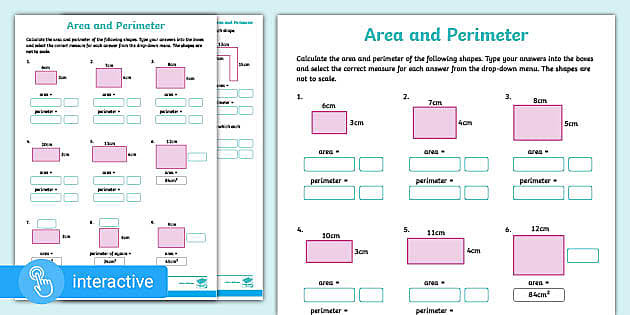
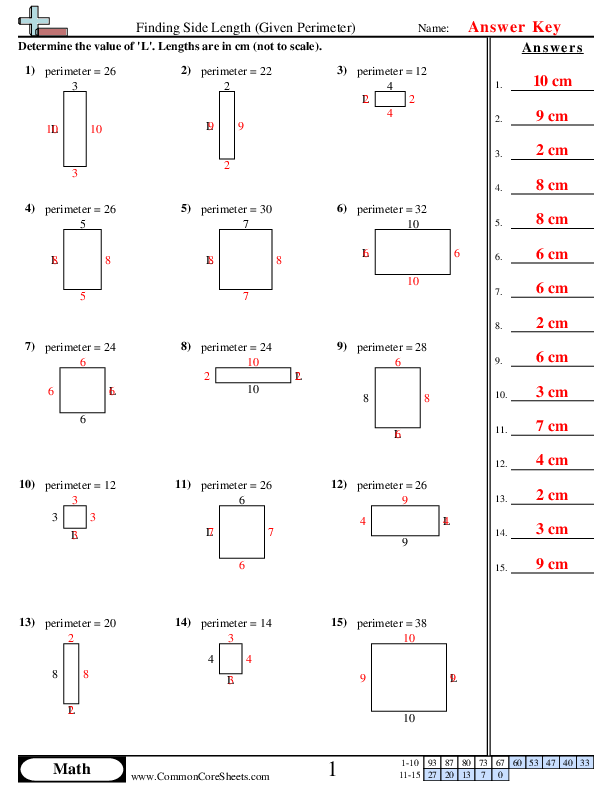
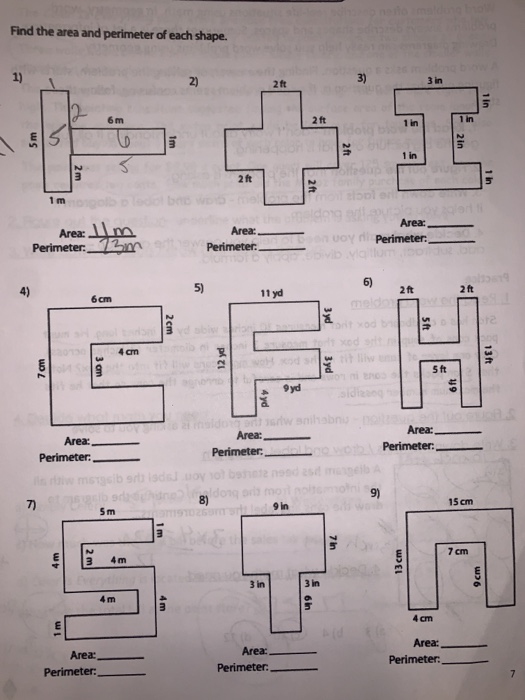
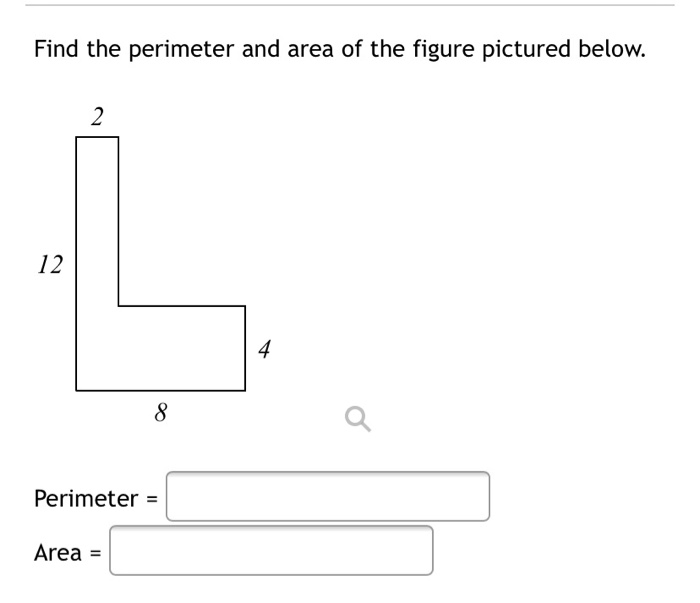
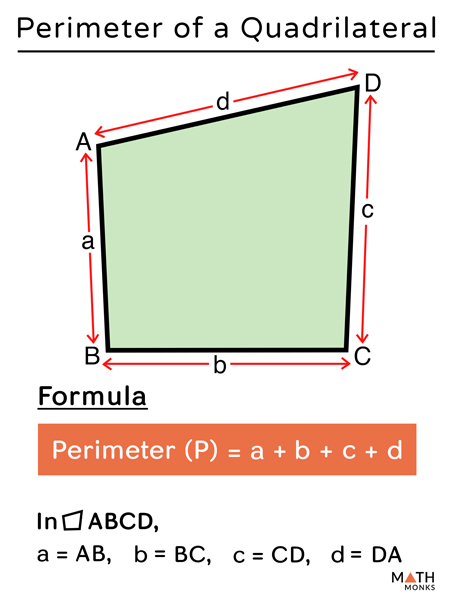
Topic write two expressions for the perimeter of the figure: Explore how to effectively write two expressions for the perimeter of any figure in this practical guide. Whether you're dealing with rectangles, triangles, or more complex shapes, we provide clear methods and examples to enhance your understanding. Ideal for students and educators looking to deepen their geometry skills.
Table of Content
- Expressions for the Perimeter of a Figure
- Understanding Perimeter in Geometry
- Writing Expressions for the Perimeter
- Perimeter of Basic Geometric Figures
- Advanced Perimeter Calculations
- Practical Examples and Exercises
- Conclusion and Further Reading
- YOUTUBE: Xem video này để hiểu cách biểu diễn chu vi của các hình học cơ bản và phức tạp.
Expressions for the Perimeter of a Figure
To find the perimeter of a geometric figure, we can write expressions depending on the shape and dimensions of the figure. Below are examples for two common figures: a rectangle and a triangle.
1. Rectangle
A rectangle has two pairs of equal sides. Let the length be \( l \) and the width be \( w \). The perimeter \( P \) can be expressed as:
\( P = 2l + 2w \) \( P = 2(l + w) \)
2. Triangle
A triangle has three sides, typically denoted as \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \). The perimeter \( P \) can be expressed as:
\( P = a + b + c \) - If it's an equilateral triangle, \( P \) can also be expressed as \( P = 3a \) where all sides are equal \( (a = b = c) \).
Examples
| Figure | Dimensions | Perimeter Expressions |
| Rectangle | Length \( l = 5 \), Width \( w = 3 \) |
|
| Triangle | Sides \( a = 3 \), \( b = 4 \), \( c = 5 \) |
|
| Equilateral Triangle | Side \( a = 4 \) |
|

READ MORE:
Understanding Perimeter in Geometry
Perimeter is the total length of the boundary of a geometric figure. It is essentially the sum of the lengths of all the sides of the figure.
When dealing with different geometric figures, the method to calculate perimeter may vary. Let's explore how to write expressions for the perimeter of various figures:
- Perimeter of a Rectangle: For a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \), the perimeter \( P \) can be expressed as: \( P = 2l + 2w \).
- Perimeter of a Triangle: In a triangle with side lengths \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \), the perimeter \( P \) is given by: \( P = a + b + c \).
- Perimeter of a Square: For a square with side length \( s \), the perimeter \( P \) can be written as: \( P = 4s \).
- Perimeter of a Circle (Circumference): When dealing with a circle with radius \( r \), the circumference \( C \) (which is analogous to perimeter) is calculated using the formula: \( C = 2\pi r \).
These expressions provide a systematic way to find the perimeter of common geometric figures. Understanding how to derive and apply these formulas is essential for solving problems in geometry.
Writing Expressions for the Perimeter
When writing expressions for the perimeter of geometric figures, it's essential to understand the properties of each figure and how its perimeter is calculated. Here are two common examples:
- Perimeter of a Rectangle: Given a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \), the perimeter \( P \) can be expressed as: \( P = 2l + 2w \). This expression accounts for the fact that a rectangle has two pairs of equal-length sides.
- Perimeter of a Circle (Circumference): For a circle with radius \( r \), the perimeter, or circumference \( C \), is given by the formula: \( C = 2\pi r \). This expression relates the circle's perimeter to its radius, utilizing the constant \( \pi \) to account for the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter.
These expressions demonstrate the versatility of writing perimeter formulas for different geometric figures, providing a foundation for further exploration and problem-solving in geometry.
Perimeter of Basic Geometric Figures
Understanding the perimeter of basic geometric figures is fundamental in geometry. Let's explore two expressions commonly used to calculate the perimeter of such figures:
- Perimeter of a Square: A square has all four sides of equal length. Given the length of one side \( s \), the perimeter \( P \) can be expressed as: \( P = 4s \). This formula simply multiplies the length of one side by 4, as all sides are equal.
- Perimeter of a Triangle: Triangles come in various types, but the perimeter \( P \) is calculated by adding the lengths of all three sides. For a triangle with side lengths \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \), the perimeter can be expressed as: \( P = a + b + c \).
These expressions illustrate the straightforward methods used to find the perimeters of basic geometric figures, providing a solid foundation for more complex geometric concepts.
Advanced Perimeter Calculations
Advanced perimeter calculations involve more complex geometric figures and scenarios. Here are two expressions commonly used for such calculations:
- Perimeter of Polygons: Polygons are closed shapes with straight sides. To find the perimeter \( P \) of a polygon, add the lengths of all its sides. For example, in a pentagon with side lengths \( a_1, a_2, a_3, a_4, \) and \( a_5 \), the perimeter can be expressed as: \( P = a_1 + a_2 + a_3 + a_4 + a_5 \).
- Perimeter of Composite Figures: Composite figures are made up of two or more simpler shapes. To find the perimeter \( P \) of a composite figure, add the perimeters of all its component shapes. For instance, if a composite figure consists of a rectangle and a semicircle, with respective perimeters \( P_1 \) and \( P_2 \), then the total perimeter \( P \) can be expressed as: \( P = P_1 + P_2 \).
These expressions showcase the versatility of perimeter calculations, extending beyond basic geometric figures to encompass more intricate shapes and arrangements.
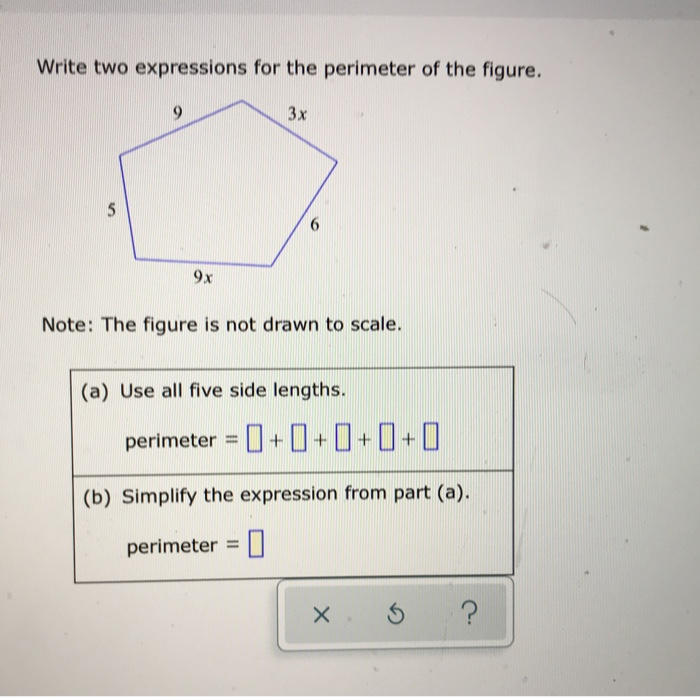
Practical Examples and Exercises
Engaging in practical examples and exercises is a great way to solidify understanding of perimeter concepts. Let's delve into two exercises:
- Real-World Applications of Perimeter: Consider a rectangular garden with length \( 10 \) meters and width \( 5 \) meters. Calculate the perimeter of the garden using the formula \( P = 2l + 2w \).
- Practice Problems and Solutions: Given a triangular plot of land with side lengths \( 6 \) meters, \( 8 \) meters, and \( 10 \) meters, calculate its perimeter using the formula \( P = a + b + c \).
These exercises provide hands-on experience in applying perimeter formulas to real-world scenarios and mathematical problems, reinforcing learning and promoting mastery.
Conclusion and Further Reading
In conclusion, understanding perimeter in geometry is crucial for solving various mathematical problems and real-world scenarios. By mastering the concepts and formulas discussed in this guide, you can confidently calculate the perimeter of different geometric figures.
For further exploration into geometry and perimeter calculations, consider the following resources:
- Textbooks on geometry and mathematical problem-solving
- Online tutorials and videos covering advanced perimeter concepts
- Interactive geometry tools and applications for hands-on learning
Continued practice and exploration will enhance your proficiency in perimeter calculations and deepen your understanding of geometry as a whole.
Xem video này để hiểu cách biểu diễn chu vi của các hình học cơ bản và phức tạp.
Biểu diễn Chu vi
READ MORE:
Xem video này để học cách viết biểu thức đại số cho chu vi của các hình học cơ bản và phức tạp.
Viết biểu thức đại số cho chu vi của một hình học