Topic what is 4 square root: Curious about what 4 square root means in mathematics? Discover its fundamental concepts and how to calculate it. This article provides a clear explanation of 4 square root, its significance in mathematical operations, and practical examples to deepen your understanding. Explore its applications and gain insights into how this concept is used in various contexts.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Square Root of 4
- Understanding 4 Square Root: A Complete Overview
- Calculation Methods for 4 Square Root
- Applications and Uses of 4 Square Root in Mathematics
- Real-Life Examples and Scenarios Involving 4 Square Root
- Comparative Analysis: 4 Square Root vs. Other Mathematical Concepts
- Conclusion: Importance and Practical Implications of 4 Square Root
- YOUTUBE: Xem video hướng dẫn về cách tính căn bậc hai của 4 bằng cách sử dụng phương pháp cây yếu tố. Học cách đơn giản hóa bài toán này một cách dễ dàng và hiệu quả.
Understanding the Square Root of 4
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. The square root of 4 is a fundamental concept in mathematics.
Mathematical Definition
The square root of 4 is represented as \( \sqrt{4} \). Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
\[
\sqrt{4} = 2 \quad \text{because} \quad 2^2 = 4
\]
Properties of the Square Root of 4
- Perfect Square: 4 is a perfect square because it is the product of an integer (2) multiplied by itself.
- Radical Form: The simplest radical form of the square root of 4 is \( \sqrt{4} \).
- Exponent Form: The square root of 4 in exponent form is \( 4^{1/2} \).
- Principal Square Root: The principal square root of 4 is 2, denoted by \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \).
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 4
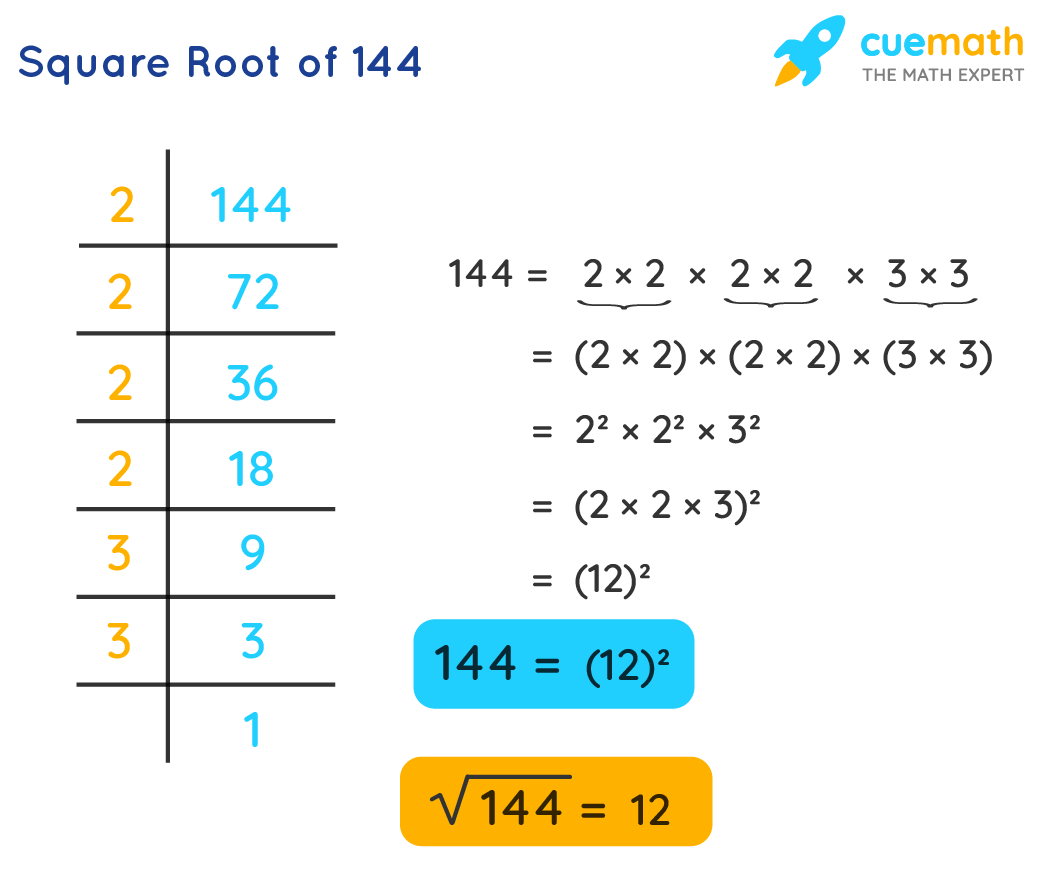
1. Prime Factorization Method
In this method, we express 4 as the product of its prime factors:
\[
\sqrt{4} = \sqrt{2 \times 2} = \sqrt{2^2} = 2
\]
2. Repeated Subtraction Method
Subtract odd numbers starting from 1 until the remainder is 0. The number of subtractions gives the square root:
\[
4 - 1 = 3 \\
3 - 3 = 0
\]
Since the number of iterations is 2, \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \).
3. Long Division Method
This method involves grouping the digits and finding the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 4. Since \( 2 \times 2 = 4 \), the square root of 4 is 2.
Applications of the Square Root of 4
- Geometry: Finding the side length of a square with an area of 4 square units.
- Physics: Calculating distances and magnitudes in various equations.
- Statistics: Standard deviations and variances often involve square root calculations.
Visualizing the Square Root of 4
Visual aids can help in understanding the concept of square roots. Consider a square with an area of 4 square units; each side of the square will be \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \) units long.
Related Calculations
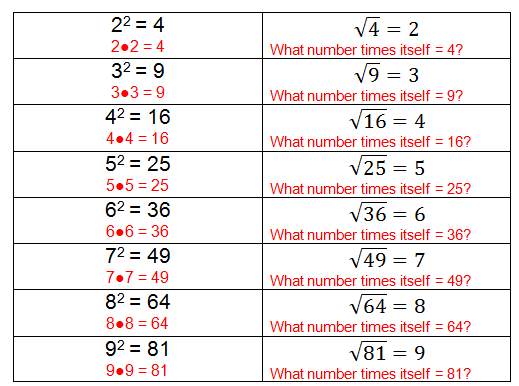
The square root of other related numbers can be calculated similarly:
- \(\sqrt{16} = 4\)
- \(\sqrt{64} = 8\)
- \(\sqrt{49} = 7\)
For non-perfect squares, the square root may not be an integer but can be approximated using various methods, including long division.
FAQs on the Square Root of 4
- What is the value of \(16 \sqrt{4}\)? The value is \(16 \times 2 = 32\).
- Is 4 a perfect square? Yes, because \(2^2 = 4\).

READ MORE:
Understanding 4 Square Root: A Complete Overview
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Specifically, the 4th square root of a number \( x \) is denoted as \( \sqrt[4]{x} \) or \( x^{1/4} \). Here’s how you can understand and calculate the 4 square root:
- Start with a number \( x \).
- Estimate or calculate the value of \( x^{1/4} \) using methods like prime factorization, successive approximation, or using a calculator.
- Verify your result by squaring \( x^{1/4} \) to ensure it equals \( x \).
For example, the 4 square root of 16 is 2 because \( 2^4 = 16 \). This concept is crucial in various fields including mathematics, physics, and engineering for solving equations and understanding relationships between variables.
Calculation Methods for 4 Square Root
Calculating the 4 square root of a number involves several methods depending on the complexity of the number and the accuracy required:
- Prime Factorization Method: Decompose the number into its prime factors and then extract the fourth root of each factor.
- Successive Approximation: Use iterative methods to approximate the fourth root, adjusting until the desired accuracy is achieved.
- Using a Calculator: Most scientific calculators have functions to directly compute the fourth root of a number.
- Tables and Reference Books: Historically, mathematical tables and reference books provided precomputed values of fourth roots for common numbers.
These methods are essential in mathematics and various scientific fields for solving equations, performing computations, and understanding relationships between variables.
Applications and Uses of 4 Square Root in Mathematics
The square root of 4, which is 2, finds applications in various mathematical contexts and real-life scenarios. Here are some key areas where the square root of 4 is used:
-
Geometry:
In geometry, the square root of 4 is frequently encountered in problems involving areas and volumes. For example, if the area of a square is 4 square units, the length of each side is the square root of 4, which is 2 units.
-
Algebra:
In algebra, solving quadratic equations often involves taking square roots. For instance, to solve the equation \(x^2 = 4\), we find that \(x = \pm \sqrt{4}\), giving solutions \(x = 2\) and \(x = -2\).
-
Trigonometry:
In trigonometry, the square root of 4 is used in various formulas and identities. For example, when calculating distances in coordinate geometry or when simplifying expressions involving trigonometric functions.
-
Physics:
In physics, the square root of 4 is used in equations related to kinematics, waves, and other areas. For example, the distance formula in physics, derived from the Pythagorean theorem, often requires computing square roots.
-
Statistics:
In statistics, the square root of 4 is used in standard deviation calculations and other statistical measures. For instance, if a variance is 4, the standard deviation is the square root of the variance, which is 2.
The square root of 4 also simplifies complex calculations in various fields such as engineering, computer science, and economics, making it a fundamental concept in both theoretical and applied mathematics.
Examples and Problems
-
Given a circle with an area of 4π square units, the radius of the circle is calculated as follows:
\[A = πr^2\]
\[4π = πr^2\]
\[r^2 = 4\]
\[r = \sqrt{4} = 2\]
-
If the side length of a cube is the square root of 4, its volume can be calculated as:
\[V = (\sqrt{4})^3 = 2^3 = 8\] cubic units
Real-Life Examples and Scenarios Involving 4 Square Root
The square root of 4, which is 2, finds numerous applications in various real-life scenarios and mathematical contexts. Below are some detailed examples and scenarios where the square root of 4 is applied:
-
Geometry and Area Calculations: In geometry, the square root of 4 is often used to determine the side lengths of squares and rectangles. For example, if the area of a square is 4 square units, the length of each side is √4 = 2 units. This principle helps in constructing geometric shapes and understanding their properties.
-
Scaling and Proportion: In art and design, proportions are crucial. If a designer needs to scale up a model proportionally and one dimension is doubled (square root of 4), the area will increase by a factor of four, maintaining the correct proportions.
-
Physics and Engineering: The square root function is significant in physics and engineering. For instance, in kinematic equations, when determining the velocity or displacement over time, if a parameter involves squaring or square roots, such as finding the time taken for an object to travel a specific distance under constant acceleration.
-
Statistics: In statistics, the standard deviation of a dataset is often involved with square roots. For a variance of 4, the standard deviation is the square root of the variance, which is 2. This helps in understanding the spread or dispersion of data points.
-
Real Estate and Construction: When calculating the dimensions of a plot of land or a room, knowing the area and applying the square root can help in determining the length of sides. For example, if a rectangular plot has an area of 4 square meters and is meant to be square-shaped, each side would be 2 meters.
-
Finance: The concept of compound interest sometimes involves square roots when dealing with annual interest rates over a specific period. If an investment’s value needs to be squared or unsquared over time to find the rate or time period, the square root is applied.
-
Astronomy: In astronomy, calculations involving distances, areas of celestial bodies, or light intensity often use square roots. For example, if the intensity of light decreases with the square of the distance from a source, knowing the distance can involve finding the square root of the intensity ratio.
Overall, the square root of 4 is a fundamental mathematical operation with wide-ranging applications across different fields, enhancing our understanding and solving practical problems effectively.
Comparative Analysis: 4 Square Root vs. Other Mathematical Concepts
The square root of 4, denoted as \( \sqrt{4} \), is a fundamental concept in mathematics. Understanding how it compares to other mathematical concepts can provide deeper insights into its significance and applications.
-
Square Root vs. Square
The square of a number is obtained by multiplying the number by itself. For example, the square of 2 is \( 2^2 = 4 \). Conversely, the square root operation finds the original number that was squared to produce a given value. Thus, \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \) because \( 2^2 = 4 \).
-
Square Root vs. Cube Root
While the square root of a number \( x \) is a value \( y \) such that \( y^2 = x \), the cube root is a value \( z \) such that \( z^3 = x \). For example, \( \sqrt[3]{8} = 2 \) because \( 2^3 = 8 \). In comparison, the square root of 4 (which is 2) deals with squaring, whereas the cube root involves cubing.
-
Square Root vs. Exponential Functions
Exponential functions involve raising a number to a power. For instance, \( 2^3 = 8 \). The square root can be considered a special case of the power function, specifically \( x^{1/2} \). Thus, \( \sqrt{4} \) is the same as \( 4^{1/2} \), which simplifies to 2.
-
Square Root vs. Logarithms
Logarithms are the inverse of exponential functions. The logarithm base 10 of 100, written as \( \log_{10}{100} \), equals 2 because \( 10^2 = 100 \). While logarithms determine the power to which a number must be raised to obtain another number, square roots find the base number that must be squared.
-
Square Root vs. Absolute Value
The absolute value of a number is its distance from zero on the number line, disregarding the sign. For example, \( |-4| = 4 \). While absolute value measures magnitude, the square root operation finds a value that, when squared, returns the original number. Notably, both \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \) and \( \sqrt{4} = -2 \) demonstrate how square roots can yield both positive and negative results, but the principal square root is the non-negative one.
Understanding these comparisons highlights the unique role of the square root function in mathematics, bridging various mathematical concepts and offering practical tools for problem-solving.
Conclusion: Importance and Practical Implications of 4 Square Root
The square root of 4, denoted as \(\sqrt{4}\), is a fundamental concept in mathematics with significant implications across various fields. Understanding this concept is crucial for both academic and practical applications.
The value of the square root of 4 is 2, since \(2^2 = 4\). This simple yet profound result lays the foundation for more complex mathematical operations and theories.
-
Foundation for Higher Mathematics:
The concept of square roots is essential in algebra, calculus, and other advanced mathematical disciplines. It serves as a building block for understanding more complex equations and functions.
-
Practical Applications:
Square roots are widely used in real-life scenarios, including engineering, physics, and computer science. For example, they are crucial in calculating distances, areas, and in algorithms that require precise measurements.
-
Educational Importance:
Mastering the square root of 4 helps students grasp the fundamental properties of numbers and prepares them for more advanced mathematical challenges. It also enhances problem-solving skills and logical thinking.
-
Geometric Interpretations:
In geometry, the square root of 4 is used to determine the side length of a square with an area of 4 square units. This understanding is crucial for solving various geometric problems and for practical tasks like construction and design.
-
Scientific Relevance:
In the sciences, the square root function is used in formulas and equations to describe natural phenomena. For instance, in physics, it is used to calculate wave speeds and in statistics to find standard deviations.
In conclusion, the square root of 4 is a simple yet indispensable mathematical concept. Its applications range from education to complex scientific computations, making it a cornerstone in the world of mathematics and beyond. Understanding and utilizing \(\sqrt{4}\) is not only a step towards mathematical proficiency but also a key to unlocking numerous practical and theoretical insights.
Xem video hướng dẫn về cách tính căn bậc hai của 4 bằng cách sử dụng phương pháp cây yếu tố. Học cách đơn giản hóa bài toán này một cách dễ dàng và hiệu quả.
Gốc rễ của 4 bằng cách sử dụng cây yếu tố
READ MORE:
Khám phá căn bậc hai là gì qua video hướng dẫn của thầy J. Tìm hiểu về khái niệm này một cách dễ hiểu và trực quan.
Căn bậc hai là gì? | Toán học với thầy J