Topic perimeter formula pentagon: Discover the intriguing world of geometry with our deep dive into the "Perimeter Formula Pentagon", a fundamental concept that bridges mathematical theory and real-world applications, making geometry accessible and engaging for all.
Table of Content
- Overview of Pentagon and Its Perimeters
- YOUTUBE: Perimeter of Pentagon Formula and Examples for Regular and Irregular Pentagons
- Formula for Calculating Perimeter of a Regular Pentagon
- Method for Determining Perimeter of an Irregular Pentagon
- Practical Examples of Perimeter Calculation
- Additional Geometric Concepts Related to Pentagons
- Interactive Tools and Calculators for Pentagon Perimeters
- Frequently Asked Questions About Pentagon Perimeters
- Advanced Concepts and Further Learning Resources
Overview of Pentagon and Its Perimeters
The pentagon is a unique geometric shape, consisting of five straight sides. Understanding its perimeter involves different approaches based on the type of pentagon - regular or irregular.
Regular Pentagons
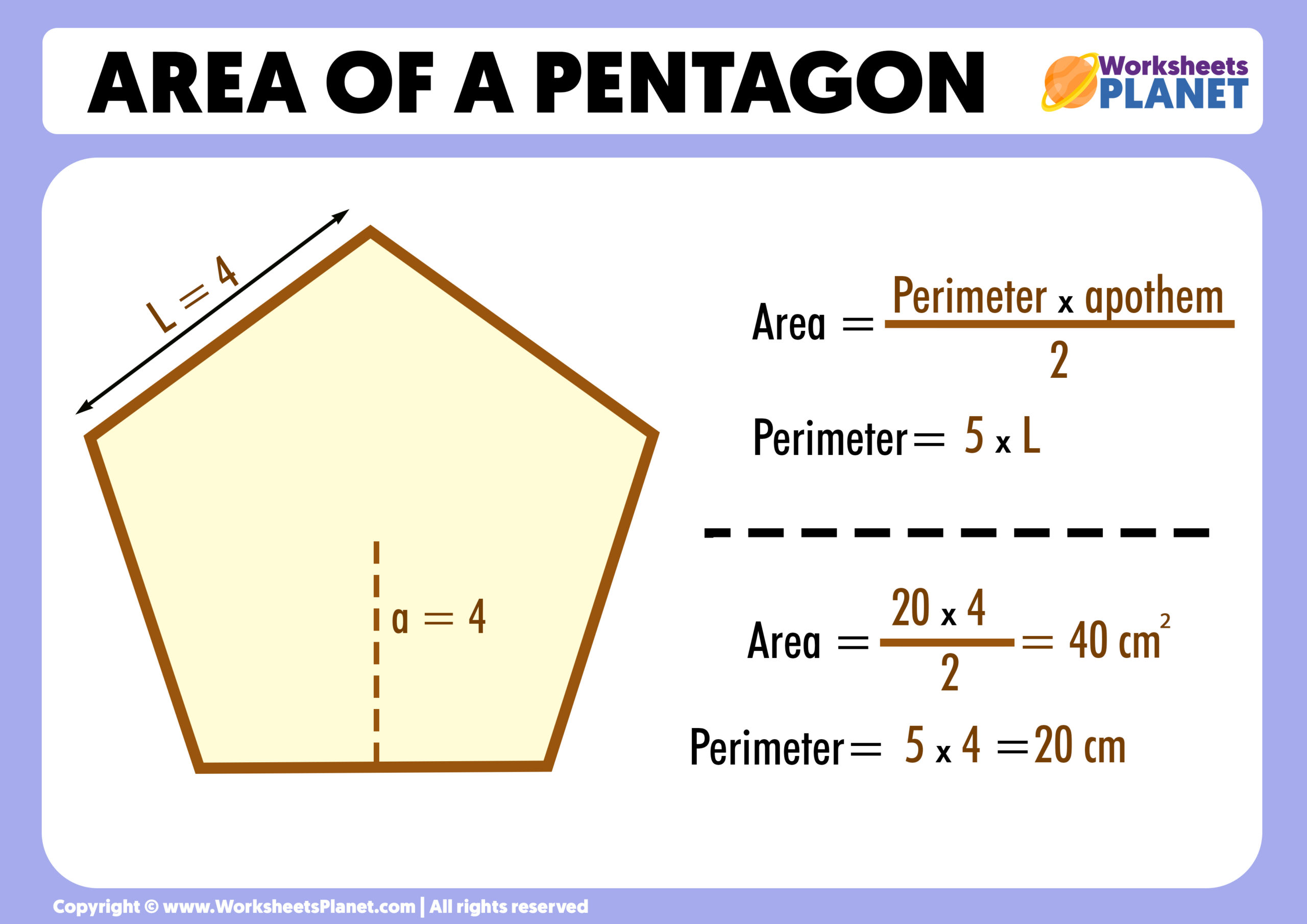
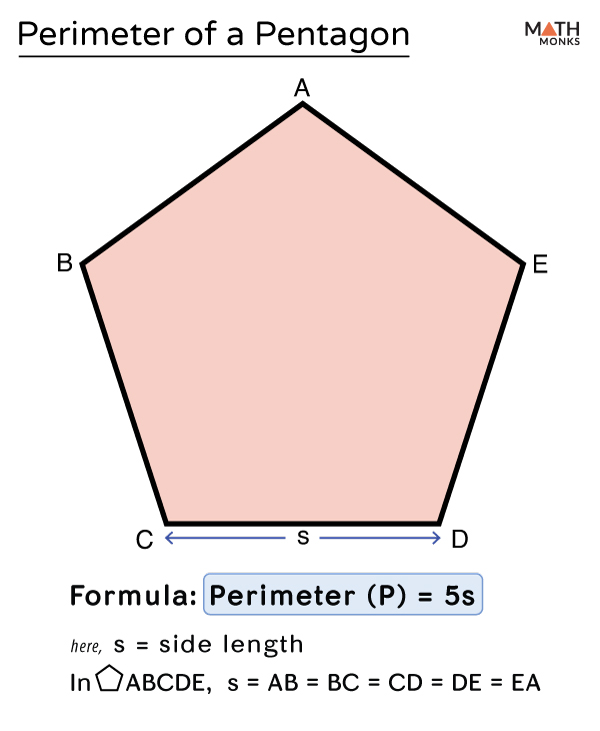
Regular pentagons have equal sides and angles, making their perimeter calculation straightforward. The formula for the perimeter of a regular pentagon, represented as P, is P = 5 × s, where \"s\" is the length of one side. This formula simplifies the process as it multiplies the side length by 5, the number of sides in a pentagon.
Irregular Pentagons
In contrast, irregular pentagons have sides and angles of different lengths and measures. To find their perimeter, one needs to measure and sum up the lengths of all five sides individually.
Examples and Applications
For example, if a regular pentagon has a side length of 3 cm, its perimeter is calculated as 5 × 3 cm, equating to 15 cm. In the case of an irregular pentagon with side lengths of 3, 7, 8, 9, and 6 units, its perimeter would be the total sum of these lengths, resulting in 33 units.
Calculating Perimeters with Radius or Apothem
The perimeter can also be calculated using other pentagon dimensions like the radius or apothem. The radius, or circumradius, is the line from the pentagon’s center to a vertex. The apothem is a line from the center to a side, perpendicular to that side. Formulas involving these dimensions help in calculating the side length, which can then be used to find the perimeter for regular pentagons.
Further Insights
Understanding the perimeter of a pentagon opens doors to broader geometric concepts and applications, making it a vital topic in geometry education and practical applications.

READ MORE:
Perimeter of Pentagon Formula and Examples for Regular and Irregular Pentagons
\"Unlock the secrets of success with this mind-blowing Formula! Discover the winning strategy that will revolutionize your life and help you achieve your goals faster than ever before. Get ready to unleash your full potential and watch your dreams come true!\"
Perimeter of Regular Pentagon Formula
\"Looking for a way to make positive changes a Regular part of your life? Look no further! This incredible video will guide you on a journey towards personal growth, offering practical tips to effortlessly incorporate powerful habits into your daily routine. Start living your best life now!\"
Formula for Calculating Perimeter of a Regular Pentagon
The formula to calculate the perimeter of a regular pentagon, denoted as P, is straightforward and efficient. A regular pentagon is characterized by having all sides of equal length and equal angles. To find the perimeter, you simply multiply the length of one side by the total number of sides, which is five in the case of a pentagon.
The formula is expressed as:
P = 5 × s
Here, P represents the perimeter, and s is the length of one side of the pentagon.
For example, if a regular pentagon has a side length of 10 units, its perimeter would be calculated as 5 × 10, resulting in a perimeter of 50 units.
This formula is applicable only to regular pentagons, where each side is of equal length. In contrast, calculating the perimeter of an irregular pentagon, where sides are of varying lengths, requires adding the length of each individual side.
Understanding this formula is crucial for students and professionals in fields that involve geometric calculations. It\"s a fundamental concept in geometry that lays the groundwork for more advanced studies and practical applications in various disciplines.
For further exploration and practice, many educational resources offer a range of examples and problems to solidify understanding of this concept.

Method for Determining Perimeter of an Irregular Pentagon
Calculating the perimeter of an irregular pentagon, which has sides of different lengths, requires a different approach than that used for regular pentagons. The method involves adding up the lengths of all the sides of the pentagon. This process is straightforward yet requires accurate measurement of each side.
The formula for the perimeter of an irregular pentagon is given by:
P = a + b + c + d + e
Here, P represents the perimeter, and a, b, c, d, e are the lengths of the individual sides of the pentagon.
For example, if an irregular pentagon has side lengths of 3 units, 7 units, 8 units, 9 units, and 6 units, then the perimeter would be calculated by adding these lengths:
Perimeter = 3 + 7 + 8 + 9 + 6 = 33 units
This formula is applicable to any irregular pentagon, regardless of the variability in its side lengths. It is a crucial aspect of understanding geometry as it applies to more complex shapes and real-world scenarios, where perfect regularity is less common.
Furthermore, in real-life applications, such as when measuring for fencing or decoration, understanding how to calculate the perimeter of irregular shapes is essential. It helps in determining the exact amount of material needed for such projects.
Thus, mastering the perimeter calculation of irregular pentagons forms an important part of geometric learning and practical applications.
Practical Examples of Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of a pentagon, whether regular or irregular, is a straightforward process. The perimeter is the total distance around the pentagon\"s boundary. In this section, we will explore various examples to understand how to calculate the perimeter in different scenarios.
Example 1: Regular Pentagon with Known Side Length
Consider a regular pentagon where each side is of equal length. For instance, if the length of each side is 3 units, the perimeter is calculated using the formula P = 5s, where s is the side length. Therefore, P = 5 * 3 = 15 units. The perimeter of this pentagon is 15 units.
Example 2: Irregular Pentagon with Different Side Lengths
For an irregular pentagon, where sides are of different lengths, add each side\"s length to find the perimeter. For example, if the sides are 3, 7, 8, 9, and 6 units long, the perimeter is the sum of these lengths: 3 + 7 + 8 + 9 + 6 = 33 units. Thus, the perimeter is 33 units.
Example 3: Regular Pentagon with Given Radius
When a regular pentagon is inscribed in a circle (circumradius), the perimeter can also be determined. If the radius (r) is known, first calculate the side length using the formula: Side length = 2r × Sin(180/n). For a pentagon (n=5) with a radius of 5 units, the side length is calculated as: 10 × Sin(36) ≈ 5.8 units. Hence, the perimeter P = 5 × 5.8 = 29 units.
Additional Considerations
- The formula for a regular pentagon relies on all sides being of equal length, making the calculation simpler.
- For irregular pentagons, precise measurement of each side is essential for accurate perimeter calculation.
- Understanding the relationship between the radius and the side length in a regular pentagon inscribed in a circle is crucial for perimeter calculations in such cases.
These examples illustrate the versatility and simplicity of calculating the perimeter of a pentagon, whether regular or irregular. By understanding these concepts, one can easily tackle various geometric problems related to pentagons.

Additional Geometric Concepts Related to Pentagons
Pentagons, being five-sided polygons, encompass a range of geometric concepts beyond just their perimeter. Understanding these concepts provides a deeper insight into the nature and applications of pentagons in various fields.
Types of Pentagons
- Regular Pentagon: Characterized by equal sides and angles, with each internal angle measuring 108 degrees.
- Irregular Pentagon: Has sides and angles of varying lengths and measurements.
- Convex Pentagon: All internal angles are less than 180 degrees, and sides do not intersect.
- Concave Pentagon: Has at least one internal angle greater than 180 degrees, and some sides may intersect.
Geometric Properties
A regular pentagon displays unique properties such as five lines of symmetry and a rotational symmetry of order 5. Its diagonals intersect in the golden ratio to its sides, showcasing a fascinating aspect of geometric harmony.
Construction Techniques
Pentagons can be constructed using various methods, such as using a compass and straightedge or through geometric principles like the Pythagorean theorem.
Area Calculation
The area of a regular pentagon can be calculated using formulas involving the side length or apothem, showcasing the relationship between different geometric elements of the shape.
Historical Significance
The term “pentagon” has its origins in Euclid\"s Elements, written around 300 BC. Since then, pentagons have been integral to various architectural and design elements, including the iconic Pentagon building in the United States.
Practical Applications
Pentagons are not just theoretical geometric figures but have practical applications in areas like architecture, design, and nature, where their unique shape and properties are utilized.
By delving into these additional geometric concepts related to pentagons, we gain a more comprehensive understanding of this fascinating five-sided polygon.

_HOOK_
Interactive Tools and Calculators for Pentagon Perimeters
There are various online tools and calculators available that can assist in calculating the perimeter of a pentagon. These tools often provide step-by-step solutions and allow for input of different parameters to suit specific needs.
Using an Online Pentagon Perimeter Calculator
Online calculators, like those found on Kyle\"s Converter, Omni Calculator, and Calculator.tech, provide a simple interface where you input the side length of a pentagon, and the tool calculates the perimeter for you. The formula used in these calculators is typically P = 5 * a, where P is the perimeter and a is the length of one side of the pentagon.
Features of Online Calculators
- User-friendly Interface: Easy to navigate and input data.
- Flexibility: Some calculators, like the one on Calculators.tech, offer the ability to calculate other properties like the area, diagonal, and height of a pentagon.
- Customization: Options to choose units of measurement and decimal precision, as seen in Spike\"s Calculators.
- Visual Aids: Certain calculators provide images or diagrams to help visualize the pentagon and its dimensions.
Examples and Step-by-Step Calculations
These calculators often include examples and a step-by-step guide on how to perform the calculations manually. This can be particularly helpful for educational purposes or for those looking to understand the underlying mathematics.
Considerations When Using Online Calculators
While these tools are quite accurate for regular pentagons, they may not be suitable for irregular pentagons where sides and angles vary. It\"s also important to ensure the accuracy of input data to get reliable results.
In summary, online tools and calculators for calculating the perimeter of a pentagon provide a convenient, accurate, and educational way to understand and compute this geometric measurement.

Frequently Asked Questions About Pentagon Perimeters
When it comes to understanding the perimeter of a pentagon, several common questions often arise. This section aims to address these frequently asked questions in a clear and concise manner.
What is the Perimeter of a Pentagon?
The perimeter of a pentagon is the total distance around its five sides. For a regular pentagon, the perimeter can be calculated using the formula P = 5s, where P is the perimeter and s is the side length. For irregular pentagons, the perimeter is the sum of all its side lengths.
How Do You Calculate the Perimeter of a Regular Pentagon?
To calculate the perimeter of a regular pentagon, multiply the length of one side by 5. If each side is of length \"a\", then the perimeter P = 5a.
Can the Perimeter of an Irregular Pentagon be Calculated in the Same Way as a Regular Pentagon?
No, for an irregular pentagon, where sides are not equal, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. You need to measure each side and add them together to get the perimeter.
What is the Formula for the Perimeter of an Irregular Pentagon?
For an irregular pentagon, the formula for the perimeter is P = a + b + c + d + e, where a, b, c, d, and e are the lengths of the five sides.
Is the Perimeter of a Pentagon Always Five Times the Length of One Side?
This is only true for a regular pentagon. In a regular pentagon, all sides are equal, so the perimeter is indeed five times the length of one side. However, this is not the case for an irregular pentagon.
How Does the Perimeter of a Pentagon Compare to Its Area?
The perimeter and area of a pentagon are different properties. The perimeter is the total distance around the pentagon, while the area is the amount of space enclosed within it. They are calculated using different formulas.
These questions cover the basics of calculating and understanding the perimeter of both regular and irregular pentagons.

READ MORE:
Advanced Concepts and Further Learning Resources
The study of pentagons in geometry extends beyond basic perimeter calculations. Advanced concepts delve into various properties, mathematical relationships, and the application of these shapes in different fields. This section aims to explore some of these complex ideas and guide towards additional resources for further learning.
Advanced Geometric Properties of a Pentagon
- Interior Angles: In a regular pentagon, each interior angle measures 108 degrees.
- Symmetry: Regular pentagons exhibit five lines of reflectional symmetry and rotational symmetry of order 5.
- Golden Ratio: The diagonals of a regular pentagon have a unique relationship with its sides, often linked to the golden ratio.
- Construction Techniques: Regular pentagons can be constructed using compass and straightedge, involving intricate geometric steps.
Further Learning Resources
For those interested in exploring these concepts in more depth, the following resources are invaluable:
- Cuemath: Offers visual explanations and practice questions on pentagon shapes, helping break down complex concepts.
- Wikipedia: Provides detailed information on the mathematical properties of regular pentagons, including formulas for height, width, and circumradius.
- Art of Problem Solving: An excellent resource for learning how to construct a pentagon and understanding its properties through problem-solving.
- Calcresource: Offers insights into the geometric properties of pentagons, such as bounding box dimensions and analytical expressions.
These resources are ideal for students, educators, or anyone interested in advancing their understanding of pentagon geometry.
Embark on a journey through the intriguing world of pentagon geometry, where the simple perimeter formula unravels a universe of mathematical beauty and complexity. Explore this fascinating topic and discover the elegance hidden in every angle and line.