematics and real-life scenarios.
- Regular Pentagon: This is a pentagon where all sides are equal in length, and all interior angles are equal. Its symmetry simplifies calculations.
- Irregular Pentagon: Here, the sides and angles may not be equal. Calculating its perimeter involves summing the lengths of all individual sides.
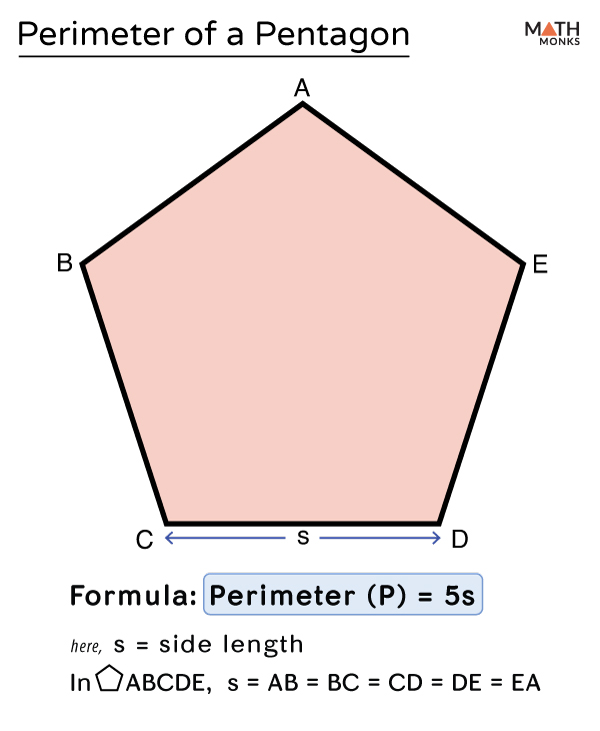
- Perimeter Formula for a Regular Pentagon: The formula is P = 5s, where P represents the perimeter and s the length of a side.
- Perimeter of an Irregular Pentagon: It is calculated as the sum of the lengths of all five sides, represented as P = a + b + c + d + e, with each letter representing a side length.
- Unit of Measurement: The perimeter is measured in linear units such as meters, centimeters, inches, or feet.
Understanding these key concepts is essential for correctly applying the perimeter formula of a pentagon in various mathematical problems and real-world applications.

Perimeter of Pentagon: Formula, Examples, and Regular vs Irregular
Discover the hidden secrets of the Pentagon in this intriguing video that explores its fascinating history, unique architecture, and mysterious symbolism. Prepare to be amazed by the incredible stories behind this iconic landmark!
Regular vs. Irregular Pentagon: Different Formulas
The calculation of a pentagon\"s perimeter differs based on its type – regular or irregular. It\"s crucial to understand these differences to apply the appropriate formula.
- Regular Pentagon: In a regular pentagon, all sides are of equal length and all interior angles are identical. This uniformity allows for a simpler formula for the perimeter, which is P = 5s, where P is the perimeter and s is the side length. The calculation is straightforward as it involves multiplying the length of one side by the total number of sides.
- Irregular Pentagon: An irregular pentagon does not have equal sides or equal angles. To calculate its perimeter, you need to know the length of each side and sum them up. The formula is P = a + b + c + d + e, where a, b, c, d, and e represent the lengths of each side. This formula accounts for the variability in side lengths.
These distinct formulas reflect the inherent differences in the geometry of regular and irregular pentagons, making it essential to identify the type of pentagon before calculating its perimeter.

Perimeter of Regular Pentagon Calculation
Dive into the captivating world of calculations with this mind-blowing video that showcases the power and beauty of numbers. Learn helpful techniques, witness mind-boggling equations, and uncover the fascinating role calculations play in our everyday lives.
Visual Proof: Areas and Perimeters of Regular Polygons
Prepare to have your mind blown by the astonishing visual proof showcased in this captivating video. Watch as complex concepts are visually demonstrated, making it easier than ever to understand and appreciate the intricate beauty of mathematical and scientific phenomena.
Step-by-Step Calculation of Regular Pentagon Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a regular pentagon is a straightforward process. Follow these steps to ensure accuracy:
- Determine Side Length: Identify the length of one side of the pentagon. In a regular pentagon, all sides are of equal length.
- Apply the Perimeter Formula: Use the formula for the perimeter of a regular pentagon, which is P = 5s. Here, P represents the perimeter and s the length of a side.
- Perform the Calculation: Multiply the length of one side by 5. For instance, if the side length is 4 cm, the calculation would be P = 5 × 4 = 20 cm.
- Verify Units: Ensure that the unit of your answer matches the unit of the side length. The perimeter is a linear measure.
- Finalize the Perimeter: The resulting product from step 3 is the perimeter of the regular pentagon. In our example, it\"s 20 cm.
By following these steps, one can easily calculate the perimeter of a regular pentagon, which is a fundamental concept in geometry.
Calculating Perimeter for an Irregular Pentagon
Calculating the perimeter of an irregular pentagon, where sides are not equal, involves a different approach compared to a regular pentagon. Follow these detailed steps:
- Measure Each Side: Begin by accurately measuring the length of each of the five sides of the pentagon. Label them as a, b, c, d, and e.
- Sum Up the Side Lengths: Add the lengths of all five sides. The formula to calculate the perimeter is P = a + b + c + d + e, where P is the perimeter.
- Perform the Addition: Carefully add the measurements. For instance, if the sides are 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 4.5 cm, and 6 cm, then the perimeter is 3 + 4 + 5 + 4.5 + 6 = 22.5 cm.
- Unit Consistency: Ensure that all measurements are in the same unit before adding. Convert if necessary.
- Check Your Work: Double-check your measurements and calculations for accuracy.
This method requires precise measurement of each side, as the irregularity of the pentagon means each side can vary in length, impacting the total perimeter.

Practical Examples of Pentagon Perimeter Calculation
Understanding the perimeter calculation of pentagons is further enhanced by exploring practical examples. Here are some scenarios illustrating how to apply the formulas for both regular and irregular pentagons.
Example 1: Regular Pentagon
Consider a regular pentagon with each side measuring 6 cm. To find the perimeter:
- Use the formula P = 5s, where s is the side length.
- Calculate: P = 5 × 6 = 30 cm.
- Thus, the perimeter is 30 cm.
Example 2: Irregular Pentagon
Suppose an irregular pentagon has side lengths of 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 4.5 cm, and 6 cm. To calculate its perimeter:
- Apply the formula P = a + b + c + d + e.
- Add the side lengths: P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 4.5 + 6 = 22.5 cm.
- The perimeter of the irregular pentagon is 22.5 cm.
These examples illustrate the direct application of perimeter formulas, reinforcing the concepts in a tangible way.

_HOOK_
Common Misconceptions and Corrections
When learning about the perimeter of a pentagon, certain misconceptions can arise. It\"s important to address and correct these to ensure a proper understanding of the concept.
- Misconception: All pentagons have equal sides and angles. Correction: This is only true for regular pentagons. Irregular pentagons have varying side lengths and angles.
- Misconception: The formula for the perimeter of a pentagon is complex. Correction: The perimeter formula is straightforward. For a regular pentagon, it\"s P = 5s, and for an irregular pentagon, it\"s the sum of all its sides.
- Misconception: The perimeter of a pentagon is the same as its area. Correction: Perimeter and area are different concepts. The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of the sides, while the area is the space enclosed within the pentagon.
- Misconception: A pentagon’s side lengths can be determined from its perimeter. Correction: For irregular pentagons, knowing the perimeter alone isn’t enough to determine individual side lengths without additional information.
- Misconception: Calculating the perimeter of a pentagon always requires complex mathematics. Correction: Basic arithmetic is sufficient for calculating the perimeter, though understanding the properties of pentagons is essential.
By clarifying these misconceptions, learners can more accurately grasp how to calculate and understand the perimeter of pentagons.

Importance of Apothem and Area in Pentagon Calculations
While the perimeter of a pentagon is a key measure, understanding the apothem and area is equally important for a comprehensive grasp of pentagonal properties.
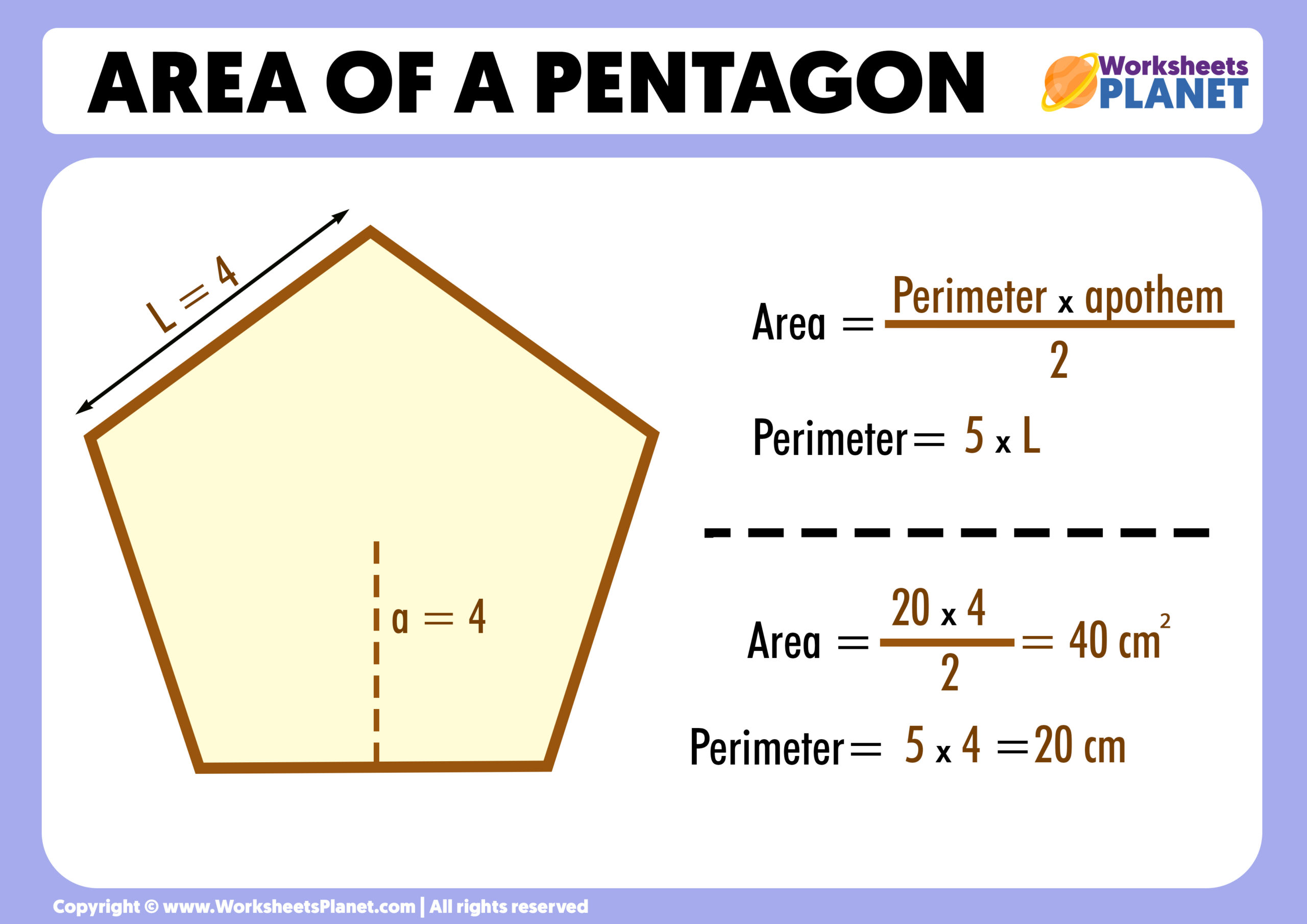
- Apothem: The apothem of a regular pentagon is a line from the center to the midpoint of one of its sides. It is crucial in calculating the area of the pentagon, especially when the side lengths are known. The apothem is used in formulas that relate the area, perimeter, and the interior angles of the pentagon.
- Area Calculation: The area of a pentagon can be calculated using the formula Area = (1/2) × Perimeter × Apothem. This emphasizes the interrelation between the perimeter and the apothem in understanding a pentagon’s geometry.
- Practical Applications: In real-world scenarios, like architectural design or crafting, both the perimeter and area of a pentagon-shaped object are crucial. The apothem can be a helpful measure in these applications.
- Relation to Pentagon\"s Properties: The apothem also relates to other properties of the pentagon, like its internal angles and symmetry, which are fundamental in advanced geometric studies and applications.
Overall, the apothem and area calculations complement the understanding of a pentagon\"s perimeter, offering a more complete picture of its geometric properties.

Comparative Analysis with Other Polygons
Understanding the perimeter formula of a pentagon is enhanced when compared with other polygons. This comparison highlights the unique properties of pentagons in the context of polygonal geometry.
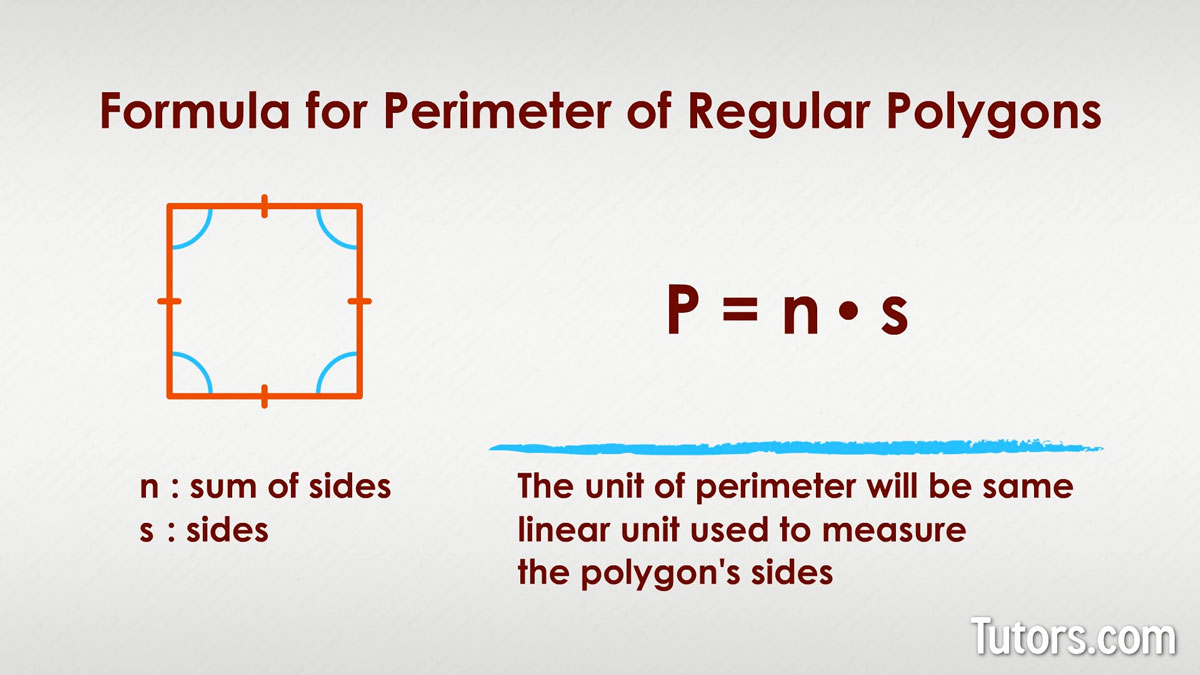
- Triangles: The simplest polygons, triangles have a perimeter formula of P = a + b + c, where a, b, and c are the sides. Unlike pentagons, the number of sides is fewer, making the formula simpler.
- Squares and Rectangles: These four-sided polygons have straightforward perimeter formulas (P = 4s for squares and P = 2(l + w) for rectangles). The regularity of squares and rectangles makes their perimeter calculation more straightforward than irregular pentagons.
- Hexagons: Regular hexagons have a perimeter formula of P = 6s. The calculation is similar to that of a regular pentagon but with an additional side, illustrating the direct relationship between side count and perimeter in regular polygons.
- Higher Order Polygons: As the number of sides increases (like in octagons, decagons, etc.), the perimeter formula remains a summation of all side lengths. However, the complexity increases with more sides, especially in irregular shapes.
Comparing pentagons with other polygons reveals the diversity and complexity of polygonal shapes and their perimeter calculations.
Interactive Tools and Calculators for Pentagon Perimeter
Various interactive tools and calculators are available online to simplify the process of calculating the perimeter of a pentagon. These tools are especially useful for students and professionals in fields like geometry and design.
- Online Pentagon Calculators: These calculators allow users to input the side length of a regular pentagon or the lengths of each side for an irregular pentagon to quickly compute the perimeter. Some also offer visual representations of the pentagon.
- Geometry Software: Advanced geometry software programs provide tools for drawing and measuring polygons, including pentagons. They can automatically calculate perimeters and other properties like area and angles.
- Mobile Apps: There are mobile applications available for smartphones and tablets that include pentagon perimeter calculators, making it convenient to perform calculations on the go.
- Educational Websites: Educational platforms often feature interactive tools that not only calculate perimeters but also provide step-by-step tutorials on how these calculations are derived.
- Interactive Learning Modules: Some websites offer interactive modules or games that involve calculating the perimeter of pentagons, aiding in a more engaging learning experience.
These digital tools and resources make the calculation of pentagon perimeters more accessible and understandable, especially for educational purposes.
Additional Resources and Learning Materials
To deepen your understanding of the perimeter formula of a pentagon and related geometric concepts, there are numerous resources and materials available. Here are some valuable sources for further exploration and learning:
- Geometry Textbooks: Traditional textbooks offer comprehensive insights into geometric principles, including detailed sections on polygons like pentagons.
- Educational Videos: Platforms like YouTube have a wealth of instructional videos, where educators explain the perimeter of pentagons and demonstrate problems.
- Online Tutorials and Courses: Websites like Khan Academy and Coursera offer courses and tutorials on geometry, providing interactive lessons on polygons, including pentagons.
- Math Blogs and Websites: Many educational blogs and websites offer articles, problem sets, and quizzes focused on pentagon properties and calculations.
- Math Forums: Online forums and communities such as Stack Exchange are great places to ask questions and share knowledge about geometry, including pentagon calculations.
- Interactive Geometry Apps: Apps like GeoGebra offer interactive tools to visualize and calculate properties of various geometric shapes, including pentagons.
These resources cater to a range of learning styles and can greatly aid in comprehending and applying the concepts of pentagon geometry.
Mastering the perimeter formula of a pentagon unlocks a deeper appreciation of geometry\"s elegance and practicality. Embrace this knowledge, and let it enhance your mathematical journey and real-world applications.
_HOOK_
