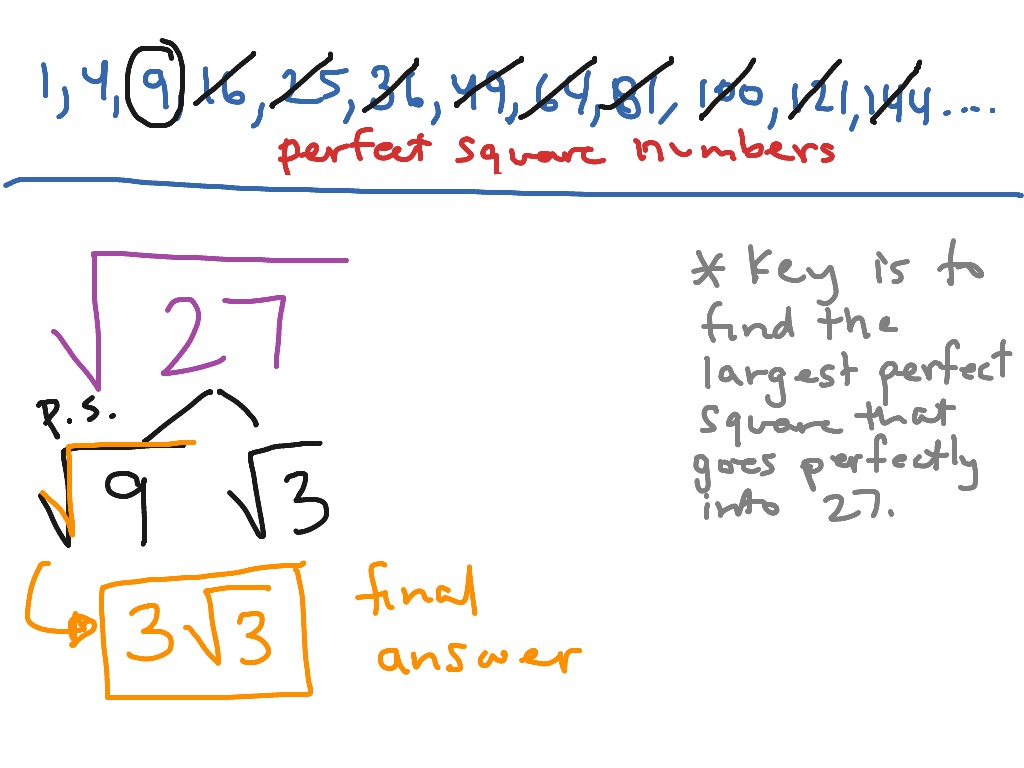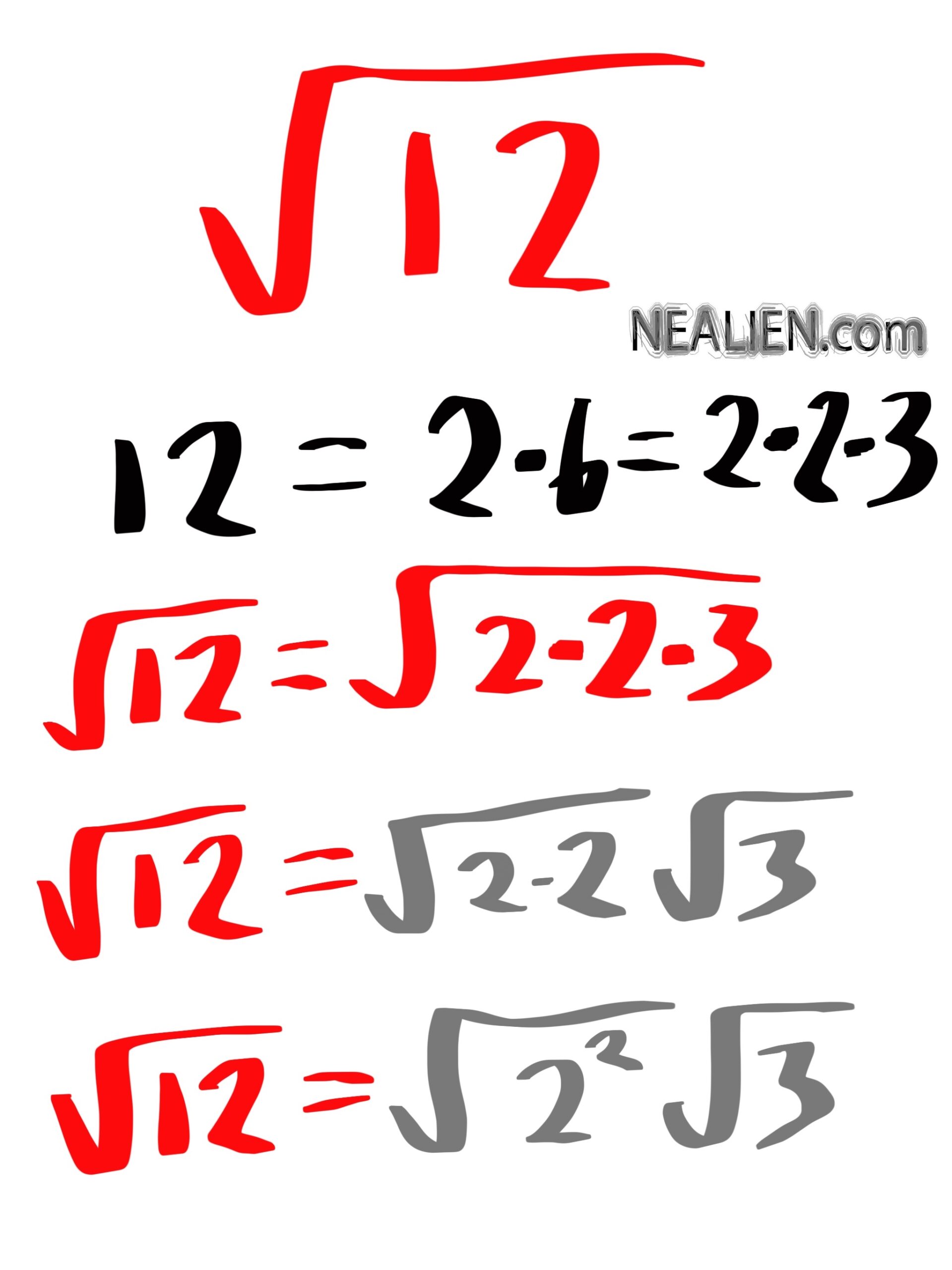Topic square root of 74 simplified: Discover the easy and effective method to simplify the square root of 74. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process, providing clear instructions and helpful tips to ensure you understand and can apply the technique confidently. Perfect for students and math enthusiasts alike!
Table of Content
- Square Root of 74 Simplified
- Introduction
- Understanding Square Roots
- Prime Factorization Method
- Finding Perfect Square Factors
- Simplifying the Square Root of 74
- Step-by-Step Simplification Process
- Verifying the Simplified Form
- Decimal Approximation of Square Root of 74
- Applications of Square Root of 74
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Practice Problems
- FAQs
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Xem video hướng dẫn Giản đơn Căn bậc hai 74 để hiểu rõ hơn về chủ đề này và áp dụng vào bài viết.
Square Root of 74 Simplified
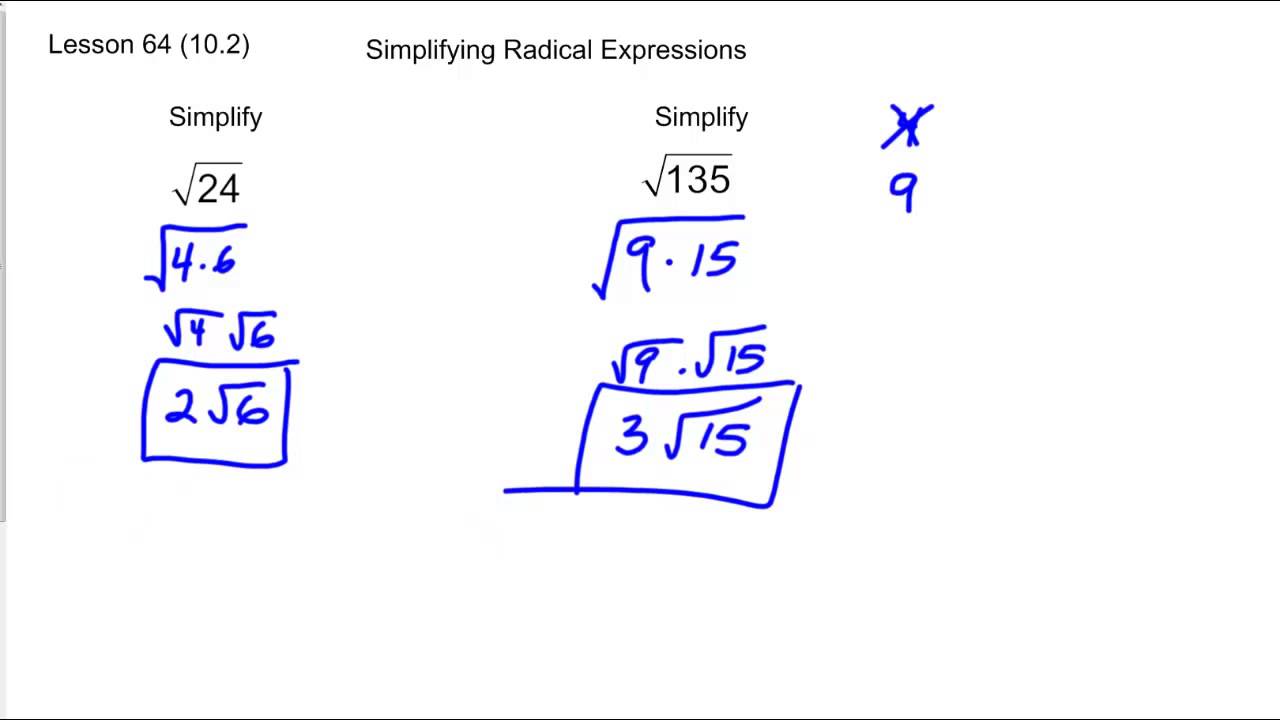
To simplify the square root of 74, we start by looking for perfect square factors. Here’s a step-by-step explanation:
Step 1: Prime Factorization
Find the prime factors of 74:
Since 37 is a prime number, the prime factorization of 74 is:
Step 2: Identify Perfect Squares
Check if any of the factors are perfect squares. The factors of 74 (2 and 37) are not perfect squares. Therefore, 74 cannot be simplified further by taking out any perfect square factors.
Step 3: Simplify the Radical
Since there are no perfect square factors other than 1, the square root of 74 remains:
The simplified form of the square root of 74 is:
Step 4: Decimal Approximation
To find a decimal approximation of the square root of 74, use a calculator:
Therefore, the square root of 74 is approximately 8.6.

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 74, denoted as \( \sqrt{74} \), is an irrational number. This means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal form is non-repeating and non-terminating. In this section, we will explore the properties of \( \sqrt{74} \), its approximate value, and various methods to compute it.
Firstly, the approximate value of the square root of 74 is 8.6. This approximation can be useful in various practical calculations.
There are three common methods to find the square root of a number:
- Prime Factorization Method
- Long Division Method
- Repeated Subtraction Method
Let's explore each method step by step:
Prime Factorization Method
In this method, we factorize the number 74 into its prime factors. The prime factors of 74 are 2 and 37. Since 74 does not have any repeated prime factors, we cannot simplify \( \sqrt{74} \) using prime factorization. Hence, \( \sqrt{74} \) remains in its simplest radical form.
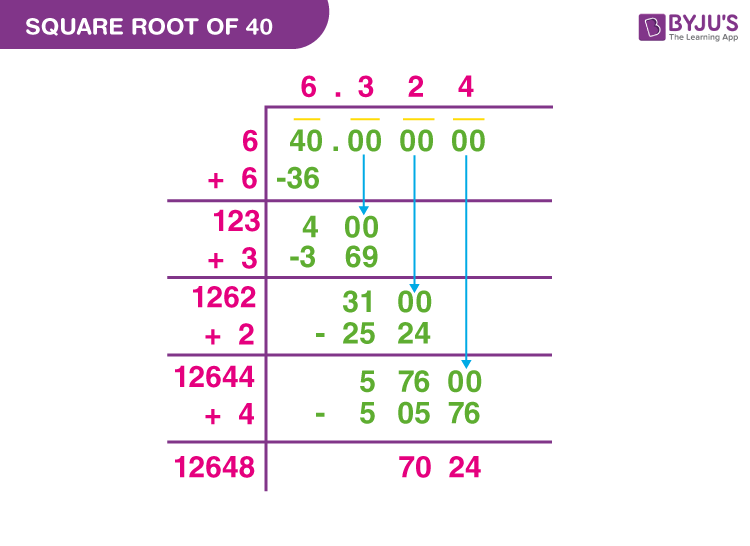
Long Division Method
The long division method involves dividing the number into pairs of digits from right to left and finding the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the number. Here's how it works for 74:
- Pair the digits: 74 becomes 74.00.
- Find the largest square less than or equal to 74, which is 8 (since \( 8^2 = 64 \)).
- Subtract 64 from 74 to get the remainder 10, and bring down the next pair of zeros to get 1000.
- Double the quotient (8) and find a digit (x) such that \( 16x \times x \leq 1000 \).
- Continue the process to get the decimal approximation.
The approximate value obtained through this method is 8.602.
Repeated Subtraction Method
In this method, we repeatedly subtract successive odd numbers from 74 until we reach zero or a negative result. Here are the steps:
- 74 - 1 = 73
- 73 - 3 = 70
- 70 - 5 = 65
- 65 - 7 = 58
- 58 - 9 = 49
- 49 - 11 = 38
- 38 - 13 = 25
- 25 - 15 = 10
- 10 - 17 = -7
Since the result becomes negative, we stop. The number of steps gives an approximation of the square root, but this method is less precise than others.
In conclusion, while the square root of 74 cannot be simplified further, it can be approximated using different methods. Understanding these methods can be helpful in various mathematical and practical applications.
Understanding Square Roots
A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. In mathematical terms, if \( x \) is the square root of \( y \), then \( x^2 = y \). Every positive number \( y \) has two square roots: a positive root and a negative root. For example, the square roots of 9 are 3 and -3, since \( 3^2 = 9 \) and \( (-3)^2 = 9 \).
The square root symbol is \( \sqrt{} \), and the number under the square root symbol is called the radicand. For instance, in \( \sqrt{74} \), 74 is the radicand.
Let's explore the properties and methods of finding square roots in detail.
- Principal Square Root: The principal square root of a number is the non-negative root. For example, the principal square root of 25 is 5, denoted as \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \).
- Perfect Squares: A perfect square is an integer that is the square of another integer. For example, 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25 are perfect squares because they are squares of 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, respectively.
- Irrational Numbers: Some numbers, like 74, are not perfect squares. Their square roots are irrational numbers, which cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and have non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansions. For example, \( \sqrt{74} \approx 8.6023 \).
Finding the square root of a non-perfect square involves approximation methods. Let's consider the common methods used to find the square roots.
- Prime Factorization Method: This method involves expressing the number as a product of its prime factors. For 74, the prime factorization is 2 and 37. Since there are no pairs of the same factor, \( \sqrt{74} \) remains as \( \sqrt{74} \).
- Long Division Method: This method involves a step-by-step division process to find the square root to a desired degree of accuracy. It's useful for finding decimal approximations of square roots.
- Repeated Subtraction Method: This method involves repeatedly subtracting odd numbers from the original number until zero is reached, indicating a perfect square, or the process stops, indicating an irrational square root.
Understanding these concepts and methods is crucial for solving problems involving square roots, whether they are perfect squares or not.
Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization method is an effective way to find the square root of a number by breaking it down into its prime factors. Here’s a detailed, step-by-step explanation of how to simplify the square root of 74 using the prime factorization method:
-
Perform prime factorization on the number 74. Identify and divide by its smallest prime factor:
- 74 is an even number, so divide it by 2:
- 37 is a prime number.
74 ÷ 2 = 37
-
Express 74 as a product of its prime factors:
74 = 2 × 37
-
Check for pairs of prime factors. Since 74 is expressed as 2 × 37 and neither of these numbers can be paired with another identical factor, there are no pairs to simplify further.
-
Since we cannot pair the factors, the square root of 74 remains in its simplified form as:
√74 = √(2 × 37)
-
Therefore, the simplified form of the square root of 74 is:
√74
The prime factorization method demonstrates that the square root of 74 cannot be simplified further due to the lack of paired prime factors.
Finding Perfect Square Factors
To simplify the square root of 74 using the method of finding perfect square factors, follow these steps:
- Identify the factors of 74. The factors are: 1, 2, 37, 74.
- Determine if any of these factors are perfect squares. In this case, 1 is the only perfect square factor.
- Since 1 is the only perfect square factor, and it does not help in simplifying the square root further, the square root of 74 cannot be simplified into a simpler radical form.
Thus, the simplest form of the square root of 74 remains \( \sqrt{74} \). However, if you are looking for its decimal approximation, it is approximately 8.60233.
For clarity, here is the breakdown:
- \(74 = 1 \times 74\) - Neither 1 nor 74 are squares that can simplify the radical further.
- The square root of 1 is 1, which does not change the expression.
- Thus, \( \sqrt{74} \) stays as it is.
If we are interested in expressing \( \sqrt{74} \) in other forms, we can write it as:
- Decimal form: 8.60233
- Exponent form: \( 74^{1/2} \)

Simplifying the Square Root of 74
Simplifying the square root of 74 involves determining if 74 has any perfect square factors. The goal is to express the square root in its simplest radical form. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
-
Check for perfect square factors: We need to see if 74 can be divided by any perfect squares (like 4, 9, 16, etc.). A quick check shows that 74 is not divisible by any of these.
-
Prime factorization: Break down 74 into its prime factors.
74 is even, so it's divisible by 2:
\(74 \div 2 = 37\)
37 is a prime number, so the prime factorization of 74 is:
\(74 = 2 \times 37\)
-
Identify perfect square factors: Since 74 is composed of the prime factors 2 and 37, and neither of these are perfect squares, 74 does not have any perfect square factors other than 1.
-
Express in simplest form: Since there are no perfect square factors in the prime factorization, the square root of 74 cannot be simplified further.
\(\sqrt{74}\) remains \(\sqrt{74}\).
In conclusion, the square root of 74 cannot be simplified and is already in its simplest radical form. Therefore, \(\sqrt{74}\) remains as \(\sqrt{74}\).
Step-by-Step Simplification Process
Simplifying the square root of 74 can be done through a detailed step-by-step process. Here’s how you can approach it:
-
Identify if 74 has perfect square factors:
First, check if 74 can be divided by any perfect squares such as 4, 9, 16, 25, etc.:
- 74 is not divisible by 4 (\(74 \div 4 = 18.5\))
- 74 is not divisible by 9 (\(74 \div 9 \approx 8.22\))
- 74 is not divisible by 16 (\(74 \div 16 \approx 4.625\))
- 74 is not divisible by 25 (\(74 \div 25 \approx 2.96\))
Since 74 is not divisible by any of these, it has no perfect square factors other than 1.
-
Perform prime factorization:
Break down 74 into its prime factors:
74 is even, so it is divisible by 2:
\(74 \div 2 = 37\)
37 is a prime number, so the prime factorization of 74 is:
\(74 = 2 \times 37\)
-
Re-write the square root using prime factors:
Express the square root of 74 using its prime factors:
\(\sqrt{74} = \sqrt{2 \times 37}\)
-
Check for simplification:
Since 2 and 37 are both prime numbers and not perfect squares, the square root cannot be simplified further. Thus, the square root of 74 remains:
\(\sqrt{74}\)
-
Approximate the decimal value (optional):
For practical purposes, you might want to know the decimal approximation of \(\sqrt{74}\). Using a calculator, you get:
\(\sqrt{74} \approx 8.6023\)
In summary, the square root of 74, \(\sqrt{74}\), cannot be simplified further and remains as \(\sqrt{74}\).
Verifying the Simplified Form
To verify the simplified form of the square root of 74, we need to ensure that the simplification process is accurate and that the resulting value is correct. Since 74 is not a perfect square and cannot be simplified into smaller square roots, we will verify that the square root of 74 is in its simplest form.
Here are the steps to verify:
-
Check for Perfect Square Factors:
We start by identifying if 74 has any perfect square factors (like 4, 9, 16, 25, etc.). Since 74 is a product of the primes 2 and 37 (74 = 2 × 37), and neither of these primes are perfect squares, 74 does not have any perfect square factors.
-
Prime Factorization:
The prime factorization of 74 is:
\[ 74 = 2 \times 37 \]
Neither 2 nor 37 is a perfect square, confirming that 74 does not have any square factors other than 1.
-
Ensuring the Root is in Simplest Form:
Since there are no perfect square factors of 74, the square root of 74 cannot be simplified further.
-
Decimal Approximation:
To further verify, we can approximate the square root of 74:
\[ \sqrt{74} \approx 8.6 \]
This approximation shows that \(\sqrt{74}\) is not a simple rational number but an irrational number, confirming our result that it cannot be simplified further.
Therefore, we conclude that the square root of 74 is already in its simplest form and cannot be simplified further. The value \(\sqrt{74}\) remains as it is.
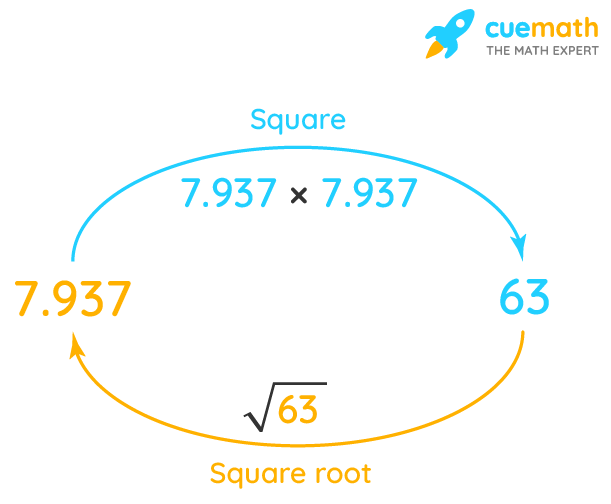
Decimal Approximation of Square Root of 74
The square root of 74 is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating. To find the decimal approximation, we can use a few different methods.
-
Using a Calculator:
The most straightforward method to approximate \(\sqrt{74}\) is to use a calculator. When you enter \(\sqrt{74}\) into a calculator, you get:
\[ \sqrt{74} \approx 8.602325267 \]
This value is precise to nine decimal places, but for most practical purposes, rounding to a few decimal places is sufficient. Commonly, \(\sqrt{74}\) is approximated as 8.60 or 8.602.
-
Long Division Method:
Another method is the long division method, which is a manual process to find the square root of a number to a desired level of accuracy. Here's a brief outline of the steps:
- Pair the digits of the number from right to left (74 becomes 74).
- Find the largest integer whose square is less than or equal to the leftmost pair. Here, it is 8, since \(8^2 = 64 \leq 74\).
- Subtract the square of this integer from the pair and bring down the next pair of digits (if any), and repeat the process.
This method can be continued to achieve the desired precision.
-
Estimating Between Perfect Squares:
We can estimate \(\sqrt{74}\) by noting it lies between two perfect squares:
\[ 8^2 = 64 \quad \text{and} \quad 9^2 = 81 \]
Since 74 is closer to 81 than to 64, \(\sqrt{74}\) will be closer to 9 than to 8. This gives a rough estimate:
\[ 8.5 < \sqrt{74} < 9 \]
Combining these methods, we confirm that the decimal approximation of \(\sqrt{74}\) is approximately 8.60. For most practical purposes, this approximation is sufficient, but more decimal places can be used if higher precision is needed.

Applications of Square Root of 74
The square root of 74, denoted as \( \sqrt{74} \), is an irrational number approximately equal to 8.602. It has various applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering. Here are some practical applications:
- Geometry: \( \sqrt{74} \) can be used in geometry to find the length of the diagonal of a square whose sides are each 37 units long.
- Finance: In financial calculations, \( \sqrt{74} \) might be used to compute the future value of an investment compounded over time.
- Physics: It appears in formulas related to acceleration due to gravity and other physical constants.
- Engineering: Engineers use \( \sqrt{74} \) in structural design calculations, such as determining the optimal length of a diagonal brace in a truss.
Understanding \( \sqrt{74} \) is crucial for various fields where precise calculations are necessary.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When simplifying the square root of 74, several common mistakes can lead to errors in calculations. Here are some pitfalls to watch out for:
- Incorrect Factorization: Mistaking the prime factors of 74 can result in an incorrect simplified form.
- Mathematical Errors: Failing to accurately follow the steps in the simplification process can lead to incorrect results.
- Ignoring Rational Approximations: Sometimes, overlooking rational approximations of \( \sqrt{74} \) can hinder finding a simplified form.
- Not Verifying Results: Forgetting to verify the accuracy of the simplified form can perpetuate mistakes.
- Confusing with Similar Numbers: Mixing up calculations with numbers close to 74, like 72 or 75, can lead to confusion.
By being mindful of these common errors, one can ensure a more accurate and reliable simplification of \( \sqrt{74} \).
Practice Problems
Practice solving these problems to reinforce your understanding of simplifying the square root of 74:
- Simplify \( \sqrt{74} \) using the prime factorization method.
- Find the closest integer approximation to \( \sqrt{74} \).
- Determine if \( \sqrt{74} \) is closer to 8 or 9, and justify your answer.
- Verify the simplified form of \( \sqrt{74} \) by squaring it and comparing the result to 74.
- Explain step-by-step how you would teach someone to simplify \( \sqrt{74} \) using prime factors.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about the square root of 74:
- What is the exact value of \( \sqrt{74} \)?
- How can I simplify \( \sqrt{74} \) to its simplest radical form?
- What are some real-world applications of \( \sqrt{74} \)?
- Is \( \sqrt{74} \) an irrational number?
- What are the common mistakes to avoid when simplifying \( \sqrt{74} \)?
- Can \( \sqrt{74} \) be expressed as a fraction?
- What is the decimal approximation of \( \sqrt{74} \)?
- How do you verify if \( \sqrt{74} \) is correctly simplified?

Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how to simplify the square root of 74 is essential for various mathematical applications. By following the prime factorization method and verifying the results, you can accurately express \( \sqrt{74} \) in its simplest form. Remember to avoid common mistakes such as incorrect factorization or mathematical errors. Knowing the practical applications and solving practice problems can further solidify your comprehension. Whether used in geometry, finance, physics, or engineering, \( \sqrt{74} \) serves as a fundamental component in precise calculations. Continuously practicing and applying these techniques will enhance your mathematical skills and problem-solving abilities.
Xem video hướng dẫn Giản đơn Căn bậc hai 74 để hiểu rõ hơn về chủ đề này và áp dụng vào bài viết.
Video Tiêu Chuẩn 74: Giản Đơn Căn Bậc Hai
READ MORE:
Xem video hướng dẫn 7 Cách Giản đơn Căn bậc hai 74 để hiểu rõ hơn về chủ đề này và áp dụng vào bài viết.
7 Cách Giản Đơn Căn Bậc Hai 74