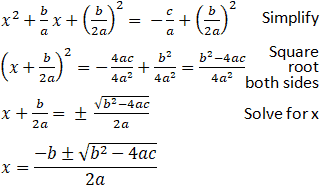Topic square root videos: Discover a variety of engaging square root videos to help you understand and master the concept of square roots. From basic introductions to advanced applications, these videos are perfect for learners of all levels. Start your journey to mathematical proficiency with these informative and easy-to-follow tutorials.
Table of Content
- Square Root Videos
- 1. Introduction to Square Roots
- 2. What are Square Roots?
- 3. Understanding Square Roots
- 4. Simplifying Square Roots
- 5. Approximating Square Roots
- 6. Square Roots of Perfect Squares
- 7. Square Roots in Algebra
- 8. Solving Quadratics by Taking Square Roots
- 9. Practical Applications of Square Roots
- 10. Square Root Functions and Their Graphs
- 11. Beginner Lessons on Square Roots
- 12. Online Resources and Worksheets for Square Roots
- YOUTUBE: What are Square Roots? | Math with Mr. J
Square Root Videos
Discover a range of educational videos on square roots, perfect for different learning levels from beginner to advanced.
Introduction to Square Roots
-
A comprehensive introduction to the concept of square roots, explaining the basics and providing examples to help learners understand.
-
This video covers the fundamental concepts of square roots, tailored for 8th grade students and beginners.
Square Roots in Practice
-
This video provides a deeper understanding of square roots, including how to find them and their practical applications in mathematics.
-
Learn how to approximate square roots using various methods, suitable for students looking to enhance their problem-solving skills.
Special Topics on Square Roots
-
This video explores both square roots and cube roots, providing a comprehensive understanding of these concepts and their differences.
-
A beginner lesson on square roots, ideal for pre-algebra students looking to grasp the basics in a step-by-step manner.
-
This resource includes videos, worksheets, games, and activities to help students master the concept of perfect squares and their roots.
Additional Resources
For more videos and interactive lessons on square roots, visit:

READ MORE:
1. Introduction to Square Roots
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on square roots! In mathematics, the square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Understanding square roots is fundamental in various mathematical contexts, from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus and beyond.
Here's a structured overview to help you navigate through this topic:
- Definition: Square root is denoted by the symbol √. For a non-negative real number \( x \), √\( x \) is the non-negative number \( y \) such that \( y^2 = x \).
- Basic Properties:
- Every positive real number has two square roots: one positive and one negative.
- The square root function \( \sqrt{x} \) is the inverse of squaring function \( x^2 \).
- Notation: In algebra and calculus, square roots are often expressed using radical notation or exponent notation.
- Applications: Square roots are used in various scientific and practical applications, such as in physics (to calculate distances), engineering (for complex calculations), and even in computer graphics and cryptography.
Understanding how to calculate, approximate, and manipulate square roots is crucial for advancing your mathematical skills. Each section in this guide will delve deeper into specific aspects of square roots, providing you with the tools to master this essential mathematical concept.
2. What are Square Roots?
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. In mathematical notation, the square root of a number a is written as √a. For example, the square root of 9 is 3, because 3 × 3 = 9.
Square roots can be positive or negative because both positive and negative values can be squared to yield the same number. For instance, both 3 and -3 are square roots of 9.
- Positive Square Roots: For any non-negative number a, the principal square root is denoted as √a and is always non-negative.
- Negative Square Roots: The negative square root of a is denoted as -√a.
To illustrate, consider the following examples:
- √4 = 2 because 2 × 2 = 4
- √16 = 4 because 4 × 4 = 16
- √25 = 5 because 5 × 5 = 25
Square roots are fundamental in various mathematical concepts and real-life applications. Here's a table showing some common numbers and their square roots:
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 9 | 3 |
| 16 | 4 |
| 25 | 5 |
When dealing with square roots, it's also important to understand the concept of irrational numbers. An irrational number cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal form is non-repeating and non-terminating. The square roots of non-perfect squares are typically irrational. For example, √2 is approximately 1.414, and it cannot be exactly expressed as a fraction.
In summary, square roots are an essential part of mathematics, helping to simplify expressions and solve equations. Understanding square roots is crucial for progressing in both pure and applied mathematics.
3. Understanding Square Roots
Understanding square roots is essential for mastering many mathematical concepts. A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 16 is 4 because 4 × 4 = 16.
Let's break down the concept step-by-step:
- Definition: If x is the square root of a, then x² = a. Mathematically, this is written as x = √a.
- Perfect Squares: Numbers like 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, and so on are perfect squares because they can be expressed as the square of an integer.
- Non-Perfect Squares: Numbers that are not perfect squares have square roots that are irrational, meaning their decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating. For example, √2 ≈ 1.414.
- Principal Square Root: The principal square root is the non-negative root of a number. For instance, √25 = 5.
- Negative Square Root: Every positive number has both a positive and a negative square root. For instance, the square roots of 25 are 5 and -5.
To better understand square roots, let's look at some examples:
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 9 | 3 |
| 16 | 4 |
| 25 | 5 |
| 36 | 6 |
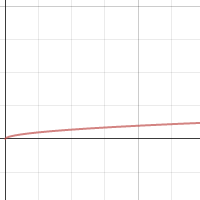
Understanding square roots also involves recognizing their graphical representation. On a graph, the function f(x) = √x produces a curve that increases gradually, reflecting the fact that as x gets larger, the square root of x also gets larger but at a decreasing rate.
Here are some key points to remember:
- Square roots are used in various areas of mathematics including algebra and geometry.
- They are fundamental in solving quadratic equations, where the solutions may involve taking the square root of both sides of the equation.
- Practical applications include calculating areas and understanding physical phenomena like sound intensity and light exposure.
By practicing these concepts and solving related problems, you can gain a deeper understanding of square roots and their applications in both academic and real-world scenarios.
4. Simplifying Square Roots
Simplifying square roots involves breaking down a radical expression into its simplest form. This process helps make complex square root expressions more manageable and easier to work with. Here’s a step-by-step guide to simplifying square roots:
- Identify Perfect Squares: Look for factors of the number under the square root that are perfect squares. For example, to simplify √72, identify that 72 = 36 × 2, where 36 is a perfect square.
- Factorize: Write the number as a product of its prime factors. For √72, you can write it as √(36 × 2) = √36 × √2.
- Take the Square Root of Perfect Squares: Simplify the square root of the perfect square. In our example, √36 = 6, so √72 = 6√2.
- Combine Results: Write the simplified form. Therefore, √72 simplifies to 6√2.
Here are some more examples:
| Original Expression | Simplified Form |
|---|---|
| √50 | 5√2 (since 50 = 25 × 2 and √25 = 5) |
| √45 | 3√5 (since 45 = 9 × 5 and √9 = 3) |
| √98 | 7√2 (since 98 = 49 × 2 and √49 = 7) |
Additional Tips for Simplifying Square Roots:
- Prime Factorization Method: Break the number into its prime factors and pair the prime numbers. Each pair of primes comes out of the square root as a single number. For instance, √72 = √(2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3) = 2 × 3√2 = 6√2.
- Division Method: Divide the number by the smallest prime number and continue the process until you get a quotient of 1. Pair the primes and simplify.
- Using Exponents: If the number is expressed in exponential form, simplify by using the properties of exponents. For example, √(a^2 b) = a√b.
By mastering these steps and methods, simplifying square roots becomes a straightforward process, making it easier to handle more complex mathematical problems.
5. Approximating Square Roots
Approximating square roots involves finding an estimated value for a number that does not have a perfect square root. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you approximate square roots:
- Identify the Nearest Perfect Squares: Determine the perfect squares that are closest to the number you are approximating. For example, to approximate √20, note that 16 (4²) and 25 (5²) are the nearest perfect squares.
- Estimate the Square Root: Determine that √20 is between 4 and 5. Since 20 is closer to 16, √20 is closer to 4.
- Refine the Estimate: Use a method such as averaging or a calculator to get a more precise estimate. For √20, a closer approximation is 4.47.
Another method to approximate square roots involves using the Babylonian Method (or Heron's Method):
- Initial Guess: Start with an initial guess. For √20, start with 4.5 as it lies between 4 and 5.
- Improve the Guess: Use the formula: \( \text{New Guess} = \frac{\text{Old Guess} + \frac{N}{\text{Old Guess}}}{2} \). For the first iteration: \[ \text{New Guess} = \frac{4.5 + \frac{20}{4.5}}{2} \approx 4.472 \]
- Repeat: Continue the process until the guess stabilizes. After a few iterations, you’ll get a value close to 4.472.
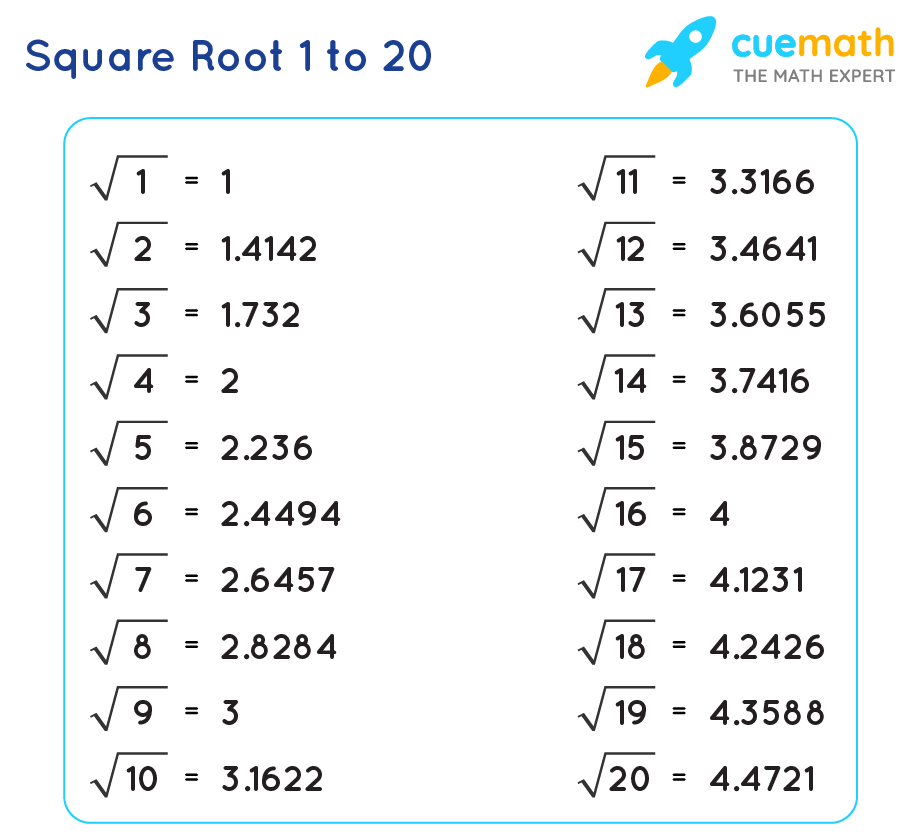
Here’s a quick reference table for approximating some common square roots:
| Number | Approximate Square Root |
|---|---|
| 2 | 1.414 |
| 3 | 1.732 |
| 5 | 2.236 |
| 7 | 2.646 |
| 8 | 2.828 |
By using these methods and tools, you can approximate the square roots of numbers that are not perfect squares with reasonable accuracy, making it easier to handle complex calculations.
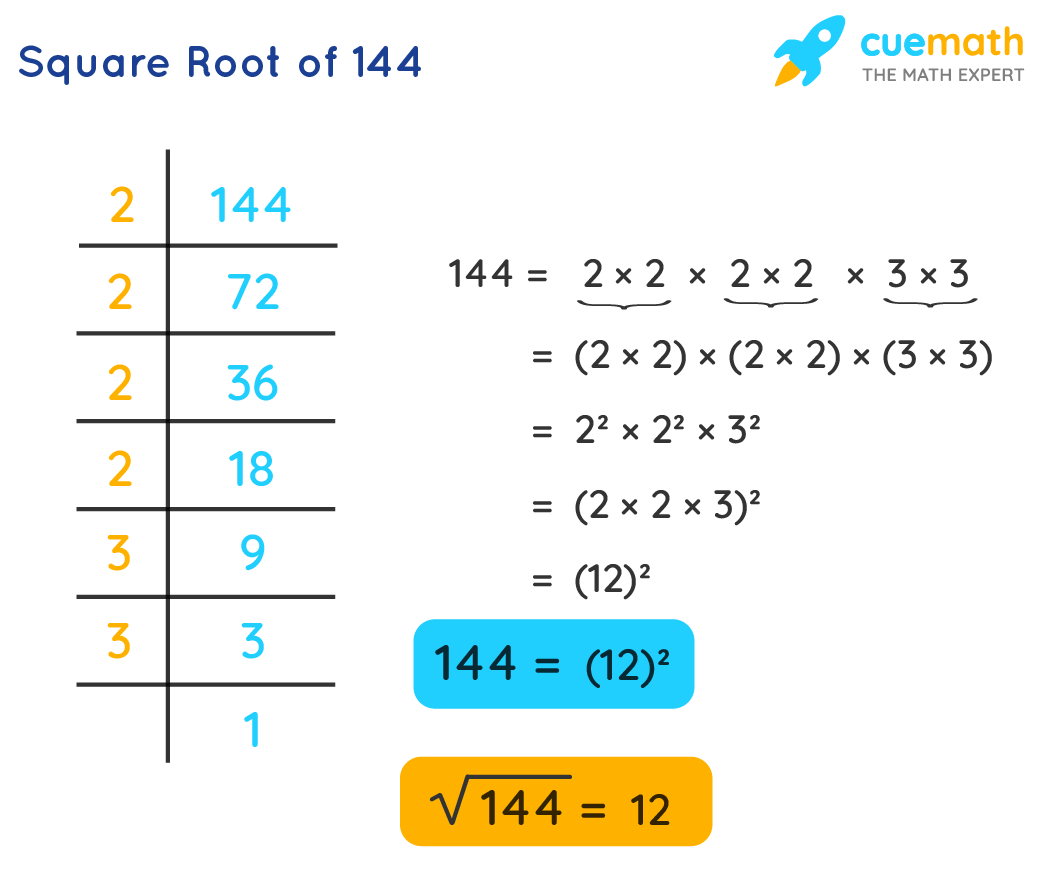
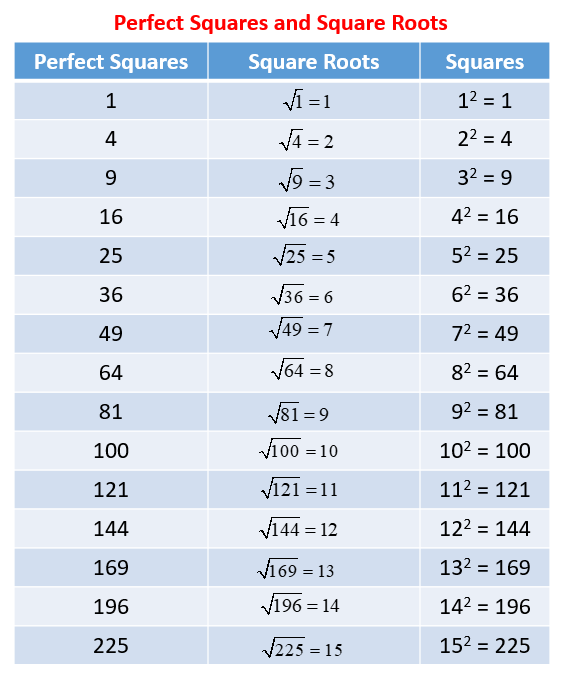
6. Square Roots of Perfect Squares
Understanding the square roots of perfect squares is a fundamental concept in mathematics. A perfect square is a number that is the product of an integer multiplied by itself. For example, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, and 36 are perfect squares because they can be expressed as 1², 2², 3², 4², 5², and 6² respectively.
Here's how to find and understand the square roots of perfect squares:
- Identify the Perfect Square: Determine if the number is a perfect square by seeing if it can be expressed as the square of an integer. For instance, 49 is a perfect square because 49 = 7².
- Find the Integer: Find the integer whose square gives the perfect square. For 49, the integer is 7 because 7 × 7 = 49.
- Square Root Symbol: Use the square root symbol (√) to represent the operation. The square root of 49 is written as √49 = 7.
Here are some examples:
| Perfect Square | Square Root |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 (since 1 = 1²) |
| 4 | 2 (since 4 = 2²) |
| 9 | 3 (since 9 = 3²) |
| 16 | 4 (since 16 = 4²) |
| 25 | 5 (since 25 = 5²) |
| 36 | 6 (since 36 = 6²) |
By recognizing and understanding perfect squares, you can easily find their square roots, which simplifies many mathematical operations.
7. Square Roots in Algebra
Square roots play a crucial role in algebra, particularly in solving equations and manipulating expressions involving variables. Understanding how square roots interact with algebraic expressions helps in various problem-solving scenarios:
- Solving Quadratic Equations: In algebra, quadratic equations often involve square roots, especially when solving for unknown variables. The process typically includes isolating the squared term and then taking the square root of both sides.
- Factoring: Square roots are utilized in factoring quadratic expressions. By finding the square roots of the constant and middle terms, one can determine factors that make up the original quadratic equation.
- Manipulating Expressions: Algebraic expressions containing square roots can be simplified and rearranged using algebraic techniques, facilitating easier analysis and computation.
- Applications in Geometry: Geometric problems often require algebraic manipulation involving square roots, such as finding distances, areas, or volumes of shapes.
- Complex Numbers: In advanced algebra, square roots are extended to include complex numbers, allowing solutions to equations that involve negative discriminants.
Mastering square roots in algebra opens pathways to solving more complex equations and understanding deeper mathematical concepts across various disciplines.
8. Solving Quadratics by Taking Square Roots
Solving quadratic equations using square roots is a fundamental technique in algebra. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Isolate the squared term: Bring all terms involving the variable to one side of the equation, leaving the squared term on its own.
- Take the square root: Apply the square root operation to both sides of the equation. Remember to consider both the positive and negative roots as solutions.
- Simplify and solve: Simplify the expression under the square root, if possible. Then, solve for the variable by isolating it on one side of the equation.
- Check solutions: Verify the solutions by substituting them back into the original equation. Ensure they satisfy all conditions.
This method is effective for quadratic equations that can be expressed in the form \( ax^2 + bx + c = 0 \), where \( a \neq 0 \). It provides a straightforward way to find solutions using basic algebraic operations.

9. Practical Applications of Square Roots
Square roots find extensive use in practical applications across various fields:
- Engineering: In structural engineering, square roots are employed to calculate forces, stresses, and material strengths.
- Physics: Square roots appear in formulas related to wave propagation, energy calculations, and electrical circuits.
- Finance: Square roots are used in financial modeling for risk assessment, volatility calculations, and option pricing.
- Medicine: In medical imaging, square roots help in image processing techniques such as noise reduction and signal enhancement.
- Statistics: Square roots are essential in statistical analysis, particularly for standard deviation calculations and normalization of data.
- Geometry: Square roots are fundamental in geometric calculations, including distances, areas, and volumes of shapes.
Understanding and applying square roots in these contexts enhance problem-solving abilities and enable precise calculations in real-world scenarios.
10. Square Root Functions and Their Graphs
Square root functions are a fundamental type of function in mathematics, characterized by the following properties:
- Domain and Range: The domain of a square root function consists of non-negative real numbers, while the range includes all non-negative real numbers.
- Behavior: Square root functions increase slowly as the input increases, exhibiting a concave shape.
- Graphical Representation: The graph of a square root function resembles a half of a sideways parabola, opening to the right from the point (0, 0).
- Transformations: Square root functions can undergo transformations such as translations, reflections, and stretches, altering their position and shape on the coordinate plane.
- Applications: They are used in various fields such as physics for modeling relationships involving square roots, including motion, waveforms, and rates of change.
Studying square root functions and their graphs provides insights into fundamental mathematical concepts and their applications in diverse disciplines.
11. Beginner Lessons on Square Roots
Welcome to the beginner lessons on square roots! This section is designed to introduce you to the fundamental concepts of square roots, making it easy to understand and apply them in various mathematical contexts.
Let's break down the lessons into simple, manageable steps:
-
What is a Square Root?
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of \(9\) is \(3\) because \(3 \times 3 = 9\).
In mathematical notation, this is written as \(\sqrt{9} = 3\).
-
Notation and Symbols
The symbol for square root is \(\sqrt{}\). For example, \(\sqrt{16} = 4\) because \(4 \times 4 = 16\).
-
Finding Square Roots
There are several methods to find the square root of a number:
- Using a calculator
- Prime factorization
- Estimation method
-
Examples
Let's look at a few examples:
- \(\sqrt{25} = 5\) because \(5 \times 5 = 25\)
- \(\sqrt{36} = 6\) because \(6 \times 6 = 36\)
- \(\sqrt{49} = 7\) because \(7 \times 7 = 49\)
-
Square Roots of Non-Perfect Squares
Sometimes, we need to find the square root of numbers that are not perfect squares, such as \(\sqrt{2}\) or \(\sqrt{3}\). These values are irrational numbers and can be approximated using a calculator.
For instance, \(\sqrt{2} \approx 1.414\) and \(\sqrt{3} \approx 1.732\).
-
Practice Problems
Try solving these problems to practice finding square roots:
- Find \(\sqrt{64}\).
- Find \(\sqrt{81}\).
- Approximate \(\sqrt{10}\).
Answers:
- \(\sqrt{64} = 8\)
- \(\sqrt{81} = 9\)
- \(\sqrt{10} \approx 3.162\)
We hope these beginner lessons help you grasp the basics of square roots. Continue practicing, and you'll become more comfortable with these concepts in no time!
12. Online Resources and Worksheets for Square Roots
Understanding and mastering square roots can be significantly enhanced with the help of various online resources and worksheets. Here is a comprehensive list of resources that provide videos, interactive worksheets, and printable materials for learning about square roots.
- Khan Academy
Khan Academy offers a wide range of resources on square roots, including video lessons and practice exercises. Their materials cover topics from the basics of square roots to more advanced concepts such as square root functions and solving equations with square roots. You can explore their content .
- Live Worksheets
Live Worksheets transforms traditional worksheets into interactive online exercises. Their square root worksheets help students practice finding the square roots of given perfect squares and other related exercises. Check out their worksheets .
- Math Worksheets 4 Kids
This site offers a variety of printable worksheets designed to help students in grades 6-8 understand square roots. These worksheets cover finding square roots of perfect squares, simplifying square roots, and more. Access their worksheets .
- Education.com
Education.com provides printable and interactive worksheets that are perfect for students looking to enhance their understanding of square roots. Their materials cater to different grade levels and learning styles. Browse their resources .
- Homeschool Math
Homeschool Math offers an unlimited supply of printable worksheets for square roots, including those for perfect squares and other operations. Their customizable worksheets can be tailored to different difficulty levels and formats. Visit their page .

What are Square Roots? | Math with Mr. J
Math Antics - Exponents and Square Roots
THE SQUARE ROOT 🚀 What is the Square Root? 👨🏻🚀 Math for Kids
Square root in 3 seconds - math trick
How To Simplify Square Roots
Introduction to square roots | Numbers and operations | 8th grade | Khan Academy
READ MORE: