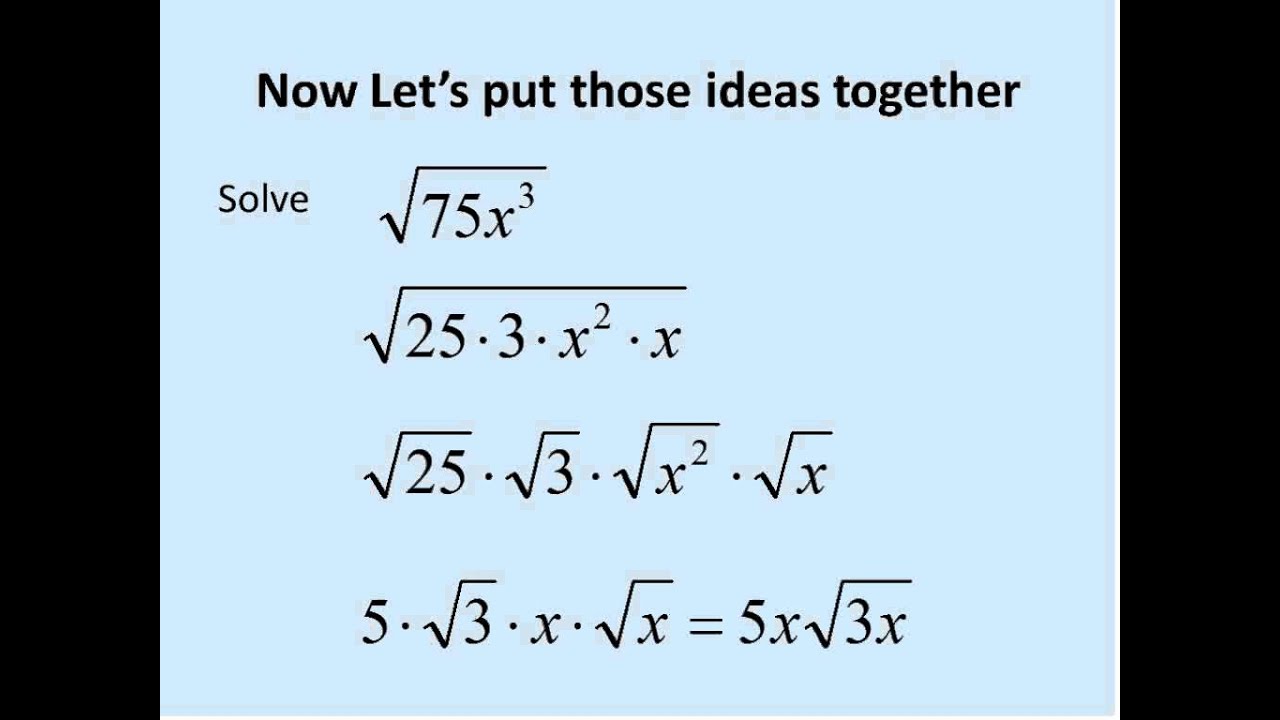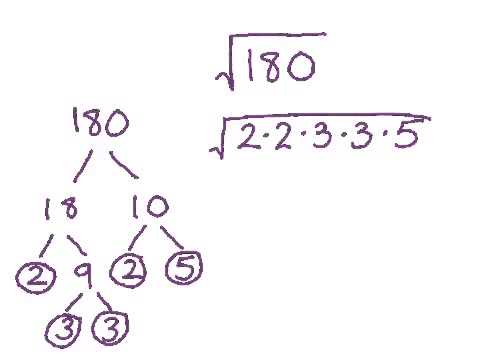Topic simplified square roots calculator: Discover the ease of simplifying square roots with our ultimate guide. Learn step-by-step methods, common mistakes to avoid, and the benefits of using a simplified square roots calculator. Whether you're a student or just brushing up on math skills, this article provides valuable insights and tools to make square root calculations effortless.
Table of Content
- Simplified Square Roots Calculator
- Introduction to Square Roots
- What is a Square Root?
- The Importance of Simplifying Square Roots
- Basic Concepts and Terminology
- Step-by-Step Guide to Simplifying Square Roots
- Prime Factorization Method
- Using the Division Method
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Advanced Techniques for Complex Roots
- Calculator Tools and Resources
- Benefits of Using a Calculator
- Comparison of Popular Calculators
- Mobile Apps for Simplifying Square Roots
- FAQs about Square Roots and Calculators
- Troubleshooting and Tips
- Further Reading and Learning Resources
- YOUTUBE:
Simplified Square Roots Calculator
A simplified square roots calculator helps in simplifying square roots to their simplest form. This involves finding the prime factors of the number under the square root and simplifying it by extracting the perfect squares.
How to Simplify Square Roots
- Find the prime factorization of the number inside the square root.
- Pair the prime factors.
- Move one of each pair outside the square root.
- Multiply the numbers outside the square root.
- Leave any numbers that do not have pairs inside the square root.
Example
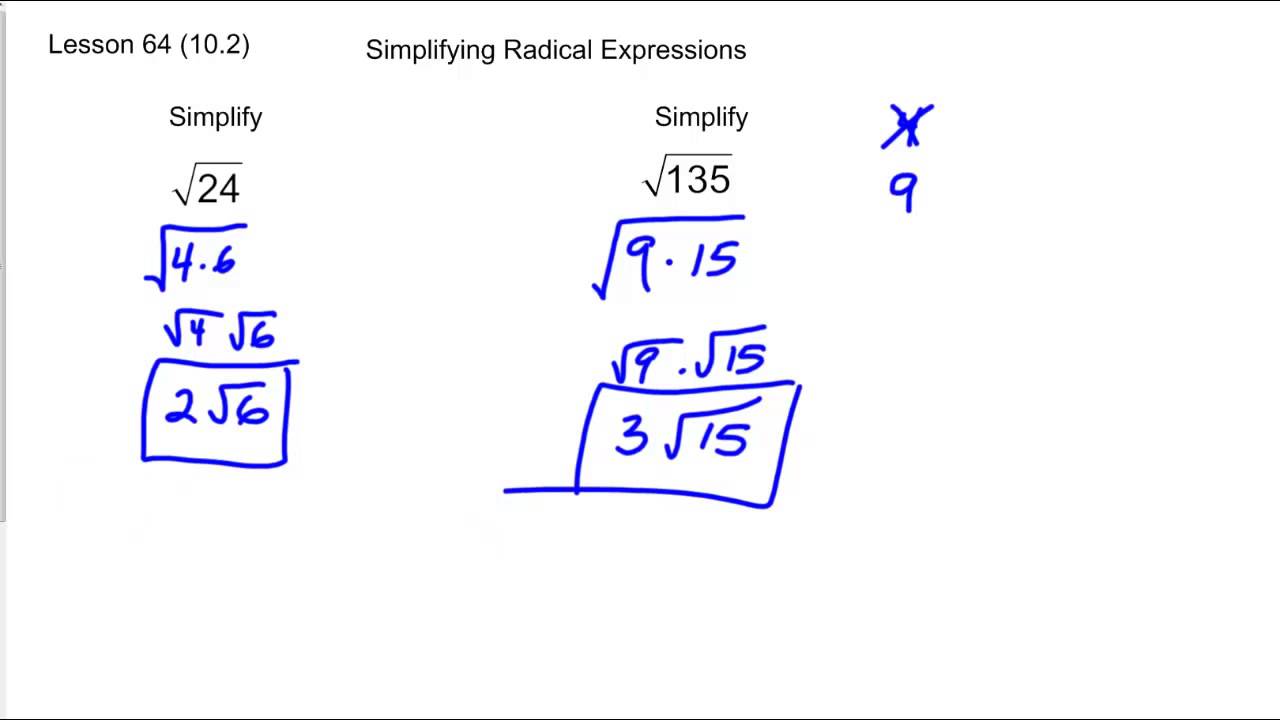
Simplify \( \sqrt{72} \):
- Prime factorization of 72: \( 72 = 2^3 \times 3^2 \)
- Pair the prime factors: \( (2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3) \times 2 \)
- Move one of each pair outside the square root: \( 2 \times 3 \sqrt{2} \)
- Multiply the numbers outside the square root: \( 6\sqrt{2} \)
Thus, \( \sqrt{72} = 6\sqrt{2} \)
Online Simplified Square Roots Calculators
- Many websites offer free online calculators to simplify square roots.
- These calculators can quickly and accurately simplify any square root.
- Simply enter the number and get the simplified form instantly.
Benefits of Using Simplified Square Roots Calculators
- Saves time and effort in manual calculations.
- Reduces the risk of errors.
- Helpful for students and professionals dealing with mathematical problems.
Conclusion
Utilizing a simplified square roots calculator is an efficient way to handle square root problems. It simplifies the process and ensures accuracy, making it an invaluable tool for anyone working with mathematics.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
Square roots are fundamental concepts in mathematics, representing a number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For instance, the square root of 16 is 4, as \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \).
Understanding square roots is crucial for solving various mathematical problems, from basic arithmetic to complex algebra.
Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide to understanding square roots:
- Definition: The square root of a number \( x \) is a value \( y \) such that \( y^2 = x \). It is denoted as \( \sqrt{x} \).
- Notation: The square root symbol is \( \sqrt{} \). For example, \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \) because \( 5^2 = 25 \).
- Properties:
- Non-negative Numbers: Square roots are defined for non-negative numbers. For instance, \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \) and \( \sqrt{0} = 0 \).
- Principal Square Root: The principal square root is the non-negative root of a number. For example, \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \), not -2.
- Product Property: \( \sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \). For example, \( \sqrt{36} = \sqrt{9 \times 4} = \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{4} = 3 \times 2 = 6 \).
- Quotient Property: \( \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \). For example, \( \sqrt{\frac{25}{4}} = \frac{\sqrt{25}}{\sqrt{4}} = \frac{5}{2} \).
- Simplifying Square Roots: To simplify a square root, factor the number into its prime factors and pair the factors. For example:
- Factor 18 into prime factors: \( 18 = 2 \times 3 \times 3 \).
- Group the pairs: \( 18 = 3^2 \times 2 \).
- Take the square root of each pair: \( \sqrt{18} = \sqrt{3^2 \times 2} = 3\sqrt{2} \).
- Using Calculators: Modern calculators and online tools can quickly find square roots and simplify them. They are especially useful for larger numbers or for verifying your manual calculations.
With these foundational concepts, you can confidently approach problems involving square roots and utilize calculators to simplify your work efficiently.
What is a Square Root?
A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. It is one of the fundamental operations in mathematics and has various applications in different fields such as geometry, algebra, and calculus.
The square root of a number \( x \) is denoted by \( \sqrt{x} \). For example, \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \) because \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \).
Here’s a detailed breakdown of square roots:
- Basic Definition: The square root of a number \( x \) is a value \( y \) such that \( y^2 = x \). It is written as \( y = \sqrt{x} \).
- Positive and Negative Roots: Every positive number has two square roots: a positive root and a negative root. For example, \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \) and \( -\sqrt{25} = -5 \) because both \( 5^2 \) and \( (-5)^2 \) equal 25.
- Principal Square Root: By convention, the principal square root is the non-negative root. Thus, \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \), not -5.
- Perfect Squares: Numbers like 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25 are perfect squares because their square roots are integers. For example, \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \).
- Non-Perfect Squares: Numbers that are not perfect squares have irrational square roots. For example, \( \sqrt{2} \) is approximately 1.414 and cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
- Properties of Square Roots:
- Product Property: \( \sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \). For instance, \( \sqrt{36} = \sqrt{9 \times 4} = \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{4} = 3 \times 2 = 6 \).
- Quotient Property: \( \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \). For example, \( \sqrt{\frac{25}{4}} = \frac{\sqrt{25}}{\sqrt{4}} = \frac{5}{2} \).
- Square of a Square Root: \( (\sqrt{a})^2 = a \). For example, \( (\sqrt{5})^2 = 5 \).
Square roots are essential for solving quadratic equations, analyzing geometric shapes, and performing various calculations in science and engineering. They simplify the understanding of numbers and their relationships, making them a critical concept in mathematics.
The Importance of Simplifying Square Roots
Simplifying square roots is a crucial skill in mathematics, providing numerous benefits in problem-solving and understanding complex concepts. Simplified square roots make calculations easier and results more comprehensible. Here’s why simplifying square roots is important:
- Improved Clarity:
- Simplified expressions are easier to read and interpret. For example, \( \sqrt{50} \) is simplified to \( 5\sqrt{2} \), which is more concise.
- Clearer expressions help avoid confusion in multi-step problems.
- Simplification in Solving Equations:
- In algebra, simplifying square roots can help solve quadratic equations more efficiently.
- It aids in isolating variables and simplifying the overall problem-solving process.
- Facilitates Further Calculations:
- Simplified square roots make subsequent mathematical operations, such as addition, subtraction, and multiplication, more manageable.
- For instance, combining like terms is easier with simplified roots: \( 2\sqrt{3} + 3\sqrt{3} = 5\sqrt{3} \).
- Enhanced Understanding:
- Understanding the process of simplification deepens comprehension of number properties and relationships.
- It reinforces knowledge of prime factorization and the properties of exponents.
- Application in Geometry:
- Simplified square roots are essential in geometric calculations, such as finding the lengths of sides in right triangles using the Pythagorean theorem.
- They help in accurately determining areas and volumes of various shapes.
- Preparation for Advanced Mathematics:
- Simplifying square roots lays the foundation for higher-level math courses, including calculus and linear algebra.
- It is a critical skill for standardized tests and advanced problem-solving scenarios.
- Use in Real-Life Applications:
- Simplified square roots are used in various fields, such as engineering, physics, and computer science, for precise calculations and modeling.
- They are also applied in financial calculations, such as determining interest rates and growth projections.
In conclusion, simplifying square roots is not just a mathematical exercise but a practical skill that enhances problem-solving capabilities and prepares individuals for advanced mathematical and real-world applications.
Basic Concepts and Terminology
Understanding the basic concepts and terminology associated with square roots is essential for mastering their simplification and application. Here are the key concepts and terms you need to know:
- Square Root (\(\sqrt{} \)):
- The square root of a number \( x \) is a value \( y \) such that \( y^2 = x \). It is represented by the symbol \( \sqrt{x} \).
- For example, \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \) because \( 5 \times 5 = 25 \).
- Perfect Squares:
- Numbers that have integer square roots are called perfect squares.
- Examples include 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, etc., where \( \sqrt{1} = 1 \), \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \), \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \), etc.
- Principal Square Root:
- The non-negative square root of a number is known as the principal square root.
- For example, while both 5 and -5 are square roots of 25, the principal square root is 5.
- Irrational Numbers:
- Numbers that cannot be expressed as simple fractions and have non-repeating, non-terminating decimal parts are called irrational numbers.
- Square roots of non-perfect squares are often irrational. For example, \( \sqrt{2} \approx 1.414 \).
- Simplifying Square Roots:
- To simplify a square root, express the number as a product of its prime factors and then simplify.
- For example, \( \sqrt{72} \) can be simplified as:
- Factorize 72 into prime factors: \( 72 = 2^3 \times 3^2 \).
- Group the pairs: \( 72 = (2^2 \times 3^2) \times 2 = (2 \times 3)^2 \times 2 = 6^2 \times 2 \).
- Take the square root of each pair: \( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{6^2 \times 2} = 6\sqrt{2} \).
- Radical Expression:
- An expression that includes a square root (or other roots) is called a radical expression.
- For example, \( \sqrt{18} \) is a radical expression.
- Radicand:
- The number inside the radical symbol is called the radicand.
- In \( \sqrt{25} \), 25 is the radicand.
- Exponentiation:
- Square roots can also be expressed as exponents. For example, \( \sqrt{x} = x^{1/2} \).
- This notation is useful in algebraic manipulation and solving equations.
Familiarity with these basic concepts and terminology will help you understand and simplify square roots effectively, making mathematical problems more manageable.
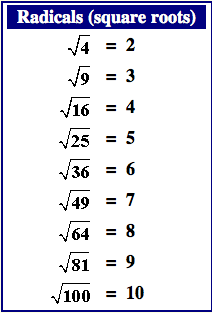
Step-by-Step Guide to Simplifying Square Roots
Simplifying square roots involves expressing the square root in its simplest form. Follow these steps to simplify square roots effectively:
- Identify the Radicand:
The radicand is the number inside the square root symbol. For example, in \( \sqrt{50} \), 50 is the radicand.
- Prime Factorization:
Break down the radicand into its prime factors. This helps in identifying pairs of factors.
- Example: \( 50 = 2 \times 5 \times 5 \).
- Group the Pairs:
Group the prime factors into pairs of identical numbers.
- Example: \( 50 = 2 \times (5 \times 5) \).
- Simplify the Pairs:
For each pair of identical numbers, take one number out of the square root.
- Example: \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2} = 5\sqrt{2} \).
- Final Simplified Form:
Combine the numbers taken out of the square root with the remaining factors inside the square root.
- Example: \( \sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2} \).
Here’s a more detailed example to illustrate the process:
- Example: Simplify \( \sqrt{72} \)
- Identify the radicand: 72
- Prime factorization: \( 72 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3 \)
- Group the pairs: \( 72 = (2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3) \times 2 \)
- Simplify the pairs: \( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{(2^2) \times (3^2) \times 2} \)
- Take one number out of each pair: \( \sqrt{72} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{2} \)
- Final simplified form: \( \sqrt{72} = 6\sqrt{2} \)
By following these steps, you can simplify any square root. Simplifying square roots makes it easier to work with them in equations and other mathematical expressions.
Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization method is a systematic approach to simplifying square roots by breaking down the radicand into its prime factors. Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide:
- Identify the Radicand:
The radicand is the number inside the square root symbol. For example, in \( \sqrt{72} \), 72 is the radicand.
- Perform Prime Factorization:
Break down the radicand into its prime factors. Prime factors are the prime numbers that multiply together to give the original number.
- Example: \( 72 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3 \)
- Group the Prime Factors:
Group the prime factors into pairs of identical numbers.
- Example: \( 72 = (2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3) \times 2 \)
- Extract the Pairs:
For each pair of identical numbers, take one number out of the square root.
- Example: \( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{(2^2) \times (3^2) \times 2} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{2} \)
- Multiply the Extracted Numbers:
Multiply the numbers taken out of the square root to get the simplified form.
- Example: \( \sqrt{72} = 6\sqrt{2} \)
Let’s apply these steps to another example:
- Example: Simplify \( \sqrt{180} \)
- Identify the radicand: 180
- Prime factorization: \( 180 = 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3 \times 5 \)
- Group the prime factors: \( 180 = (2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3) \times 5 \)
- Extract the pairs: \( \sqrt{180} = \sqrt{(2^2) \times (3^2) \times 5} \)
- Take one number out of each pair: \( \sqrt{180} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{5} \)
- Multiply the extracted numbers: \( \sqrt{180} = 6\sqrt{5} \)
By using the prime factorization method, you can simplify square roots systematically and accurately. This method is particularly useful for larger numbers and ensures that the simplification process is thorough and precise.
Using the Division Method
The division method is another effective technique for simplifying square roots. This method involves dividing the radicand by the largest possible perfect square. Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide:
- Identify the Radicand:
The radicand is the number inside the square root symbol. For example, in \( \sqrt{98} \), 98 is the radicand.
- Find the Largest Perfect Square Factor:
Determine the largest perfect square that divides the radicand evenly.
- Example: The largest perfect square that divides 98 is 49 because \( 49 \times 2 = 98 \).
- Rewrite the Radicand:
Express the radicand as a product of the largest perfect square factor and another factor.
- Example: \( 98 = 49 \times 2 \).
- Separate the Square Roots:
Use the property \( \sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \) to separate the square roots.
- Example: \( \sqrt{98} = \sqrt{49 \times 2} = \sqrt{49} \times \sqrt{2} \).
- Simplify the Perfect Square Root:
Simplify the square root of the perfect square factor.
- Example: \( \sqrt{49} = 7 \).
- Combine the Results:
Multiply the simplified square root of the perfect square by the remaining square root.
- Example: \( \sqrt{98} = 7\sqrt{2} \).
Let’s apply these steps to another example:
- Example: Simplify \( \sqrt{200} \)
- Identify the radicand: 200
- Find the largest perfect square factor: 100 (since \( 100 \times 2 = 200 \))
- Rewrite the radicand: \( 200 = 100 \times 2 \)
- Separate the square roots: \( \sqrt{200} = \sqrt{100 \times 2} = \sqrt{100} \times \sqrt{2} \)
- Simplify the perfect square root: \( \sqrt{100} = 10 \)
- Combine the results: \( \sqrt{200} = 10\sqrt{2} \)
The division method is a straightforward approach to simplifying square roots, especially useful when the radicand has an easily identifiable perfect square factor. This method helps in breaking down complex square roots into simpler, more manageable components.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When simplifying square roots, there are several common mistakes that learners often make. Being aware of these errors can help you avoid them and simplify square roots accurately. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Not Fully Factoring the Radicand:
Ensure you perform a complete prime factorization of the radicand. Missing factors can lead to incorrect simplification.
- Incorrect: \( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{8 \times 9} = 3\sqrt{8} \)
- Correct: \( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{2^3 \times 3^2} = 6\sqrt{2} \)
- Ignoring Perfect Squares:
Always check if the radicand contains perfect square factors that can be simplified.
- Incorrect: \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{5 \times 10} = \sqrt{5} \times \sqrt{10} \)
- Correct: \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25 \times 2} = 5\sqrt{2} \)
- Forgetting to Simplify Completely:
Sometimes, after partial simplification, the remaining radicand can still be simplified further.
- Incorrect: \( \sqrt{18} = \sqrt{9 \times 2} = 3\sqrt{2} \)
- Correct: \( \sqrt{18} = \sqrt{9 \times 2} = 3\sqrt{2} \) (initially correct but always recheck for further simplification)
- Misapplying the Distributive Property:
Ensure correct application of properties when dealing with sums or differences under the square root.
- Incorrect: \( \sqrt{a + b} = \sqrt{a} + \sqrt{b} \)
- Correct: \( \sqrt{a + b} \neq \sqrt{a} + \sqrt{b} \)
- Incorrect Pairing of Factors:
When grouping prime factors, ensure that pairs are correctly identified.
- Incorrect: \( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3} = 2 \times 3 = 6 \)
- Correct: \( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{(2^2) \times (3^2) \times 2} = 6\sqrt{2} \)
- Forgetting the Principal Square Root:
Remember that the square root symbol refers to the principal (non-negative) square root.
- Incorrect: \( \sqrt{25} = \pm5 \)
- Correct: \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \)
Avoiding these common mistakes will help you simplify square roots correctly and efficiently. Practice and attention to detail are key to mastering this skill.
Examples and Practice Problems
Here are some detailed examples and practice problems to help you understand and simplify square roots. We will use methods such as prime factorization and recognizing perfect squares.
Example 1: Simplifying √72
Step-by-step:
- Factor 72 into prime factors: 72 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3
- Group the prime factors into pairs: (2 × 2) and (3 × 3)
- Take one number from each pair out of the square root: 2 and 3
- Multiply the numbers taken out of the square root: 2 × 3 = 6
- The simplified form of √72 is: 6√2
Example 2: Simplifying √180
Step-by-step:
- Factor 180 into prime factors: 180 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 5
- Group the prime factors into pairs: (2 × 2) and (3 × 3)
- Take one number from each pair out of the square root: 2 and 3
- Multiply the numbers taken out of the square root: 2 × 3 = 6
- The simplified form of √180 is: 6√5
Practice Problems
Try simplifying the following square roots on your own:
- √50
- √98
- √200
- √320
Solution to Practice Problems
Check your answers:
- √50 = 5√2
- √98 = 7√2
- √200 = 10√2
- √320 = 8√5
Advanced Example: Simplifying Fractions with Square Roots
Example: Simplify √(30/10)
- Combine the numbers under a single square root: √(30/10) = √3
- The simplified form of √(30/10) is: √3
Additional Practice
Try these additional problems:
- √(45/5)
- √(48/12)
- √(80/20)
Solution to Additional Practice
Check your answers:
- √(45/5) = √9 = 3
- √(48/12) = √4 = 2
- √(80/20) = √4 = 2
Advanced Techniques for Complex Roots
When dealing with complex square roots, the process can be more intricate compared to simpler square roots. Here are some advanced techniques that can help you simplify and understand complex roots more effectively.
Understanding Complex Numbers
Before diving into techniques, it's essential to understand complex numbers. A complex number is of the form \(a + bi\), where \(i\) is the imaginary unit, satisfying \(i^2 = -1\).
Technique 1: Simplifying Square Roots of Negative Numbers
To simplify the square root of a negative number, you can use the property \( \sqrt{-a} = i\sqrt{a} \), where \(a\) is a positive number.
- Example: \( \sqrt{-16} = 4i \)
- Example: \( \sqrt{-25} = 5i \)
Technique 2: Using the Conjugate
For complex numbers, the conjugate of \(a + bi\) is \(a - bi\). Using the conjugate can help in simplifying expressions involving complex roots.
- Example: \( (3 + 4i) \cdot (3 - 4i) = 3^2 - (4i)^2 = 9 + 16 = 25 \)
Technique 3: Polar Form of Complex Numbers
Complex numbers can also be represented in polar form as \( r(\cos \theta + i \sin \theta) \), where \( r \) is the modulus and \( \theta \) is the argument.
- Convert \( a + bi \) to polar form: \( r = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \), \( \theta = \tan^{-1}(b/a) \)
- Example: Convert \( 3 + 4i \) to polar form: \( r = 5 \), \( \theta = \tan^{-1}(4/3) \)
Technique 4: De Moivre's Theorem
De Moivre's theorem is useful for finding powers and roots of complex numbers in polar form: \[ (r(\cos \theta + i \sin \theta))^n = r^n (\cos(n\theta) + i \sin(n\theta)) \]
- Example: Find \( (1 + i)^4 \):
- Convert to polar form: \( r = \sqrt{2} \), \( \theta = \pi/4 \)
- Apply De Moivre's theorem: \((\sqrt{2} (\cos \pi/4 + i \sin \pi/4))^4 = 4 (\cos \pi + i \sin \pi) = -4\)
Example Problems
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| \( \sqrt{-49} \) | \( 7i \) |
| \( (2 + 3i) \cdot (2 - 3i) \) | 13 |
| Convert \( 5 - 12i \) to polar form | \( 13(\cos(-\pi/2.84) + i \sin(-\pi/2.84)) \) |
Calculator Tools and Resources
Simplifying square roots can be challenging, but there are several tools and resources available to help you. Here are some of the best options:
Online Calculators
Online square root calculators are convenient and user-friendly. They allow you to input a number and receive the simplified square root almost instantly. Here are some recommended online calculators:
- - A simple and straightforward tool that provides quick results.
- - Offers step-by-step solutions and explanations.
- - Provides detailed solutions and graphical representations.
Mobile Apps
For those who prefer using mobile devices, several apps are available for both iOS and Android:
- - An app that solves math problems including square roots and provides step-by-step explanations.
- - A comprehensive math app that includes a square root calculator among its many features.
- - Offers a variety of mathematical tools, including a square root calculator, with detailed solutions.
Software and Desktop Applications
If you prefer desktop applications, these programs offer robust functionality for simplifying square roots:
- - A powerful computational software that can handle complex mathematical operations, including square root simplification.
- - Provides advanced mathematical tools and visualizations, perfect for in-depth study and simplification of square roots.
Step-by-Step Guide Using Online Calculators
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use an online square root calculator:
- Open your web browser and navigate to one of the recommended online calculators, such as .
- Enter the number for which you need to simplify the square root into the input field.
- Click on the "Calculate" button to process the input.
- View the result, which will display the simplified square root.
- Some calculators, like Mathway and Symbolab, will also provide step-by-step solutions to help you understand the process.
Additional Resources
For further learning and practice, consider these additional resources:
- - Offers video tutorials and practice exercises on simplifying square roots.
- - Provides comprehensive lessons and examples on working with square roots and radicals.
- - A user-friendly site with explanations and interactive tools for simplifying square roots.
Benefits of Using a Calculator
Using a calculator to simplify square roots offers numerous benefits, especially for students and professionals who frequently work with mathematical concepts. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Accuracy: Calculators provide precise results, minimizing the risk of human error. This is particularly important in complex calculations where manual simplification can lead to mistakes.
- Time-Saving: Simplifying square roots manually can be time-consuming, especially for larger numbers. Calculators can perform these operations almost instantly, allowing users to focus on understanding and applying the results rather than getting bogged down in the arithmetic.
- Accessibility: Modern calculators are easily accessible on various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and computers. This means that users can simplify square roots anytime, anywhere, without the need for specialized tools.
- Educational Support: Many calculators come with step-by-step solutions, helping users understand the process of simplification. This educational feature can reinforce learning and improve mathematical skills.
- Complex Calculations: For more advanced mathematical problems, calculators can handle complex roots and provide results that would be difficult to obtain manually. This is essential for higher-level mathematics in fields such as engineering and physics.
- Consistency: Using a calculator ensures consistent results every time. This is crucial for repeated calculations and when verifying results.
Overall, using a calculator for simplifying square roots enhances efficiency, accuracy, and understanding, making it an invaluable tool for both educational and professional purposes.

Comparison of Popular Calculators
When it comes to simplifying square roots, several online calculators stand out for their unique features and ease of use. Here, we compare some of the most popular options available:
| Calculator | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Symbolab |
|
|
|
| Calculator Soup |
|
|
|
| Mathway |
|
|
|
| Math Warehouse |
|
|
|
| Number Maniacs |
|
|
|
Each of these calculators has its own strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different types of users. For detailed explanations and educational resources, Symbolab and Math Warehouse are excellent choices. For quick and straightforward calculations, Calculator Soup and Number Maniacs offer user-friendly interfaces. Mathway provides a comprehensive mobile solution, ideal for users needing advanced problem-solving capabilities on the go.
Mobile Apps for Simplifying Square Roots
Mobile apps can be extremely helpful tools for simplifying square roots. These apps offer various features that enhance learning and make calculations more accessible. Here are some of the popular mobile apps available for simplifying square roots:
- Symbolab: This app offers a comprehensive calculator that can simplify square roots and perform a wide range of mathematical operations. It provides step-by-step solutions and explanations, which are useful for learning and understanding the process of simplification.
- Mathway: Known for its extensive problem-solving capabilities, Mathway can simplify square roots by providing exact and decimal form answers. It also allows users to take photos of their problems and receive instant solutions.
- Omni Calculator: Omni Calculator's app features a dedicated square root simplification tool that explains each step of the process. This app is particularly useful for those looking to understand the principles behind the calculations.
- Number Maniacs Simplify Square Root Calculator: This app focuses on simplifying square roots to their simplest form and provides detailed, step-by-step instructions. It is designed to help users grasp the concept of square root simplification thoroughly.
These mobile apps offer various benefits:
- Convenience: Having a square root calculator on your mobile device means you can perform calculations anywhere, anytime.
- Educational Value: Step-by-step explanations help users learn and understand the process of simplifying square roots, making these apps valuable educational tools.
- Accuracy: Mobile apps provide precise and accurate results, reducing the risk of errors in manual calculations.
- Time-Saving: These apps quickly perform complex calculations, saving users a significant amount of time compared to manual computation.
Whether you are a student, educator, or professional, using a mobile app to simplify square roots can enhance your mathematical proficiency and provide a reliable tool for quick and accurate calculations.
FAQs about Square Roots and Calculators
-
What is a square root?
A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because \(3 \times 3 = 9\).
-
How do you simplify a square root?
To simplify a square root, you factor the number into its prime factors and pair the common factors. For instance, to simplify \(\sqrt{72}\), you factor it into \(\sqrt{36 \times 2} = 6\sqrt{2}\).
-
Can you find the square root of a negative number?
Yes, but the result is an imaginary number. The square root of a negative number involves the imaginary unit \(i\), where \(i^2 = -1\). For example, \(\sqrt{-9} = 3i\).
-
What methods can be used to calculate square roots?
Common methods include the long division method and the Babylonian method. Calculators typically use iterative methods for fast approximations.
-
What is a perfect square?
A perfect square is an integer that is the square of another integer. Examples include 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25.
-
How accurate are online square root calculators?
Most online calculators provide highly accurate results for practical purposes, though they are limited by the precision of digital computation.
-
How are square roots used in real life?
Square roots are used in various fields such as engineering, physics, and statistics to solve problems involving areas, volumes, and other calculations.
-
What is the symbol for the square root?
The symbol for the square root is \(\sqrt{}\), also known as the radical sign.
-
Can all numbers have square roots?
Yes, all real numbers have square roots. Positive numbers have both positive and negative square roots, zero has one square root (which is zero), and negative numbers have imaginary square roots.
-
What is the principal square root?
The principal square root is the non-negative square root of a number. For example, the principal square root of 9 is 3.
Troubleshooting and Tips
When using a simplified square roots calculator, you might encounter some common issues. Here are some troubleshooting tips and useful advice to help you get accurate results:
Common Issues
- Incorrect Input: Ensure that you are entering the correct format for the number you want to simplify. For example, enter the number under the square root symbol correctly.
- Complex Numbers: Some calculators may not handle complex or imaginary numbers. Check if the calculator supports these types of inputs if needed.
- Decimal Results: If the calculator provides results in decimal form instead of simplified radical form, ensure you are using a calculator that specializes in radical simplification.
Tips for Accurate Calculations
- Check Prime Factorization: For manually verifying the results, always check the prime factorization of the number under the square root. This helps in understanding and verifying the simplification process.
- Use Parentheses: When inputting complex expressions, use parentheses to ensure the correct order of operations.
- Review Calculator Settings: Some calculators have settings that affect how results are displayed. Make sure these settings are configured correctly to get the desired output.
- Practice with Examples: Use example problems to familiarize yourself with the calculator’s functionality. This can help you understand how it handles different types of inputs.
Advanced Troubleshooting
If you are still having issues, consider these advanced tips:
- Clear Browser Cache: If using an online calculator, clear your browser cache to ensure the calculator loads the latest version.
- Try Different Calculators: If one calculator isn't giving accurate results, try another one. Different calculators might have varying levels of precision and methods for simplifying radicals.
- Consult Help Sections: Many online calculators have help sections or FAQs that provide detailed instructions and troubleshooting advice.
Useful Online Calculators
| Offers step-by-step solutions and supports complex numbers. | |
| Provides exact and decimal forms, useful for a variety of calculations. | |
| Displays principal and negative roots, perfect for thorough understanding. |
By following these tips and using the recommended tools, you can effectively troubleshoot and ensure accurate simplification of square roots.

Further Reading and Learning Resources
To deepen your understanding of simplifying square roots and related mathematical concepts, consider exploring the following resources:
-
Khan Academy
This comprehensive platform offers detailed lessons on simplifying square roots, along with video tutorials and practice exercises. Topics include rational exponents and radicals, providing a solid foundation for understanding square roots and their applications.
-
MathWarehouse
MathWarehouse provides an interactive square root calculator that simplifies square roots to their simplest radical form. The site also includes worksheets and additional resources to practice and master square root calculations.
-
Third Space Learning
This resource offers detailed explanations and examples for understanding square roots and their properties. It includes worksheets and problem sets designed for different levels, from GCSE to more advanced mathematics.
-
Wolfram Alpha
Wolfram Alpha is a powerful computational tool that not only simplifies square roots but also provides detailed steps for the calculations. It is an excellent resource for verifying your work and exploring more complex mathematical problems.
-
Math is Fun
This website breaks down mathematical concepts in an easy-to-understand manner. It includes sections on square roots, interactive calculators, and fun activities to reinforce learning.
These resources will provide you with extensive information and practice opportunities to master the simplification of square roots and enhance your overall mathematical skills.
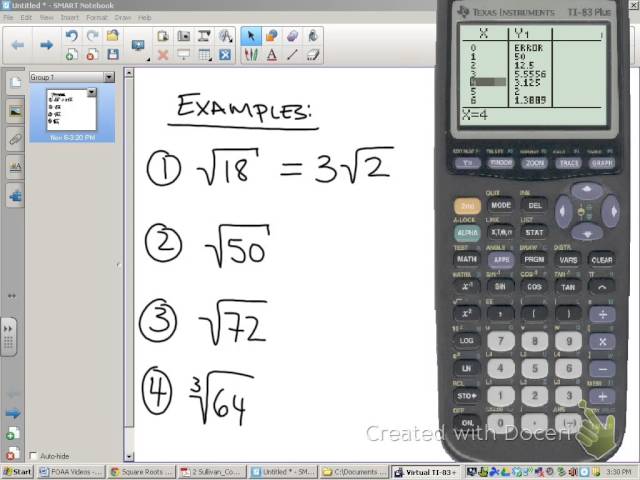
Đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai bằng máy tính đồ thị
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn sử dụng máy tính ClassWiz - Đại số 4-1 Đơn giản hóa căn thức