Topic square root of/16: The square root of 16 is a fundamental mathematical concept, resulting in 4. This article explores the definition, methods of calculation, and significance of the square root of 16, providing insights into both perfect squares and rational numbers. Discover how to calculate it using various tools, and understand its place in the broader context of mathematics.
Table of Content
Understanding the Square Root of 16
The square root of 16 is a fundamental mathematical concept often encountered in various fields of study. Here, we will explore the value, methods to find it, and some practical examples.
Value of the Square Root of 16
The square root of 16 is:
\[\sqrt{16} = 4\]
It is a rational number since it can be expressed as an integer.
Methods to Find the Square Root of 16
- Prime Factorization Method: The prime factors of 16 are \(2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2\). Grouping the factors in pairs, we get \((2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) = 4 \times 4\), hence, \(\sqrt{16} = 4\).
- Long Division Method: By performing long division, we find that 4 multiplied by itself gives 16, so \(\sqrt{16} = 4\).
Examples and Applications
- Example 1: If Noah arranges 16 cubes in a square formation, the number of cubes on each side is \(\sqrt{16} = 4\).
- Example 2: Jake has a square flower bed with 16 plants. If he expands the bed to 36 plants, the number of plants per side becomes \(\sqrt{36} = 6\). Thus, 2 extra plants are added per row (6 - 4 = 2).
- Example 3: For an equilateral triangle with an area of \(16\sqrt{3}\), the side length is \(8\) units since \(a = 2\sqrt{16} = 8\).
FAQs on the Square Root of 16
- What is the Value of the Square Root of 16? The square root of 16 is 4.
- Is the Square Root of 16 a Rational Number? Yes, because it can be expressed as an integer.
- What is the Value of \(19 + 17\sqrt{16}\)? The value is \(87\) since \(17\sqrt{16} = 68\), thus \(19 + 68 = 87\).
- Is 16 a Perfect Square? Yes, because its prime factorization results in an integer when square-rooted.
Additional Information
The square root symbol is denoted as \(\sqrt{}\), with the number under the symbol called the radicand. For the square root of 16, \(\sqrt{16}\), the radicand is 16, and the principal square root is 4.
Table of nth Roots of 16
| Index (n) | Value (161/n) |
|---|---|
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 2.5198421 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 1.7411011 |
| 6 | 1.5874011 |
| 7 | 1.4859943 |
| 8 | 1.4142136 |
Understanding the square root of 16 provides a foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts and practical problem-solving skills.

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For the number 16, its square root is 4. The concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics, especially in algebra and geometry, as it helps in solving equations and understanding geometrical shapes and their properties. This section provides a detailed explanation of the square root of 16, including its calculation methods and practical applications.
There are several methods to find the square root of 16:
- Perfect Squares Method: Since 16 is a perfect square, it can be expressed as 4 × 4. Therefore, the square root of 16 is 4.
- Prime Factorization Method: By breaking down 16 into its prime factors, 16 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2, we pair the factors to find the square root. Here, the pairs are (2 × 2) and (2 × 2), which simplifies to 4.
- Long Division Method: This method involves a step-by-step process of division to find the square root, which is particularly useful for non-perfect squares.
The square root of 16 has several interesting properties and applications:
- Positive and Negative Roots: While the principal square root of 16 is 4, it also has a negative counterpart, -4, since (-4) × (-4) = 16.
- Rational Number: The square root of 16 is a rational number because it can be expressed as an integer, 4.
- Use in Geometry: The square root function is essential in calculating the side lengths of squares and right-angled triangles. For example, if a square has an area of 16 square units, each side length is the square root of 16, which is 4 units.
Understanding the square root of 16 helps in grasping broader mathematical concepts and solving various real-life problems efficiently.
What is the Square Root of 16?
The square root of 16 is a number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number 16. Symbolically, this is expressed as \( \sqrt{16} \). The square root of 16 is 4, because \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \). Here is a detailed explanation:
- Definition: The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, results in the original number. For 16, the square root is 4, since \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \).
- Radical Form: The simplest radical form of the square root of 16 is \( \sqrt{16} \). This form is derived from the prime factorization of 16, which is \( 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \). Hence, \( \sqrt{16} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2)} = \sqrt{4 \times 4} = 4 \).
- Rational Number: The square root of 16 is a rational number because it can be expressed as a fraction, \( 4/1 \).
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 16
-
Prime Factorization Method:
To find the square root using prime factorization:
- Find the prime factors of 16: \( 16 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \).
- Group the prime factors into pairs: \( (2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) \).
- Take one factor from each pair: \( 2 \times 2 = 4 \).
Therefore, \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
-
Long Division Method:
To find the square root using the long division method:
- Pair the digits of 16 from right to left: 16.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 16. Here, it is 4 since \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \).
- The quotient is 4, and the remainder is 0.
Therefore, \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
Examples
- Example 1: Simplify \( 7\sqrt{16} + 15 \).
Solution: Since \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \), substitute 4 into the expression:
\( 7\sqrt{16} + 15 = 7 \times 4 + 15 = 28 + 15 = 43 \).
- Example 2: Determine the value of \( m \) if \( m + \sqrt{16} = 20 \).
Solution: Since \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \), substitute 4 into the equation:
\( m + 4 = 20 \)
\( m = 20 - 4 = 16 \).
- Example 3: Simplify \( 5\sqrt{16} \div \sqrt{16} + 20 \).
Solution: Since \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \), substitute 4 into the expression:
\( 5\sqrt{16} \div \sqrt{16} + 20 = 5 \times 4 \div 4 + 20 = 20 \div 4 + 20 = 5 + 20 = 25 \).
Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization method is a simple and effective way to find the square root of a number by breaking it down into its prime factors. Here is a detailed step-by-step guide to finding the square root of 16 using the prime factorization method:
-
First, find the prime factors of 16. To do this, repeatedly divide the number by its smallest prime factor until the quotient is 1.
16 ÷ 2 = 8 8 ÷ 2 = 4 4 ÷ 2 = 2 2 ÷ 2 = 1 So, the prime factorization of 16 is \(2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2\) or \(2^4\).
-
Group the prime factors into pairs of equal factors. Each pair represents a squared term.
\(16 = (2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2)\)
-
Take one factor from each pair and multiply them together to find the square root.
\(\sqrt{16} = 2 \times 2 = 4\)
Thus, the square root of 16 is 4. The prime factorization method is particularly useful for perfect squares, where each prime factor appears an even number of times.
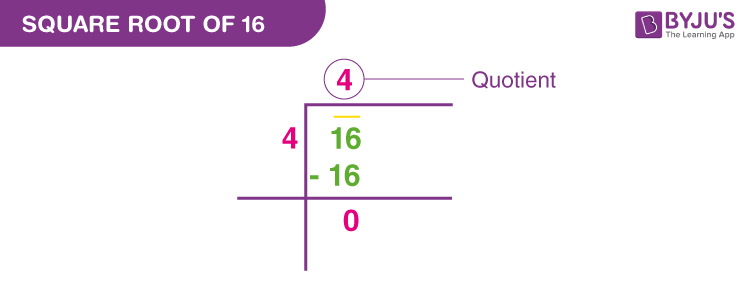
Long Division Method
The long division method is a systematic way to find the square root of a number. Here, we will detail the steps to find the square root of 16 using this method.
- Step 1: Write the number 16 and pair the digits by placing a bar over them from right to left. Since 16 has only two digits, it forms a single pair.
- Step 2: Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 16. Here, 4 × 4 = 16. So, 4 is the number we need.
- Step 3: Write 4 as both the quotient and divisor. Perform the division: 16 divided by 4 equals 4. Subtract 16 from 16 to get a remainder of 0.
- Step 4: Since the remainder is 0 and no more pairs are left, the quotient (4) is the square root of 16.
Thus, the square root of 16 using the long division method is found to be 4.
| Number | 16 |
| Step | Description |
| Step 1 | Pair the digits |
| Step 2 | Find the largest number whose square is ≤ 16 |
| Step 3 | Perform division (16 ÷ 4) |
| Step 4 | Square root is 4 |
Using this method, we have successfully calculated that the square root of 16 is 4.
Examples
Here are some detailed examples to understand the square root of 16:
- Example 1:
Find the square root of 16 using the prime factorization method.
- Prime factorize 16: \(16 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 = 2^4\).
- Take the square root of the prime factorization: \(\sqrt{16} = \sqrt{2^4} = 2^2 = 4\).
- Example 2:
Find the square root of 16 using the long division method.
- Set up the number in pairs: \(16\).
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair: \(4 \times 4 = 16\).
- The quotient is the square root: \(\sqrt{16} = 4\).
- Example 3:
Find the square root of 16 using estimation.
- Estimate numbers that, when squared, give 16. Start with 4 because \(4 \times 4 = 16\).
- Confirm that \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the value of the square root of 16?
The value of the square root of 16 is 4. This means that 4 multiplied by 4 equals 16.
-
Is the square root of 16 a rational number?
Yes, the square root of 16 is a rational number because it can be expressed as the ratio of two integers, specifically 4/1.
-
Is 16 a perfect square?
Yes, 16 is a perfect square because its square root is an integer. In this case, the integer is 4.
-
How can the square root of 16 be calculated using the prime factorization method?
To calculate the square root of 16 using the prime factorization method:
- Express 16 as a product of its prime factors: \(16 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2\).
- Group the factors into pairs: \((2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2)\).
- Each pair has a product of 4: \(4 \times 4\).
- Therefore, the square root of 16 is 4.
-
How can the square root of 16 be calculated using the long division method?
To calculate the square root of 16 using the long division method:
- Start by pairing the digits of the number from right to left. Here, 16 has only one pair, 16.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 16. This number is 4, because \(4 \times 4 = 16\).
- Write 4 as the quotient and multiply it by itself to subtract from 16, resulting in 0.
- Since there are no more digits to bring down, the process ends here. Therefore, the square root of 16 is 4.
-
What are some examples of problems involving the square root of 16?
- Example 1: Simplify \((7\sqrt{16}) + 15 = 43\)
- Example 2: If \(m + \sqrt{16} = 20\), then \(m = 16\)
- Example 3: Simplify \((5\sqrt{16} \div \sqrt{16}) + 20 = 25\)
Căn Bậc Hai của 16
READ MORE:
Căn Bậc Hai của 16! #Shorts #toán học #toán #toán học