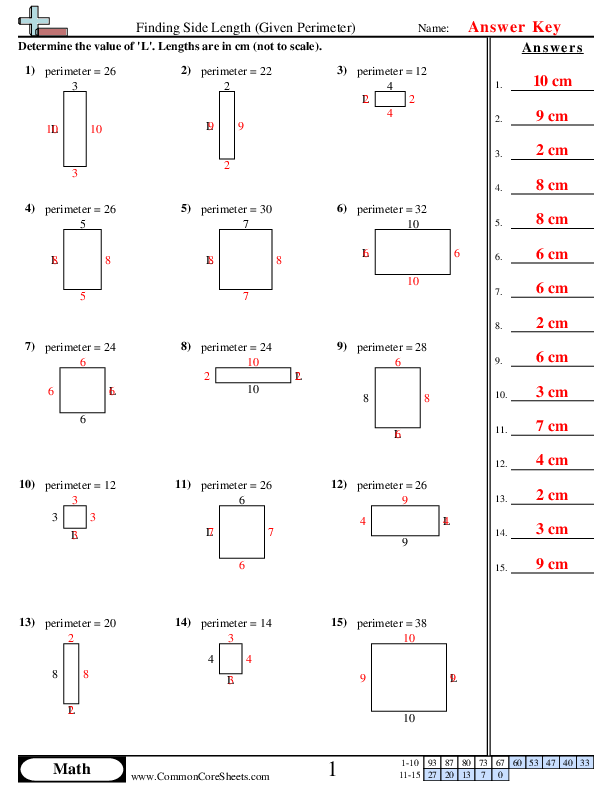
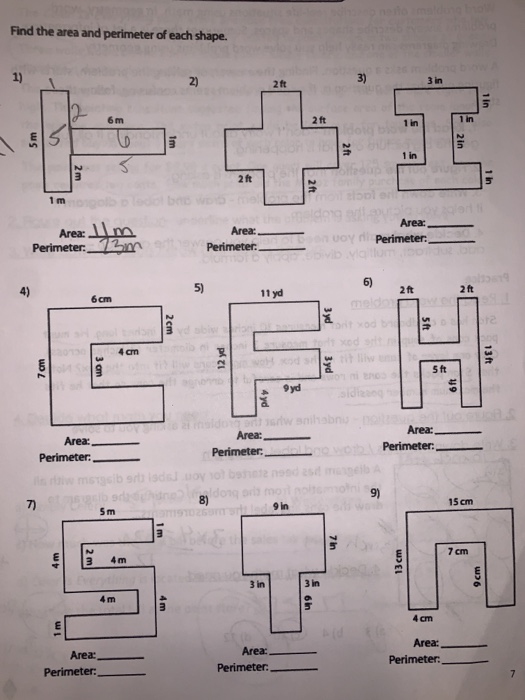
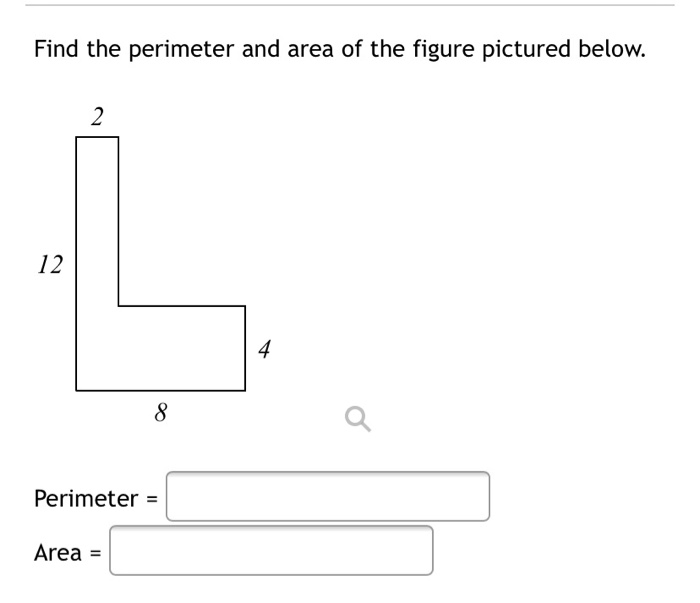
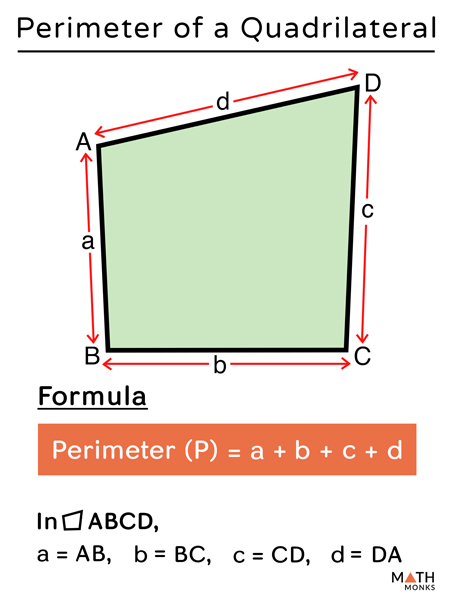
Topic area and perimeter word problems worksheets pdf: Explore a variety of area and perimeter word problems worksheets in PDF format. These resources are perfect for students and teachers looking to enhance their understanding of mathematical concepts through practical exercises. Our guide covers everything from basic definitions to advanced problems, complete with visual aids and answer keys.
Table of Content
Area and Perimeter Word Problems Worksheets PDF
Explore a variety of worksheets designed to help students master the concepts of area and perimeter through word problems. These resources are available in PDF format for easy download and printing.
Understanding Area and Perimeter
Before diving into the worksheets, it's important to have a clear understanding of what area and perimeter are:
- Area: The amount of space inside a two-dimensional shape, measured in square units.
- Perimeter: The distance around the outside of a shape, measured in linear units.
Example Word Problems
Here are some example word problems that can be found in the worksheets:
- Rectangular Garden: A garden is 10 meters long and 5 meters wide. What is the area and perimeter of the garden?
- Classroom Carpet: A classroom carpet is 8 feet long and 6 feet wide. Calculate the area and perimeter.
- Square Tile: A square tile has a side length of 4 inches. What is the area and perimeter of the tile?
Worksheet Features
The worksheets typically include:
- Word problems of varying difficulty levels.
- Detailed solutions and explanations.
- Visual aids such as diagrams and grids.
Download Worksheets
Click the links below to download the worksheets in PDF format:
Mathjax Code Example
Here is an example of how Mathjax can be used to display mathematical formulas:
\[
\text{Area of a rectangle} = \text{length} \times \text{width}
\]
\[
\text{Perimeter of a rectangle} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width})
\]
Conclusion
Practicing area and perimeter word problems helps students apply their mathematical knowledge to real-world scenarios. These worksheets are an excellent resource for reinforcing these concepts.

READ MORE:
Introduction
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is fundamental in geometry, and word problems are an effective way to apply these concepts to real-world situations. This collection of worksheets in PDF format offers a variety of problems that challenge students to calculate the area and perimeter of different shapes, enhancing their problem-solving skills and mathematical thinking. These resources are designed for different grade levels and include both simple and complex problems to cater to diverse learning needs.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Area and Perimeter
- Types of Word Problems
- Simple Shapes
- Composite Shapes
- Real-World Applications
- Step-by-Step Problem Solving Strategies
- Identifying Key Information
- Formulating Equations
- Solving for Area and Perimeter
- Examples of Area and Perimeter Word Problems
- Basic Problems
- Intermediate Problems
- Advanced Problems
- Interactive Worksheets and Activities
- Conclusion
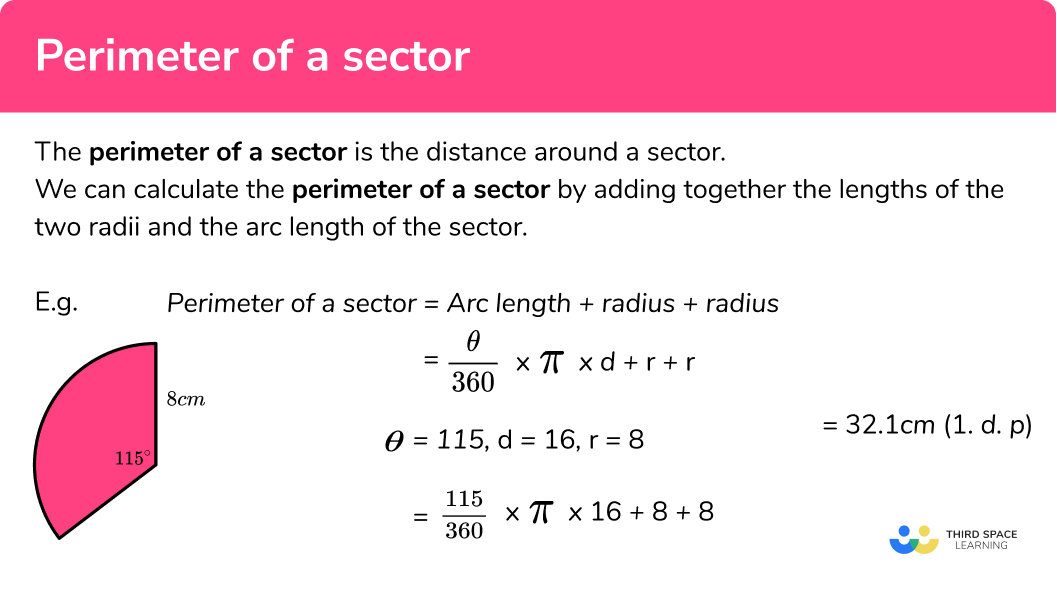
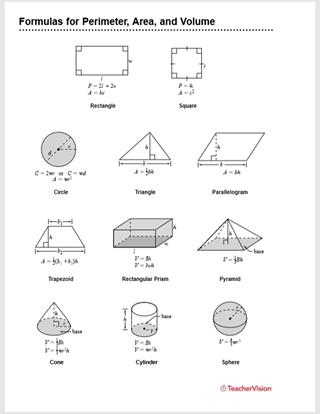
Types of Shapes and Formulas
Understanding the different types of shapes and their respective formulas is essential for solving area and perimeter word problems. This section covers the most common geometric shapes and the formulas used to calculate their area and perimeter.
- Rectangle
- Area: \( A = l \times w \) where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Perimeter: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
- Square
- Area: \( A = s^2 \) where \( s \) is the length of a side.
- Perimeter: \( P = 4s \)
- Triangle
- Area: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \) where \( b \) is the base and \( h \) is the height.
- Perimeter: \( P = a + b + c \) where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle
- Area: \( A = \pi r^2 \) where \( r \) is the radius.
- Circumference: \( C = 2\pi r \)
- Parallelogram
- Area: \( A = b \times h \) where \( b \) is the base and \( h \) is the height.
- Perimeter: \( P = 2a + 2b \) where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Trapezoid
- Area: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times (b_1 + b_2) \times h \) where \( b_1 \) and \( b_2 \) are the lengths of the parallel sides and \( h \) is the height.
- Perimeter: \( P = a + b_1 + b_2 + c \) where \( a \), \( b_1 \), \( b_2 \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
Word Problems by Difficulty Level
Word problems involving area and perimeter can vary in complexity, making them suitable for different learning levels. Here is a breakdown of problems by difficulty level to help educators and learners select the appropriate challenges.
- Beginner Level:
- Simple rectangles and squares with whole number dimensions.
- Problems involving only one shape at a time.
- Direct application of area and perimeter formulas.
- Intermediate Level:
- Composite shapes formed by combining basic shapes.
- Word problems requiring the use of both area and perimeter formulas.
- Incorporating real-world scenarios to apply the concepts.
- Advanced Level:
- Problems involving irregular shapes and polygons.
- Use of algebra to solve for unknown dimensions given area or perimeter.
- Application of area and perimeter concepts in complex, multi-step problems.
These levels ensure a progressive learning curve, making it easier for students to grasp the fundamentals before tackling more challenging problems.

Visual Aids and Diagrams
To enhance understanding of area and perimeter word problems, incorporating visual aids and diagrams is highly effective. These tools can simplify complex concepts and make learning more engaging for students. Here are some practical visual aids and diagrams to consider:
-
Grids: Using grid paper can help students visualize the dimensions of shapes. For instance, plotting rectangles or other polygons on a grid can make it easier to calculate the area and perimeter by counting the units.

-
Diagrams of Geometric Shapes: Provide diagrams with labeled dimensions. For example, a rectangle labeled with its length and width helps students apply the formula \( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \) and \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \).

-
Step-by-Step Illustrations: Create step-by-step guides that show the process of calculating area and perimeter. For example, demonstrate how to divide a composite shape into simpler shapes, calculate their areas, and sum them up.
- Divide the composite shape into simpler shapes (e.g., rectangles and triangles).
- Calculate the area of each simple shape.
- Sum the areas of all simple shapes to find the total area.
-
Interactive Tools: Utilize online interactive tools that allow students to manipulate shapes and see the immediate impact on area and perimeter. These tools can provide a hands-on learning experience.

By integrating these visual aids and diagrams, students can gain a clearer and more intuitive understanding of area and perimeter, making it easier to tackle word problems effectively.
Answer Keys and Explanations
Providing clear and detailed answer keys with explanations is essential to help students understand their mistakes and learn the correct methods for solving area and perimeter word problems. Below are some examples of how to structure these explanations effectively:
Example Problem
Problem: A rectangular garden has a length of 15 meters and a width of 10 meters. Calculate the area and perimeter of the garden.
Solution:
- Step 1: Identify the length and width of the rectangle.
- Step 2: Use the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle: \( P = 2 \times (length + width) \).
- Step 3: Calculate the perimeter: \[ P = 2 \times (15 \, \text{m} + 10 \, \text{m}) = 2 \times 25 \, \text{m} = 50 \, \text{m} \]
- Step 4: Use the formula for the area of a rectangle: \( A = length \times width \).
- Step 5: Calculate the area: \[ A = 15 \, \text{m} \times 10 \, \text{m} = 150 \, \text{m}^2 \]
Answer: The perimeter is 50 meters and the area is 150 square meters.
Detailed Explanations
In addition to providing step-by-step solutions, it's helpful to explain why each step is necessary and how it helps in solving the problem. For instance, in the example above:
- The perimeter calculation is important for determining the total length of the boundary, which can be useful for tasks such as fencing the garden.
- The area calculation is crucial for understanding the total surface space, which can be useful for activities such as planting or laying sod.
Visual Diagrams
Including visual aids such as diagrams can enhance understanding. For example, drawing a rectangle and labeling the sides with the given measurements can help students visualize the problem better.
Additional Practice Problems
To reinforce learning, provide a variety of practice problems with varying levels of difficulty. Ensure each problem is accompanied by a detailed answer key that explains the solution process.
- Practice Problem 1: A square playground has a side length of 20 meters. Calculate the perimeter and area.
Answer: Perimeter = 80 meters, Area = 400 square meters. - Practice Problem 2: A circular flower bed has a radius of 7 meters. Calculate the perimeter (circumference) and area.
Answer: Circumference ≈ 44 meters, Area ≈ 154 square meters.
Real-World Applications
Illustrate how these calculations are used in real-world scenarios, such as construction, interior design, and landscaping. Providing context helps students see the relevance and importance of learning these concepts.
Practice Worksheets
Practice worksheets are essential tools to reinforce students' understanding of area and perimeter concepts. These worksheets are designed to cater to different learning levels, ensuring comprehensive practice and mastery of the topic.
- Individual Practice Worksheets:
- These worksheets focus on individual problem-solving skills, allowing students to work through various problems independently. They cover basic to advanced level problems, providing a step-by-step approach to solve each question.
- Example:
- Calculate the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 8 meters and a width of 5 meters.
- Find the area of a triangle with a base of 6 cm and a height of 4 cm.
- Group Activity Worksheets:
- Designed for collaborative learning, these worksheets encourage students to work in groups, discussing and solving area and perimeter problems together. This helps in developing teamwork and communication skills.
- Example:
- Determine the total perimeter of a composite shape formed by a rectangle and a semicircle.
- Calculate the combined area of a garden divided into a square and a triangular section.
- Timed Challenges:
- Timed worksheets are great for testing students' speed and accuracy. These challenges are designed to be completed within a specific time frame, helping students to think quickly and efficiently.
- Example:
- Solve 10 perimeter problems within 15 minutes.
- Find the area of 5 different shapes within 10 minutes.
These practice worksheets not only strengthen problem-solving skills but also help in applying theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios. Students are encouraged to complete these worksheets regularly to achieve proficiency in calculating area and perimeter.
Real-World Applications
Understanding area and perimeter is crucial in various real-world scenarios. Below are some detailed examples illustrating how these mathematical concepts are applied in everyday life and professional fields.
-
Architecture and Construction
Architects and construction workers use area and perimeter calculations to design buildings and structures. For instance, determining the amount of flooring needed for a room requires knowing its area, while installing baseboards or fencing around a property involves calculating the perimeter.
Example: To install a fence around a rectangular garden that measures 30 meters by 20 meters, calculate the perimeter as follows:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{Length} + \text{Width}) = 2 \times (30 \, \text{m} + 20 \, \text{m}) = 100 \, \text{m}
\] -
Interior Design
Interior designers must calculate the area to ensure they purchase the correct amount of materials, such as paint, wallpaper, or carpet. Knowing the perimeter is also important for measuring spaces for furniture placement and room layout planning.
Example: To buy enough paint for a wall that is 12 feet wide and 10 feet high, calculate the area:
\[
\text{Area} = \text{Width} \times \text{Height} = 12 \, \text{ft} \times 10 \, \text{ft} = 120 \, \text{ft}^2
\] -
Landscaping
Landscapers use area and perimeter calculations to design gardens and outdoor spaces. These measurements help in planning plant placement, soil requirements, and the layout of pathways and water features.
Example: To determine the amount of grass seed needed for a triangular lawn with a base of 15 meters and a height of 10 meters, calculate the area:
\[
\text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{Base} \times \text{Height} = \frac{1}{2} \times 15 \, \text{m} \times 10 \, \text{m} = 75 \, \text{m}^2
\] -
Urban Planning
Urban planners rely on area and perimeter measurements to design efficient and sustainable city layouts, including parks, roads, and residential areas. Accurate calculations ensure optimal use of space and resources.
Example: To design a rectangular park that requires a walking path around it, knowing the perimeter helps in planning the length of the path.
-
Retail and Manufacturing
Retailers and manufacturers often need to determine the area and perimeter of products for packaging and shipping purposes. These measurements ensure that products fit correctly in their packaging and that materials are used efficiently.
Example: To create a custom rectangular box that is 2 meters long, 1 meter wide, and 0.5 meters high, calculate the surface area to determine the amount of material needed:
\[
\text{Surface Area} = 2(\text{Length} \times \text{Width}) + 2(\text{Length} \times \text{Height}) + 2(\text{Width} \times \text{Height})
\]\[
\text{Surface Area} = 2(2 \, \text{m} \times 1 \, \text{m}) + 2(2 \, \text{m} \times 0.5 \, \text{m}) + 2(1 \, \text{m} \times 0.5 \, \text{m}) = 9 \, \text{m}^2
\]

Additional Resources
To further enhance your understanding and practice of area and perimeter word problems, a variety of additional resources are available. These resources include online interactive tools, recommended books and articles, as well as educational videos and tutorials.
- Online Interactive Tools
- : Interactive worksheets and tools to practice area and perimeter problems, providing hints and step-by-step solutions.
- : A collection of printable worksheets for various levels of difficulty, including real-life scenario problems.
- : Customizable worksheets focused on specific skills, with options for different versions and difficulty levels.
- Recommended Books and Articles
- "Mathematics for Elementary Teachers" by Sybilla Beckmann: This book provides a comprehensive approach to understanding fundamental math concepts, including area and perimeter.
- "Teaching Mathematics in Elementary and Middle School" by Joseph G. R. Martinez: An insightful resource for teachers, offering strategies and problem sets related to area and perimeter.
- Articles from educational websites like and that explore effective teaching methods and practical applications of area and perimeter concepts.
- Educational Videos and Tutorials
- : Videos covering the basics and advanced concepts of area and perimeter, complete with practice exercises.
- : YouTube channel offering engaging and easy-to-understand tutorials on various math topics, including area and perimeter.
- : High-quality video tutorials that break down complex problems into simple, step-by-step solutions.
Utilizing these additional resources will help reinforce your understanding of area and perimeter, providing a well-rounded approach to mastering these essential math concepts.
Download Links
Here you can download a variety of worksheets to practice and enhance your understanding of area and perimeter. Each worksheet is available in PDF format and covers different difficulty levels and problem types.
These worksheets are designed to help students at various levels of proficiency. Each worksheet includes detailed instructions and problems focused on calculating the area and perimeter of different geometric shapes. Additionally, some worksheets incorporate real-world applications to enhance practical understanding.
These resources offer a variety of problems that help students practice and apply mathematical concepts in different contexts. By using these worksheets, students can build a strong foundation in understanding and solving area and perimeter problems.
Toán học - Lớp 5: Chu vi - Giải phương trình tìm cạnh thiếu
READ MORE:
Khám phá các bài toán thực tế về diện tích và chu vi trong video này. Hãy xem ngay để nâng cao kỹ năng giải toán của bạn!
Bài toán thực tế về Diện tích và Chu vi