Topic simplify square root of 512: Unlock the mystery of simplifying the square root of 512 with our comprehensive guide. Discover step-by-step instructions, prime factorization methods, and practical tips to make the process straightforward and easy. Whether you're a student or math enthusiast, this guide will help you master the technique and understand the underlying concepts.
Table of Content
- How to Simplify the Square Root of 512
- Introduction to Simplifying Square Roots
- Understanding the Square Root of 512
- Prime Factorization Method
- Identifying Perfect Squares
- Grouping Factors for Simplification
- Step-by-Step Simplification Process
- Decimal Representation
- Exponent Form Representation
- Visual Examples and Illustrations
- Practical Applications
- Frequently Asked Questions
- YOUTUBE:
How to Simplify the Square Root of 512
To simplify the square root of 512, follow these steps:
Step-by-Step Process
- Prime Factorization:
First, factor 512 into its prime factors:
512 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2
This can be written as \(2^9\).
- Group Factors:
Next, group the factors in pairs:
\((2^2) × (2^2) × (2^2) × (2^2) × 2\)
- Simplify:
Take one factor from each pair and multiply them together:
\(\sqrt{512} = \sqrt{(2^2) × (2^2) × (2^2) × (2^2) × 2} = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 \sqrt{2} = 16 \sqrt{2}\)
Result
The simplified form of the square root of 512 is:
\(\sqrt{512} = 16 \sqrt{2}\)
Decimal Form
In decimal form, the square root of 512 is approximately:
\(\sqrt{512} ≈ 22.62742\)
Using Exponent Form
The square root of 512 can also be expressed in exponent form:
\(512^{\frac{1}{2}} = 16 \times 2^{\frac{1}{2}}\)
This method ensures that the square root of 512 is expressed in its simplest radical form.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Simplifying Square Roots
Square roots can initially seem daunting, but simplifying them can make calculations easier and more understandable. Simplifying the square root of a number involves breaking it down into its prime factors and expressing the square root in its simplest form. This section will guide you through the step-by-step process of simplifying square roots, using the square root of 512 as an example.
To simplify the square root of 512, follow these steps:
- Prime Factorization: First, find the prime factors of 512. The prime factorization of 512 is \(2^9\) or \(2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2\).
- Grouping Factors: Group the prime factors in pairs. In this case, you can group the nine 2's as \( (2^4 \times 2^4) \times 2\).
- Extracting the Square Root: Take one factor from each pair. For \( (2^4 \times 2^4) \), this would be \(2^4\) which equals 16. The remaining factor is \( \sqrt{2}\).
- Final Simplified Form: Multiply the extracted factors. So, the simplified form of \(\sqrt{512}\) is \(16\sqrt{2}\).
Therefore, the simplified form of the square root of 512 is \(16\sqrt{2}\), which is approximately equal to 22.627 in decimal form.
Understanding the Square Root of 512
The square root of 512 can be simplified to a more manageable form using prime factorization. The process involves breaking down 512 into its prime factors and identifying perfect squares. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- List the factors of 512: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512.
- Identify the perfect squares from the list: 1, 4, 16, 64, 256.
- Divide 512 by the largest perfect square: 512 ÷ 256 = 2.
- Calculate the square root of the largest perfect square: √256 = 16.
- Combine the results: √512 = 16√2.
Thus, the simplest form of the square root of 512 is . This method ensures a simplified radical form, making it easier to work with in various mathematical contexts.
Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization method is a straightforward way to simplify the square root of a number. Here's a step-by-step guide to simplify the square root of 512 using this method:
-
First, we need to find the prime factors of 512. We start by dividing 512 by the smallest prime number, which is 2:
\(512 \div 2 = 256\)
-
We continue dividing by 2 until we can no longer divide evenly by 2:
\(256 \div 2 = 128\)
\(128 \div 2 = 64\)
\(64 \div 2 = 32\)
\(32 \div 2 = 16\)
\(16 \div 2 = 8\)
\(8 \div 2 = 4\)
\(4 \div 2 = 2\)
\(2 \div 2 = 1\)
-
We now express 512 as a product of its prime factors:
\(512 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2\)
Or, more compactly:
\(512 = 2^9\)
-
Next, we use the property of square roots that \(\sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}\) to simplify:
\(\sqrt{512} = \sqrt{2^9} = \sqrt{(2^8) \times 2} = \sqrt{2^8} \times \sqrt{2}\)
-
We know that \(\sqrt{2^8} = 2^4 = 16\), so:
\(\sqrt{512} = 16 \times \sqrt{2}\)
Thus, the simplified form of \(\sqrt{512}\) is \(16\sqrt{2}\).
Identifying Perfect Squares
To simplify the square root of 512, we first need to identify perfect squares within its prime factorization. This process involves breaking down 512 into its prime factors and looking for pairs of prime factors that form perfect squares.
-
Start by finding the prime factorization of 512:
\[ 512 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \] or \[ 512 = 2^9 \]
-
Identify pairs of 2's within the prime factorization:
We can group the factors of 2 in pairs:
- \( 2 \times 2 = 4 \) (a perfect square)
- \( 2 \times 2 = 4 \) (a perfect square)
- \( 2 \times 2 = 4 \) (a perfect square)
- \( 2 \times 2 = 4 \) (a perfect square)
- \( 2 \) (leftover factor)
-
Combine the perfect squares:
\( 4 \times 4 \times 4 \times 4 \times 2 \)
\[ 512 = (2^2) \times (2^2) \times (2^2) \times (2^2) \times 2 \]
-
Rewrite the expression using exponents:
\[ 512 = (2^2)^4 \times 2 = 4^4 \times 2 \]

Grouping Factors for Simplification
To simplify the square root of 512, we start by breaking it down into its prime factors and then grouping these factors to simplify the expression under the square root. Here is the step-by-step process:
-
Perform the prime factorization of 512:
\[
512 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 = 2^9
\] -
Group the factors in pairs of two since the square root function pairs identical factors:
\[
512 = (2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) \times 2 = (2^2)^4 \times 2
\] -
Rewrite the expression under the square root as the product of the square roots of the groups:
\[
\sqrt{512} = \sqrt{(2^2)^4 \times 2} = \sqrt{(2^2)^4} \times \sqrt{2}
\] -
Simplify the square root of each group:
\[
\sqrt{(2^2)^4} = 2^4 = 16
\] -
Combine the simplified terms to get the final simplified form:
\[
\sqrt{512} = 16 \sqrt{2}
\]
Therefore, the square root of 512 simplifies to \(16 \sqrt{2}\).
Step-by-Step Simplification Process
To simplify the square root of 512, we will use the prime factorization method and follow a step-by-step process:
-
Prime Factorization:
Start by finding the prime factors of 512:
\[
512 = 2 \times 256 = 2 \times (2 \times 128) = 2 \times (2 \times (2 \times 64)) = 2 \times (2 \times (2 \times (2 \times 32)))
\]
\[
= 2 \times (2 \times (2 \times (2 \times (2 \times 16)))) = 2 \times (2 \times (2 \times (2 \times (2 \times (2 \times 8)))))
\]
\[
= 2 \times (2 \times (2 \times (2 \times (2 \times (2 \times (2 \times 4))))))
\]
\[
= 2^9
\] -
Group the Factors:
To simplify the square root, pair the factors in groups of two:
\[
\sqrt{512} = \sqrt{2^9} = \sqrt{(2^8) \times 2} = \sqrt{(2^4)^2 \times 2}
\] -
Simplify:
Take the square root of each group of perfect squares:
\[
\sqrt{(2^4)^2 \times 2} = 2^4 \times \sqrt{2} = 16 \sqrt{2}
\] -
Result:
The simplest form of \(\sqrt{512}\) is:
\[
\boxed{16 \sqrt{2}}
\]
By following these steps, we have successfully simplified the square root of 512 to \(16 \sqrt{2}\).
Decimal Representation
The decimal representation of the square root of 512 can be found by converting the simplified form into its decimal form. Let's go through the steps to find this representation.
-
We start with the simplified form of the square root of 512. As we have seen, the simplified form is \( 16\sqrt{2} \).
-
Next, we need to find the decimal value of \( \sqrt{2} \). The square root of 2 is approximately 1.41421.
-
Now, we multiply this value by 16 to find the decimal representation of \( 16\sqrt{2} \):
\[
16 \times 1.41421 \approx 22.62736
\] -
Therefore, the decimal representation of the square root of 512 is approximately 22.62736.
To summarize, the square root of 512 in decimal form is \( \approx 22.62736 \).
For a more precise value, you can use a calculator to get more decimal places. Using a calculator, the square root of 512 is approximately 22.62741699796.
This decimal representation can be very useful in various practical applications where an approximate value is sufficient.
Exponent Form Representation
The square root of 512 can be expressed in various forms, including its exponent form. Understanding this representation helps in various algebraic operations and simplifications.
The square root of 512 can be written as:
\[
\sqrt{512}
\]
Using prime factorization, we first express 512 as a product of its prime factors:
\[
512 = 2^9
\]
Taking the square root of both sides, we get:
\[
\sqrt{512} = \sqrt{2^9}
\]
This can be simplified by expressing the exponent as a fraction:
\[
\sqrt{2^9} = 2^{9/2}
\]
We can further break down the exponent:
\[
2^{9/2} = 2^{4.5} = 2^4 \cdot 2^{1/2}
\]
Simplifying the terms, we get:
\[
2^4 \cdot \sqrt{2} = 16\sqrt{2}
\]
Therefore, the exponent form representation of the square root of 512 is:
\[
\sqrt{512} = 2^{4.5} = 16 \sqrt{2}
\]
This representation is useful in higher-level mathematics, making it easier to handle large numbers and simplify expressions involving radicals.
The decimal approximation of the square root of 512 is approximately 22.6274, but the exact form using exponents and radicals provides a clearer mathematical insight.

Visual Examples and Illustrations
To better understand the process of simplifying the square root of 512, let's explore some visual examples and illustrations that will help clarify each step.
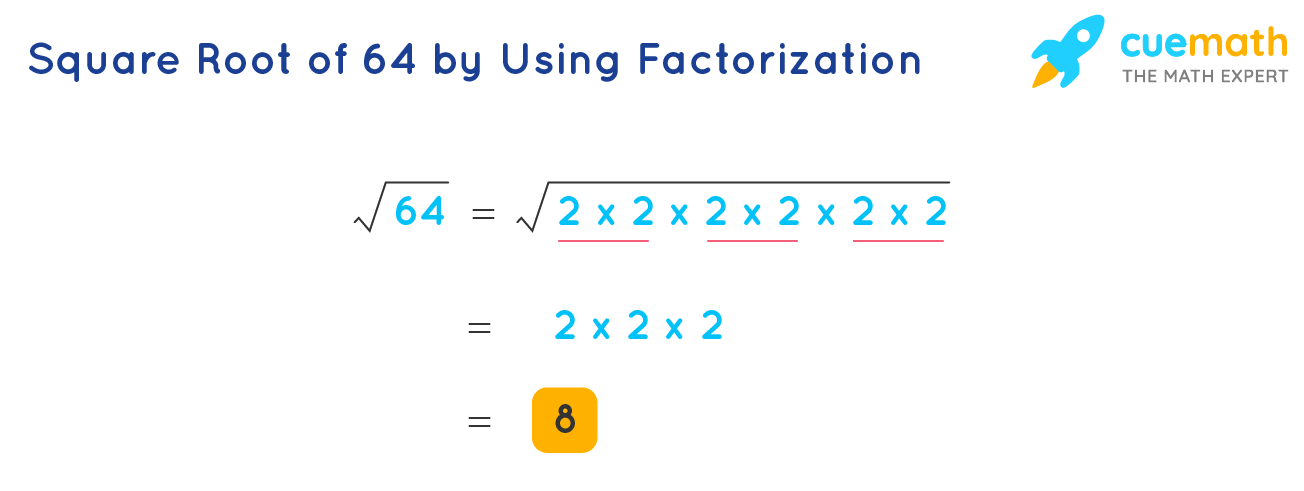
Prime Factorization Method
We start by expressing 512 as a product of its prime factors:
\[
512 = 2^9
\]
Next, we group the factors into pairs:
\[
\sqrt{512} = \sqrt{2^9} = \sqrt{(2^4)^2 \cdot 2} = 2^4 \cdot \sqrt{2} = 16\sqrt{2}
\]
Step-by-Step Illustration
- Prime factorize 512:
- 512 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2
- Group the factors into pairs and simplify:
- Group: (2 × 2) × (2 × 2) × (2 × 2) × (2 × 2) × 2
- Simplify: 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × √2 = 16√2
Illustrative Example
Consider the square root of 512 simplified visually:

This image shows the step-by-step prime factorization and grouping of 512.
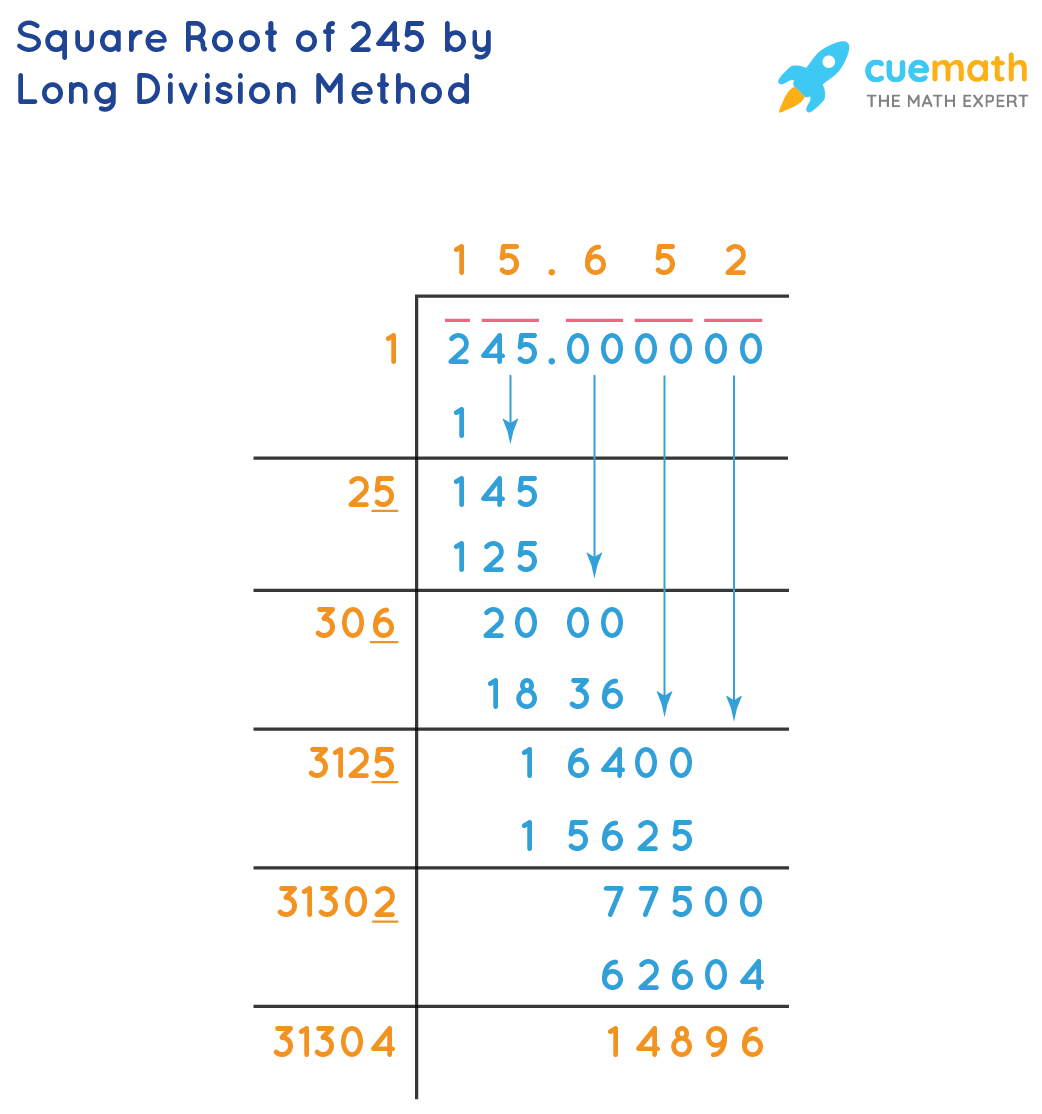
Long Division Method
Another method to find the square root of 512 is the long division method:
\[
\begin{array}{r|l}
22 & \overline{512.000000} \\
\hline
& 4\cdot22=88 \\
\end{array}
\]
Follow these steps for each pair of digits to continue the long division process.
Practical Example
Suppose we need to find the length of the side of a square with an area of 512 square units. We can use the simplified form of the square root:
\[
\text{Area} = s^2 = 512 \implies s = \sqrt{512} = 16\sqrt{2} \approx 22.63 \, \text{units}
\]
These visual aids and step-by-step methods make it easier to understand and simplify the square root of 512 effectively.
Practical Applications
The square root of 512, approximately 22.63, finds diverse applications across various fields, making it a valuable mathematical tool.
Engineering and Architecture
- Structural Design: Engineers use the square root of 512 to calculate the dimensions of beams, columns, and other structural elements, ensuring stability and safety in constructions.
- Electrical Engineering: It is utilized in calculating the RMS (root mean square) value of alternating current (AC) signals, crucial for power consumption and energy distribution.
- Surveying: Surveyors apply the square root of 512 in calculating distances, angles, and areas, leading to accurate land measurements and map designs.
Mathematics and Physics
- Geometry: The square root of 512 helps in calculating the length of the diagonal of a square with sides of 512 units, based on the Pythagorean theorem.
- Waveform Analysis: It is used in analyzing waveforms like sound waves or electromagnetic waves, determining their amplitude and intensity.
- Probability and Statistics: The square root of 512 is significant in standard deviation calculations, measuring data variability around the mean.
Computer Science and Programming
- Graphics and Image Processing: This value is used in image processing algorithms for resizing images while maintaining aspect ratios or applying scaling filters.
- Data Compression: It plays a role in certain data compression techniques, such as the square root transform, reducing redundancy and optimizing storage.
- Machine Learning: The square root of 512 may be used in feature scaling, normalizing values for fair comparisons in algorithms.
Real-world Examples
- Gravity: The time it takes for an object to fall from a certain height can be calculated using the square root. For example, the time \( t \) in seconds for an object to fall from a height \( h \) feet is given by \( t = \frac{\sqrt{h}}{4} \).
- Accident Investigation: The speed of a car before applying brakes can be determined by the length of skid marks using the formula \( \sqrt{24d} \), where \( d \) is the length of the skid marks.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
How do I calculate the square root of 512?
To calculate the square root of 512, you can use the prime factorization method. Here are the steps:
- Find the prime factors of 512: \(512 = 2^9\).
- Group the factors into pairs: \(512 = (2^4)^2 \times 2\).
- Take the square root of each pair: \(\sqrt{512} = \sqrt{(2^4)^2 \times 2} = 16\sqrt{2}\).
- Thus, the square root of 512 is \(16\sqrt{2}\).
-
What is the square root of 512 rounded to the nearest tenth?
The square root of 512 rounded to the nearest tenth is approximately 22.6.
-
Why is \( \sqrt{512} \) an irrational number?
A number is considered irrational if its decimal expansion is non-terminating and non-repeating. Since \( \sqrt{512} \) equals approximately 22.62741699797..., which is non-terminating and non-repeating, it is classified as an irrational number.
-
How can I express the square root of 512 in exponential form?
The square root of 512 can be expressed in exponential form as \( 512^{1/2} \), which simplifies to \( 16 \times 2^{1/2} \).
-
What are some practical applications of simplifying the square root of 512?
Simplifying square roots can be useful in various fields such as engineering, physics, and computer science. For instance, it helps in optimizing calculations, solving equations more efficiently, and understanding geometrical properties of shapes in design and analysis.
Đơn Giản Hóa √(512k^2)
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 512m^3 một cách chi tiết và dễ hiểu. Phù hợp cho người học muốn nắm vững các khái niệm toán học cơ bản.
Đơn Giản Hóa √(512m^3) - Video Hướng Dẫn