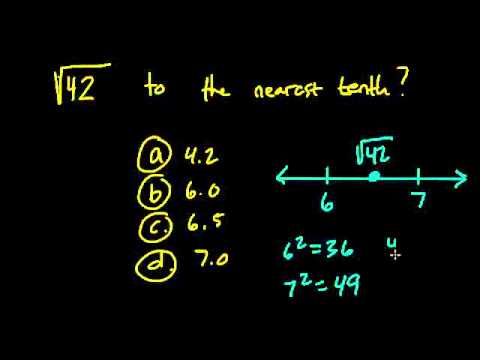Topic simplify square root of 33: Welcome to our comprehensive guide on simplifying the square root of 33! In this article, you'll discover simple and effective methods to simplify √33, understand its significance, and learn practical applications. Whether you're a student or math enthusiast, this guide will help you master the concept with ease and confidence.
Table of Content
- Simplify Square Root of 33
- Introduction
- Understanding Square Roots
- What is the Square Root of 33?
- Methods to Simplify the Square Root of 33
- Estimating Square Roots
- Using a Calculator
- Step-by-Step Simplification Process
- Practical Applications of Simplified Square Roots
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Frequently Asked Questions
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của một số không phải là số chính phương một cách dễ hiểu và chi tiết.
Simplify Square Root of 33
The square root of 33, denoted as , cannot be simplified into a smaller radical form because 33 is not a perfect square and does not have any perfect square factors other than 1.
Prime Factorization Method
To understand why cannot be simplified further, we can use the prime factorization method. The prime factorization of 33 is:
- 33 = 3 × 11
Neither 3 nor 11 is a perfect square, and therefore, cannot be simplified further.
Decimal Form
In decimal form, the square root of 33 is approximately:
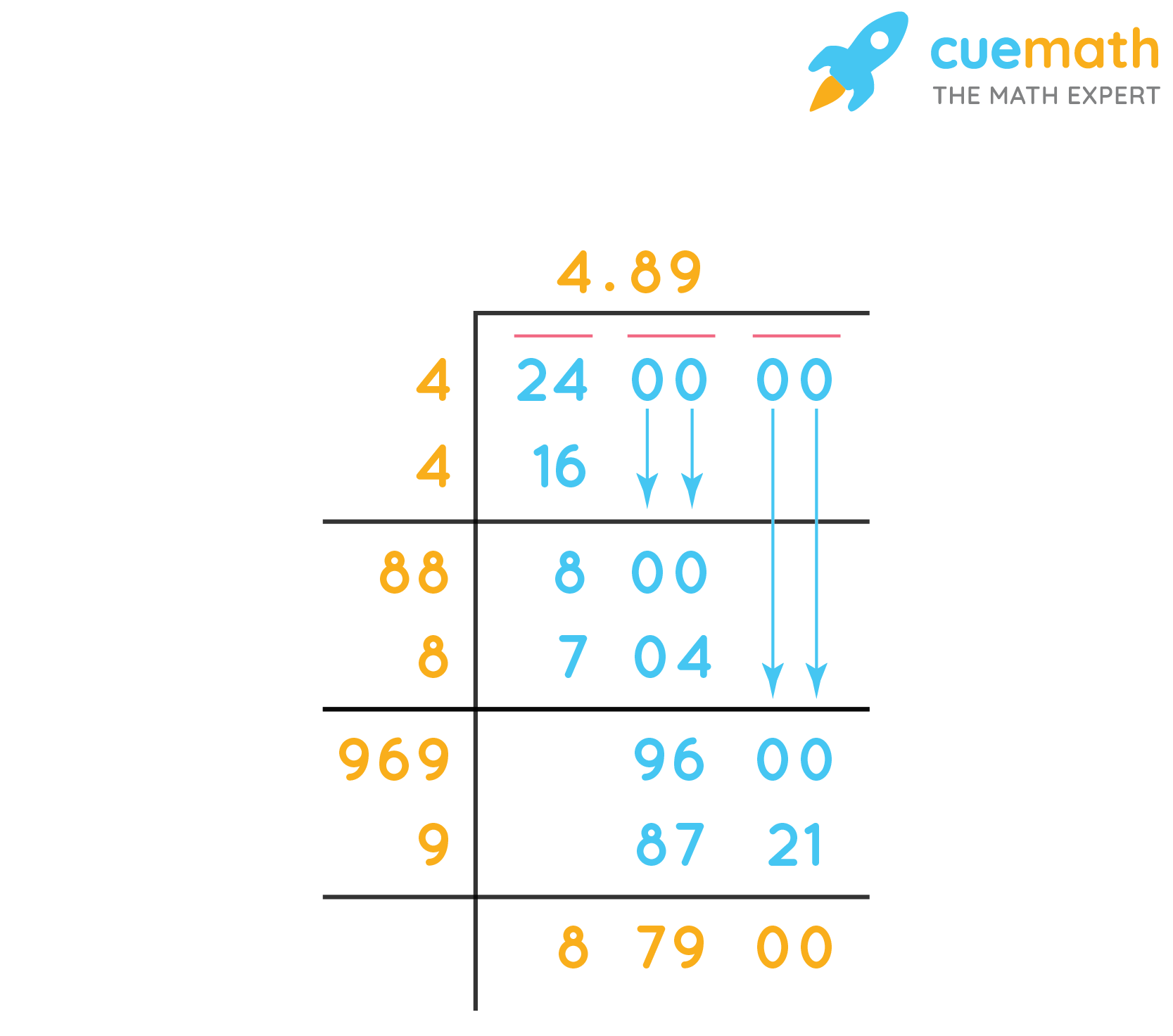
This value is obtained using a calculator or by applying the long division method for square roots.
Using the Property of Square Roots
Another way to express the square root of 33 is by using the property of square roots:
However, since neither nor is a perfect square, this does not simplify the expression.
Conclusion
The square root of 33 cannot be simplified into a simpler radical form. Its most precise form is , and its approximate decimal form is 5.7446.

READ MORE:
Introduction
Simplifying the square root of 33 can seem challenging, but with the right approach, it becomes manageable. This guide will help you understand the process step by step. We'll explore the significance of square roots, methods to simplify them, and why √33 is unique. Let's dive in and simplify the square root of 33 together!
Square roots are a fundamental concept in mathematics, representing a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. In this case, the square root of 33 (√33) is the number which, when squared, equals 33.
Since 33 is not a perfect square, its square root is an irrational number. However, we can simplify √33 to a more manageable form using different methods, including prime factorization and estimation.
- Prime Factorization: This method involves breaking down 33 into its prime factors to see if it can be simplified further.
- Estimation: Here, we estimate the value of √33 to get an approximate decimal value.
By understanding these methods, you'll be better equipped to simplify the square root of 33 and apply this knowledge to other similar problems.
Let's start by exploring the prime factorization method.
Understanding Square Roots
Square roots are a fundamental mathematical concept used to find a number which, when multiplied by itself, results in the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because \(3 \times 3 = 9\). This concept is symbolized by the radical sign (√).
Let's break down the key points about square roots:
- Definition: The square root of a number \(x\) is a number \(y\) such that \(y^2 = x\).
- Perfect Squares: Numbers like 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25 are perfect squares because their square roots are whole numbers.
- Irrational Numbers: When a number is not a perfect square, its square root is an irrational number. Irrational numbers cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and have non-repeating, non-terminating decimal parts.
To further understand square roots, consider the properties and operations:
- Product Property: \(\sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}\)
- Quotient Property: \(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\)
- Square of a Square Root: \((\sqrt{a})^2 = a\)
Square roots are widely used in various fields, including geometry, algebra, and calculus. They are essential for solving quadratic equations, calculating areas, and understanding various natural phenomena.
In the context of simplifying the square root of 33, it's important to recognize that 33 is not a perfect square, making its square root an irrational number. However, we can still simplify and approximate it to understand its value better. In the next sections, we'll explore the methods to simplify √33 effectively.
What is the Square Root of 33?
The square root of 33, denoted as \(\sqrt{33}\), is a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 33. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
\[
\sqrt{33} \times \sqrt{33} = 33
\]
Since 33 is not a perfect square, its square root is an irrational number. This means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and has a non-terminating, non-repeating decimal representation. The approximate value of \(\sqrt{33}\) is:
\[
\sqrt{33} \approx 5.744
\]
Let's understand this step by step:
- Prime Factorization: First, we try to factorize 33 into prime numbers. The prime factors of 33 are 3 and 11, since:
- 33 = 3 × 11
- Simplification: Since neither 3 nor 11 is a perfect square, we cannot simplify \(\sqrt{33}\) further using prime factorization.
- Estimation: We can estimate the square root by finding perfect squares close to 33. We know that:
- \(5^2 = 25\) and \(6^2 = 36\)
- \(\sqrt{33} \approx 5.744\)
Understanding the square root of 33 is crucial as it helps in various mathematical problems and applications. Although \(\sqrt{33}\) cannot be simplified into a simpler radical form, knowing its approximate value is beneficial in calculations and real-world applications.
Methods to Simplify the Square Root of 33
To simplify the square root of 33, we can use various methods that help in understanding and estimating the value more clearly.
-
Prime Factorization Method
Although 33 cannot be simplified directly using prime factorization, it is important to understand this method:
- Factor 33 into its prime components: \(33 = 3 \times 11\).
- Since neither 3 nor 11 is a perfect square, the square root of 33 remains \(\sqrt{33}\).
-
Estimation Method
Estimating the square root can give us a good approximation:
- Identify two perfect squares between which 33 falls: \(25 (5^2)\) and \(36 (6^2)\).
- Since \(33\) is closer to \(36\), we estimate that \(\sqrt{33}\) is slightly less than \(6\).
-
Using a Calculator
The most straightforward method is to use a calculator:
- Enter 33 and press the square root button.
- The calculator will display approximately \(5.744\).
By using these methods, you can simplify and better understand the square root of 33, even though it does not simplify neatly into an integer or a simpler radical form.

Estimating Square Roots
Estimating the square root of a number like 33 can be done using approximation methods. Here's a simple way to estimate:
- First, identify two perfect squares between which 33 lies. For instance, \(25\) (where \(\sqrt{25} = 5\)) and \(36\) (where \(\sqrt{36} = 6\)). Thus, \(5 < \sqrt{33} < 6\).
- To refine the estimate, divide 33 by 6, yielding approximately 5.5.
- Take the average of 5.5 and 6: \( \frac{5.5 + 6}{2} = 5.75\).
- This gives a rough estimate of \( \sqrt{33} \approx 5.75\).
This method helps in quickly approximating square roots without a calculator. The actual value of \( \sqrt{33} \) is about 5.744, which confirms our estimate is quite close.
Using a Calculator
Finding the square root of 33 using a calculator is straightforward and can provide a quick and accurate result. Follow these steps:
- Turn on your calculator and ensure it is in standard mode.
- Enter the number 33. You can use the numeric keypad or touch screen, depending on your calculator.
- Press the square root button (√). This function may be directly on the keypad or accessible through a function key.
- Read the result. The calculator will display the square root of 33, which is approximately 5.7446.
Using a calculator is beneficial for quick estimates and checking your manual calculations. It ensures precision, which is especially useful in scientific and mathematical applications.
Step-by-Step Simplification Process
Simplifying the square root of 33 involves determining if it can be broken down into simpler radical terms. Follow these steps:
- List the factors of 33: The factors are 1, 3, 11, and 33.
- Identify perfect squares: Among the factors, 1 is the only perfect square.
- Attempt to simplify: Since there are no perfect squares other than 1, the square root of 33 cannot be simplified further.
The square root of 33 remains \( \sqrt{33} \) in simplest radical form. However, it can also be represented in decimal form as approximately 5.7446 or as an exponent: \( 33^{1/2} \).
Practical Applications of Simplified Square Roots
Simplified square roots are used in various real-world applications across different fields. Here are some practical examples:
-
Construction and Design:
In construction, calculating the dimensions of a square area is often necessary. For instance, if you need to find the side length of a square lawn or garden area, you can use the square root to determine it. For example, if the area is 33 square feet, the side length is approximately \( \sqrt{33} \approx 5.74 \) feet.
-
Physics and Gravity:
Square roots are used to calculate the time it takes for an object to fall from a certain height under the influence of gravity. The formula \( t = \frac{\sqrt{h}}{4} \) helps determine the time \( t \) in seconds for an object to fall from a height \( h \) in feet. For example, if an object is dropped from a height of 33 feet, the time taken to reach the ground is \( t = \frac{\sqrt{33}}{4} \approx 1.44 \) seconds.
-
Accident Investigation:
In forensic science, particularly in accident investigation, the length of skid marks can be used to estimate the speed of a vehicle before braking. The formula \( \text{Speed} = \sqrt{24 \times \text{Skid Length}} \) helps investigators determine the vehicle's speed. If the skid marks measure 33 feet, the estimated speed is \( \sqrt{24 \times 33} \approx 28.1 \) mph.
These examples illustrate how understanding and simplifying square roots can provide valuable insights and solutions in everyday problems and professional practices.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
When simplifying square roots, it is essential to avoid common mistakes to ensure accurate results. Here are some key pitfalls to watch out for:
- Forgetting to Check for Perfect Squares: One of the most common errors is not recognizing perfect squares within the number. Always check if the number can be factored into perfect squares. For instance, can be simplified to because 18 is 9 times 2, and 9 is a perfect square.
- Rushing Through the Process: Simplification requires careful step-by-step work. Rushing can lead to mistakes such as incorrect factorization or missed simplifications. Take your time to ensure each step is correct.
- Ignoring Prime Factorization: Prime factorization is crucial for simplifying square roots. Break down the number into its prime factors to identify and pull out pairs of factors. For example, can be simplified by recognizing that 72 is , resulting in .
- Overlooking the Product Rule: The product rule states that . Applying this rule correctly is essential, especially when dealing with larger numbers.
- Misinterpreting Simplified Roots: Ensure that once a square root is simplified, the result is correctly understood and used. For instance, understanding that is not the same as .
- Inconsistent Application of the Properties: Consistency is key when applying properties of square roots, such as the product and quotient rules. Any deviation can lead to incorrect simplifications.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure a more accurate and efficient simplification of square roots.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the square root of 33?
The square root of 33 is approximately 5.744. It is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
-
Can the square root of 33 be simplified?
No, the square root of 33 cannot be simplified further because 33 is not a perfect square and it does not have any square factors other than 1.
-
How can I estimate the square root of 33?
To estimate the square root of 33, you can use a calculator or apply methods such as the approximation method or the long division method. For a rough estimate, note that \(\sqrt{33}\) is between \(\sqrt{25} = 5\) and \(\sqrt{36} = 6\).
-
Why is simplifying square roots important?
Simplifying square roots is important for solving equations more easily, reducing complex expressions, and making calculations simpler in various mathematical and practical applications.
-
Are there any common mistakes to avoid when simplifying square roots?
Yes, common mistakes include not recognizing perfect squares, incorrectly factoring the number, and misapplying properties of square roots. Always double-check your work to avoid these errors.
Hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của một số không phải là số chính phương một cách dễ hiểu và chi tiết.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của Một Số Không Phải Là Số Chính Phương
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn cách nhân tử và đơn giản hóa biểu thức căn bậc hai của số 33 một cách chi tiết và dễ hiểu.
33 Nhân Tử và Đơn Giản Hóa Biểu Thức Căn Bậc Hai