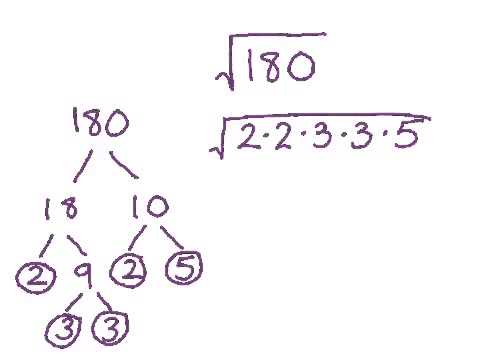Topic whats the square root of 18: Curious about the square root of 18? This article dives deep into the calculation and significance of √18, offering simplified forms, properties, and real-world applications. Whether you're a student, teacher, or math enthusiast, you'll find valuable insights and practical examples to understand and utilize this mathematical concept.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 18
- Introduction to Square Root of 18
- Decimal Representation of Square Root of 18
- Simplified Radical Form of Square Root of 18
- Properties of Square Root of 18
- How to Calculate Square Root of 18
- Mathematical Applications of Square Root of 18
- Real-world Examples Involving Square Root of 18
- Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
- FAQs about Square Root of 18
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 18. Tìm hiểu phương pháp chi tiết để tính √18 một cách dễ dàng.
Square Root of 18
The square root of 18 is a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 18. The value can be expressed in different forms:
Decimal Form
The square root of 18 in decimal form is approximately:
√18 ≈ 4.242640687
Simplified Radical Form
The square root of 18 can be simplified by factoring the number into its prime factors:
√18 = √(9 × 2) = √9 × √2 = 3√2
Mathematical Expression
Using MathJax to represent the mathematical expression:
\\( \sqrt{18} = 3\sqrt{2} \\)
Properties
- \\( \sqrt{18} \\) is an irrational number, which means it cannot be exactly expressed as a fraction of two integers.
- \\( \sqrt{18} \\) is positive since the square root function returns the principal (non-negative) root.
Applications
The square root of 18 can appear in various mathematical contexts, such as geometry, where it might be used to find the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle with specific side lengths, or in algebraic equations and functions.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Root of 18
The square root of 18 is a mathematical value that represents a number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 18. This value is crucial in various fields of mathematics and its applications, such as geometry, algebra, and number theory.
To understand the square root of 18 better, let's explore its different representations:
- Decimal Form: The square root of 18 in decimal form is approximately 4.242640687.
- Simplified Radical Form: By simplifying the radical, the square root of 18 can be expressed as 3√2, since 18 can be factored into 9 × 2, and the square root of 9 is 3.
Mathematically, this can be shown as:
\\( \sqrt{18} = \sqrt{9 \times 2} = \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{2} = 3\sqrt{2} \\)
Here is a step-by-step breakdown of the calculation:
- Factorize 18 into its prime factors: 18 = 9 × 2.
- Take the square root of each factor: \\( \sqrt{9} \\) and \\( \sqrt{2} \\).
- Simplify the square roots: \\( \sqrt{9} = 3 \\) and \\( \sqrt{2} \\) remains as it is.
- Combine the simplified values: \\( 3 \sqrt{2} \\).
The square root of 18, represented as 3√2, is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be exactly expressed as a simple fraction. This makes it an interesting and important value in various mathematical contexts and problems.
Decimal Representation of Square Root of 18
The square root of 18, when expressed in decimal form, is an approximation since it is an irrational number. This means that its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating. To obtain a useful approximation, we can round it to a certain number of decimal places.
Here is the step-by-step process to find the decimal representation of \\( \sqrt{18} \\):
- Using a Calculator: The simplest way to find the decimal form of \\( \sqrt{18} \\) is by using a calculator. When you enter the square root of 18, the calculator provides an approximation.
- Approximation: The value of \\( \sqrt{18} \\) rounded to nine decimal places is approximately 4.242640687.
For practical purposes, we often round the decimal to fewer digits. Here are some common approximations:
- \\( \sqrt{18} \\) ≈ 4.24 (rounded to 2 decimal places)
- \\( \sqrt{18} \\) ≈ 4.243 (rounded to 3 decimal places)
- \\( \sqrt{18} \\) ≈ 4.2426 (rounded to 4 decimal places)
In many mathematical and scientific applications, the precision of the decimal approximation is adjusted based on the required accuracy. For example:
| Decimal Places | Approximation |
|---|---|
| 2 | 4.24 |
| 3 | 4.243 |
| 4 | 4.2426 |
| 5 | 4.24264 |
The decimal representation of \\( \sqrt{18} \\) helps in various applications where an exact radical form is less practical. This approximation is essential for calculations in fields like engineering, physics, and everyday problem-solving.
Simplified Radical Form of Square Root of 18
The simplified radical form of the square root of 18 is derived by expressing 18 as a product of its prime factors and then simplifying the square root expression. This process makes it easier to work with the square root in various mathematical contexts.
Here is the step-by-step process to simplify \\( \sqrt{18} \\):
- Factorize 18: Begin by expressing 18 as a product of its prime factors.
- 18 can be written as 9 × 2.
- Further, 9 is a perfect square (3 × 3).
- So, 18 = 3 × 3 × 2.
- Apply the Square Root: Use the property of square roots that \\( \sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \\).
- \\( \sqrt{18} = \sqrt{9 \times 2} \\).
- \\( \sqrt{9 \times 2} = \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{2} \\).
- Simplify the Expression: Since 9 is a perfect square, we know that \\( \sqrt{9} = 3 \\).
- \\( \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{2} = 3\sqrt{2} \\).
Thus, the simplified radical form of \\( \sqrt{18} \\) is \\( 3\sqrt{2} \\).
Expressed mathematically:
\\( \sqrt{18} = 3\sqrt{2} \\)
This simplified form is particularly useful in algebra and higher mathematics as it provides a more manageable way to handle the square root of 18 without resorting to a lengthy decimal representation.
In summary, by factorizing 18 and applying the properties of square roots, we can express \\( \sqrt{18} \\) in its simplified radical form \\( 3\sqrt{2} \\), which is easier to use in many mathematical operations.
Properties of Square Root of 18
The square root of 18, denoted as \\( \sqrt{18} \\), possesses several interesting mathematical properties. These properties make it a useful number in various mathematical and scientific contexts. Let's explore these properties in detail:
- Irrational Number:
\\( \sqrt{18} \\) is an irrational number. This means it cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating, approximately 4.242640687.
- Simplified Radical Form:
As previously derived, the simplified radical form of \\( \sqrt{18} \\) is \\( 3\sqrt{2} \\). This is obtained by factorizing 18 into 9 and 2, and then simplifying.
- Non-negative Value:
The principal square root of 18 is non-negative. This means \\( \sqrt{18} \\) is positive, as square roots are defined to return the non-negative root.
- Algebraic Property:
\\( \sqrt{18} \\) can be used in algebraic expressions and equations. For example, it can be utilized to solve quadratic equations where the square root of a number is required.
- Geometric Interpretation:
In geometry, \\( \sqrt{18} \\) can represent the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle with sides of specific lengths. For example, a right triangle with legs of length \\( 3\sqrt{2} \\) each will have a hypotenuse of length \\( \sqrt{18} \\).
- Exponential Form:
\\( \sqrt{18} \\) can be expressed in exponential form as \\( 18^{1/2} \\). This notation is often used in advanced mathematics to simplify the manipulation of roots.
- Relationship with Squares:
The square of \\( \sqrt{18} \\) is 18. This property is fundamental to the definition of square roots: \\( (\sqrt{18})^2 = 18 \\).
Understanding these properties helps in recognizing how \\( \sqrt{18} \\) behaves in various mathematical operations and applications, providing a deeper insight into its role within mathematics.
How to Calculate Square Root of 18
Calculating the square root of 18 can be approached in several ways, including manual calculation, approximation methods, and using a calculator. Here, we will explore these methods step-by-step:
1. Using Prime Factorization
This method involves breaking down the number into its prime factors and simplifying the radical expression.
- Factorize 18: Start by finding the prime factors of 18.
- 18 = 9 × 2
- 9 = 3 × 3, so 18 = 3 × 3 × 2
- Simplify the Square Root: Apply the square root to the prime factors.
- \\( \sqrt{18} = \sqrt{9 \times 2} \\)
- \\( \sqrt{9 \times 2} = \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{2} \\)
- Since \\( \sqrt{9} = 3 \\), \\( \sqrt{18} = 3\sqrt{2} \\)
2. Using a Calculator
The simplest and most straightforward method is to use a calculator:
- Enter the number 18.
- Press the square root (√) button.
- The calculator displays the result: approximately 4.242640687.
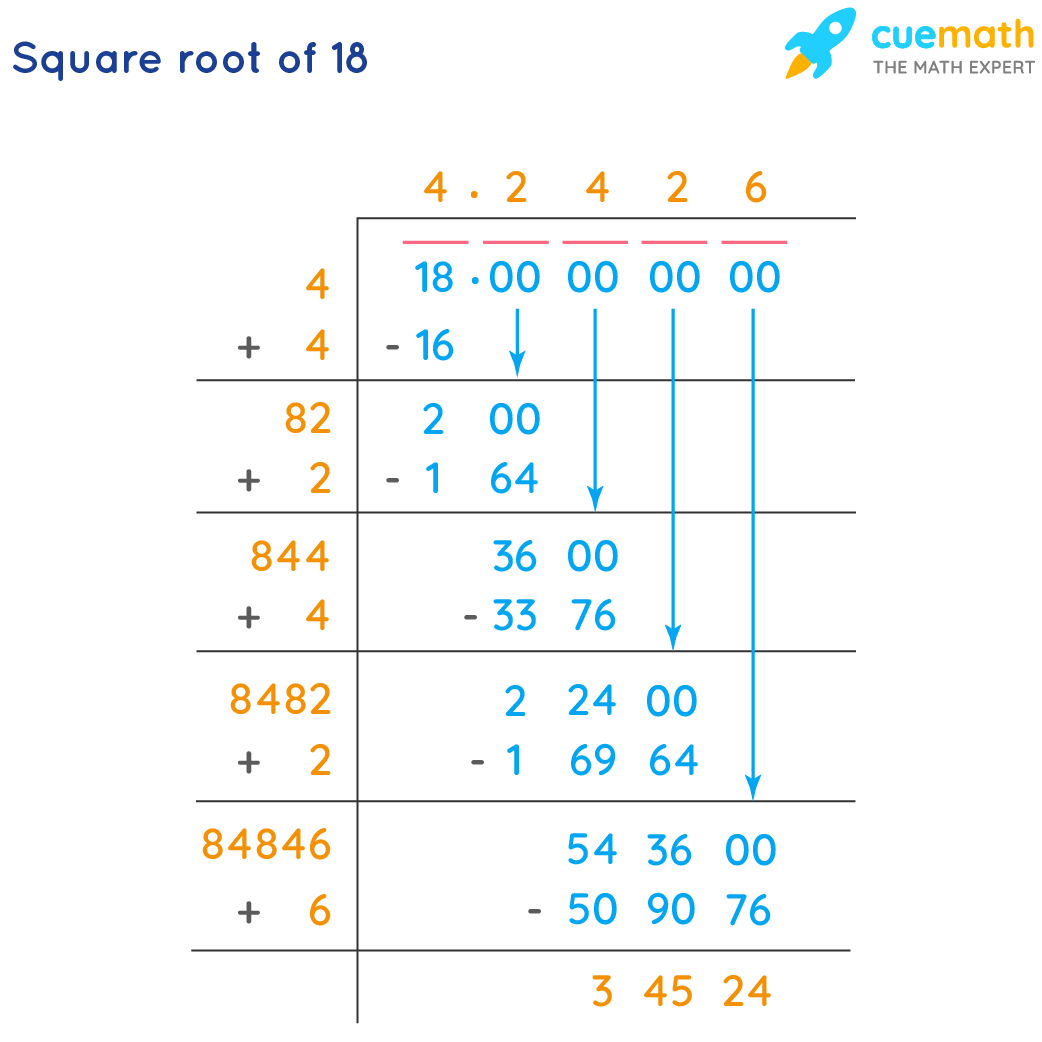
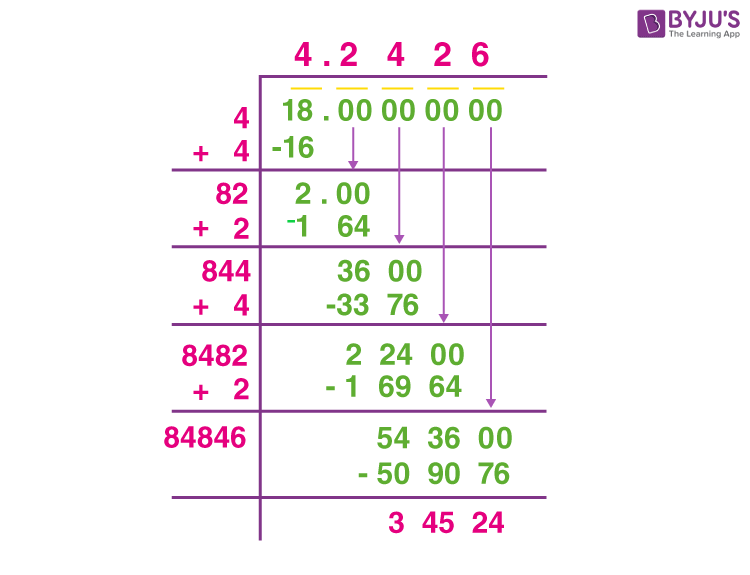
3. Long Division Method
This manual method approximates the square root to a desired number of decimal places.
- Pair the Digits: Start from the decimal point and pair the digits in twos.
- For 18, the pairs are (18.00)
- Find the Largest Square: Find the largest integer whose square is less than or equal to the first pair.
- The largest integer is 4, because 4 × 4 = 16
- Subtract 16 from 18 to get the remainder 2
- Bring Down the Next Pair: Bring down the next pair of zeros to get 200.
- Double the Quotient: Double the current quotient (4) and use it as the starting digit for the next divisor.
- The new divisor is 8_
- Find a digit x such that 8x × x is less than or equal to 200.
- x is 2 because 82 × 2 = 164
- Subtract 164 from 200 to get the remainder 36
- Repeat: Continue the process to add more decimal places.
The result of this method will be the same: approximately 4.242640687, accurate to the desired number of decimal places.
Using these methods, you can calculate the square root of 18 with varying degrees of precision and understanding.
Mathematical Applications of Square Root of 18
The square root of 18, \\( \sqrt{18} \\), appears in various mathematical contexts and applications. Its properties make it a useful number in fields such as geometry, algebra, and trigonometry. Here, we explore some of the key applications of \\( \sqrt{18} \\):
1. Geometry
In geometry, \\( \sqrt{18} \\) can be used to determine lengths and distances:
- Right Triangles: The square root of 18 can represent the length of the hypotenuse in a right triangle. For example, in a right triangle where each leg is \\( 3\sqrt{2} \\), the hypotenuse is \\( \sqrt{(3\sqrt{2})^2 + (3\sqrt{2})^2} = \sqrt{18 + 18} = \sqrt{36} = 6 \\).
- Diagonal of a Rectangle: If a rectangle has sides of length 3 and \\( 3\sqrt{2} \\), the diagonal can be found using the Pythagorean theorem: \\( \sqrt{3^2 + (3\sqrt{2})^2} = \sqrt{9 + 18} = \sqrt{27} = 3\sqrt{3} \\).
2. Algebra
In algebra, \\( \sqrt{18} \\) is useful in solving equations and simplifying expressions:
- Quadratic Equations: The square root of 18 might appear in the solutions of quadratic equations. For instance, solving \\( x^2 - 18 = 0 \\) gives \\( x = \pm\sqrt{18} = \pm3\sqrt{2} \\).
- Simplification: Expressions involving \\( \sqrt{18} \\) can be simplified for easier manipulation. For example, \\( 2\sqrt{18} = 2 \times 3\sqrt{2} = 6\sqrt{2} \\).
3. Trigonometry
In trigonometry, \\( \sqrt{18} \\) can be used in calculations involving trigonometric functions:
- Unit Circle: The square root of 18 might appear in the coordinates of points on the unit circle. For instance, in certain angle calculations where distances need to be normalized.
- Trigonometrical Identities: It can help in proving and simplifying trigonometric identities where roots and squares are involved.
4. Real-world Problems
\\( \sqrt{18} \\) also finds applications in real-world problems where precise calculations are needed:
- Engineering: Engineers might use \\( \sqrt{18} \\) in calculations involving distances, forces, and other measurements.
- Physics: In physics, \\( \sqrt{18} \\) could be used to solve problems related to motion, energy, and wave functions.
In summary, the square root of 18 is a versatile number with numerous applications in various branches of mathematics and science. Understanding its properties and how to work with it is essential for solving a wide range of problems.
Real-world Examples Involving Square Root of 18
Understanding the square root of 18 can be applied to various real-world scenarios, where precise calculations are necessary:
- Engineering: In structural engineering, calculating the diagonal of a square with a side length of 18 units involves the square root of 18.
- Physics: In physics, particularly in mechanics, the square root of 18 appears when determining velocities or accelerations involving distances or energies proportional to the square of 18.
- Finance: In financial modeling, understanding the square root of 18 can be relevant when calculating certain types of risk or volatility metrics.
These examples illustrate how the concept of the square root of 18 extends beyond theoretical mathematics into practical applications across different fields.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
There are common misunderstandings surrounding the square root of 18 that can be clarified:
- Misconception: Some believe that the square root of 18 is a simple whole number.
- Mistake: Incorrect calculations often occur due to improper application of the square root function.
- Misconception: It's sometimes thought that the square root of 18 has no real-world applications.
- Mistake: Confusion arises when distinguishing between the square root of 18 and other nearby square roots.
Clearing up these misconceptions ensures a better understanding of the true nature and applications of the square root of 18.
FAQs about Square Root of 18
Here are some frequently asked questions about the square root of 18:
-
What is the exact value of the square root of 18?
The square root of 18 is an irrational number, approximately equal to 4.24264068712.
-
Is the square root of 18 a whole number?
No, the square root of 18 is not a whole number; it is an irrational number.
-
What is the simplest radical form of the square root of 18?
The simplest radical form of the square root of 18 is \(3\sqrt{2}\).
-
How is the square root of 18 calculated?
The square root of 18 can be calculated using numerical methods or by approximation using mathematical tools.
-
What are the practical applications of the square root of 18?
The square root of 18 appears in various fields such as mathematics, physics, engineering, and finance for calculating distances, velocities, and certain metrics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the square root of 18 is a fundamental mathematical concept with practical applications across various disciplines. Understanding its properties, both in decimal and radical form, allows for precise calculations in fields such as engineering, physics, and finance. By dispelling common misconceptions and addressing frequently asked questions, we enhance our comprehension of this irrational number and its significance in real-world scenarios. Whether calculating distances, velocities, or risk metrics, the square root of 18 remains a critical tool in problem-solving and theoretical exploration.
Hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 18. Tìm hiểu phương pháp chi tiết để tính √18 một cách dễ dàng.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai Của 18: √18
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách tính căn bậc hai của số 18. Tìm hiểu chi tiết về √18 và cách giải bài toán này.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 18