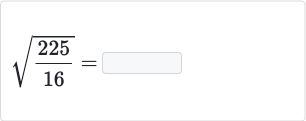
Topic whats the square root of 16: The square root of 16 is 4. Understanding square roots is essential in mathematics, as it helps in solving various problems. This article will guide you through the concept of square roots, different methods to find them, and why they are important. Dive in to explore more about the fascinating world of square roots!
Table of Content
- Understanding the Square Root of 16
- Introduction
- What is the Square Root of 16?
- Methods to Find the Square Root of 16
- Square Root of 16 in Radical Form
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Visual and Interactive Examples
- Practice Problems
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Khám phá cách tìm căn bậc hai của 16 qua video này, cung cấp các phương pháp và ví dụ thực tế để hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm này.
Understanding the Square Root of 16
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. In mathematical terms, the square root of 16 is represented as √16.
Value of the Square Root of 16
The square root of 16 is:
This is because 4 multiplied by 4 equals 16.
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 16
-
Perfect Square Method
We know that 16 can be expressed as 4×4, thus the square root of 16 is 4.
-
Long Division Method
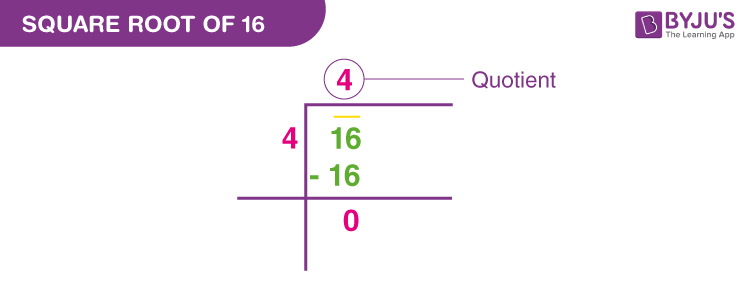
In this method, we find the largest number which, when multiplied by itself, will give 16. Here, that number is 4.
16 4 4 4
Examples
-
Example 1
If you have a square table with an area of 16 square inches, the side length of the table is:
inches.
-
Example 2
If you arrange 16 flower plants in a square formation, the number of plants on each side is:
plants.
FAQs
- What is the square root of 16? The square root of 16 is 4.
- Is the square root of 16 rational? Yes, because 4 is a whole number.
- Is 16 a perfect square? Yes, because it can be expressed as 4×4.
Additional Information
The square root of 16 is expressed as √16 in radical form and as 161/2 in exponential form. It is both positive and negative; however, the principal square root is the positive value, 4.

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 16 is a fundamental mathematical concept, commonly taught in early algebra. A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For 16, the square root is 4, because \(4 \times 4 = 16\). In this section, we will explore the definition, calculation methods, and significance of the square root of 16, providing a step-by-step guide to understand it thoroughly.
- Definition: The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number.
- Calculation Methods: There are several methods to calculate the square root of a number, including prime factorization, the long division method, and using a calculator.
- Example: For 16, the square root is 4, because \(4^2 = 16\).
- Significance: Understanding square roots is essential for solving quadratic equations, understanding geometric concepts, and in various applications in science and engineering.
| Method | Steps |
|---|---|
| Prime Factorization |
|
| Long Division Method |
|
Understanding the square root of 16 provides a foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts, and its applications span various fields, making it a crucial element in education and practical problem-solving.
What is the Square Root of 16?
The square root of 16 is a fundamental mathematical concept that is both simple and essential. Understanding this concept involves recognizing that the square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For 16, the square root is 4, because \(4 \times 4 = 16\).
- Definition: The square root of 16 is represented as \( \sqrt{16} \) and equals 4.
- Perfect Square: 16 is a perfect square, meaning it can be expressed as \( 4^2 \).
- Rational Number: The square root of 16 is rational, as it can be written as a fraction, \( \frac{4}{1} \).
- Calculation Methods:
- Prime Factorization: \( 16 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \). Pairing the factors gives \( (2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) = 4 \times 4 \), hence \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
- Long Division: Using the long division method, we divide 16 by 4, which also results in 4.
| Square Root | Value |
| \( \sqrt{16} \) | 4 |
| \( 16^{1/2} \) | 4 |
Understanding the square root of 16 is crucial in various mathematical applications, from solving quadratic equations to simplifying radical expressions. It's a concept that not only aids in basic arithmetic but also forms the foundation for more advanced topics in algebra and beyond.
Methods to Find the Square Root of 16
Finding the square root of 16 can be done using several methods, each with its own approach and steps. Here, we will discuss three common methods: the prime factorization method, the long division method, and the repeated subtraction method.
- Prime Factorization Method:
- Express 16 as a product of its prime factors: \( 16 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \) or \( 2^4 \).
- Group the prime factors into pairs: \( (2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) = 4 \times 4 \).
- Take the square root of both sides: \( \sqrt{16} = \sqrt{4^2} = 4 \).
- Long Division Method:
- Write the number 16 under the long division bar.
- Find the largest number that, when multiplied by itself, gives 16 or less. Here, that number is 4.
- Perform the division: 16 divided by 4 equals 4.
- The quotient, 4, is the square root of 16.
- Repeated Subtraction Method:
- Start with the number 16 and subtract successive odd numbers until you reach zero.
- Subtract 1: \( 16 - 1 = 15 \).
- Subtract 3: \( 15 - 3 = 12 \).
- Subtract 5: \( 12 - 5 = 7 \).
- Subtract 7: \( 7 - 7 = 0 \).
- The number of steps taken (4 steps) is the square root of 16.
These methods help in understanding the concept of square roots and provide different approaches to finding the square root of a number, making it easier to grasp for various learning styles.
Square Root of 16 in Radical Form
The square root of 16 in radical form is a mathematical expression used to represent one of the two numbers which, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number, 16. In radical form, this is expressed as \(\sqrt{16}\).
- Step 1: Identify the number.
- Step 2: Express the number as a product of its prime factors.
- Step 3: Simplify the radical.
The number we are dealing with is 16.
We can write 16 as \(2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2\) or \(2^4\).
Taking the square root of both sides, we have \(\sqrt{16} = \sqrt{4^2} = 4\).
Therefore, the square root of 16 in radical form is \(\sqrt{16} = 4\).
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions regarding the square root of 16:
-
What is the square root of 16?
The square root of 16 is 4.
-
Is 16 a perfect square?
Yes, 16 is a perfect square because its square root is a whole number, which is 4.
-
Is 16 a rational number?
Yes, 16 is a rational number because it can be expressed as a fraction of two integers (16/1).
-
What are some methods to find the square root of 16?
There are several methods to find the square root of 16:
- Prime Factorization: 16 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2, so √16 = 4.
- Repeated Subtraction: Subtract successive odd numbers from 16 until reaching zero in 4 steps.
- Using a Calculator: Simply enter 16 and press the square root (√) button to get 4.
-
What is the principal square root of 16?The principal (positive) square root of 16 is 4.
Visual and Interactive Examples
Understanding the square root of 16 can be made easier through visual and interactive examples. Below, you'll find methods to visualize and interact with the concept to enhance your learning experience.
- Visualizing Square Roots:
To visualize the square root of 16, imagine a perfect square with an area of 16 square units. Each side of this square will be equal to the square root of 16. Here's a simple grid representation:
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Each cell represents 1 square unit, and as you can see, a 4x4 grid perfectly fits within the area, demonstrating that the square root of 16 is 4.
- Interactive Example: Finding Square Roots:
Use the following interactive example to explore how the square root works:
Step-by-Step Process to Find the Square Root of 16 Using Prime Factorization:
- Write 16 as a product of its prime factors: \(16 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2\).
- Group the prime factors into pairs: \(16 = (2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2)\).
- Take one number from each pair: \(2 \times 2 = 4\).
- Thus, the square root of 16 is 4.
Using MathJax, we can represent the square root calculation as:
\(\sqrt{16} = \sqrt{2^4} = 2^2 = 4\)
Try altering the numbers and observe the results to understand the concept of square roots better.
- Interactive Example: Visualizing Different Square Roots:
Use this interactive visualization tool to see how the square root changes with different values:
Enter any perfect square value below to see its square root:
Practice Problems
Practice problems are essential for reinforcing the understanding of square roots. Below are several practice problems involving the square root of 16. Work through each step-by-step for better comprehension.
-
Problem 1: Simplify the expression \( (7\sqrt{16}) + 15 \).
Solution:
- Given: \( (7\sqrt{16}) + 15 \)
- Since \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \), substitute 4 into the expression:
- \( (7 \times 4) + 15 = 28 + 15 = 43 \)
- Answer: 43
-
Problem 2: Determine the value of \( m \) if \( m + \sqrt{16} = 20 \).
Solution:
- Given: \( m + \sqrt{16} = 20 \)
- Since \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \), substitute 4 into the equation:
- \( m + 4 = 20 \)
- Solve for \( m \): \( m = 20 - 4 = 16 \)
- Answer: \( m = 16 \)
-
Problem 3: Simplify the expression \( \left( \frac{5\sqrt{16}}{\sqrt{16}} \right) + 20 \).
Solution:
- Given: \( \left( \frac{5\sqrt{16}}{\sqrt{16}} \right) + 20 \)
- Since \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \), substitute 4 into the expression:
- \( \left( \frac{5 \times 4}{4} \right) + 20 = \left( \frac{20}{4} \right) + 20 = 5 + 20 = 25 \)
- Answer: 25
-
Problem 4: Calculate the area of a square with a side length equal to the square root of 16.
Solution:
- Given side length: \( \sqrt{16} \)
- Since \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \), the side length is 4.
- Area of a square: side length squared \( (4^2) \)
- \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \)
- Answer: The area is 16 square units.
-
Problem 5: If you multiply the square root of 16 by itself, what is the result?
Solution:
- Given: \( \sqrt{16} \times \sqrt{16} \)
- Since \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \), substitute 4 into the expression:
- \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \)
- Answer: 16
Conclusion
Understanding the square root of 16 provides a solid foundation for grasping the concept of square roots in general. The value of the square root of 16 is a straightforward example, being 4, which helps illustrate various mathematical principles and methods used to determine square roots.
Through this exploration, we've covered:
- Definition and Concept: The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For 16, this value is 4.
- Methods to Find the Square Root: We explored methods such as prime factorization and long division to find the square root of 16, both leading to the result of 4.
- Radical Form: We discussed that the square root of 16 can be represented in its simplest radical form as \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
- Examples: Practical examples demonstrated how to apply the square root of 16 in real-world scenarios, such as calculating the side length of a square, distributing items evenly, and more.
- FAQs: Common questions about the square root of 16 were addressed, reinforcing why it is considered a rational number and confirming that 16 is indeed a perfect square.
- Visual and Interactive Learning: Visual tools and interactive methods helped solidify the understanding of finding square roots, making the concept more accessible.
By examining these aspects, it becomes clear that the square root of 16 is a fundamental example that aids in the comprehension of broader mathematical concepts. Whether through visual aids, practical examples, or methodical calculations, grasping the square root of 16 lays the groundwork for tackling more complex mathematical challenges.
As you continue your mathematical journey, remember that the principles applied to finding the square root of 16 are universally applicable. This foundational knowledge will serve you well in various mathematical endeavors, enhancing both your analytical skills and problem-solving abilities.
Keep practicing and exploring different mathematical concepts to deepen your understanding and appreciation of the beauty and logic that mathematics offers.

Khám phá cách tìm căn bậc hai của 16 qua video này, cung cấp các phương pháp và ví dụ thực tế để hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm này.
Căn Bậc Hai của 16
READ MORE:
Video này hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 16: sqrt(16), cung cấp các phương pháp và ví dụ thực tế để hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm này.
Làm Thế Nào Để Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 16: sqrt(16)